Law of Supply and Demand
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Law of Supply
Price has direct relationship to Qs
Changes in Qs
caused by a change in price
shown as movement along curve
Price Variables (Supply)
Profit Incentive
Law of Increasing Opp. Cost
changes in supply
caused by non-price variables
shown as shift of the curve

Non-Price Variables
SPENT
SPENT: S_____
Suppliers Input Price (inverse)
SPENT: P____
Price of related goods
SPENT: E____
Expectations
SPENT: N____
Number of sellers (direct)
SPENT: T____
Taxes (inverse)
Temperature
Technology (increase)
Tampering
Law of Diminishing Returns or Diminishing Marginal Product
Add factors of production to fixed factors of production, total output increases initially but eventually the additional output diminishes to the point of negative returns
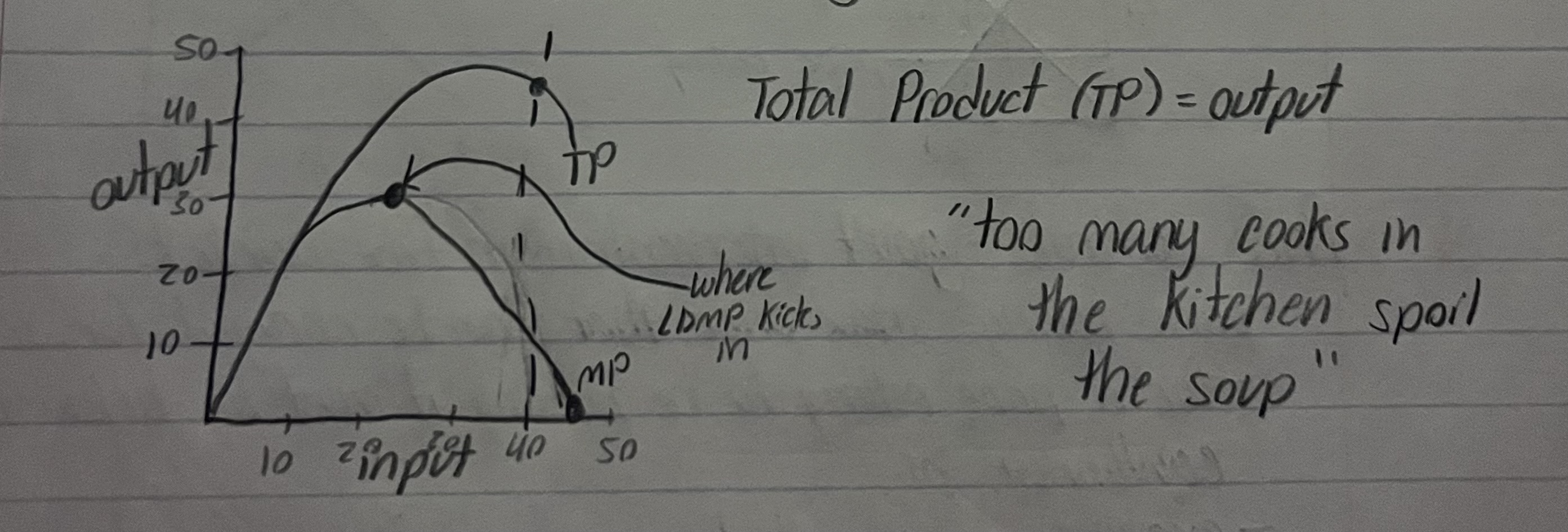
Elasticity of Supply
determined by time
short-run vs long run
Short Term for Es
time frame in which some inputs are fixed
long-run for Es
time frame in which all inputs variable
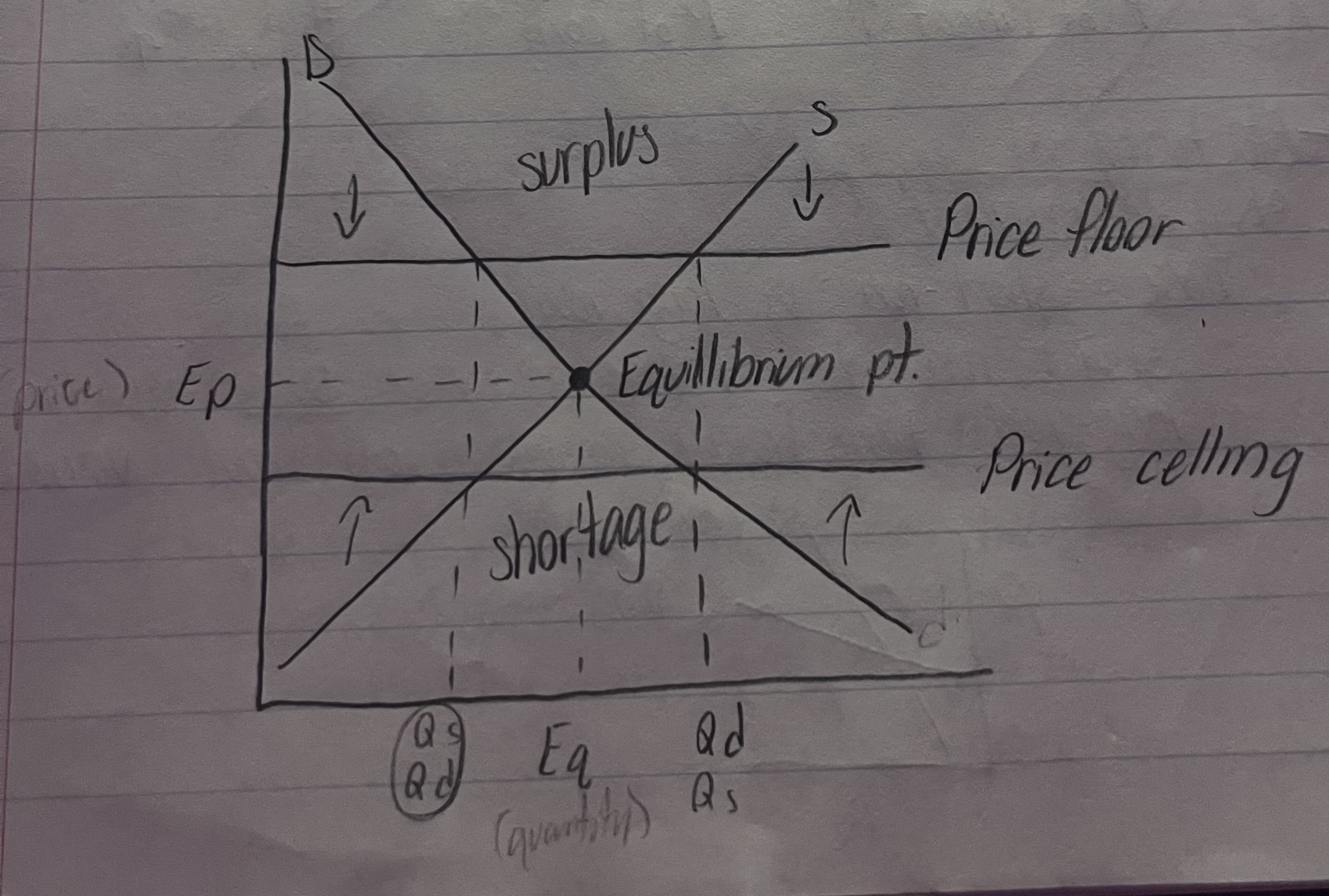
Market Equilibrium
where supply+demand intersect and sets market price + market output
Price Controls
gov’t intervention in free market
Price Celling
max price that can be charged for a g/s
below equilibrium point
rent control
result - Qd > Qs = shortage
consequence - slum lords
Price Flooring
minimum price that can be charged for a g/s
above equilibrium point
wage laws
result - Qs > Qd = surplus (labor)
consequence - increased unemployment
Market Equilibrium Graph
In Market Equilibrium: If demand increases
supply stays constant
price increases
quantity increases
In Market Equilibrium: If demand decreases
supply stays constant
price decreases
quantity decreases
In Market Equilibrium: If supply increases
demand stays constant
price decreases
quantity increases
In Market Equilibrium: If supply decreases
demand stays constant
price increases
quantity decreases
In Market Equilibrium: If both demand and supply increase
price stays constant
quantity increases
In Market Equilibrium: If both demand and supply decrease
price stays constant
quantity decreases
In Market Equilibrium: If demand increases and supply decreases
price increases
quantity stays constant
In Market Equilibrium: If demand decreases and supply increases
price decreases
quantity stays constant
Law of Demand
P-up Qd-down + P-down Qd-up; inverse relationship
Ceteris Paribus
basic assumption in law of supply+demand
means all other variables that can influence Demand remain constant
Changes in Qd
caused by change in price; shown as movement along the demand curve
3 Price Variables
Substitution Effect, Real Income Effect, and Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility (DMU)
Substitution Effect
When price of good X increases, then people buy more good Y; PRIMARY CAUSE
Real Income Effect
When price increases or decreases but income (Y) stays the same
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility (DMU)
the more you consume of a g/s the less additional satisfaction received
The only way to consume more is to decrease price
Changes in Demand
caused by non-price variables and involve a shift in the demand curve
PYNTE - P____
Price of relates goods
PYNTE - Y___
Income
PYNTE - N____
Number of consumers (population)
PYNTE - T____
Taste and Preferences
PYNTE - E____
Expectations about a future change in price or event
Elasticity of Demand
responsiveness of changes in Qd to a change in price
Elasticity of Demand Coefficient (Ed)
Ed>1 = elastic
Ed<1 = inelastic
Ed=1 = unit elastic
*ignore negative value
4 determinants of Ed
Luxury (E) vs Necessity (In)
Can it be substituted? (yes=E, no=In)
% of income spent (large=E, small=In)
Time → increases elasticity
Midpoint Formula (Simplified) (Ed)
\frac{Q2-Q1}{Q2+Q1}\cdot\frac{P2+P1}{P2-P1}
Total Revenue Test of Elasticity
Elastic = P-up TR-down + P-down TR-up
Inelastic = P-up TR-up + P-down TR-down
Cross Elasticity
measures the impact of change in price of goods x, on the change in demand of goods y
Cross Elasticity Formula (Exy)
% change D y / % change P x
negative value = complementary
positive value = substitutes
Income Elasticity
measures the change in D in response to a change in income
Income Elasticity Formula (Ey)
% change in D / % change in Y
negative value = inferior good
positive value = normal good
perfectly inelastic
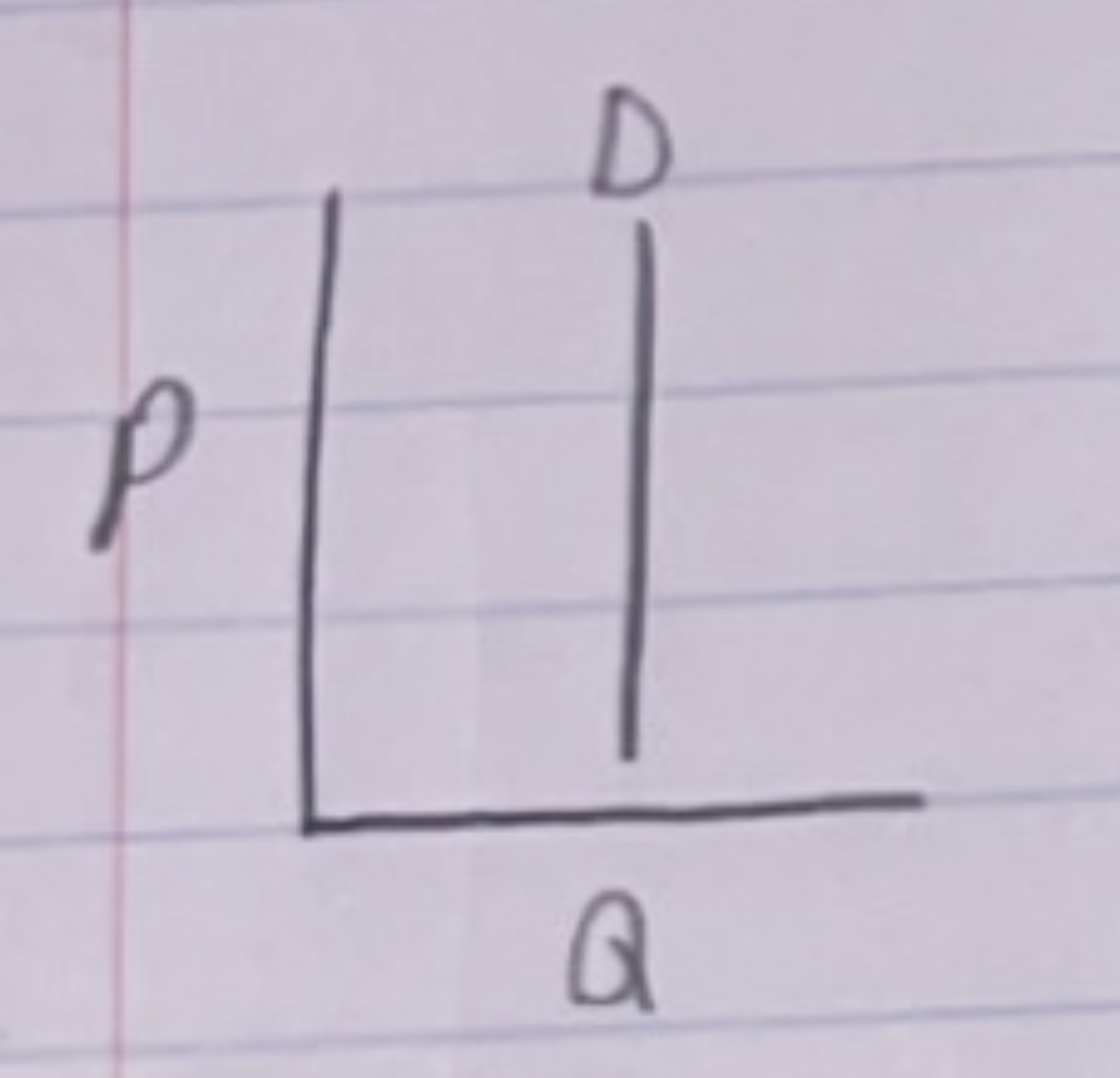
perfectly elastic