Biology Quiz #7 Study Material on Reflexes and Neuronal Responses
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
1. integrating center
2. sensory neuron axon
3. sensory neuron cell body
4. sensory receptor
5. effector
6. motor neuron axon
7. motor neuron cell body
ID 1-7
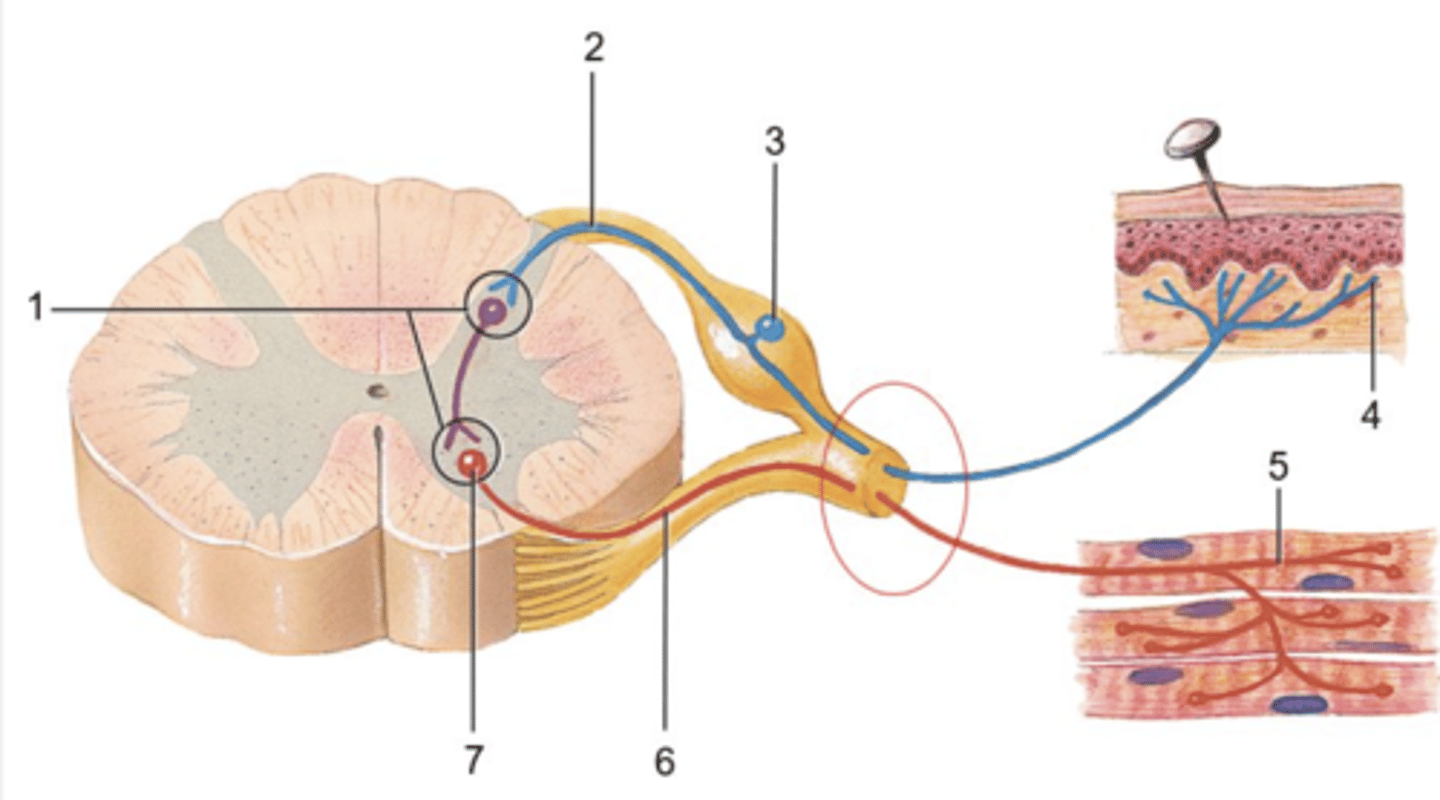
1. receptor
2. sensory neuron
3. integrating center of reciprocal innervation
4. integrating center for patellar reflex arc
5. motor neuron for patellar reflex arc
6. motor neuron for reciprocal innervation
7. effector for patellar reflex arc
8. effector for reciprocal innervation
ID 1-8
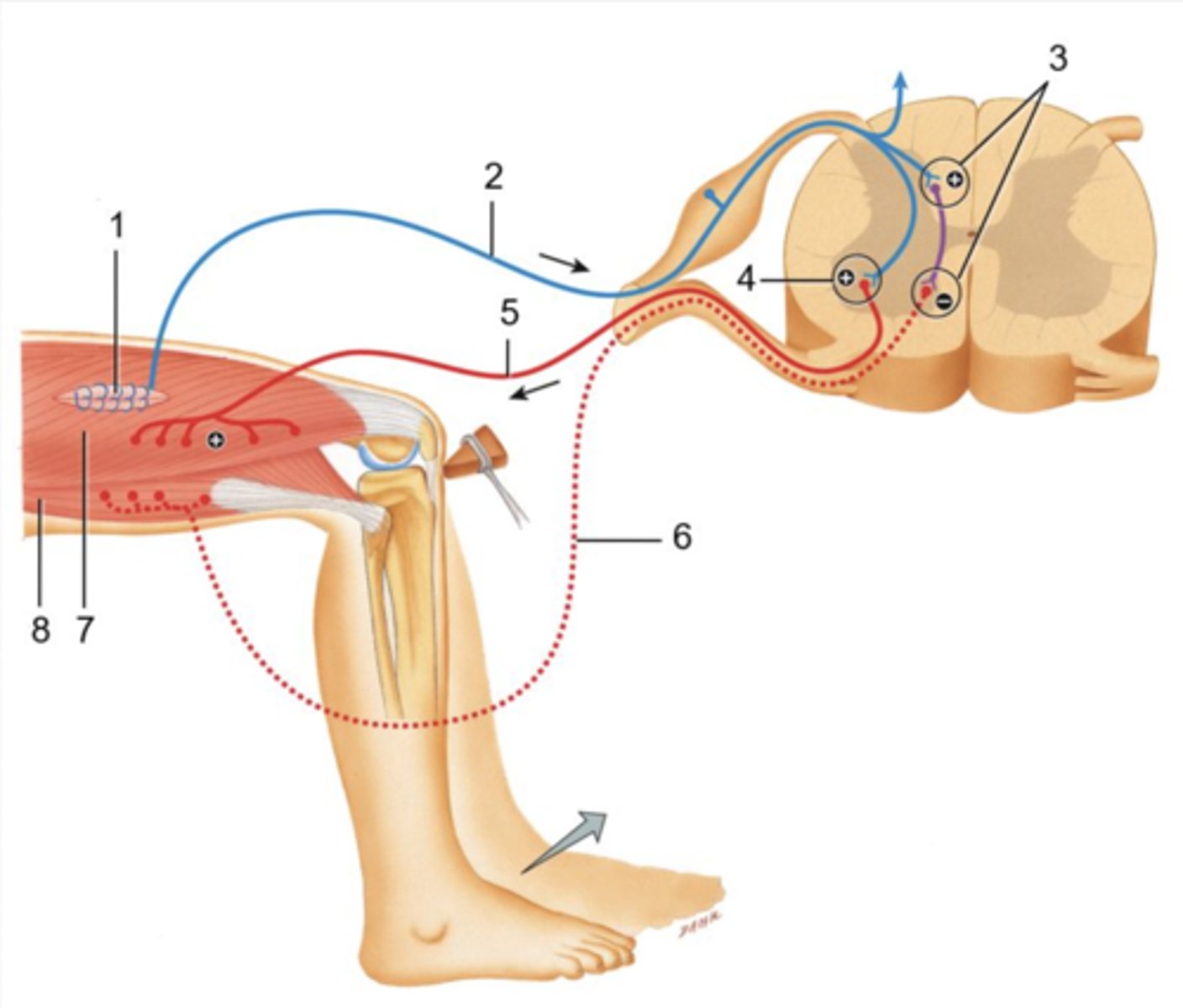
1. sensory neuron
2. interneuron sending impulses up and down the spinal cord
3. interneuron synapsing with motor neurons
4. motor neuron causing reflexion
5. motor neuron causing extension
ID 1-5
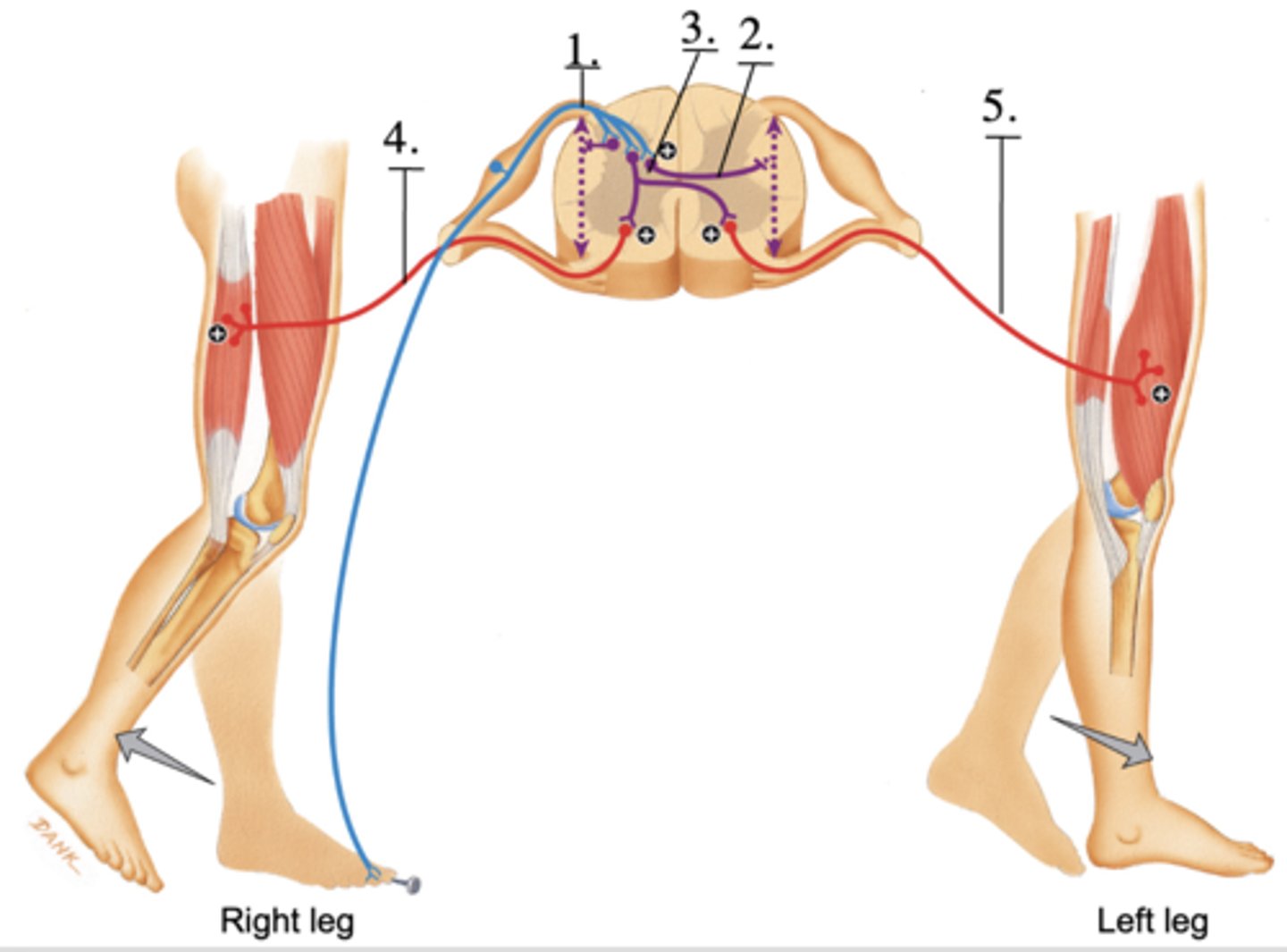
monosynaptic reflex arc
the sensory (afferent, presynaptic) neuron fires directly onto the motor (efferent, postsynaptic) neuron
(Integrating center-> single synapse between a sensory and motor neuron)
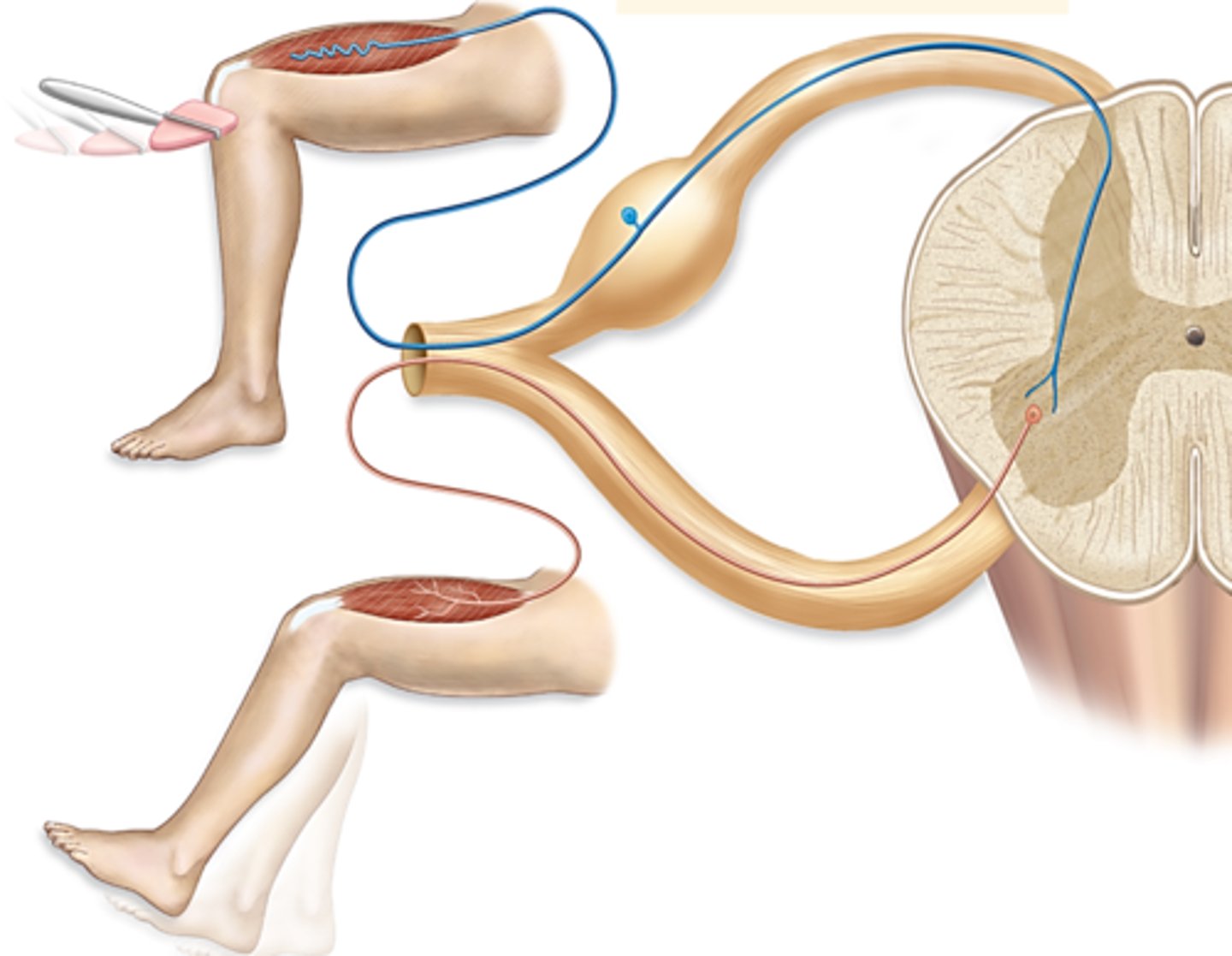
polysynaptic reflex arc
-if there is at least one interneuron b/w the sensory and motor neurons
Ex: withdrawal reflex
(Integrating center-> consists of multiple synapses involving one or more interneurons (association neurons) between a sensory and a motor neuron
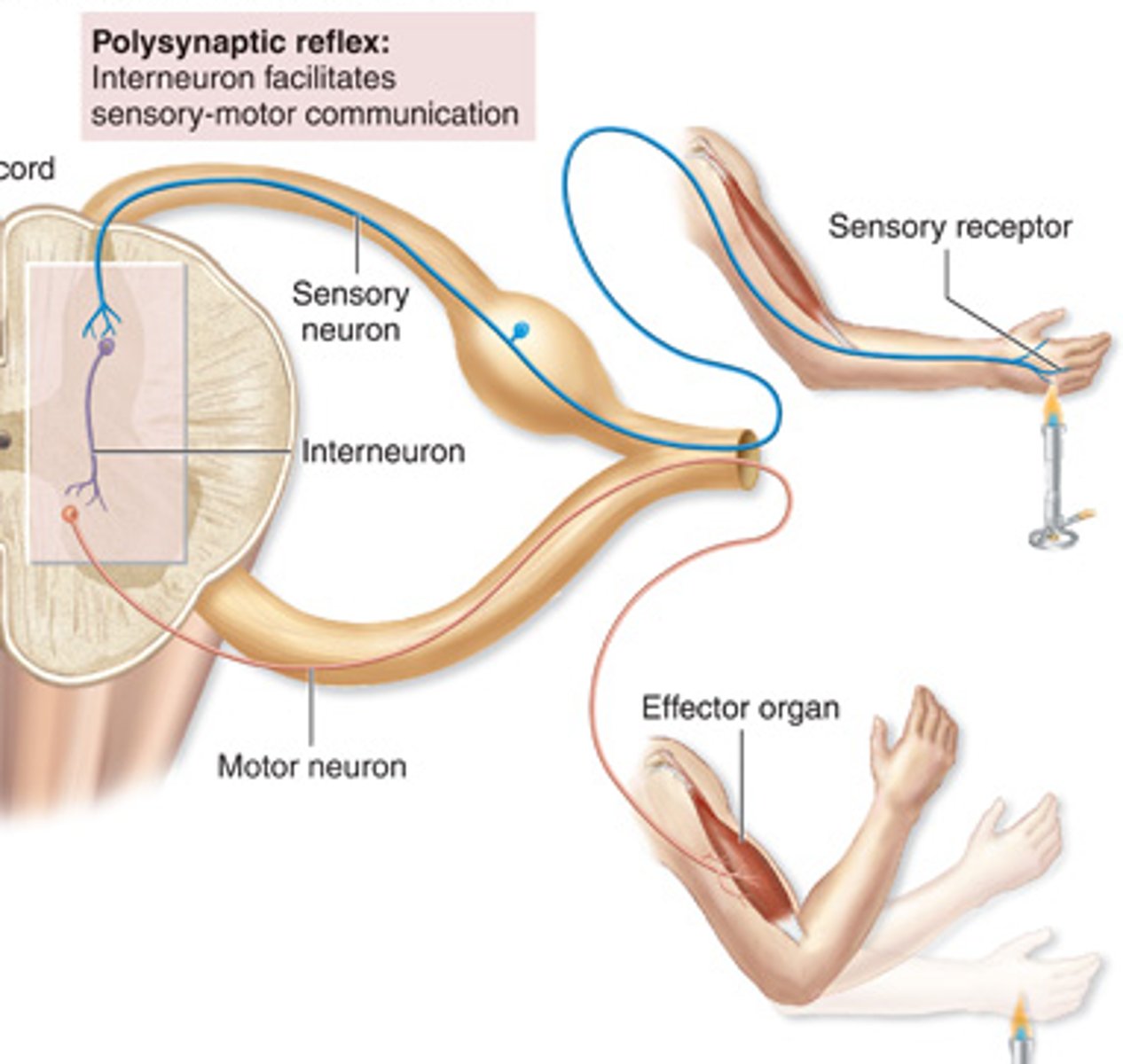
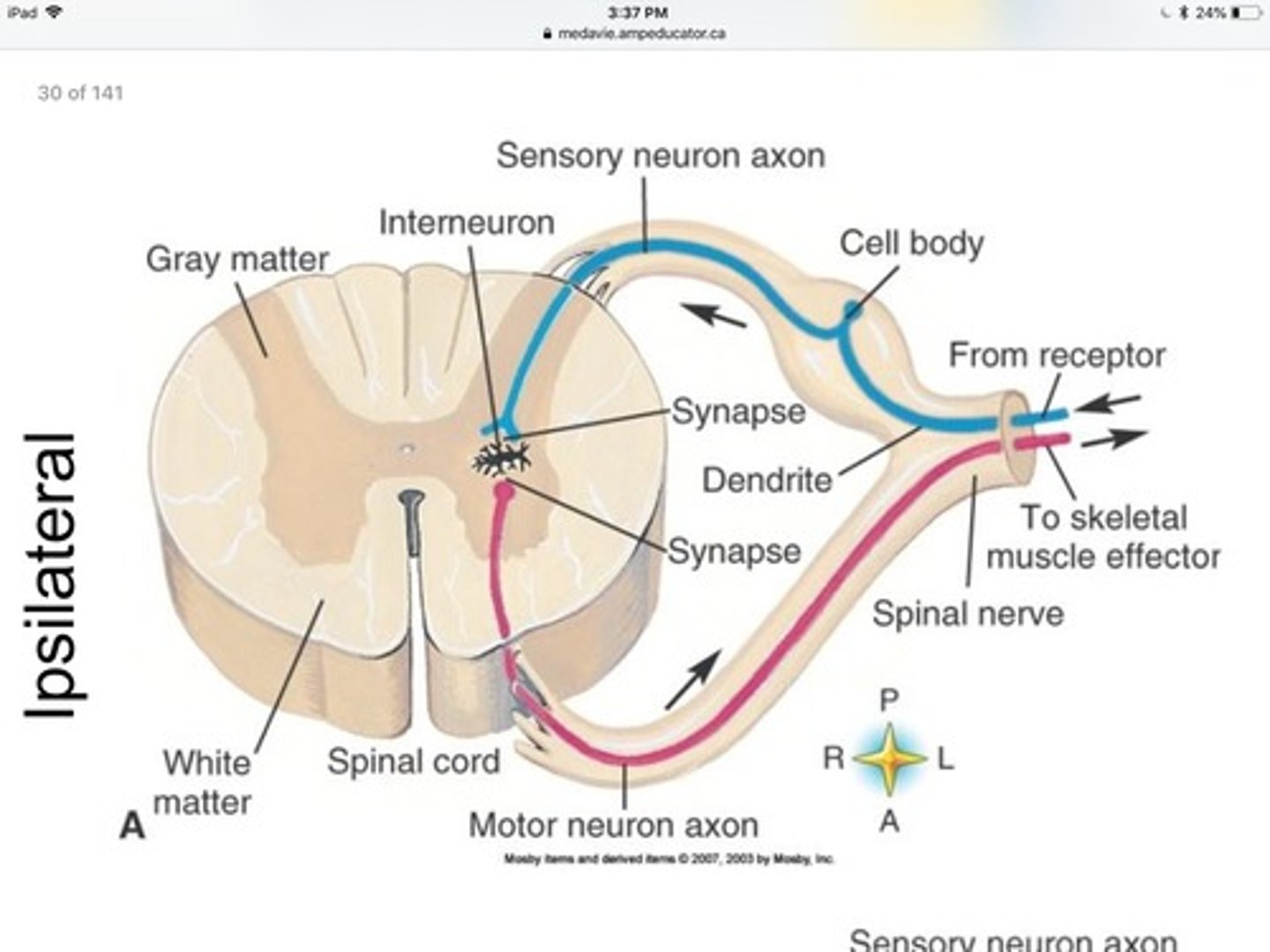
ipsilateral reflex arc
one in which the sensory input and the motor output are on the same sides of the spinal cord
Ex. flexor reflex
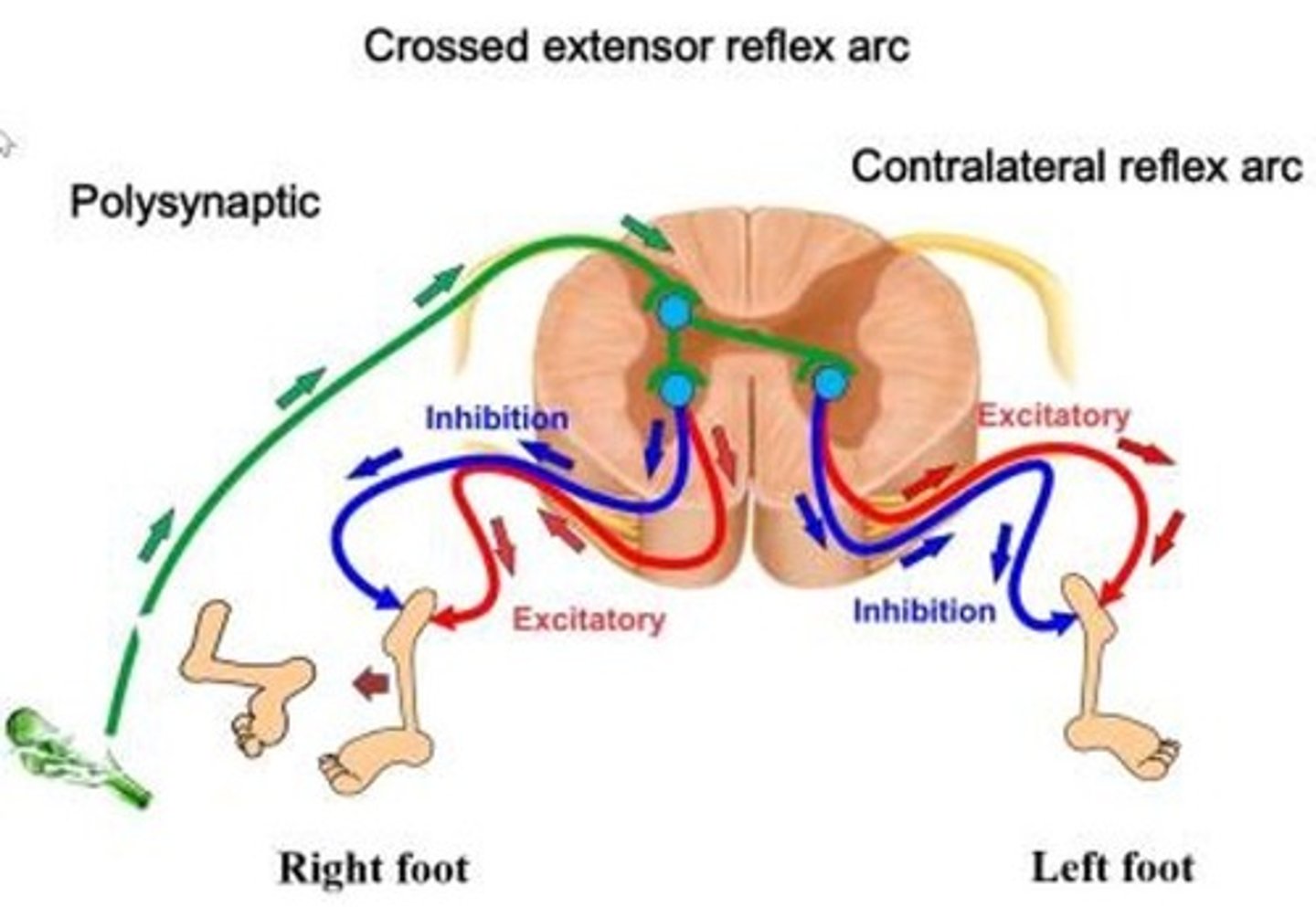
contralateral reflex arc
sensory impulses enter one side of the spinal cord and motor impulses exit on the opposite side
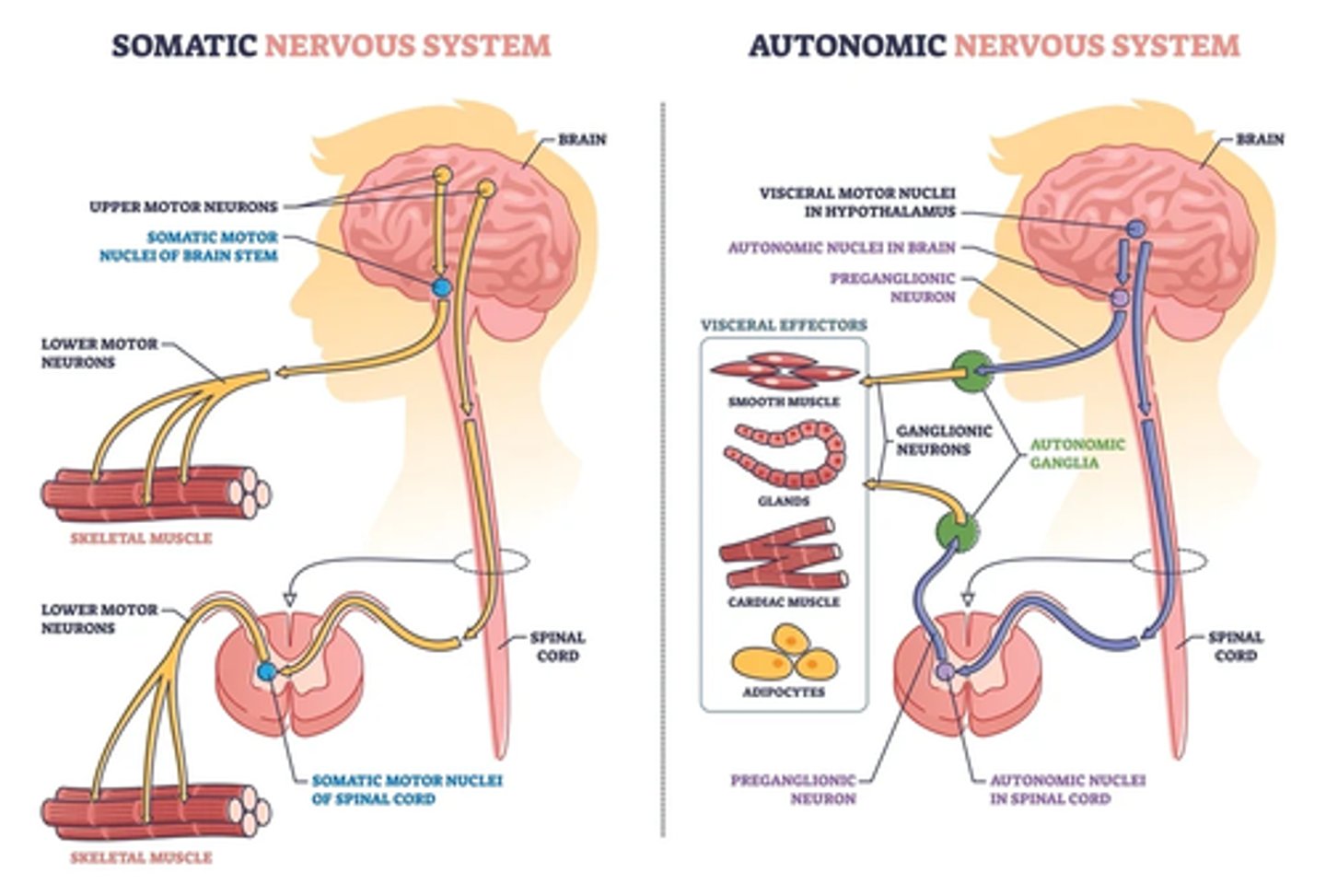
somatic reflex arc
effectors are skeletal fibers
-sensory neurons (any reflex arc) the neuron is unipolar neuron
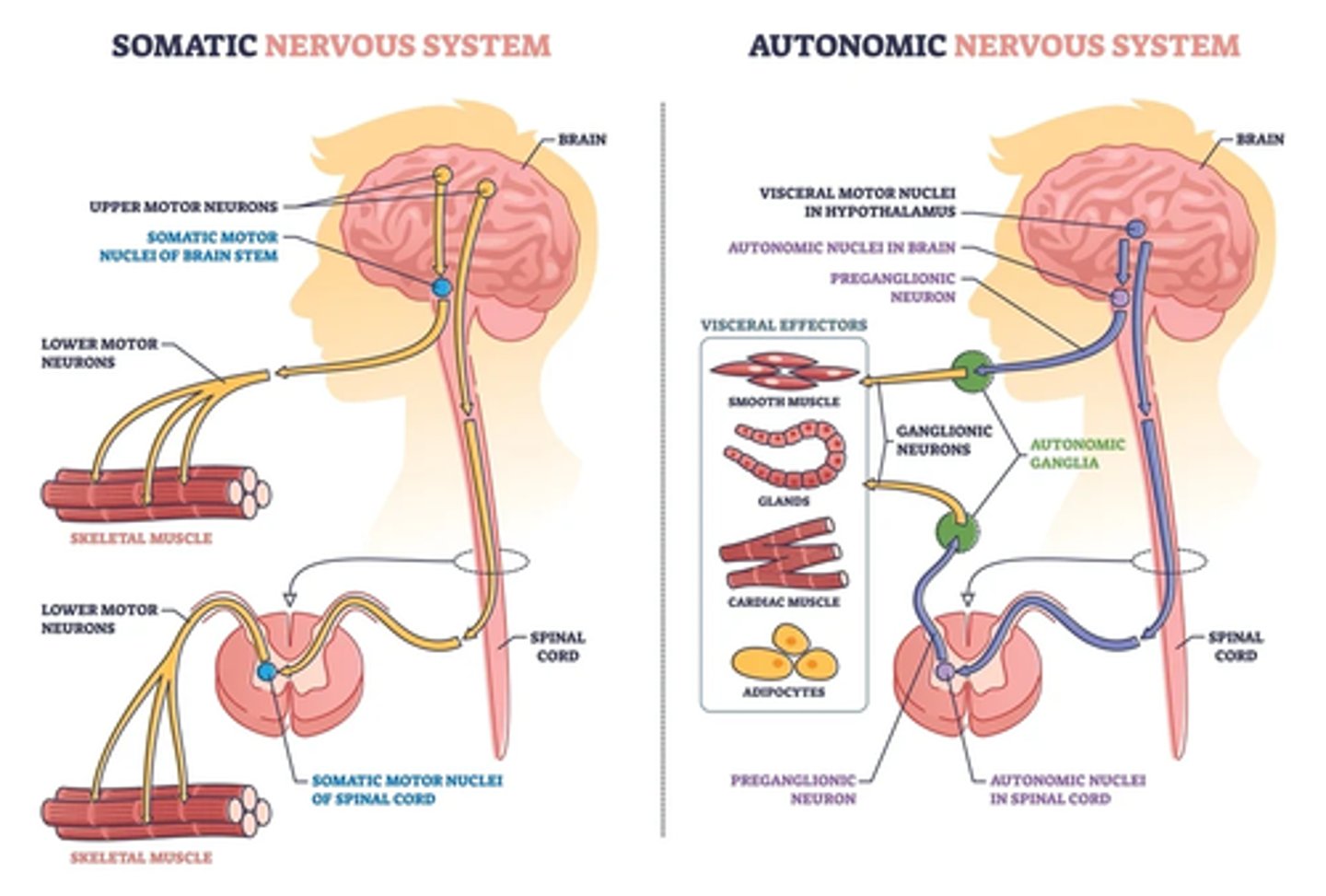
visceral reflex arc
motor response involves cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, or glands
1. Receptors: nerve endings that detect stretch, tissue damage, blood chemicals, body temperature, and other internal stimuli
2. Afferent neurons: leading to the CNS
3. Interneurons: in the CNS
4. Efferent neurons: carry motor signals away from the CNS
5. Effectors: that make adjustments
sensory receptor, sensory neuron, integrating center, motor neuron, effector
list the 5 components of a reflex arc
inhibited (stretching so they are relaxed and not contracted)
Determine if the motor neurons supplying the hamstrings are stimulated or inhibited during the patellar reflex test
Intensifying (occupies the brain to naturally respond instead of lifting leg due to being aware of the hit about to occur)
Determine whether the effect of the clasping and pulling of the hands during the patellar reflex have an intensifying or diminishing effect on the patellar reflex
reflex
response of the effector to stimulation by the motor neuron of the reflex arc
fast, involuntary, fast (don't think about them - no brain), automatic
The doctor hits your knee and it automatically jumps.
characteristic and example of reflex
somatic
contraction of skeletal muscle
autonomic (visceral)
motor response involves cardiac and smooth muscle, or glands
cranial
mediated by cranial nerves
spinal
meaning of spinal nerves
somatic reflex
contraction of skeletal muscles
involuntary movements in response to a stimulus
pull your hand away from a hot object
characteristic and example of somatic reflex
Autonomic (viseral) reflexes
motor response involves cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, or glands
unconscious motor reflexes relayed from the organs and glands to the CNS through afferent signaling
pupillary reflex, breathing, defecation reflex/ urination reflex, coughing
characteristic and example of autonomic (visceral) reflexes
cranial reflexes
reflexes mediated by cranial nerves
take place in the facial or head area
blink reflex, jaw jerk, masseter inhibitory reflex
characteristic and example of cranial reflexes
spinal reflexes
reflexes mediated by spinal nerves
involuntary and instantaneous movement in response to stimuli
stretch reflex, crossed extensor reflex, withdrawal reflex, inverse stretch (tendon reflex)
characteristic and example of spinal reflexes
reciprocal innervation
stimulation of contraction in muscles with simultaneous inhibition (relaxation) of antagonistic muscles
the process that controls agonist and antagonist muscle actions
patellar reflex
characteristic and example of reciprocal innervation
cerebral cortex
inhibitory signals are sent via the corticospinal tract to override certain reflexes
not responsible for reflexes, has association areas. It has a broad range of functions including perception and awareness of sensory information, planning, and initiation of motor activity
primary motor cortex- voluntary muscle movement
characteristic and example of cerebral cortex
ipsilateral
input and output are on the same side of the body
tumor involving the right side of the brain may affect vision ipsilaterally that is, in the right eye
patellar reflex, withdrawal reflex, during crossed extensor reflex the ipsilateral limb reacts with a withdrawal reflex (stimulating flexor muscles and inhibiting extensor muscles on the same side)
example of ipsilateral
contralateral
input and output are on opposite sides of the body
stroke? involving the right side of the brain may cause contralateral paralysis of the left leg
crossed extensor reflex-the contralateral extensor muscles contract so that the person can appropriately shift balance to the opposite foot during reflex
example of contralateral
effector
skeletal muscle (somatic reflex), cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, or glands (autonomic reflexes)
motor (efferent) neuron
carries the action potential initiated by the integrating center to the effector
integrative center
where the actual value and the set point are compared; if a difference is detected, effector systems are activated that change the regulated variable in the direction back toward the set point
(located within the gray matter of the CNS and transfers information from the sensory neuron to the motor neuron)
sensory neurons
neurons that receive information from the external world and convey this information to the brain via the spinal cord
sensory receptor
encapsulated nerve ending, free nerve ending or specialized sensory cell
detect changes in the internal as well as external environment. Send signals to the CNS and brain for processing and integration
Pacinian corpuscle, touch receptors in the skin, also located in the tendons, ligaments, visceral organs.
characteristic and example of sensory receptor
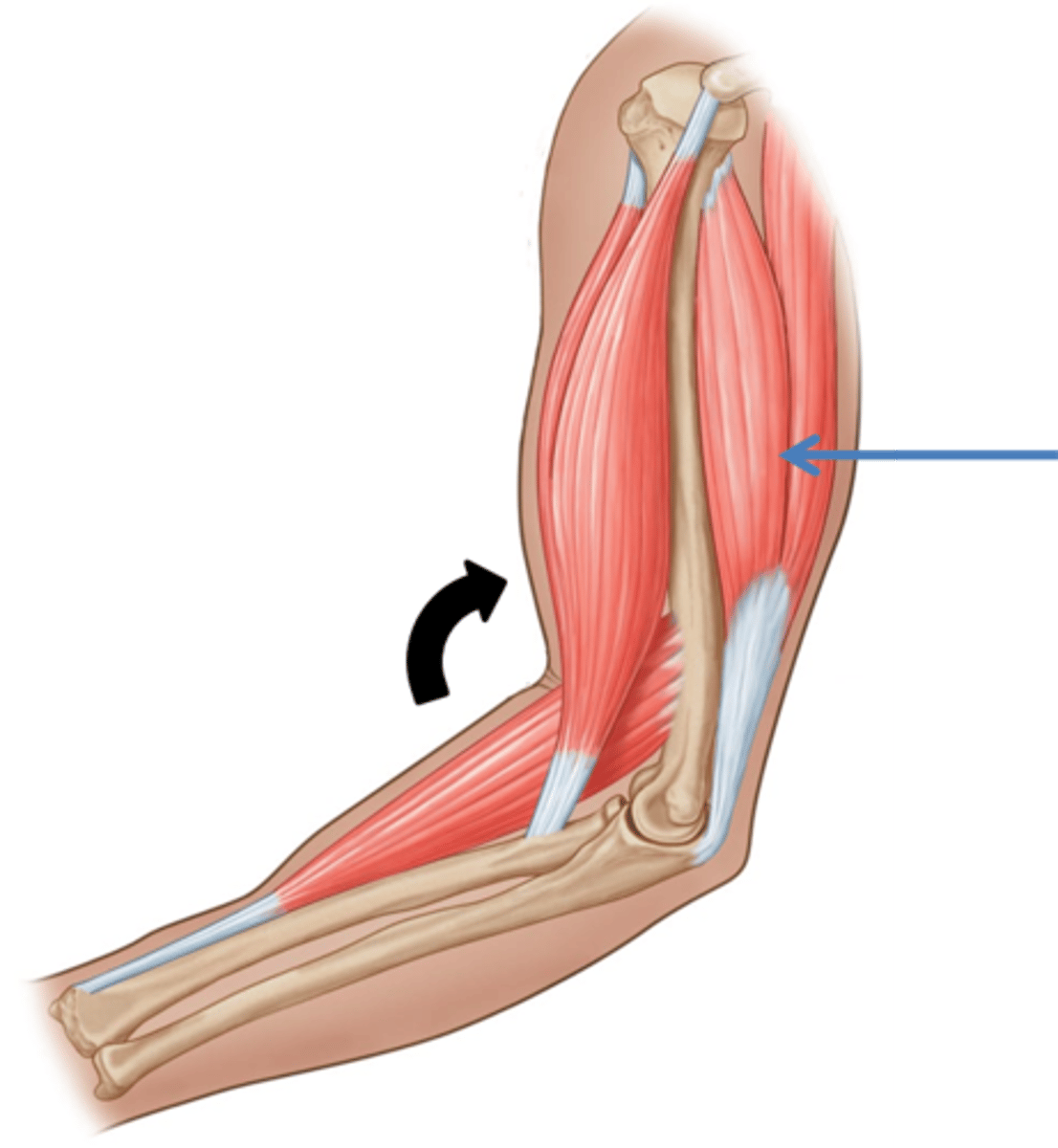
agonist muscle
muscle that contracts to produce a movement
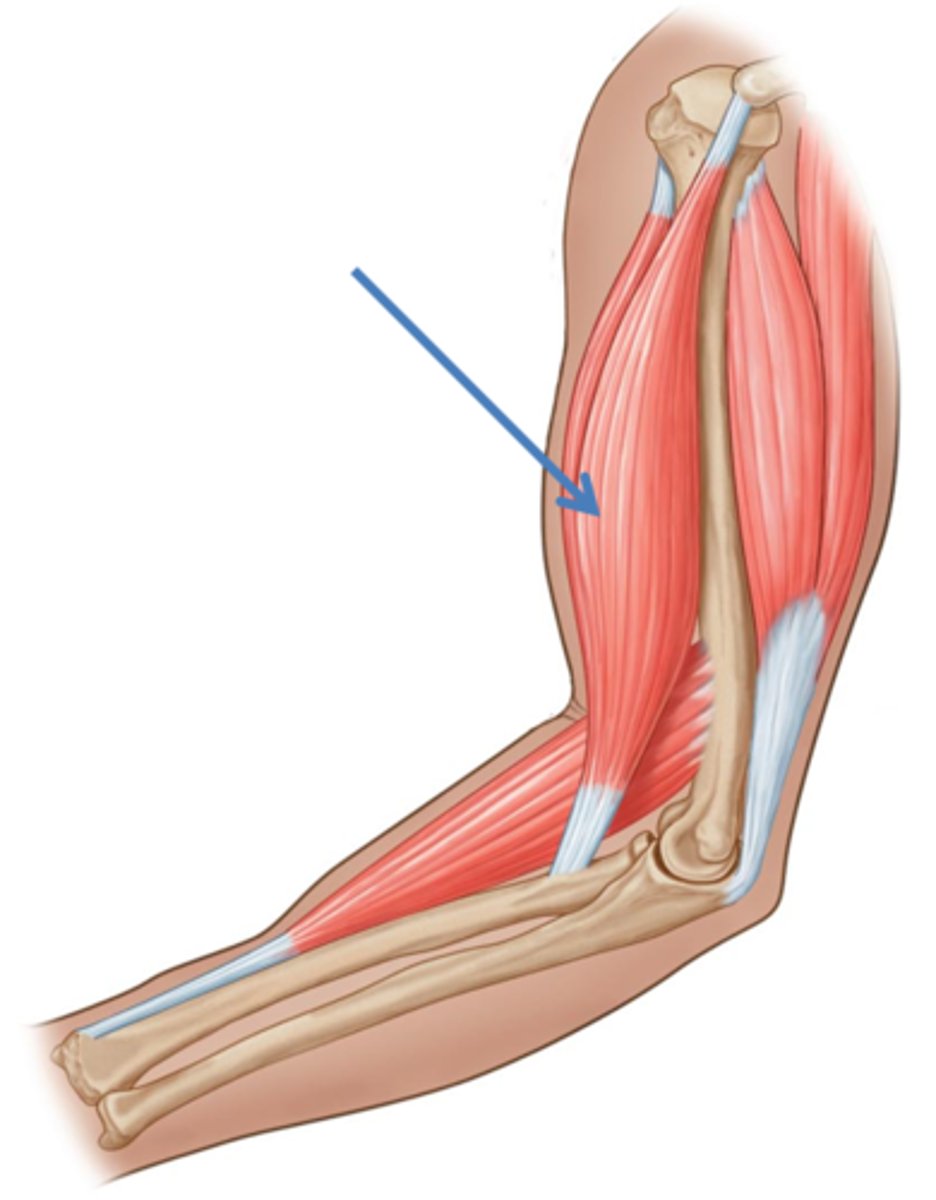
antagonist muscle
The muscle opposite the agonist, which must relax and lengthen during contraction of the agonist.
2; 1
how many neurons are in monosynaptic reflex arc?
how many synapses are in the integrating center?
3 or more; 3
how many neurons are in a polysynaptic reflex arc?
how many synapses are in a polysynaptic reflex arc containing two interneurons in the integrating center?
motor neuron
which type of neuron does the sensory neuron synapse with in a monosynaptic reflex arc?
interneurons
which type of neuron does the sensory neuron synapse with in a polysynaptic reflex arc
tibial nerve; musculocutaneous; femoral; tibial; radial; not normal
name the nerve that is tested in each of the following reflexes
1. achilles reflex
2. biceps reflex
3. patellar reflex
4. plantar flexion reflex
5. triceps reflex
6. is a Babinski's sign normal in adults?
sciatic
nerve carrying motor information causing right leg flexion
femoral
nerve carrying motor information causing left leg extension
quadricepts
agonistic muscles for right leg flexion
hamstrings
agonistic muscles for left leg extension
somatic; spinal nerve reflexes
Identify if somatic or autonomic reflex and identify if spinal nerve reflexes or cranial nerve reflexes:
Plantar flexion of foot when Achilles tendon is stretched
autonomic; cranial nerve reflexes
Identify if somatic or autonomic reflex and identify if spinal nerve reflexes or cranial nerve reflexes:
Salivation in response to lemon juice on tongue
autonomic; cranial nerve reflexes
Identify if somatic or autonomic reflex and identify if spinal nerve reflexes or cranial nerve reflexes:
Blinking in response to touching the cornea
somatic; spinal nerve reflexes
Identify if somatic or autonomic reflex and identify if spinal nerve reflexes or cranial nerve reflexes:
Flexion of arm in response to touching a hot object
polysynaptic; ipsilateral
Reflex arc:
Is it monosynaptic or polysynaptic?
Is it ipsilateral or contralateral?
ipsilateral; inhibited; occupies your brain due to it naturally having response instead of lifting your leg (knowingly the hit will occur)
Patellar reflex:
Is it ipsilateral or contralateral?
Are the motor neurons supplying the hamstrings stimulated or inhibited?
Describe the effect that clasping and pulling the hands has on the patellar reflex compared with the first patellar reflex?
musculocutaneous nerve; tricepts brachii
Biceps reflex:
Name the nerve that carries the sensory and motor axons for this reflex arc?
Name the antagonistic muscles that are inhibited by reciprocal innervation?
radial; biceps brachii
Triceps reflex:
Name the nerve that carries the sensory and motor axons for this reflex arc?
Name the antagonistic muscles that are inhibited by reciprocal innervation?
tibial; tibialis anterior
Achilles reflex:
Name the nerve that carries the sensory and motor axons for this reflex arc?
Name the antagonistic muscles that are inhibited by reciprocal innervation?
flexor; flexor muscles of the ankle
Plantar flexion:
Name the nerve that carries the sensory and motor axons for this reflex arc?
Name the antagonistic muscles that are inhibited by reciprocal innervation?
contralateral
In a crossed-extensor reflex, the _____ extensor muscles contract so that the person can appropriately shift balance to the opposite foot during the reflex. (Choose one: contralateral or ipsilateral)
ipsilateral
In a crossed-extensor reflex, the _____ limb reacts with a withdrawal reflex (stimulating flexor muscles and inhibiting extensor muscles on the same side. (Choose one: contralateral or ipsilateral)
sensory
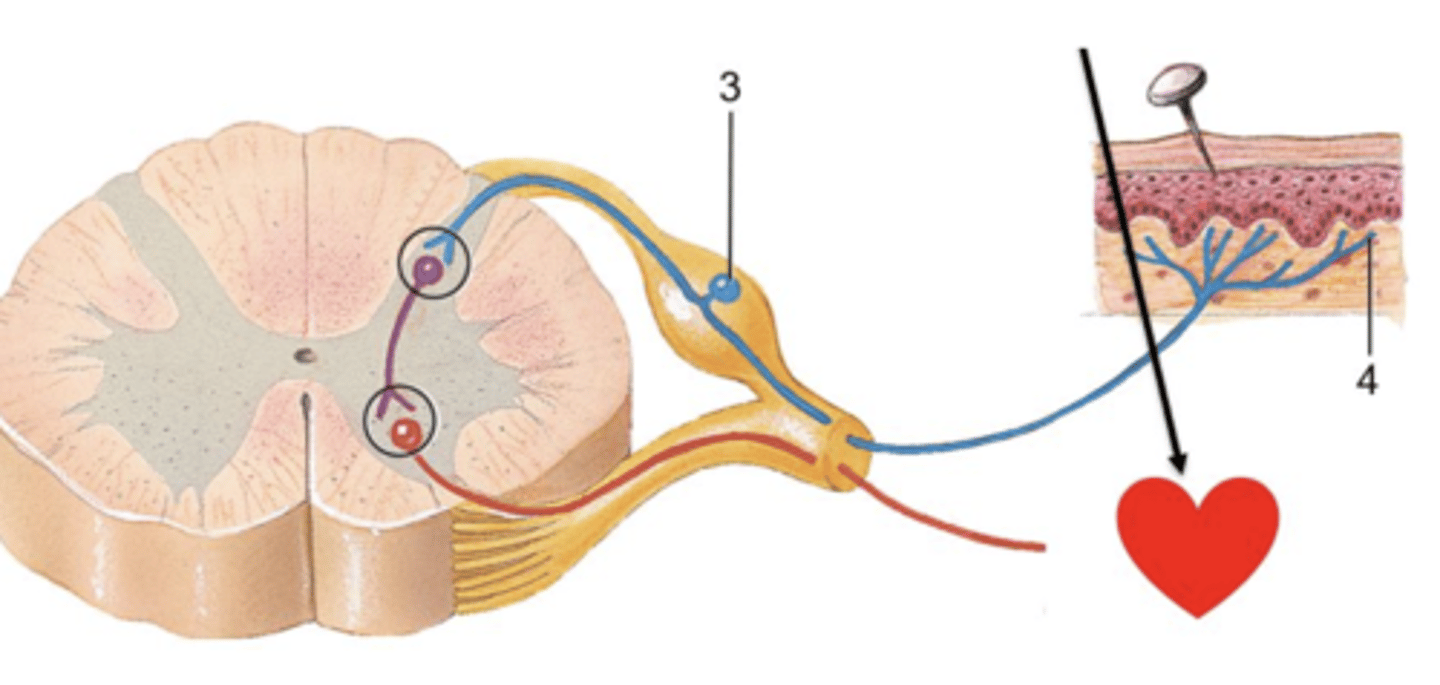
Item 4 in the picture below is ______. Motor, Sensory
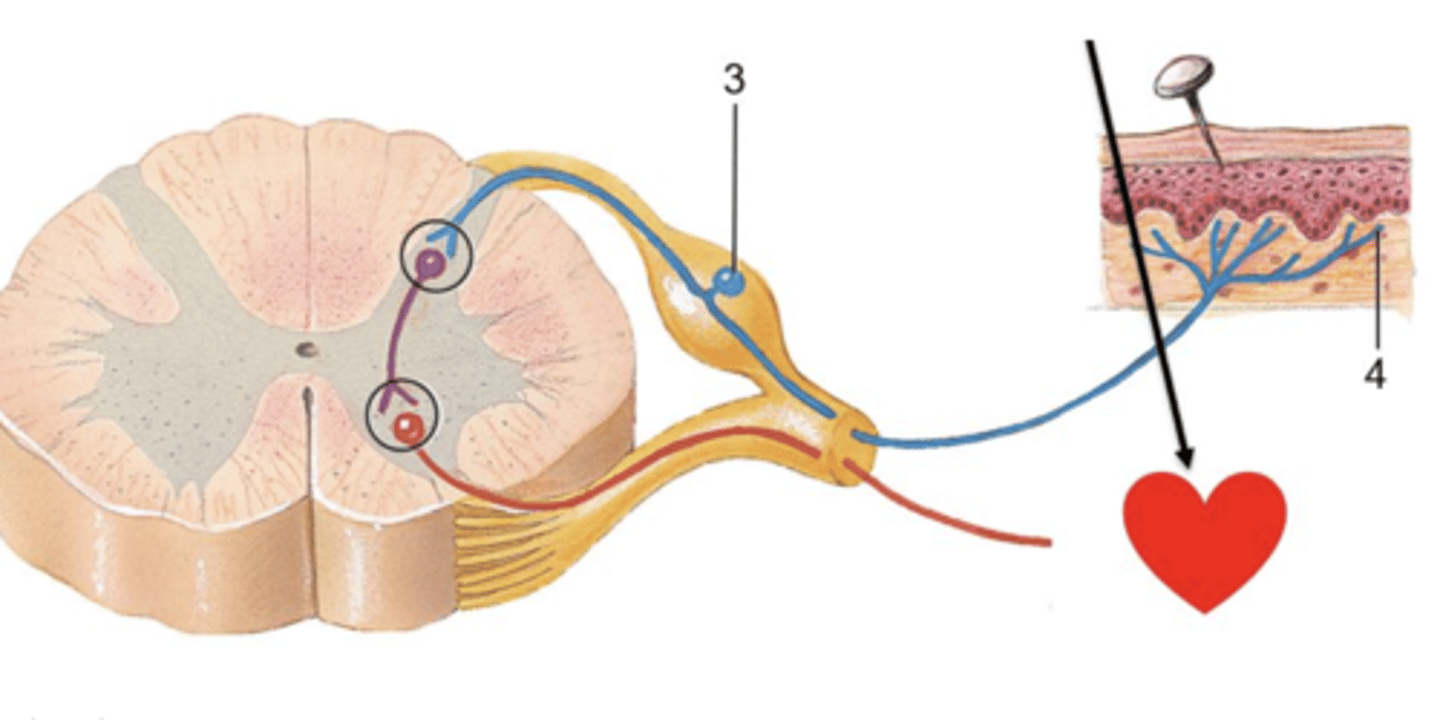
sensory
Item 3 in the picture below is a(n) ______ neuron cell body. Motor or Sensory
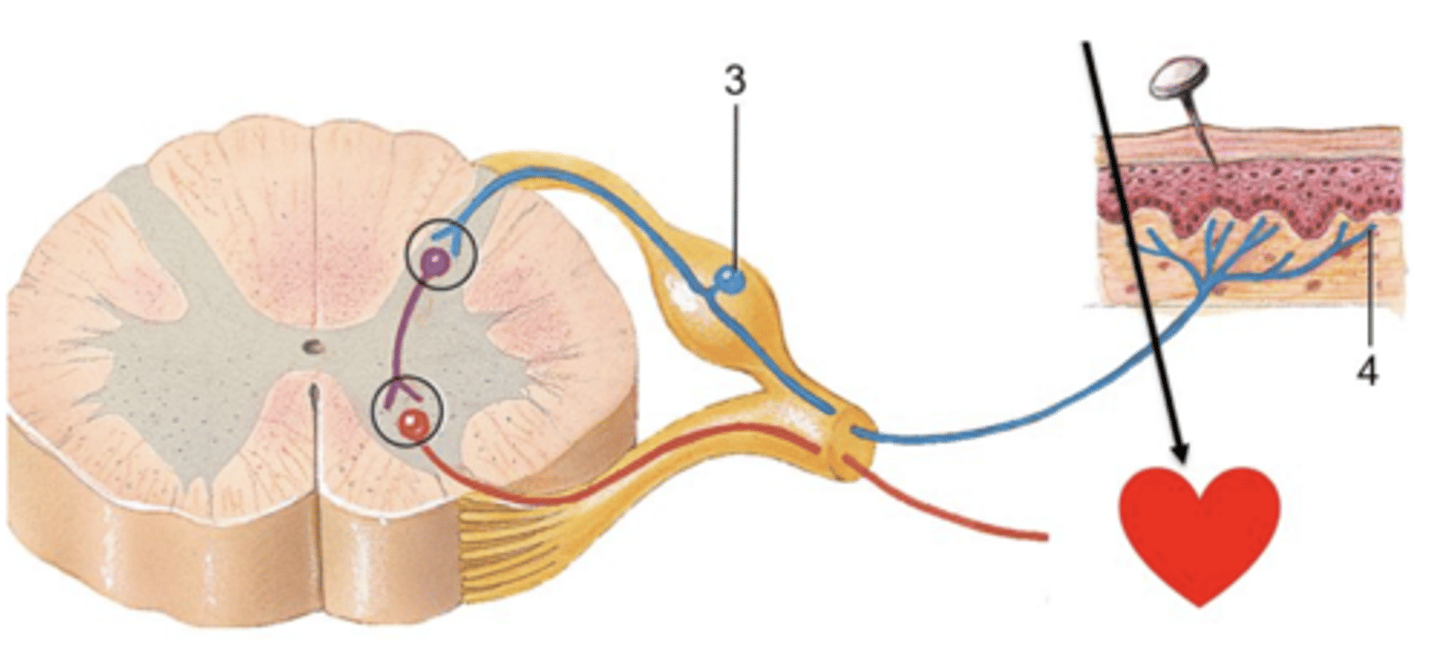
autonomic
The reflex arc shown below is an example of which of these: Autonomic or Somatic?
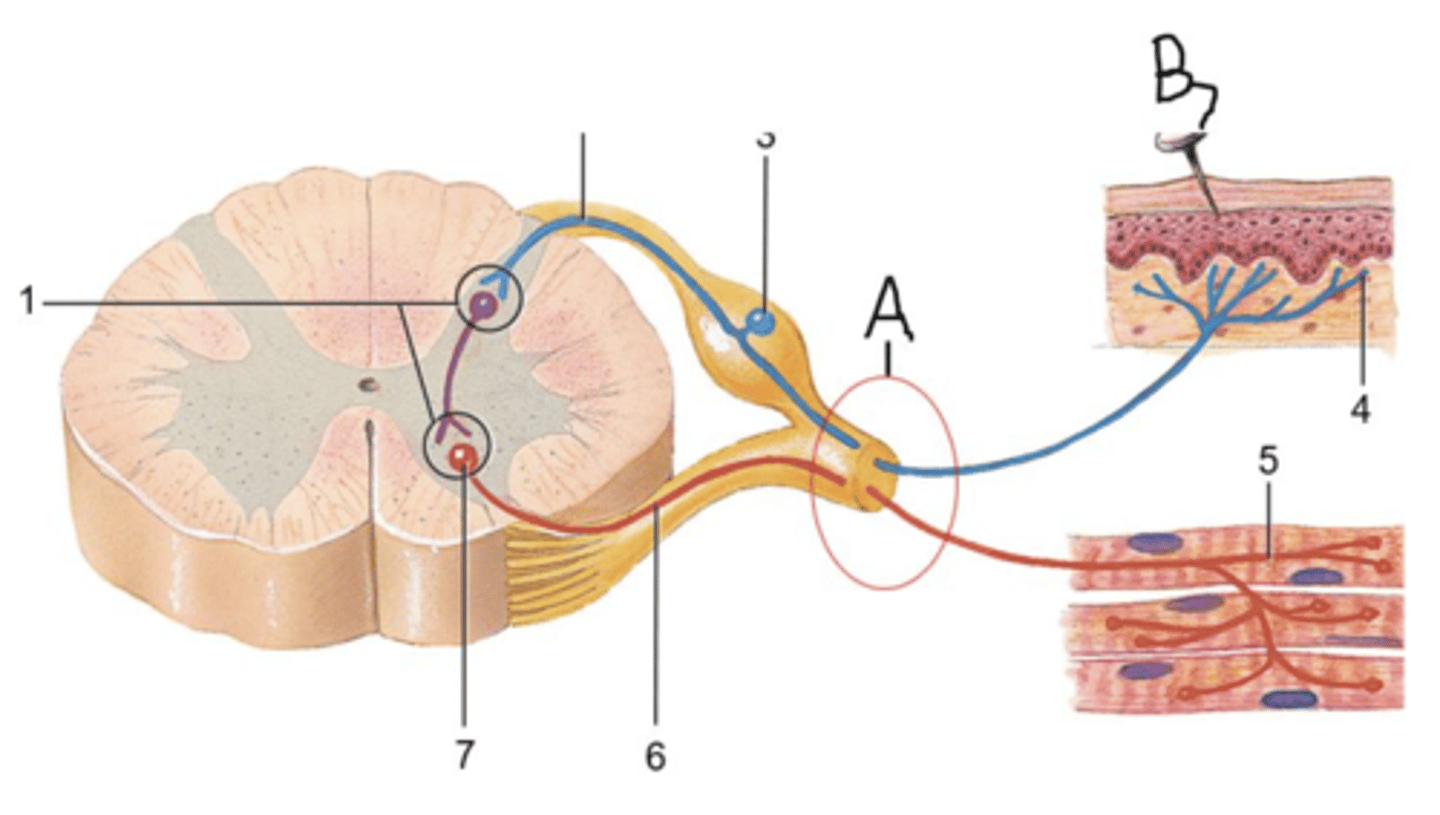
true
The item labeled B in the picture below represents a stimulus, a painful one at that, causing a reflex action to occur spontaneously. Even though it is a spontaneous, involuntary reaction, it is part of a somatic reflex arc because it results in stimulation of voluntary, skeletal muscle fibers.
true or false
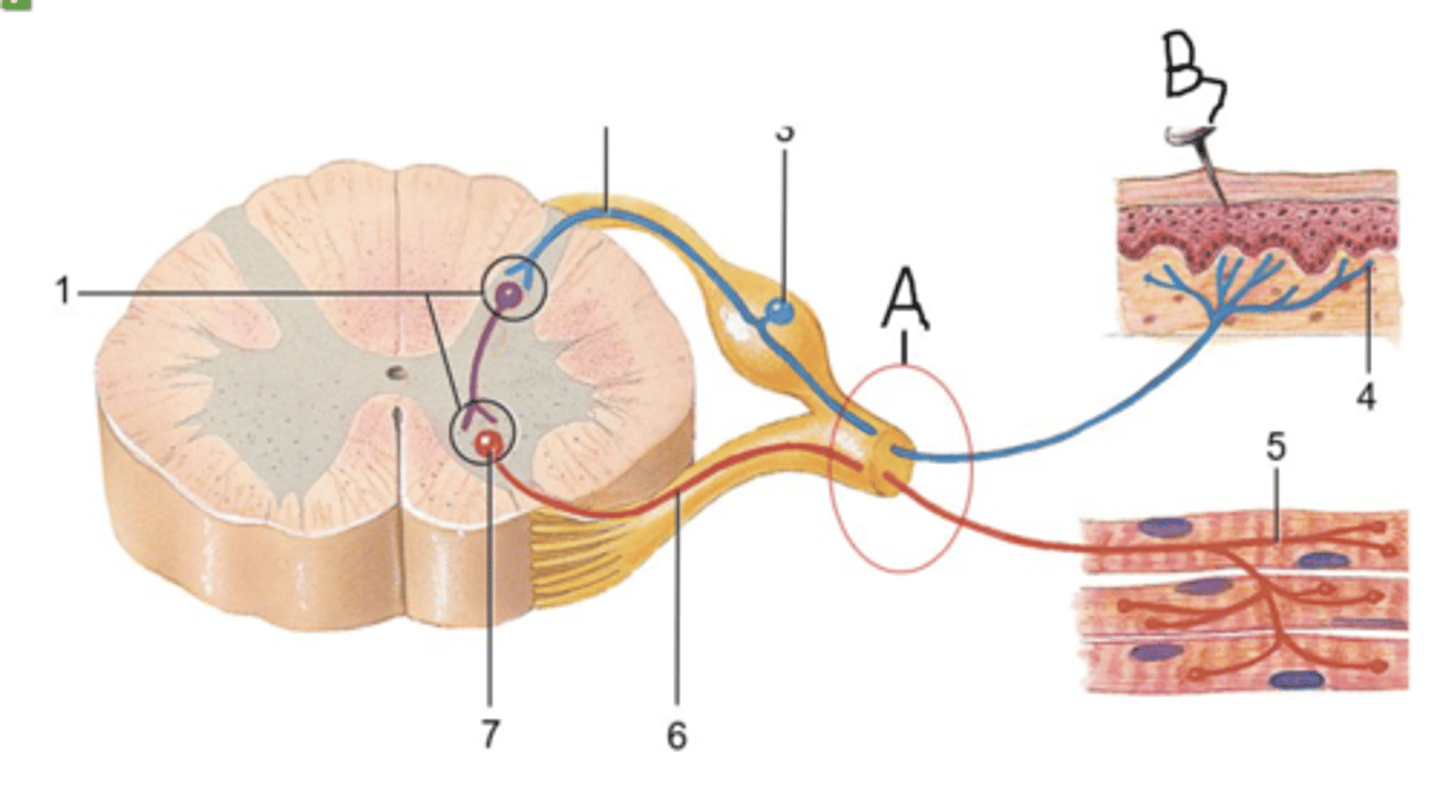
false
Collectivley, A in the picture below is a spinal nerve and is, therefore, part of the central nervous system.
true or false
false
Somatic reflex arcs involve only the autonomic nervous system.
true or false