Chapter 4, Lesson 3: DNA Replication and the Cell Cycle
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 4, Lesson 3 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Law of Complementary Base Pairing
States that we can predict the base sequence of one DNA strand if we know the sequence of another
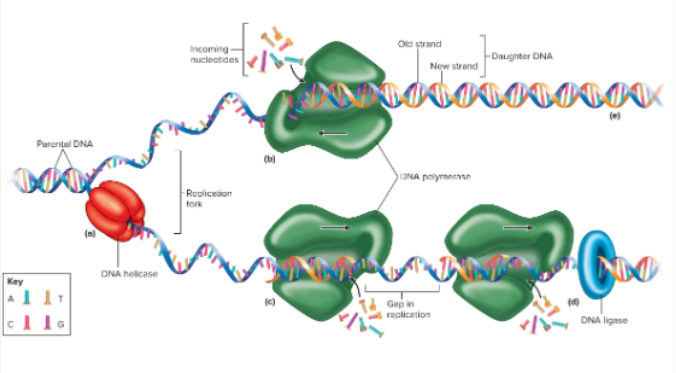
DNA replication steps
Unwinding
Unzipping
Building new strands
Repackaging
Replication fork
The point of DNA opening, this is made in step 1 after unwinding form histones
DNA helicase
The enzyme that unzips a segment of the DNA’s double helix structure in step 2
DNA polymerase
The enzyme that builds new DNA strands by matching free nucleotides to the unwinded DNA strand in step 3; the DNA is then repackaged and replicated for step 4
DNA Damage Response (DDR)
Mechanisms in place to correct replication errors by DNA polymerase; replaces unstable base pairs with correct pairs for a 1/1000000000 failure rate
Mutations
Changes in DNA structure due to replication errors or environmental factors; some may be harmless while others can cause defects or cancer later on
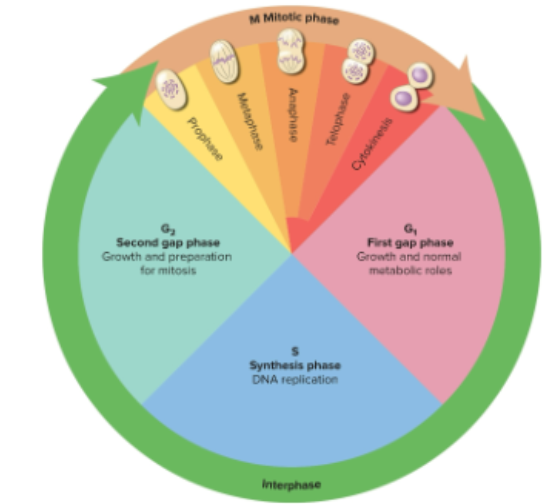
Cell cycle
The interphase and mitotic phases
Interphase
A part of the cell cycle that includes the first gap phase (G1), synthesis phase (S), and second gap phase (G2)
Mitotic phase
A part of the cell cycle that includes the prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis
First gap phase (G1)
Interval between cell birth and DNA replication; cell carries out normal tasks and accumulates materials for next phase
Synthesis phase (S)
Phase in interphase when the cell replicates all nuclear DNA and duplicates centrioles
Second gap phase (G2)
Interval between DNA replication and cell division; repairs errors and synthesizes enzymes
Mitotic phase
Phase where the cell replicates its nucleus
G zero phase (G0)
Cells that have left the cycle and ceased dividing for a long time
Mitosis
The cell division resulting in two genetically identical daughter cells; develops fertilized egg to 50 trillion cells and helps tissue growth
Phases of mitosis
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
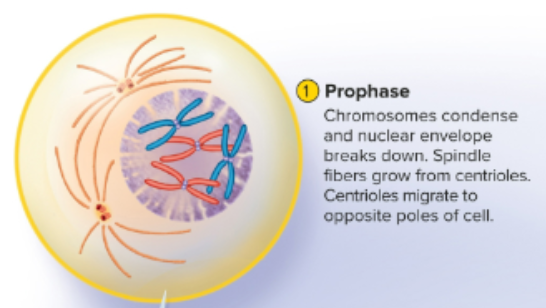
Prophase
First phase in mitosis where genetic material condenses into compact chromosomes; nuclear envelope disintegrates and centrioles sprout spindle fibers
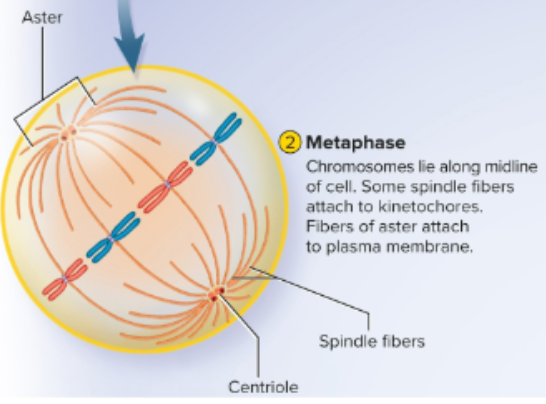
Metaphase
Second phase in mitosis where chromosomes align on the cell equator; microtubules extend from side to middle
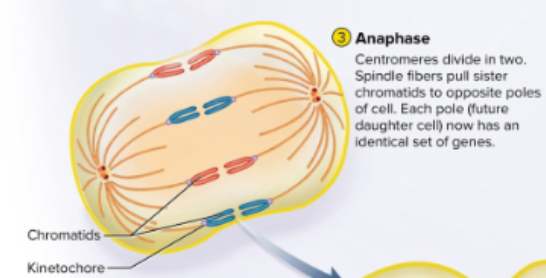
Anaphase
Third phase in mitosis where the spindle fibers cleave chromatids apart to opposite poles of cell
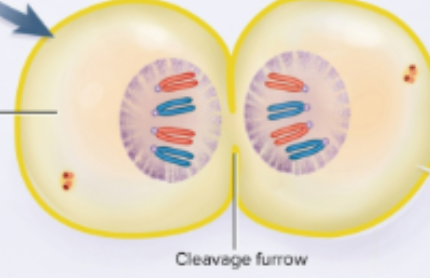
Telophase
Fourth phase where chromosomes cluster on each side of the cell; the rough ER makes a new nuclear envelope and the mitotic spindles disintegrate
Cytokinesis
Divison of the cytoplasm into two cells where the cell pinches in two; comes after telophase
Cell division factors
Starts when:
Adequate cytoplasm
DNA replicated
Nutrients supplied
Cell stimulated
May stop when:
Neighboring cells
Nutrients or growth factors withdrawn