5C Separation Techniques
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
When using Thin Layer Chromatography(TLC), the stationary phase is ____ and made of ____ and the mobile phase is _____.
Polar, silica gel
Nonpolar
Define the 2 types of ion exchange Chromatography:
Anion Exchange:
Cation Exchange:
Anion Exchange: Column is (+) charged, (-) charged proteins bind to it
Cation Exchange:Column is (-)charged, (+) charged proteins bind to it
To determine the pH of the ideal binding buffer we must consider the _____ of the proteins
What kind of buffers do we want to use in Cation Exchange and anyone Exchange colums?
For instance, if we had a proteins that was very high in Lyseine and arginine, what do we want to use to separate it out of a solution?
Isoelectric point
Example: These compounds have a very high pI, so we would need to use a buffer with a pH greater than 11
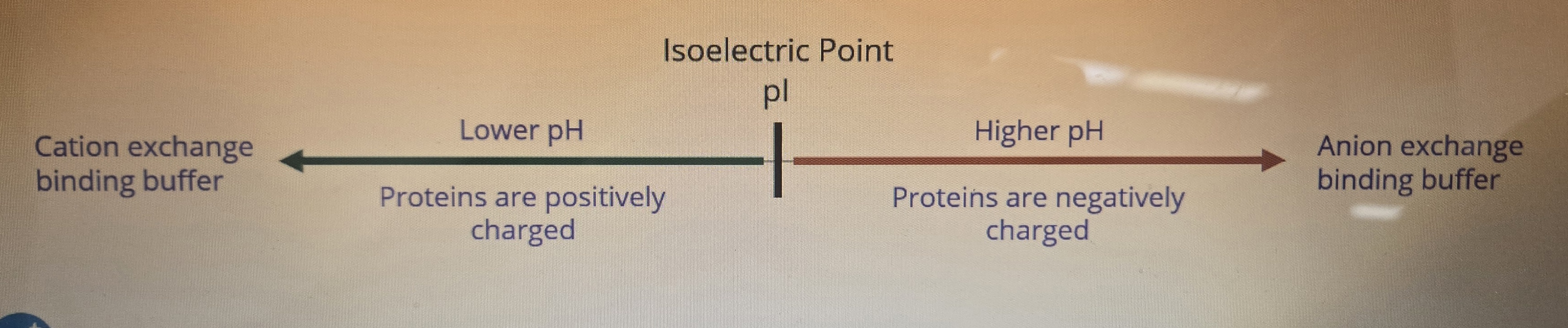
Can you describe the two elution methods of anion exchange and their orders of elution? Why exactly does it happen?
With the salts like NaCl, the Cl- will displace the anionic protein from the resin, essentially kicking it out and taking its place

Can you describe the two elution methods of cation exchange and their orders of elution?
With the salts like NaCl, the Na+ will displace the cationic protein from the resin, essentially kicking it out and taking its place

A major drawback of affinity Chromatography is that it is not useful if the protein is mostly____. That’s where we use alternative forms of Chromatography like:
Uncharacterized
Nickel Colums to bind to proteins with His tags and elute with imidazole
Ligand colums that bind to protein and elute with free ligand
If the question is asking to not just separate, but ISOLATE a particular protein, how can we relate this to Chromatography?
We want the method that will allow the desired protein to be isolated to STICK to the column
To ideally separate proteins thru a cation/anion exchange column, we would want the pH of the buffer to _____.
Make the proteins have an opposite charge
Simple distillation can be used if the boiling points are under ____ and are at least _____. Fractional distillation should be used if the boiling points are ________ apart because it allows __________.
150°C
25°C apart.
less than 25"C
more refined separation of liquids by boiling point
What kind of compound are in the aqueous and organic phase respectively ? What do we need to consider if given a density of a organic layer and it is like 0.7 and the aqueous is water?
Aqueous: Polar
Organic: Nonpolar
The organic layer is less dense than the water, so organic will be on top while aqueous will be on the bottom. That means nonpolars will be on top and polar like acids will be on the bottom
Alcohols dissolve better in a ____ solvent that in a ___ solvent. So if we are using TLC to analyze some alcohols we can expect Rf values with a solvent like heptabe to be ____ than with a solvent like water.
Polar
Nonpolar
Less
Rank the following compounds from least to most polar and why:
Pentane
Pentanol
Pentanone
Pentanoic acid
Polarity Ranking (Least → Most Polar):
Pentane (nonpolar hydrocarbon)
Pentanone (polar ketone group)
Pentanol (polar alcohol group with hydrogen bonding)
Pentanoic acid (most polar – carboxylic acid group with strong hydrogen bonding and dipole)
Mnemonic: "Happy Kids Always Cry" → Hydrocarbon < Ketone < Alcohol < Carboxylic acid
How can something like 1-chlorobutane and 1-butanol be separated by fractional distillation?
They have different BPs!
1-butanol> 1-chlorobutane because it participates in a strong intermolecular force H BONDING
Difference between SDS-PAGE and Natuve
SDS: Separates just by size (coats all negative)
Native: Goes by their individual charge
What does gel filtration do
Separates molecules by size using porous beads (small go slow)
Lets say we need to separate a solution of two polar molecules but one is more basic than the other, how do we isolate the basic one?
We add string base to quench the acid, and then we add ether to separate the layers and evaporate the base out
Whats a pyrophosphate versus a phosphatide?
Pyro has 4 phosphates linked while a phosphatides is PC which has a tertiary n attached to the phosphate
If something like a liposome has fluorescence during size exclusion what could be the reason?
Liposomes don’t have much conjugation or aromatics because they are just phospholipids which are just hydrocarbon chains
If we are observing a gel electrophoresis and the native gel has one mRNA running more down than the others while the denatured is at the same level, what can that tell us?
The structure is more compact which makes it smaller and move faster while after denaturing its shown that its made by the same amount of “stuff”
What is the only way to know that a compound is in its native state?
If its as functional as usual, so it should have the same natural affinities.