Pulmonary Edema - Patho 2
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What does this refer to
Primary gas-exchange units
Pores of Kohn
Permit air to pass through the septa from alveolus to alveolus
Collateral ventilation and even air distribution
Lungs contain approximately 25 million ____ at birth and 300 million by adulthood
Alveoli
What does this refer to
Formed by shared alveolar and capillary walls
Thin membrane of alveolar epithelium, the alveolar basement membrane, interstitial space, the capillary basement membrane, and the capillary endothelium
Alveolocapillary membrane (Pulmonary and Bronchial Circulation)
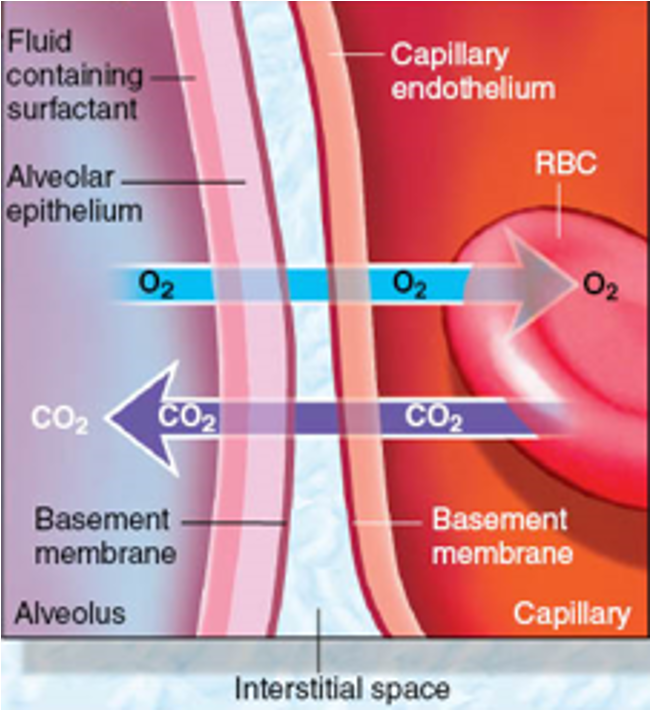
What does this refer to
Blood-gas barrier
What does this refer to
Adequate inspired O2 – (FiO2)
Ventilation and perfusion of alveoli
A permeable alveolocapillary membrane
Adequate blood flow
Ability to transport O2 and CO2
Ability of cell to use O2 and eliminate CO2
Requirements for Ventilation, Perfusion, and Diffusion
What does this refer to
Tendency of water molecules to contract to the smallest possible surface area (bead) with exposure to air
Increased ______= increased work of breathing
Surface Tension of Water
What does this refer to
The smaller a sphere’s radius (alveoli) the greater the surface tension and the more difficult (work) to expand the alveoli
Surfactant reduces fluid surface tension lining the alveoli and decreases tendency to collapse, preventing atelectasis
Laplace’s Law
What does this refer to
Four steps
Ventilation of the lungs
Diffusion of oxygen from the alveoli into the capillary blood
Perfusion of systemic capillaries with oxygenated blood
Diffusion of oxygen from systemic capillaries into the cells
Diffusion of CO2 occurs in reverse order
Gas Transport
What does this refer to
Accumulation of fluid in lung interstitium and alveoli
Impaired gas exchange → hypoxia
Common cause of respiratory distress
Pulmonary Edema
What does this refer to
Maintained by Starling forces
Low pulmonary capillary hydrostatic pressure
Effective lymphatic drainage
Normal Pulmonary Fluid Balance
What does this refer to
Fluid movement = Kf [(Pc - Pi) - σ(πc - πi)]
Kf = filtration coefficient
Pc = capillary hydrostatic pressure
πc = capillary oncotic pressure
Starling Equation
What does this refer to
Increased hydrostatic pressure
Decreased oncotic pressure
Increased capillary permeability
Lymphatic obstruction
Mechanisms of Pulmonary Edema
What does this refer to
Drain excess fluid from interstitium
Obstruction or overload can exacerbate edema
Chronic edema may impair lymphatic clearance
Lymphatic Role in Pulmonary Edema
What does this refer to
Fluid in alveoli blocks oxygen diffusion
V/Q mismatch and shunt physiology
Hypoxia and dyspnea result
Gas Exchange Impairment
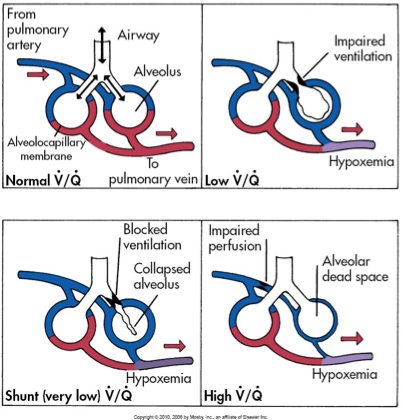
What does this refer to
Ventilation-Perfusion
What does this refer to
Dyspnea, orthopnea, crackles on auscultation
Pink frothy sputum (severe cases)** know this
Tachypnea, hypoxia, cyanosis
Clinical Features of Pulmonary Edema
What does this refer to
Cardiogenic: Kerley B lines, perihilar infiltrates, cardiomegaly
Non-cardiogenic: bilateral infiltrates, normal heart size
CT may show ground-glass opacities
Radiologic Findings
What does this refer to
Due to elevated left atrial pressure
Common causes: LV failure, mitral stenosis
↑ Pulmonary capillary hydrostatic pressure
Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema
What does this refer to
Backward transmission of pressure
Fluid leaks into interstitium → alveoli
Often seen in congestive heart failure
Hemodynamic Changes in Cardiogenic Edema
What does this refer to
Normal cardiac pressures
Caused by increased capillary permeability
Etiologies: ARDS, sepsis, aspiration, trauma
Non-Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema
What does this refer to
Endothelial damage → protein-rich fluid
Inflammatory cytokines: TNF-α, IL-1
Seen in ARDS and infections
Capillary Leak Syndrome
What does this refer to
Severe form of non-cardiogenic edema
Diffuse alveolar damage and inflammation
Leads to hypoxemia and stiff lungs
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
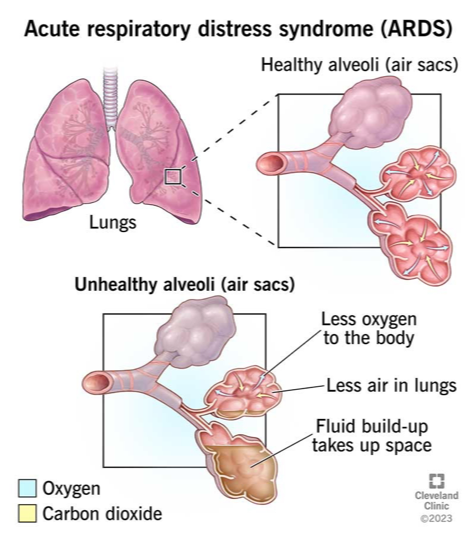
What does this refer to
Non-cardiogenic: triggered by hypoxia
Vasoconstriction → elevated pulmonary pressures
Capillary stress failure and leakage
High Altitude Pulmonary Edema (HAPE)
What does this refer to
Occurs after CNS insult (e.g., head trauma)
Sympathetic surge causes vasoconstriction
↑ Hydrostatic pressure in pulmonary circulation
Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema
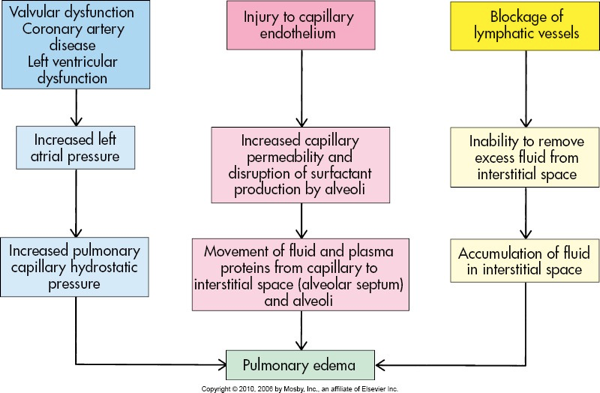
What does this refer to
Fluid overload and hypoalbuminemia
↓ Oncotic pressure → fluid transudation
Often mixed mechanism with cardiac involvement
Pulmonary Edema in Renal Failure
What does this refer to
Pulmonary edema arises from various pathophysiological pathways
Cardiogenic vs. non-cardiogenic classification aids management
Understanding mechanisms is key to diagnosis and treatment
Summary
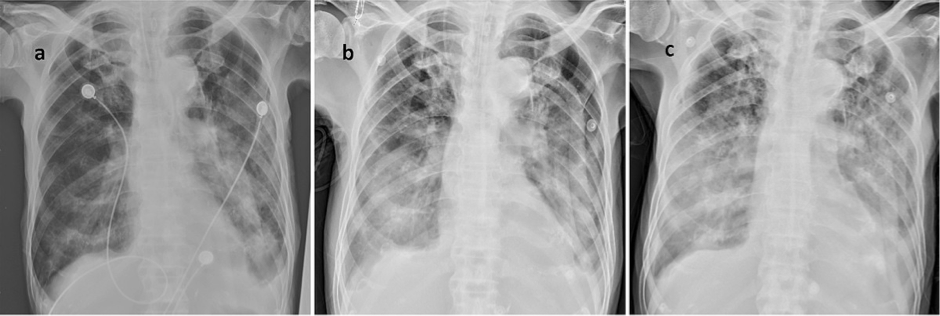
What does this refer to
ARDS Chest x-ray
What is black on a chest x-ray
air
What is dark gray on a chest x-ray
fat
What is light gray on a chest x-ray
soft tissue
What is white on a chest x-ray
metal
What is off-white on a chest x-ray
bone
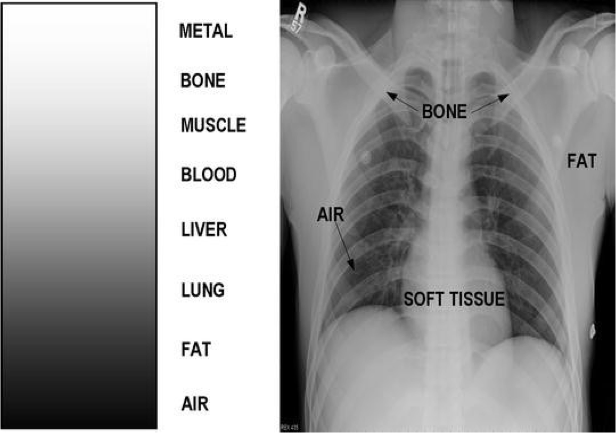
What does this refer to
Densities
What does this refer to
D – Details
R – RIPE
S – Soft tissues and bones
A – Airways
B – Breathing
C – Circulation
D – Diaphragm
E - Extras
Chest x-ray system DRS-ABCDE
What does this refer to
Is this my patient’s X-ray done today?
Patient’s information.
Type of film. PA, AP, lat, erect/supine, L/R
Date and time of X-ray.
Details (system of chest-x-ray)
What does this refer to
R – Rotation. Look at clavicles.
I – Inspiration. 5-6 anterior ribs/8-10 posterior ribs in MCL
P – Picture. All of lung fields included. Angulation.
E – Exposure aka Penetration. Look at spinous processes, diaphragm.
RIPE (system of chest-x-ray)
What does this refer to
Pneumothorax. Look at apices.
Lung fields.
Vascularity.
Lesions, masses, air-fluid levels
Pleura
Breathing (system of chest-x-ray)
What does this refer to
Shoulders, clavicles, ribs, sternum, spine
Soft tissue symmetry, swelling, subcutaneous air, masses
Breasts
Calcifications – especially in vessels
Soft tissues and bones (system of chest-x-ray)
What does this refer to
Trachea midline
Mediastinal masses
Carina and main stem bronchi
Aortic knob
Hilum
Vessels
Airways and mediastinum (system of chest-x-ray)
What does this refer to
Heart position
Heart size
Heart borders
Heart shape
Aortic stripe
Circulation (system of chest-x-ray)
What does this refer to
Diaphragm shape
Hemidiaphragms
Costophrenic angles
Gastric bubble
Pneumoperitoneum
Diaphragm (system of chest-x-ray)
What does this refer to
Tubes and lines– ETT, NGT, central lines, chest tube, PICC lines
Wires - Pacemaker, AICD, EKG electrodes
Metal –bone fixators, bullets, buck shot, coins
Extras (system of chest-x-ray)