Old Exam (9, 10, 11)
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
How has biotechnology improved our lives?
A. Production of industrial enzymes used in detergents, paper production and food industry.
B. The use of DNA profiling techniques for paternity identification and crime scene investigation.
C. Development of herbicide and pest-resistant crop plants.
D. Production of needed pharmaceutical products.
E. all of the above are ways that biotechnology has improved our lives.
E. all of the above are ways that biotechnology has improved our lives.
Pathogenic microorganisms belong to which of the following categories?
A. photoautotrophs
B. chemoheterotrophs
C. chemoautotrophs
D. photoheterotrophs
B. chemoheterotrophs
Most microbes causing disease in humans grow fastest in a pH range of ________.
A. 3.0 to 5.0
B. 6.5 to 7.5
C. 6.5 to 9.5
D. 5.5 to 8.0
B. 6.5 to 7.5
Which of the following cellular processes produces acidic products that will preserve food?
A. glycolysis
B. fermentation
C. aerobic respiration
D. anaerobic respiration
B. fermentation
Optimum growth rate is above 80oC for ________.
A. hyperthermophiles
B. psychrophiles
C. thermophiles
D. mesophiles
A. hyperthermophiles
The bracket marked 'y'; is the range of temperature where ________ bacteria have their optimum growth temperature.
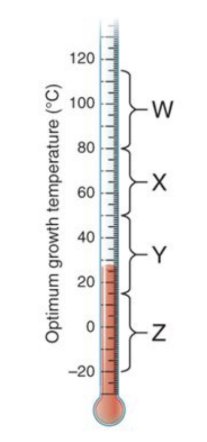
A. thermophiles
B. hyperthermophiles
C. mesophiles
D. psychrophiles
C. mesophiles
Which of the following cell types cannot protect itself from lysis when placed in a hypotonic environment?
A. bacterial cells
B. protozoan cells
C. fungal cells
D. animal cells
D. animal cells
In a hypotonic environment, which way will water flow via osmosis?
A. Neither because there will be no movement of water into or out of the cell
B. Into the cell
C. Neither since movement of water particles in and out of the cell will be equal
D. Out of the cell
B. Into the cell
Most microbes grow fastest in a pH range of ________.
A. 3.5 to 5.0
B. 6.5 to 8.5
C. 6.5 to 7.5
D. 7.5 - 9.0
C. 6.5 to 7.5
The terminator sequence for transcription is the ________.
A. DNA sequence that binds factors to stop transcription and release newly formed mRNA complex
B. binding site for enzymes that bind RNA polymerase to DNA at the beginning of the gene- coding region
C. RNA sequence that binds factors to stop translation and release newly formed mRNA complex
D. RNA sequence that binds factors to stop transcription and release newly formed mRNA complex
A. DNA sequence that binds factors to stop transcription and release newly formed mRNA complex
All of the following is correct about the genetic code EXCEPT:
A. uses one of three codons that do not code for an amino acid to stand for the end of the protein
B. is redundant because there is often more than one choice of codon for most amino acids
C. uses AUG coding for Methionine as the start of every protein
D. is contained in anti-codon sequences found in DNA
D. is contained in anti-codon sequences found in DNA
Which of the following does NOT describe how the lac operon in E. coli works?
A. When the repressor is active, it binds to the promoter sequence which blocks binding of RNA polymerase to the lac operon coding for enzymes required for metabolizing lactose.
B. The lac operon controls the expression of enzymes needed to transport lactose into the cell and break it down into glucose and galactose.
C. When lactose is absent the repressor blocks transcription of structural genes that code for enzymes that split apart lactose into simple sugars.
D. When lactose is present the repressor is inhibited thereby permitting the production of enzymes that break up lactose and transport the byproducts into the cell.
A. When the repressor is active, it binds to the promoter sequence which blocks binding of RNA polymerase to the lac operon coding for enzymes required for metabolizing lactose.
Which of the following nitrogen-containing bases would NOT be found in a molecule of RNA?
A. cytosine
B. uracil
C. thymine
D. guanine
C. thymine
Serratia marscecens produces a red pigment at 25°C but not when grown at 35°C. This is an example of a _________ change.
A. genotypic
B. allelic
C. missense
D. phenotypic
D. phenotypic
A particular bacterial gene encodes an mRNA which has 210 nucleotides; what is the maximum number of amino acids possible in the resulting polypeptide?
A. 21
B. 210
C. 420
D. 70
D. 70
During translation (after initiation), which of the following sequences show the correct order that tRNA will bind to sites on the ribosome?
A. A site, E site, P site
B. A site, P site, E site
C. P site, E site, A site
D. E site, P site, A site
B. A site, P site, E site
Which enzyme is matched INCORRECTLY with its function?
A. DNA polymerase – synthesizes DNA strand during DNA replication
B. DNA ligase – joins Okazaki fragments during DNA synthesis
C. RNA polymerase- transcribes mRNA
D. topoisomerase – relaxes DNA at replication fork; helps new strands of DNA separate
E. helicase - synthesizes the RNA primer
E. helicase - synthesizes the RNA primer
A particular genome of an organism has 200 base pairs; if there are 73 guanine residues, how many thymidine residues are there?
A. 73
B. 146
C. 346
D. 127
D. 127
Which of the following causes mutations by creating thymine dimers?
A. ultraviolet light
B. benzopyrene
C. nitrous acid
D. gamma rays
A. ultraviolet light
Transposons are small mobile pieces of DNA which can move into a cell and randomly their DNA into that cell's chromosome. Which of the following mutations is MOST LIKELY created by transposons?
A. missense
B. base substitution
C. frameshift
D. nonsense
C. frameshift
What is the outcome of changing the DNA sequence from AAA to AAC (see chart included)?
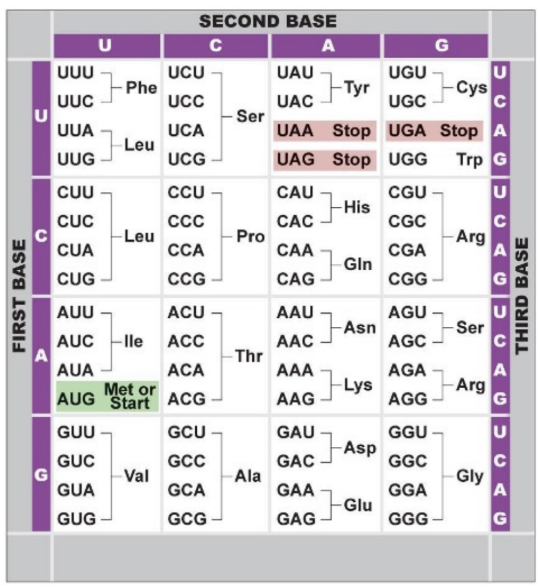
A. frameshift mutation
B. lys --> asn
C. phe--> leu
D. deletion mutation
C. phe--> leu
A gene is BEST defined as:
A. A transcribed segment of DNA
B. Three nucleotides that code for an amino acid
C. A sequence of nucleotides in RNA that codes for a functional product
D. A sequence of nucleotides in DNA that codes for a functional product
D. A sequence of nucleotides in DNA that codes for a functional product
The restriction endonuclease Hae III cuts per the following sites: What type of ends are produced?

A. overlapping cuts
B. blunt ends
C. sticky ends
B. blunt ends
How many copies of DNA would be present after 6 cycles of PCR starting with one copy in the reaction tube?
A. 6
B. 16
C. 8
D. 64
E. 32
D. 64
The structure which holds the donor and recipient cell together during conjugation is the_____.
A. capsule
B. pilus
C. flagellum
D. plasmid
B. pilus
Mutating the promoter site would affect what cellular process?
A. the elongation step in protein synthesis
B. mRNA capping
C. translocation of mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm
D. recognition of the transcription initiation site
D. recognition of the transcription initiation site
If glucose and lactose were both present in the medium for growing bacteria, one would expect that:
A. the lac operon would be inhibited and no genes would be expressed
B. the repressor protein would not be able to bind to the operator site of the lac operon
C. the beta-galactosidase enzyme which breaks down lactose would be synthesized at maximal levels
D. the lactose would be metabolized before the glucose would be
B. the repressor protein would not be able to bind to the operator site of the lac operon
The strands that make up DNA are antiparallel. This means that:
A. the 5’ to 3’ direction of one strand runs counter to the 5’ to 3’ direction of the other strand
B. one strand contains only purines and the other contains only pyrimidines
C. the twisting nature of DNA creates nonparallel strands
D. one strand is positively charged and the other is negatively charged
A. the 5’ to 3’ direction of one strand runs counter to the 5’ to 3’ direction of the other strand
The NAD+ utilized in glycolysis and other processes actually comes from the water-soluble B vitamin known as niacin. NAD+ is an organic electron carrier that becomes activated when it is reduced to NADH. On the cellular level what do you think would happen to a person who is malnourished and lacks adequate B vitamins?
A. They will suffer from fatigue and recuperation will be faster than expected
B. Subsequent to their malnutrition they will not have enough NAD+ to carry the electrons released and the cells will become too acidic and die.
C. They will not have enough NAD+ to serve as energy carriers and subsequently will not be able to produce enough ATP to fuel cellular functions.
D. They will build up too much glucose in the bloodstream and will develop Diabetes Type I.
C. They will not have enough NAD+ to serve as energy carriers and subsequently will not be able to produce enough ATP to fuel cellular functions.
Chemoheterotrophs use organic compounds as their primary carbon source and the same compounds as their energy resource. This group includes ________.
A. humans and other animals
B. fungi
C. most protozoa
D. most pathogenic bacteria
E. all of the above
E. all of the above
Sulfanilimide is an antimicrobial drug that mimics the shape of an important substrate for a particular bacterial enzyme, thereby inhibiting the enzyme. This type of inhibition is known as:
A. feedback inhibition
B. competitive inhibition
C. non-competitive inhibition
D. allosteric inhibition
B. competitive inhibition
If a cell produced 10 molecules of NADH and 6 molecules of FADH2 during the oxidation of glucose, how many ATP molecules could be produced theoretically in oxidative phosphorylation?
A. 42
B. 34
C. 48
D. 51
A. 42
Which of the following is NOT one of the three most common electron acceptors in anaerobic respiration?
A. nitrate
B. sulfate
C. methane
D. oxygen
D. oxygen
Bacteria genomes are considered to be:
A. diploid
B. haploid
B. haploid
If the genetic code required only two nucleotides for incorporation of amino acids, the amino acid sequence of the transcript AUGAUGAUGAUG would be:
A. B-D-E-B-D-E
B. B-B-B-B-B-B
C. B-B-B-D-D-D
D. B-B-D-D-E-E
A. B-D-E-B-D-E
How is ATP generated in the reaction shown in this figure?
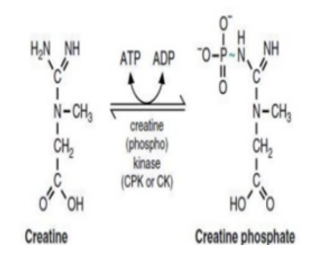
A. substrate-level phosphorylation
B. oxidative phosphorylation
C. photophosphorylation
D. all of the above
A. substrate-level phosphorylation
Catabolism is a set of reactions that__.
A. exergonic; results in the synthesis of a large macromolecule from smaller subunits
B. endergonic; results in the synthesis of a large macromolecule from smaller subunits
C. exergonic; results in the breakdown of a large macromolecule into smaller subunits
D. endergonic; results in the synthesis of a large macromolecule from smaller subunits
C. exergonic; results in the breakdown of a large macromolecule into smaller subunits
A redox reaction occurs when one compound is and _ electrons while another compound is ___ and __ electrons.
A. reduced; loses; oxidized; gains
B. reduced; gains; oxidized; loses
C. oxidized; gains; reduced; gains
D. reduced; loses; oxidized; loses
B. reduced; gains; oxidized; loses
Which of the following is the small unit which makes up protein?
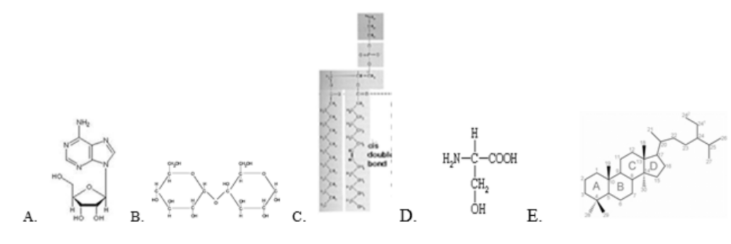
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
D. D
The rates of O2 and glucose consumption by a bacterial culture are shown in this figure. Assume a bacterial culture was grown in a glucose medium without O2. Then O2 was added at the time marked X. The data indicate that
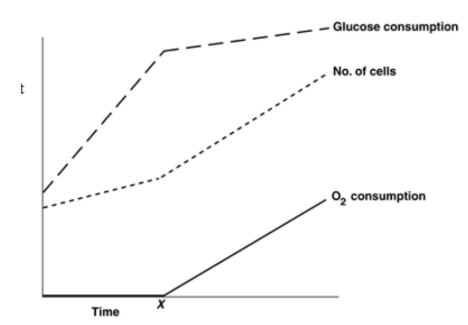
A. these bacteria get more energy anaerobically
B. aerobic metabolism is more efficient than fermentation
C. these bacteria don't use O2
D. these bacteria cannot grow anaerobically
B. aerobic metabolism is more efficient than fermentation
An organism that requires high levels of salt in the environment for growth is
A. neutrophile
B. salinophile
C. thermophile
D. halophile
D. halophile
The bacteria which causes peptic ulcers because it can grow in the acidic peptic region of the body is
A. Escherichia coli
B. Helicobacter
C. Shigella
D. Salmonella
B. Helicobacter
The enzyme catalase
A. breaks down hydrogen peroxide in to water and oxygen
B. converts oxygen into superoxide radicals
C. converts superoxide radicals into hydrogen peroxide
D. None of the answers are correct
A. breaks down hydrogen peroxide in to water and oxygen
The molecules that microbes utilize to sequester iron is
A. hemoglobin
B. siderophore
C. lactoferrin
D. transferrin
B. siderophore
Which of the following would NOT be considered as a micronutrient for bacterial cells?
A. cobalt
B. cesium
C. zinc
D. nitrogen
D. nitrogen
Bacterial cell division requires all of the following EXCEPT
A. partitioning of the daughter cell genomes
B. centriole
C. duplication of the genome
D. division of the two daughter cells
B. centriole
At what stage of the bacterial cell growth cycle would endospores dominate?
A. log phase
B. stationary phase
C. lag phase
D. death phase
D. death phase
Which of the following methods of measuring cell density would be the best to choose when you know that you do not have a lot of bacteria present in your sample?
A. Spectrophotometry because it is sensitive to low bacterial numbers.
B. Dilution plating because you will be able to count between 30-300 cells on a plate
C. A Petroff-Hausser chamber because you are visually counting bacteria.
D. filtration because the number of bacteria may be concentrated on the filter prior to plating
D. filtration because the number of bacteria may be concentrated on the filter prior to plating
The purpose of agar in bacteriological medium is
A. to inhibit the fungi that might be present in the sample
B. solidify the medium
C. add more nutrient value to the medium
D. add an additional energy source for the bacteria to metabolize
B. solidify the medium
A growth medium in which the exact chemical concentrations are known is termed ________.
A. defined medium
B. complex medium
C. undefined medium
D. enrichment medium
A. defined medium
A medium that turns pink when the lactose is fermented would be identified as
A. complex medium
B. enrichment medium
C. selective medium
D. differential medium
D. differential medium
Which of the following is NOT a physical method of controlling microbial growth?
A. use flame to burn the loop
B. filtration
C. use low temperatures
D. using an alcohol gel
D. using an alcohol gel
Surfactants
A. dissolve lipids and disrupt cell membranes
B. disrupts and oxidizes protein and nucleic acid structure
C. rapidly dentaures proteins
D. cause loss of membrane structure or function and inhibits fatty acid synthesis
A. dissolve lipids and disrupt cell membranes
Which of the following treatments may be used to sterilize heat-sensitive material?
A. 95% alcohol
B. autoclave
C. ethylene oxide
D. quaternary ammonium compounds
C. ethylene oxide
Cultures from infections that are deep in the body are ________.
A. collected with culturettes
B. collected using needle aspirates
C. placed in sample bottles that are cultured aerobically and anaerobically
D. placed in refrigerated sterile containers with secure lids
B. collected using needle aspirates
Which of the following is NOT true about carbon.
A. Carbon is acquired by chemoautotrophs in a process called carbon fixation
B. Carbon is the backbone for all organic macromolecules
C. Carbon is acquired by photosynthetic organisms in a process called carbon fixation
D. Carbon is acquired by chemoheterotrophs from the intake of other inorganic molecules
D. Carbon is acquired by chemoheterotrophs from the intake of other inorganic molecules
An aerobic organism would be expected to produce the enzymes:
A. superoxide dismutase only
B. catalase and superoxide dismutase
C. peroxidase and catalase only
D. catalase only
B. catalase and superoxide dismutase
A facultative anaerobe ________.
A. grows best by fermentation but is not harmed by presence of oxygen
B. can only grow in anaerobic conditions
C. may use either fermentation or anaerobic respiration
D. must have oxygen for aerobic respiration
C. may use either fermentation or anaerobic respiration
When we look at the ion and micronutrients required for microbial growth, which of these statements is NOT true?
A. Potassium, sodium and chloride help maintain osmotic conditions inside the cell when external changes take place in the environment.
B. Nitrogen is required for the synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins.
C. Sulfur is required for synthesis of several sugars added to proteins.
D. Phosphorus is required for production of ATP and nucleic acids and phospholipids.
C. Sulfur is required for synthesis of several sugars added to proteins.
Starting with one bacterial cell, what is the minimum amount of time required to end up with over 1000 cells if the generation time is 30 minutes?
A. 10 hrs
B. 4.5 hrs
C. 7 hrs
D. 5 hrs
D. 5 hrs
Of the following microbial forms listed, which would be the HARDEST to sterilize?
A. fungal spores
B. gram-positive bacteria
C. bacterial endospores
D. enveloped viruses
C. bacterial endospores
________ is used to slow or stop microbial metabolism and growth but does not kill microbes.
A. Pasteurization
B. Cooling
C. Heating a liquid until it boils
D. Filtration
B. Cooling
A particular biocide displays a 90% killing rate per minute. How many of the original 10^6 bacteria would be present after 5 minutes exposure to the biocide?
A. 10^1
B. 10^3
C. 10^4
D. 10^2
A. 10^1
When bacteria are introduced into a new environment, they often go through four phases of growth. The phase which will change most dramatically if cells are shifted from glucose-containing medium to lactose-containing medium is:
A. death phase
B. log phase
C. stationary phase
D. lag phase
D. lag phase
Rifamycins ___.
A. inhibit bacterial RNA polymerase
B. cause breaks in DNA during separation of daughter chromosomes during semi-conservative replication
C. inhibits DHFA reductase enzyme in bacteria
D. are structural analogs of PABA that are competitive inhibitors of first enzyme in pathway for microbial THFA synthesis
A. inhibit bacterial RNA polymerase