ch3 - carbohydrates
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
what biological elements are carbohydrates made up of
C, H, O
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
what is a monomer
small units which can be joined to form long chain of molecules
what is a polymer
long chain of molecules formed by joining monomers during a condensation reaction
what is a condensation reaction
joining molecules together by removing water causing chemical bonds to be formed
what are condensation reactions also known as and why
anabolic reactions - building large molecules from smaller ones this process requires and uses energy to form bonds
what is hydrolysis reaction
splitting apart molecules through the addition of water causing chemical bonds to be broken
what are hydrolysis reactions also known as
catabolic reactions - breakdown of a large molecule into smaller ones this process releases energy as bonds are broken
condensation = … reaction
hydrolysis = … reaction
condensation = anabolic
hydrolysis = catabolic
is glucose a monomer or polymer
a monomer
what is the chemical formula for glucose and why is glucose important
C6H12O6
its important for all living things for respiration so energy can be generated
what are the two isomers of glucose
Alpha glucose
Beta glucose
what does isomers mean
when a molecule has the same chemical formula but structure is different
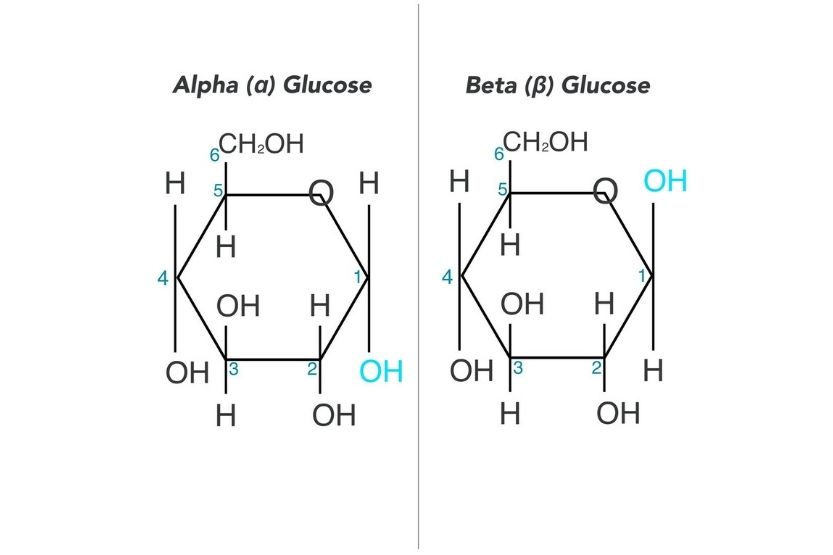
what is the structural difference between the isomers of glucose
Beta BEATS Alpha
-in beta glucose the hydroxyl, OH, group is above the plane
-in alpha glucose the hydroxyl, OH, group is below the plane
what is a monosaccharide and name all 4
a small simple sugar
-glucose
-fructose
-galactose
-ribose
what is the difference between glucose and ribose
glucose - hexose monosaccharide
ribose - pentose monosaccharide
what is a disaccharide and name all 3
two monosaccharides joined together by glycosidic bonds - formed via a condensation reaction
-maltose
-lactose
-sucrose
how is maltose formed
glucose + glucose > maltose + water
how is lactose formed
glucose + galactose > lactose + water
how is sucrose formed
glucose + fructose > sucrose + water
how do glycosidic bonds form
when two monosaccharides undergo a condensation reaction
what are the two types of glycosidic bonds which can be formed
1-4 (between 1C of one glucose and 4C of another glucose)
1-6 (between 1C of one glucose and 6C of another glucose)
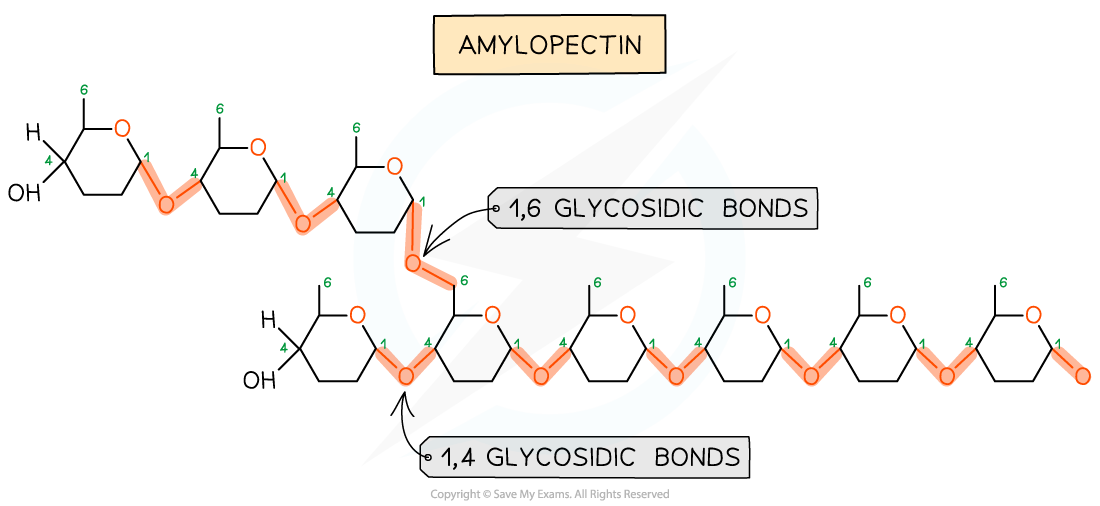
what is a polysaccharide and name all 3
a polymer made up of many monosaccharides joined together (formed via condensation reactions)
-cellulose
-starch
-glycogen
what is cellulose and where is it found
found in plant cell walls to provide structural support
what monomer is cellulose made up of and what is the bond between the monomers
BETA glucose with 1-4 glycosidic bonds
What is unique about the arrangement of beta monomers
They are inverted - each monomer is flipped by 180º creating an alternating inversion pattern, so the OH groups are close enough to react
what is the structure of cellulose
Beta glucose monomers join to form long, straight unbranched cellulose chains
Alternating inversion allows hydrogen bonds to form between each chain forming microfibrils
Microfibrils bundle together to make macrofibrils
Macrofibrils combine to form strong cellulose fibres in the cell wall
2 adaptations that enable cellulose carry out its function
Long straight unbranched chains - provide rigidity
Hydrogen bonds - collectively provide tensile strength
is cellulose soluble or insoluble and whys that important
insoluble meaning it does not affect water potential
what is starch and where is it found
found in plants inside chloroplast, as energy storage/ stores glucose
what are the 2 forms of starch
amylose and amylopectin
what monomer are the starch chains made up of and what is the bond between the monomers
ALPHA glucose
amylose - 1-4 glycosidic bonds
amylopectin - 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
what is the structure of amylose
Alpha glucose monomers join to form long, unbranched helix
what is the structure of amylopectin
Alpha glucose monomers join to form long, highly branched molecule
Adaptations for each type of starch that enable to carry out its function
Amylose - compact so can fit a lot of glucose in a small space
Amylopectin - branched molecule increases surface area for fast hydrolysis back into glucose to be readily available for respiration
> both are large so cannot diffuse out of cells
is starch soluble or insoluble and whys that important
insoluble meaning it does not affect water potential
what is glycogen and where is it found
found in animals to store glucose
what monomer is glycogen made up of and what is the bond between the monomers
ALPHA glucose with 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
what is the structure of glycogen
Alpha glucose monomers join to form highly branched molecule
Adaptations for each type of starch that enable to carry out its function
Highly branched molecule increases surface area for fast hydrolysis back into glucose to be readily available for respiration
> both are large so cannot diffuse out of cells
is glycogen soluble or insoluble and whys that important
insoluble meaning it does not affect water potential