Oral Histology6: Enamel & Dentin
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key terminology and concepts related to enamel and dentin from the DMD700 Oral Histology lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
Enamel
Avascular structure covering the tooth, consisting of interlocking rods, non-vital, and not renewable.
Avascular
Lacking blood vessels; characteristic of enamel.
Ameloblasts
Cells responsible for the formation of enamel.
Hydroxyapatite
A crystalline calcium phosphate that constitutes about 95% of enamel.
Striae of Retzius
Incremental lines in enamel resulting from rhythmic deposition.
Neonatal line
A notable line of Retzius associated with birth indicating a change in nutrition and environment.
Enamel tufts
Cracks in the enamel surface extending from the DEJ toward the enamel.
Enamel lamellae
Cracks in the surface of enamel visible to the naked eye.
Dentinoenamel junction (DEJ)
The interface where dentin meets enamel.
Dentin
Living, sensitive hard tissue that makes up the bulk of the tooth.
Odontoblasts
Cells responsible for the formation of dentin.
Sclerotic dentin
Dentin with obliterated tubules believed to protect the pulp.
Secondary dentin
Dentin formed in response to mastication after the crown has engaged in occlusal function.
Tertiary dentin
Also known as reparative dentin; forms in response to pulpal stimulation or injury.
Incremental lines
Lines formed in dentin due to the periodic deposition of dentin.
Dentinal tubules
Microscopic channels in dentin containing odontoblast processes.
Peritubular dentin
Highly mineralized dentin surrounding the dentinal tubules.
Intertubular dentin
Dentin found between the dentinal tubules.
Granular layer of Tomes
Granular appearing layer of dentin underlying the cementum covering the root.
enamel
avascular, lacks nerve supply, not renewable
enamel rods
keyhole shaped ameloblasts that lay down enamel
enamel
95% inorganic mineral substance primarily composed of hydroxyapatite and 5% water and organic matter
hydroxyapatite
crystalline calcium phosphate found on bone dentin and cementum
organic component of mature enamel
protein called enamelin
enamel: gray as…
dentin: yellow
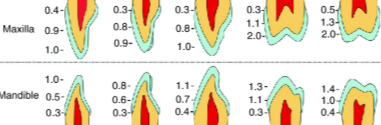
enamel thickness
ranges from thin knifelike edge at cervical margins to 2.5 mm over occlusal or incisal surfaces
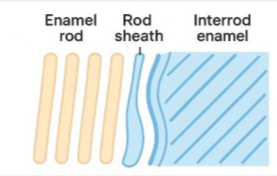
rod structure
extend from DEJ to enamel outer surface
one enamel rod
formed by 4 ameloblasts
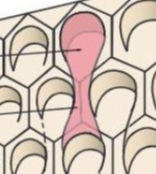
keyhole/ raquet/fish shaped
enamel rod shape used to maximize space of crystalline matter to ensure structural integrity and strength. the more crystal=less organic material=harder to degrade
rod orientation of each part of the crystal
crystals in the head follow the long axis of the rod
crystals from the tail are perpendicular to the head
rod orientation
rods are perpendicular to the DEJ and curve toward cusp tips
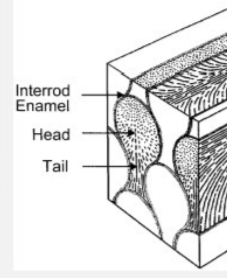
parts of a rod
sheath surrounding surface with a core at the center
the sheath contains more organic material than the core
interrod enamel
enamel running between the crystalline rod structures with the purpose of filling the space with even more enamel
ordered correctly
perpendicular at cervical region and intertwined at cusp tips
enamel rod pattern
because enamel rods interdigitate
the hunter-schreger bands phenonenon occurs
hunter-schreger band phenomenon
banding appearing in the 1/2 -2/3 thickness of the tooth due to lights bouncing off interdigitated enamel rods
outer enamel
prismless enamel with no banding effect due to completely perpendicular enamel rods
incremental lines in enamel
due to rythmic changes in deposition of enamel
Lines of Retzius or striae
lines of entrapped air molecules accentuating developmental lines
most famous line of Retzius due to major changes in nutrition and environment
neonatal lines
prenatal enamel
has fewer defects than post natal enamel
enamel lamellae
cracks in the surface of enamel that are visible to the naked eye
enamel lamellae
extend from surface DEJ, are a possible avenue for bacteria, and can be due to impact or temperature
enamel tufts
areas of disorganized enamel rods mixed with enamalin located at DEJ. thought to be areas of more dentin like structure between layer seperation
enamel spindles
extensions of dentinotubles that arise in DEJ and extend to enamel
enamel spindles are
shorter and thinner that enamel tufts
enamel tufts

enamel spindles
enamel surface
smooth or with fine ridges called perikymata or imbrication lines on facial surfacethat cover the outer layer of the tooth, providing protection and aesthetic quality.
imbrication lines/perikymata
permeability of enamel
caused by…
leakage around restorations
decomposition of tooth
lamellae, cracks, tufts and spindles
microlamellae
irregular surfaces
microlamellae
minute spaces around enamel rods that increase tooth permeability and can harbor bacteria.
etching
dilute acids that alter surface enamel and provide adherence to enamel rods
peripheral enamel rods…
resist demineralization to a greater extent than rod core
attrition
tooth on tooth contact wear
abrasion
caused by external forces like brushing
erosion
caused by acid wear
abfraction
loss of structure due to occlusal force imbalances
dentin
body of the tooth
dentin is living
true
dentin coverings at
root is covered by cementum
crown covered by enamel
dentin is like bone…
as it is made of mostly organic matrix of collagen fibers and mineral hydroxyapatite crystals
dentin classification
based on time of development
primary, secondary, tertiary
dentin
bulk of tooth made of 70% hydroxyapatite, 20
5% organic collagen and 10% water
dentin is has less ____ and is ____ than enamel
mineral
softer
radiolucency of dentin
more than enamel and less than pulp
dentin resilience
due to dentino tubules present in matrix the elasticity and strength make for a material that resists mastication forces and prevents fractures.
where is dentin first laid
initial dentin is formed at cusp tips and activates more odontoblasts to activate along the DEJ eventually being moved towards the pulp as the tooth develops.
what is present in a dentinotubuole
odontoblast processes dentinal fluid and extracellular matrix substances
predentin
band of newly formed unmineralized dentin at pulpal border
dentin formation
stage 1: organic matrix is deposited
stage 2: mineral substance is added
predentin is evidence of
step 1 of dentin formation
mineralization occurs at
the predentin-dentin junction
mantle dentin
first primary dentin formed, deposited at the DEJ extending pulpally, serves as a covering over the rest if dentin, and nearly free of defects
globular dentin/ interglobular dentin
beneath mantle dentin, exists only in the crown, contains hypomineralized areas
circumpulpal dentin
beneath globular dentin forms the bulk of primary dentin with thick areas in crown and thin areas in roots
order of layers of primary dentin
circumpulpal, globular, mantle
primary dentin
makes up the bulk of dentin in a tooth
dentinotubules from primary and secondary dentin
form an s curve
odontoblast INITIALLY have multiple processes that secrete
mantle dentin
as odontoblast elongate
they branch at right angles giving dentin vitality
dentin area
surface is much larger than pulp interface
larger surface area makes
dentinotubles much closer together at the pulp and sparse on the surface area
peritubular dentin
dentinal matrix immediately surrounding the tubule
intertubular dentin
dentin between dentinotubules
peritubular dentin is more
mineralized than intertubular dentin
when peritubular dentin proliferates
dentinaltubles diameter shrinks
secondary dentin
formed internally to primary dentin
is a normal response to mastication
occurs with aging
when does secondary dentin form
after crown has started masticatory function and roots are nearly complete
secondary dentin forms _____ than primary dentin
slower
a slow rate of dentin formation
preserves pulp from being obliterated
tubules from primary and secondary dentin
are Continuous
secondary dentin can also be laid
above pulp horns to appose occlusal forces
tertiary dentin/reparative dentin
is formed in response to injury or irritation of the dental pulp
forms at the site of odontoblast activation
can be deposited rapidly
appears irregular
cells found in tertiary dentin
odontoblasts, fibroblasts, blood cells
tertiary dentin is deposited slowly and forms more regular dentin due to
fewer or less intense stimuli
reparative dentin
closely associated with bone and can be referred to as osteodentin
sclerotic dentin
formed when dentin tubules are obliterated
forming sclerotic dentin
increases with age
protects pulp
eliminated permeability to pulp