Fall Final Review - AP Human Geography 2024-25
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
scale of inquiry
at what scale of analysis is the best to answer a question?
location
The position of a place or object on the Earth's surface.
Direction
The orientation or course along which something moves or faces (e.g., north, south, east, west).
Size
The dimensions or extent of an object or area.
Scale
The relationship between a portion of the Earth and the Earth as a whole; also, the level of detail or scope of a study (e.g., local, regional, global).
Physical Attributes
Natural characteristics of a place, such as climate, vegetation, and landforms.
Cultural Attributes
Human-made characteristics or elements of a place, such as language, religion, and customs.
Changing Attributes of Place
How the physical and cultural characteristics of a location can change over time due to various factors.
Environmental Determinism
The theory that the physical environment, including climate and terrain, shapes human activities and cultures.
Environmental Possibilism
The idea that while the environment may set certain constraints, humans have the ability to adapt and overcome these limitations through technology and innovation.
Spatial Interaction
How and why places interact with each other.
Network
A set of interconnected nodes (e.g., transportation systems).
Time-Space Compression
The reduction in the time it takes to reach a destination due to technological advancements.
Diffusion
The process by which phenomena spread from one place to another.
Hearth
The original source or place of origin of a phenomenon.
Relocation Diffusion
The spread of an idea or phenomenon through the physical movement of people.
Expansion Diffusion
The spread of a phenomenon outward from its hearth, often in a snowballing process.
Hierarchical Diffusion
Spread from larger to smaller places or from influential individuals to less influential ones.
Contagious Diffusion
Rapid, widespread diffusion from person to person. (ex. disease)
Stimulus Diffusion
The spread of an underlying principle or concept rather than the exact phenomenon.
Distribution
The way something is spread out or arranged over a geographic area.
Density
The frequency with which something occurs in a given area.
Arithmetic Density
The total number of people per unit area of land.
Physiological Density
The number of people per unit area of arable land.
Dispersion/Concentration
The arrangement of objects or phenomena in space, either dispersed/scattered or clustered/agglomerated.
Pattern
The geometric arrangement of objects in space, such as linear, centralized, or random.
Region
An area distinguished by certain common characteristics, categorized as formal/uniform, functional/nodal, or perceptual/vernacular.
sense of place
the emotions and memories attached to a place by people
absolute location
precise plotting of where on Earth’s surface something is located. ex. latitude and longitute
relative location
describes the location of something in relation to human and physical features around it
site
absolute location, plus physical characteristics, (temperature, weather). ex. New Orleans is located on a bend of the Mississippi River, a low-lying delta. The latitude of New Orleans, LA, USA, is 29.951005 and the longitude is -90.071533.
cultural landscape
the visible imprint of human activity on the physical landscape
sequent occupence
imprints made by a sequence of different occupants (ex. conquerors) who’s imprints are layered on top of each other. (ex. German city names in Texas, Tex-Mex)
distance/proximity
area between objects on Earth’s surface
region
an area that shares distinct characteristics and is different from another region
distribution/patterns
ways in which things are arranged within a given space
spatial interaction
the interaction between places
accesibility
ability to access another location easily
connectivity
the degree of linkage between location in a network (how connected places are)
spatial perspective
the arrangement of phenomena studied across the surface of the Earth, such as the movement of people and things that change in places over time, and human perceptions of
landscape
the material character of a place, the combo of natural features, human and man-made structures and other tangible objects that give a place a particular form (flavor)
situation
relative location; the area around settlement/cities; close proximity of raw materials, other settlements/cities and trade
friction of distance
the further away place A and place B are, the less they interact with each other
time-space compression
improved methods of transportation and communication reduces the distance between places (friction)
Globalization
increased due to multinational corporations getting global reach and power; travel and shipping is cheap and safe; governments have decreased tariffs and regulations on international trade.
positives of globalization
increases world economic output (more money)
more people can live better (less poverty)
globalization has effected culture…
fewer languages are spoken
less cultural diversity
more novels are translated
football reached America
globalization (shortend)
brings local culture and economics caused by increased interaction between geological distinct regions
formal regions
has one or more traits; can be physical, political, economical, cultural; has measurable, obvious borders. (ex. the US, Brazil, climate zones)
functional regions
defined with an activity; often organized around a center node; multiple places interact to create (ex. school districts, food delivery zone)
perceptual regions
not concrete; created by human perceptions of regions; shaped by stereotypes and half-baked ideas (the Deep South, the West Coast)
map scale
distance on map compared to distance on the ground
scale of analysis
how information is grouped (ex. regional, global, national)
distance decay theory
friction = time, effort, money
because of friction, less spatial interaction between places with large distance between them
human geography
focuses on how people make places, how we organize space and society, how we interact with each other in places and across space, and how we make sense of others and ourselves in our localities, regions, and the world
physical geography
the study of spatial and material characteristics of physical environment
spatial
relating to or occupying space
spatial distribution
the study of the relationship between objects in physical space
folk culture
traditionally practiced by a small rural group, isolated from others
pop culture
found in large societies that shares traits despite being different (popular)
local culture
a group of people in a particular place who seem themselves as a community who share experiences, customs, and traits and work to preserve their culture
material culture
Bracero Program
In the 1940s, the US government encourages Mexicans to come to the US and work as contract laborers.
refugee camps
a temporary settlement built to receive refugees.
remittances
the money migrants send home
reverse remittances
money that migrant’s families in their home country send to working migrants
cyclic movement
short, regular trips away from home for defined amount of time
periodic movement
long periods away from home, but less frequent
emmigration
the movement of people leaving a place
immigration
the movement of people entering a place
activity spaces
a daily routine that takes people through a sequence of short moves in a local area
nomadism
a way of life that people who do not continually live in the same place year-round
transhumance
a system of pastoral farming in which ranchers move livestock according to seasonal availability of pastures
international/transnational migration
movement across country borders
internal migration
migration that occurs within a single country’s borders
forced migration
when push factors drive people out of a place
voluntary migration
when people choose to leave a place because of pull factors of another place
human trafficking
an example of forced migration
examples of human trafficking
sex trafficking, forced labor, recruitment of child soldiers, etc
arithmetic density
population/total land
physiological density
population/total arable land
agricultural density
farmers/arable land
sex ratio
number of resident male births/number of resident female births
dependency ratio
population 15-64/0-15+65+
old age dependency ratio
population 65+/population 16-64
youth dependency ratio
population 0-15/population 16-64
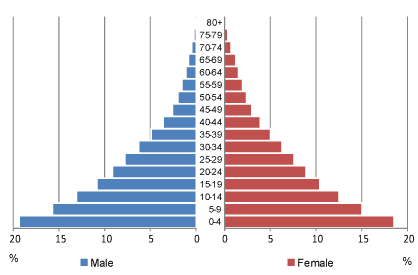
skinny pyramid
high birth rate/low death rate
short life expectancy/high IMR
high youth dependency
periphery/agriculture
high stationary growth
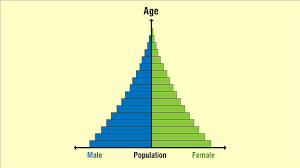
early expanding growth
triangle
high birth rate/falling death rate
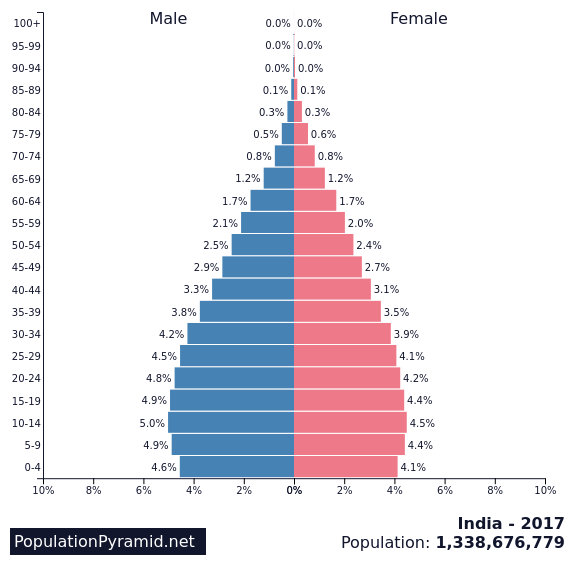
Late Expanding Growth
onion dome
falling birth rate/death rate falls slower
high life expectancy/low IMR
high youth depen/rising elderly depen
increasing industry/secondary
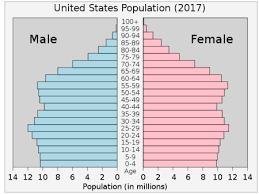
low stationary growth
box pyramid
low birth rate/low death rate
high life expectancy/low IMR
low youth depen/rising elderly depen
service dominated/tertiary
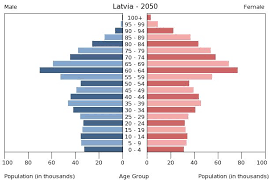
cup pyramid
low birth rate/low death rate
high life expectancy/low IMR
high elderly dependency
service oriented
negative population growth
Epidemiologic Model Stage 1
High stationary; pestilence and famine
Epidemiologic Model Stage 2
Early Expanding; receding pandemics
Epidemiologic Model Stage 3
Late Expanding; degenerative and man-made disease
Epidemiologic Model Stage 4
Low Stationary; delayed degenerative diseases