Edexcel GCSE Computer Science, Unit 1: Computational Thinking
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Algorithm
Set of step-by-step instructions to complete a task, or solve a problem
Decomposition
Break down a problem into smaller sub-problems
Abstraction
Remove unnecessary information from a problem
Pattern recognition
Seeing similarities and differences in a range of problems
Computational thinking
Using methods to solve complex problems
Flowchart
Diagram that represents an algorithm showing the steps as boxes of various kinds, and their order by connecting them with arrows.
3 basic programming constructs
Selection - Sequence - Iteration
3 elements of a successful algorithm
Accurate - Efficient - Consistent
Logical operators - AND
Two conditions must both be true for the whole statement to be true
Logical operators - OR
Either one of two conditions must be true for the whole statement to be true
Logical operators - NOT
Reverses the logic of a statement
Logic error
Error that results in incorrect or unexpected behaviour
Trace table
Used to identify logic errors in an algorithm or to determine the purpose of an algorithm
BIDMAS - order of calculations
BRACKETS - INDICES - DIVISION - MULTIPLICATION - ADDITION - SUBTRACTION
Iteration
Programming construct that allows the repetition of a process, also called a loop
Selection
Programming construct that allows a choice to be made between different options
Repetition
Repeating a block of code; for example a while loop which is controlled by a condition
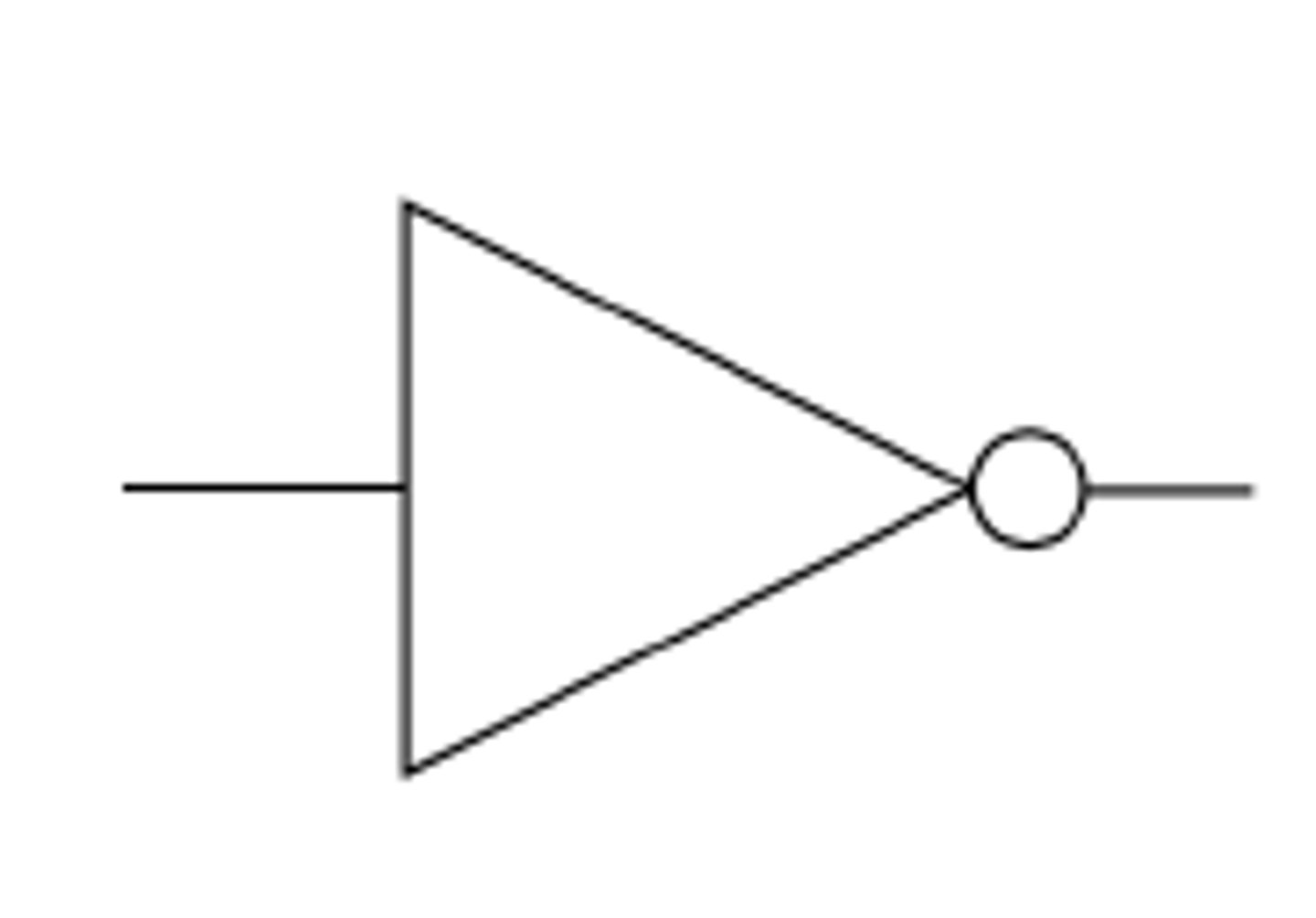
Logic gate - NOT
"Accepts one input and produces one output. If the input is TRUE (1), the output will be FALSE (0). If the input is FALSE (0), the output will be TRUE (1)."
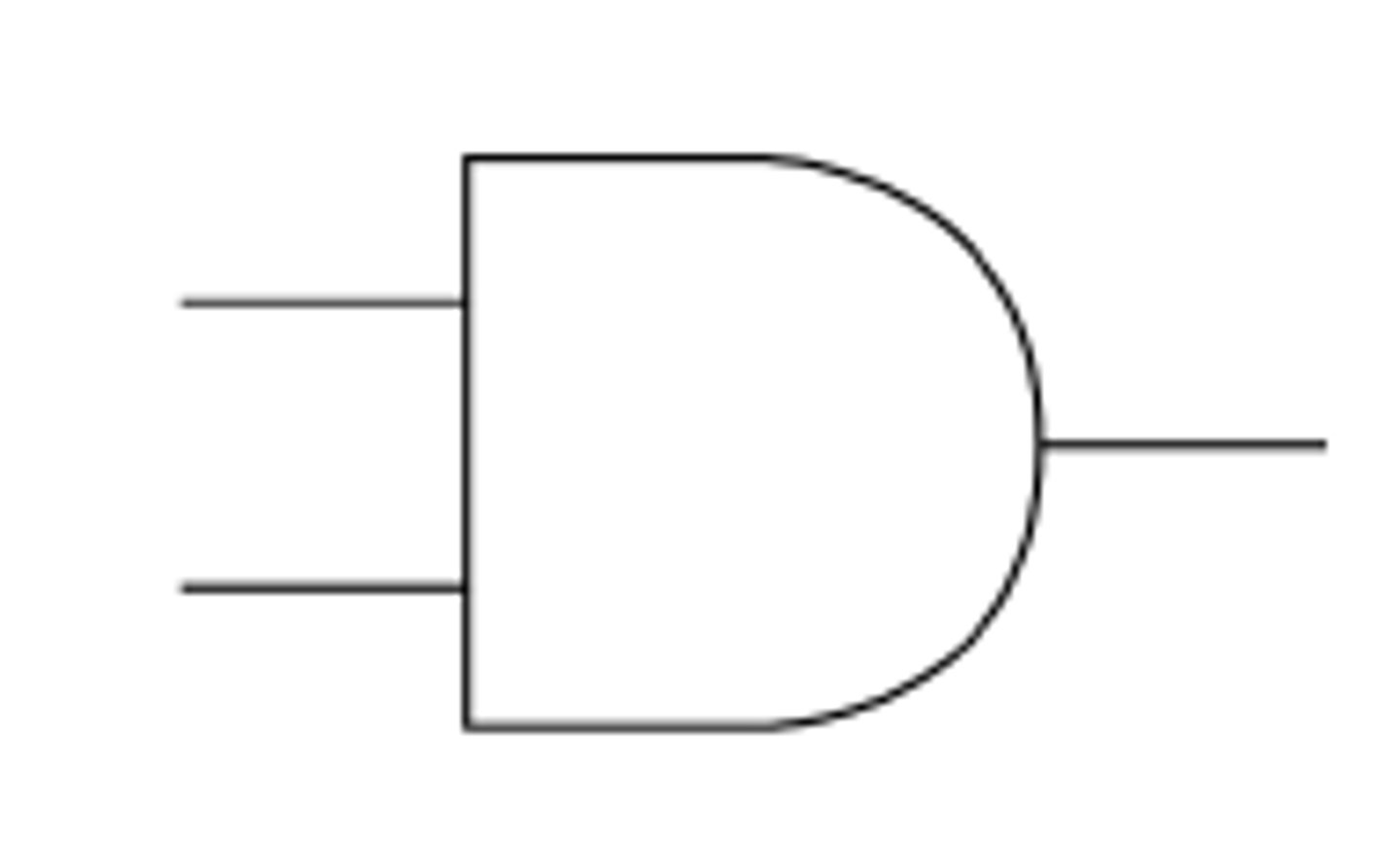
Logic gate - AND
"Accepts two inputs and produces one output. Both inputs must be TRUE (1) for the output to be TRUE (1) - otherwise, the output will be FALSE (0)."
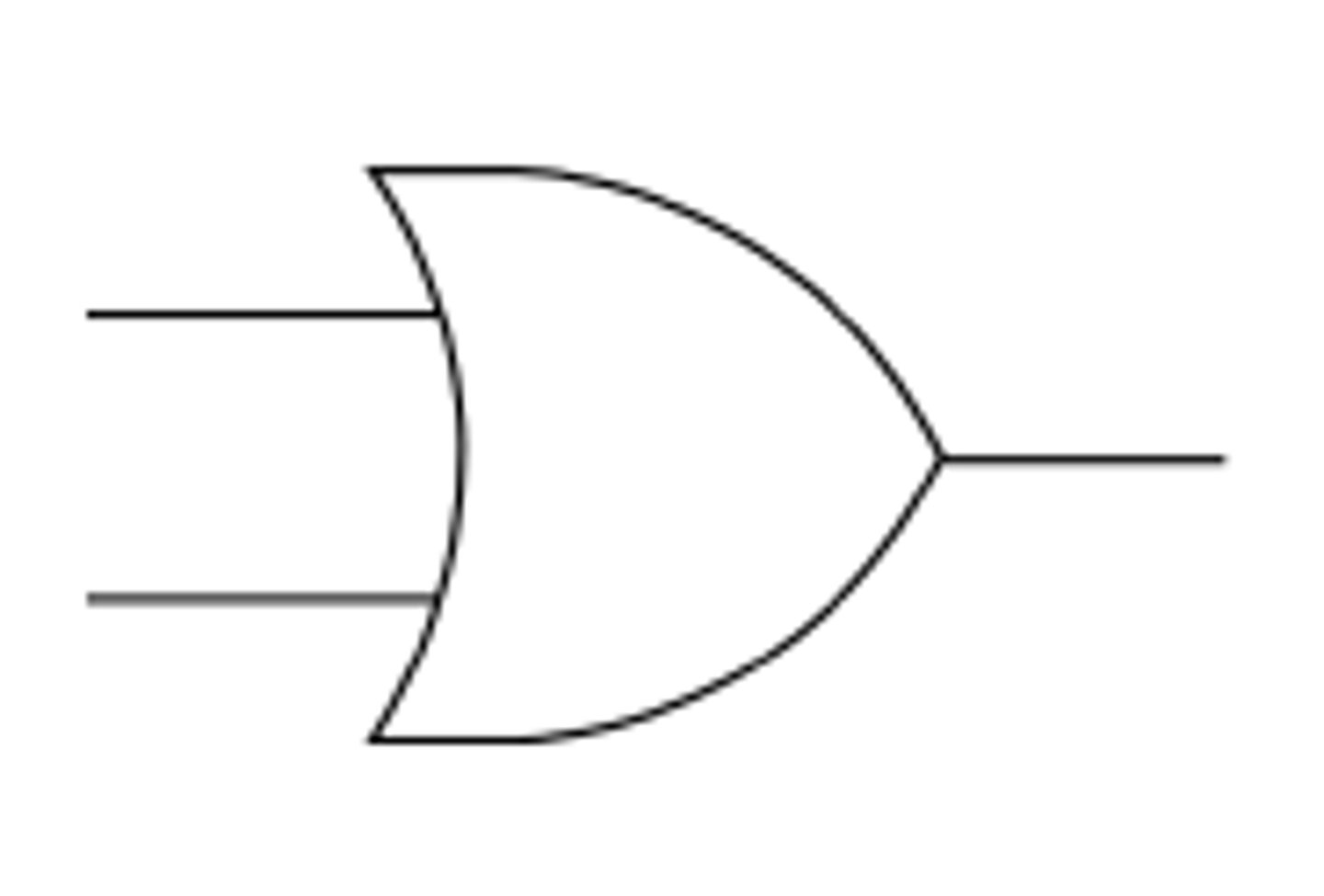
Logic gate - OR
"Accepts two inputs and produces one output. At least one input must be TRUE (1) for the output to be TRUE (1) - otherwise, the output will be FALSE (0)."
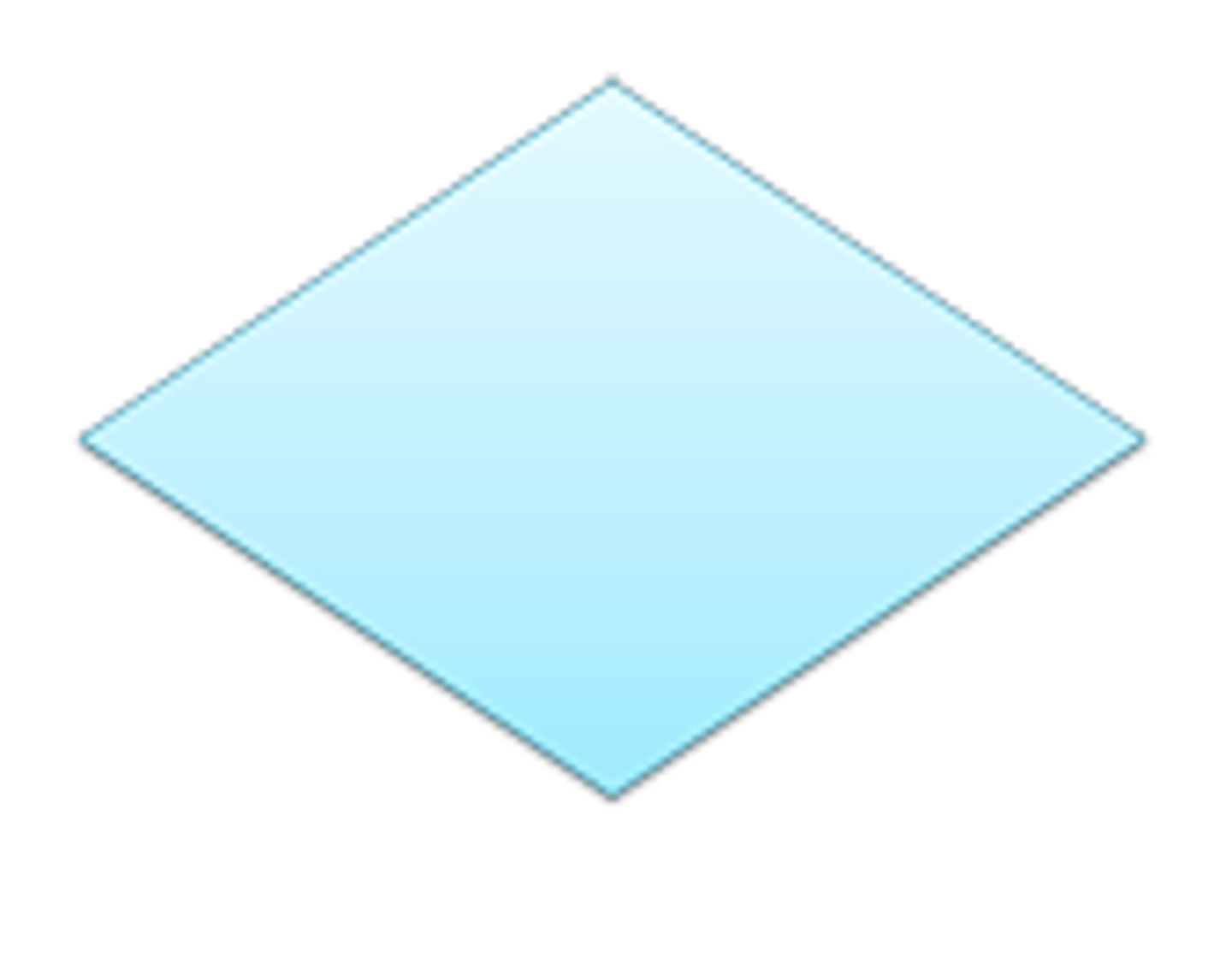
Flowchart - selection symbol
Flowchart - process symbol

Flowchart - start / end symbol

Flowchart - input / output symbol

Truth table
Lists all possible combinations of input values to a logical expression and the corresponding output values.
Syntax error
A mistake in the program where the rules of the programming language are not followed.
Runtime error
Occurs while the program is running. A piece of code that contains an error causes the program to stop.
Sequence
Instructions are processed in order, one after the other