Microbial Growth Media and Bacterial Characteristics
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Thymine Dimers
formed by dimers can destroy or distort DNA
Bacteria used in Lab 12 (UV radiation on bacterial growth)
-Deinococcus radiodurans: an extremophile that measures the effectiveness of ionizing radiation in food preservation. - -Ecoli
Coliform Bacteria
-Gram Negative
- Lactose Fermenting Bacilli (in the gastrointestinal tract of mammals)
Fecal Coliform
-Present in the gut and feces
-Indicates fecal contamination ( failure in water)
Selective Media
- Allows the growth of microorganisms while suppressing others
Differential Media
-Used to differentiate closely related microorganisms (based on colors and patterns)
Fastidious
-Species that require complex growth media for culture
Hemolytic
- Rbc incompletely erythrocytes and convert hemoglobin to methoglobin, called alpha and beta hemolysis
- Beta hemolysis is the destruction of red blood cells
Blood Agar (Apperance) Alpha and Beta
Appearence
- Alpha: Greenish grey or brownish discoloration
- Beta: Clear ( around the colonies)
-
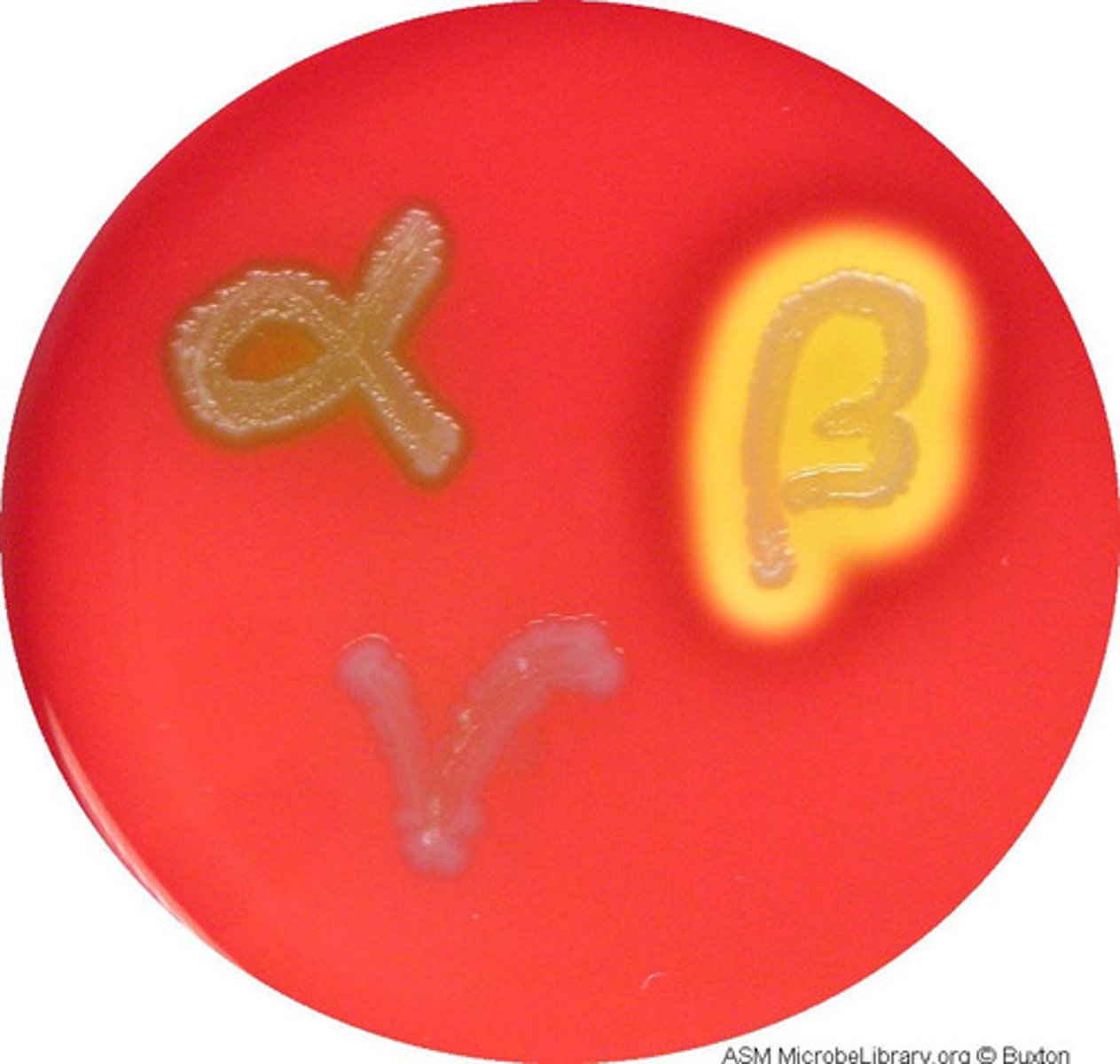

Blood Agar ( What is it)
Identifies the organism (ie: hemolysis cau7sed by growing bacteria)
EMB Agar (Apperance)
Metallic Green= Lactose/ Sucrose
Brown/Pink= Slow fermenting Lactose
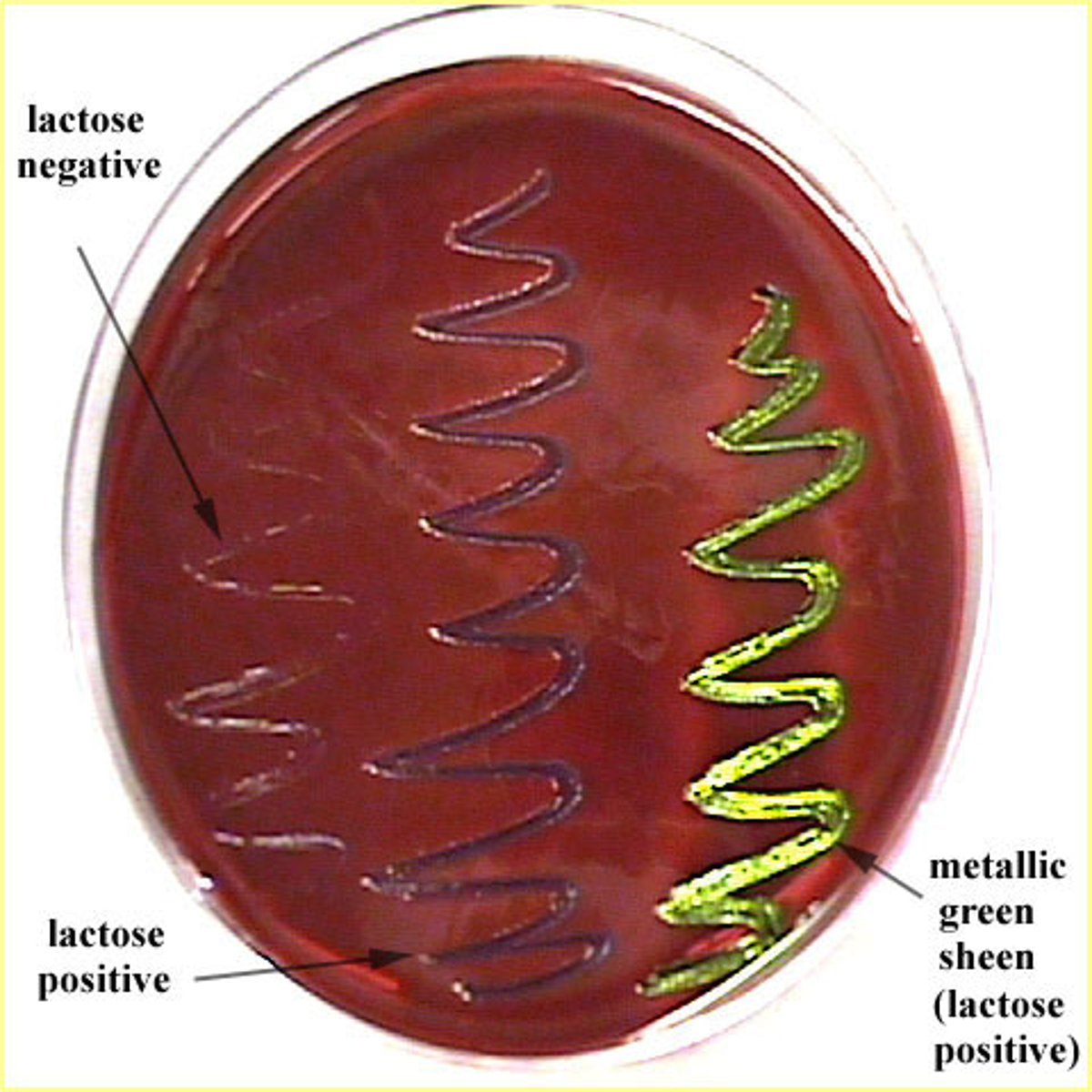
EMB Agar (Dye used)
Eosin and Methylene Blue
-The Dye is a differential indicator
-The dye inhibits the growth of many microorganism
EMB Agar (What is it)
- Lactose Fermenting
-Methylene Blue
-Gram Negative
-Selective and Differential
- Isolates Bacilli in foods
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) (Appearance)
Red AKA: "PHENOL RED", Stap E, Negative - Acid production
Yellow= "Coagulate"- Positive

Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) (What is it)
-Used as selective and differential for the identification of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis
- Only allows halophilic (salt-loving) and halotolerant ( salt-tolerant)
-supplies electrolytes
MacConkey Agar ( Appearance)
Red or Pink- Lactose Fermenting
Colorless- Non-Lactose fermenting
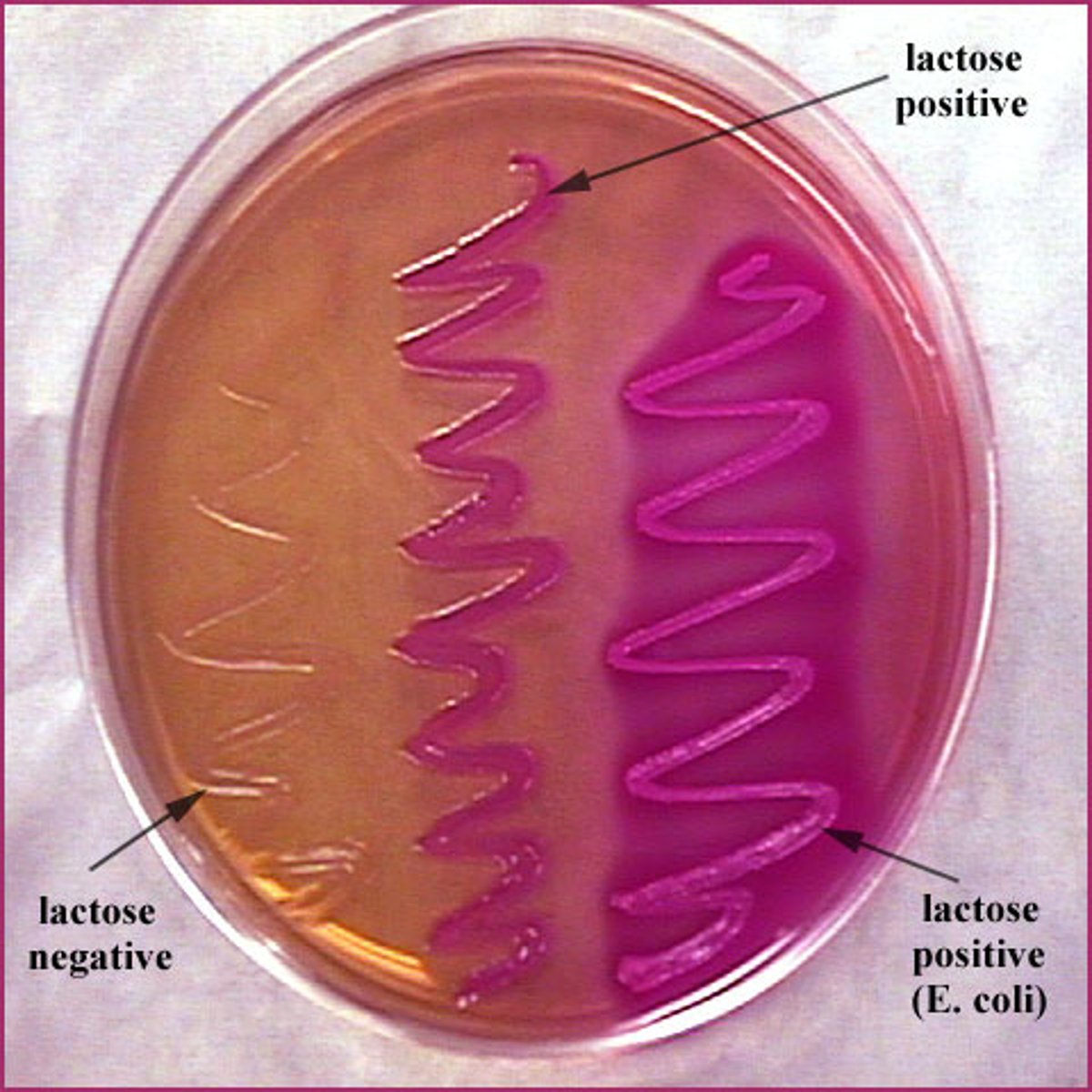
MacConkey Agar (What is it)
- Differentiation of Lactose Fermenting + Non-Lactose Fermenting
-Isolation of coliforms + intestinal pathogens in water and dairy
-Isolation of Gram-Negative Bacteria
Blood Agar: what are the two kinds of Agar
Alpha: Greenish-grey or Brownish
Beta: Clear
Names of the Agar done in class
Blood Agar
EMB
MacConkey Agar
Mannitol Salt Agar
Hemocytometer ( What is it for?)
-Used to make a direct count cells in a sample.
-Goes from small volume to Larger volume of 1 mL
Yeast cells are
fungus and unicellular
What is Methylene Blue used for?
Stains dead cells
Units for cell quantity
cells/cm3
or
cells/mL
and
1 cm3 = 1 mL
Turbidity
cloudiness of water
spectrophotometer
An instrument that measures the turbidity of a solution
and beam of light through a solution (measures absorbance)
Absorbance
Measures how much light is absorbed
Transmittance
Measures how much light passes through the solution
More Light goes through=
Higher Transmittance
ie: sterile water is high transmittance
because its clear and has no absorbance
More light blocked=
Higher Absorbance
ie: in a solution of yeast absorbance is high
Antibiotic Resistant Strains
Staphylococcus aureus
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
= infects the skin, genitourinary or respiratory tract and infections
Bacterial Lawn Steps
1) Label plate
2) Use antiseptic technique to obtain a bacterial sample from the liquid culture with sterile swab
3) Prepare a bacterial lawn on your Muller Hinton agar plate ( rotate the plate between streaks to cover the surface) Let it stand for 5 mins
4) Place four different antibiotic discs into the center of each quadrant
5) Incubate inverted plates for 18-24 hours at 35 Celsius
Disk Diffusion Test
Test how effective different antibiotics are against bacterial strain (like the antibiotic-resistant strains)
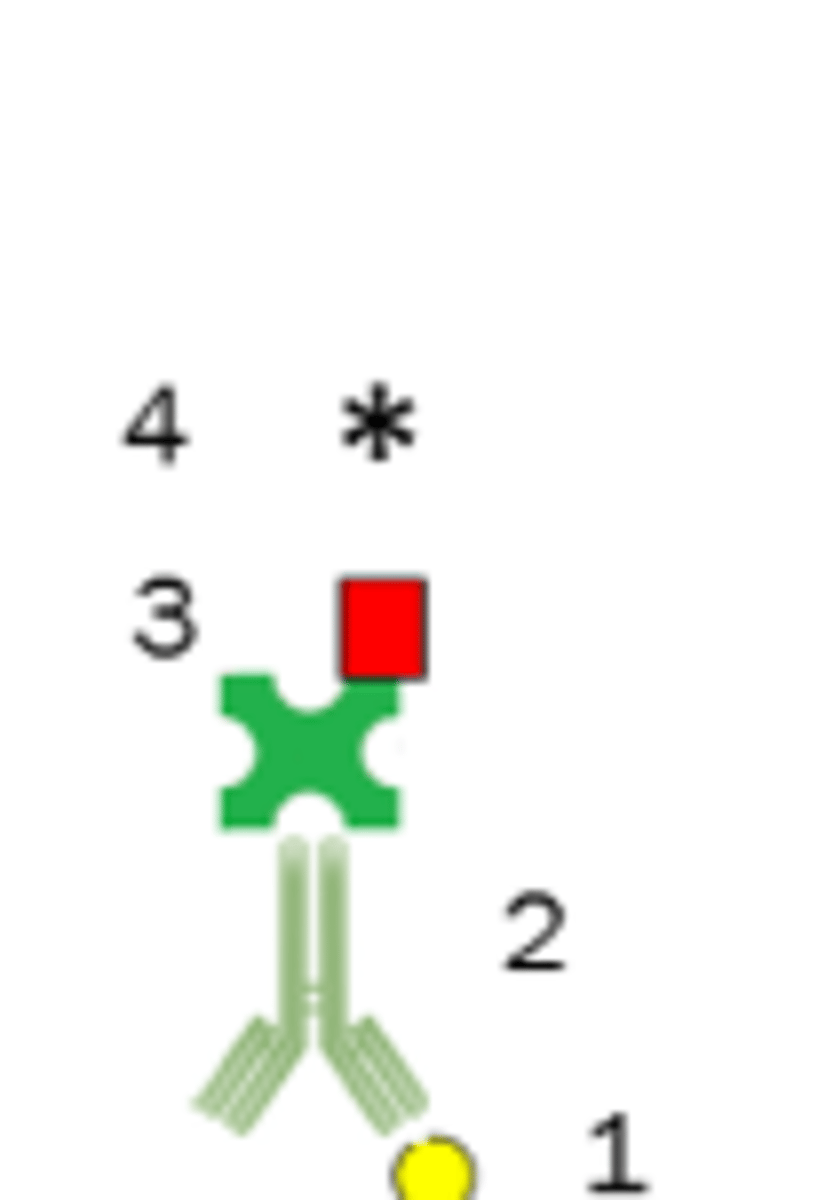
Direct Sandwich ELISA
Detects a specific antigen