Geologic History & Sequencing
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Geologic history
The study & interpretation of Earth's past
Principle of uniformitarianism
the geologic history processes that are going on now happened before.
"The present is the key to the past"
-Ex; Places today where layers of sediments are forming in a pattern, that same pattern can be found in rocks formed long ago
Relative age
When the age of a rock or event is compared to the ages of other rocks or events in geologic history, the relative of the rock or event is determined.
Absolute age
The actual age of the rock or event.
The older it is the more hard it gets to determine the absolute age
Principle of original horizontality
sediments are deposited in horizontal layers that are parallel to the surface on which they were deposited.
Tilted or folded layers indicate that the crust has been deformed.
Principle of Superposition
In a series of undisturbed layers, the oldest is on the bottom.
The principle of superposition does not apply, however, in cases where layers have been overturned or where older rocks have been forced over younger layers along a fault.
Intrusions
When molten magma forces its way into cracks or crevices in crustal rock and solidifies it forms a mass of igneous rock.
Extrusion
When lava solidifies at Earth’s surface and it forms a mass of igneous rock.
Unconformities
Buried Surfaces that indicate gaps or breaks in the geologic time record.
These gaps represent destruction of the geologic record.
Angular unconformities
Tilted folded or faulted rocks which have been eroded and then covered again.
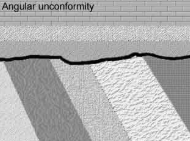
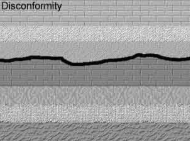
Parallel unconformities
also called disconformities, occur when parallel rock layers of different ages are separated by an erosional surface .
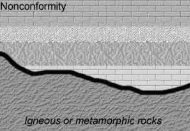
Nonconformities
Formed when sedimentary rocks are deposited on top of an eroded surface of igneous
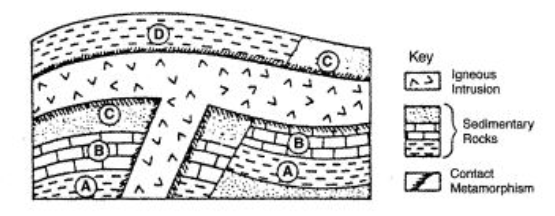
The diagram below represents folded and faulted rock layers cut by an igneous intrusion. What is the relative age of the intrusion?
younger than rock unit D and younger than the fault
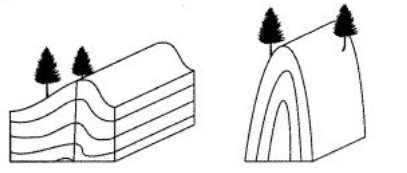
The sedimentary bedrock in both regions originally formed as…
horizontal layers
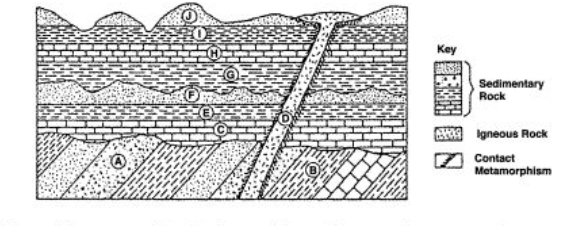
Which rock layer provides the best evidence for crustal movement?
Layer B
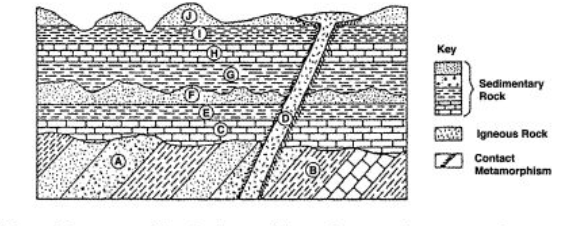
Which rock layer most likely was deposited directly on an erosional surface?
Layer C
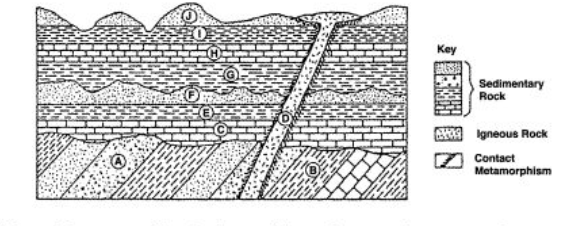
Which event occurred most recently
erosion of rock layer J