a&p test 2
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
Which of the following is constructed of elastic cartilage?
external ear
A patient is diagnosed with mesothelioma. This cancer affects the:
serous membranes.
What do skeletal and cardiac muscle cells share in common?
striations
A tissue is more likely to heal by regeneration if it:
possesses stem cells.
Keratinized, dead cells are associated with:
stratified squamous epithelium.
Which statement best describes epithelial tissue?
Paracellular or transcellular transport moves substances between or across simple epithelia.
What type of blood cell transports oxygen throughout the body?
erythrocyte
Which of the following types of tissue can be described as irregular or regular?
dense connective tissue
Cells found associated with connective tissue proper that ingest foreign substances, microorganisms, and dead and damaged cells are:
phagocytes

What fibers are common in this tissue?
both elastic and some collagen
Histology is the study of:
tissues
What type of protein fiber, commonly found in the extracellular matrix, is extensible?
elastic
Which unicellular gland is responsible for mucus secretion?
goblet cell
Glands, such as the thyroid, that secrete their products directly into the blood rather than through ducts are classified as:
endocrine
Tissues are structurally more complex than:
cells
Simple cuboidal epithelium is built for:
prevention of water loss through the skin.
Which organ system is lined by transitional epithelium to accommodate stretching?
urinary system
A serous membrane contains a superficial layer of epithelial tissue and a deeper layer of connective tissue. Thus, serous membranes are classified as:
organs
The free surface of an epithelial tissue is the:
apical surface.
What component of ground substance adheres cells to each other and to their places within the extracellular matrix (ECM)?
glycoproteins
Which of the following is composed of multiple layers of cells?
transitional epithelium
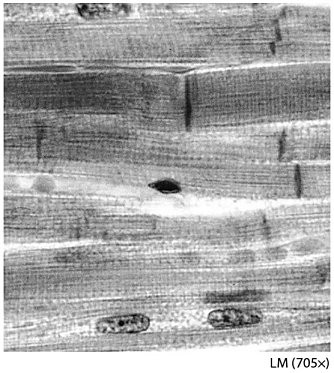
Name this tissue.
cardiac muscle tissue
You examine a tissue slide through the microscope and recognize one layer of cells that are mostly tall and elongated. You determine this tissue to be:
simple columnar epithelium.
What type of large, multinucleated cell destroys bone?
osteoclast
Striations are a structural feature associated with some
muscle cells
Protein channels that are situated between cells and create small pores for the passage of small substances are known as:
gap junctions.
What type of cell junction would most likely prevent water from flowing between our cells?
tight junctions
What makes cartilage an unusual connective tissue?
Cartilage essentially lacks blood vessels coursing through the cartilage.
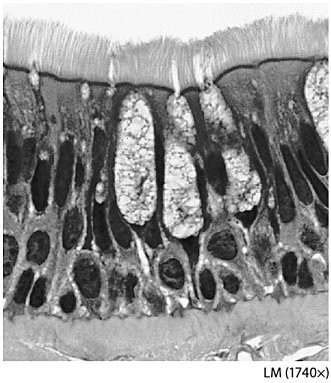
The tissue pictured in this figure is:
composed of a single layer of columnar cells appearing stratified.
Connective tissues proper (or general connective tissues) produce collagen fibers using cells known as:
fibroblasts
Which layer of the epidermis is characterized by prominent cytoplasmic granules in the cells?
stratum granulosum
What tissue composes the epidermis of the skin?
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
The main components of the skin are the:
epidermis and dermis.
What does cyanosis signify?
A person has oxygen-starved skin
Which of the following is an appropriate skin response to cold?
Dermal blood vessels vasoconstrict.
What do dead keratinized cells form?
hair shaft
Tommy fell and skinned his knee. The scrape did not bleed. He must have only damaged the:
epidermis.
What structure stands hairs on end, causing piloerection?
arrector pili muscle
How do melanocytes and keratinocytes work together to protect the skin from UV damage?
Keratinocytes accumulate melanin granules to shield the keratinocyte's DNA.
What tissue composes the reticular layer of the dermis?
dense irregular connective tissue
Thomas is deaf, but can feel the vibrations of music through sensory receptors in his skin called:
lamellated (Pacinian) corpuscles.
Which of the following is NOT a function of the skin?
vitamin A synthesis
How do nutrients reach the epidermis of the skin?
Diffusion transports nutrients from blood vessels in the dermis into the epidermis.
Eccrine glands produce:
sweat containing mostly water.
Melanin is produced upon exposure to:
UV radiation.
Thin skin contains:
one less layer of keratinocytes than thick skin.
Why is vitamin D necessary?
Vitamin D is required for calcium absorption from the small intestine.
Where is thick skin located?
palms
Why are eyelashes shorter than terminal hairs on the scalp?
The growth stage of an eyelash is shorter.
The most superficial component of the skin is the:
epidermis
Which of the following cells is associated with the dermis?
fibroblast
What type of intercellular junction bands together adjacent cells, making the epidermis stronger?
desmosome
The nail body covers the:
nail bed
For a male post-puberty, the majority of vellus hairs have transitioned to:
terminal hairs.
What do vellus hairs lack?
pigment
The cuticle around a nail is the:
eponychium
The epidermis is:
keratinized cutaneous membrane.
Jill is blind and often uses braille (a system of raised dots) to read her school assignments. What cell in the stratum basale of the epidermis helps her discriminate between the textured dots?
Merkel cell
Nail growth occurs at the nail:
matrix
Thick skin lacks
hair follicles.
You examine a tissue slide through the microscope and recognize one layer of cells that are mostly tall and elongated. You determine this tissue to be:
simple columnar epithelium.
Which of the following is NOT a function of the skin?
vitamin A synthesis
Exposure to UV radiation causes the skin to darken by increasing the production of:
melanin
Where is thick skin located?
palms
Simple squamous epithelium is found lining the
air sacs of the lungs
What do skeletal and cardiac muscle cells share in common?
striations
Which organ system is lined by transitional epithelium to accommodate stretching?
urinary system
The most superficial component of the skin is the
epidermis
Chondrocytes are to cartilage as osteocytes are to:
bone
From deep to superficial, what is the correct order of the layers of the epidermis?
stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum
James damaged cartilage in his joint while exercising. He learned that he will have to wait a few months before returning to physical activity. Discuss why you think cartilage, in general, is slow to heal based on your knowledge of cartilage structure.
Because the cartilage doesn’t have direct blood supply
What functional advantage is there for skeletal muscle cells to be multinucleate?
Multinucleation is an advantage because of skeletal muscle fiber size and the amount of protein synthesis that takes place in these metabolically active cells
Why should a surgeon cut along the tension (cleavage) lines when preforming surgery?
it heals with less minimum scarring.
The ecm is made up of 3 different components.
Protein
Glycosaminoglycan (GAG)
Glycoconjugate
fibers that make up the ecm
collagen, make up 20–25% of all proteins in
body; composed of multiple repeating subunits that
form a white fibrous protein; resistant to tension
(pulling and stretching forces) and pressure.
elastic, composed of protein elastin
surrounded by glycoproteins; extensibility allows fiber
to stretch up to one and a half times resting length
without breaking.
reticular- thin, short collagen fibers; form a
meshwork or scaffold that supports cells and ground.
substance of many tissues; form a weblike structure in organs like spleen that help trap foreign cells
type of cell junctions
• Tight junctions- hold cells closely together such that space between is
impermeable to movement of macromolecules (found between cells
in blood vessels, prevent blood from exiting vessels)
• Desmosomes- composed of linking integral proteins; allow for materials in extracellular fluid to pass through space between cells (epithelial tissues)
• Gap junctions- are small pores formed by protein
channels between adjacent cells that allow small
substances to flow freely between each cell’s cytoplasm Found in between cells that communicate with electrical signals such as cardiac muscle cells
Epithelial tissues
tightly packed sheets of cells
with no visible ECM; cover and line all body surfaces and
cavities; specialized epithelia form glands that manufacture
secretions such as sweat, saliva, or chemical messengers called
hormones found on every internal and external body surface.
Connective tissues
connect all other tissues in body to one
another; ECM is a prominent feature for most connective
tissue types with cells scattered throughout; bind, support,
protect, and allow for transportation of substances
Muscle tissues
capable of generating force by
contracting; little ECM between cells found mostly attached to
skeleton where its contraction produces body movement
Nervous tissues
consist of cells capable of
generating, sending, receiving messages, and cells
that support this activity all within a unique ECM makes up majority of brain, spinal cord, and nerves;
glandular epithelial
structure of epithelial origin that synthesizes and secretes a product from designated secretory cells. Can be classified either by their shape or by how they release products.
goblet cells
most common unicellular exocrine
gland; found in digestive and respiratory tracts; secrete
mucus, a thick sticky
liquid that protects
underlying epithelium
cells that make up of connective tissue
Fibroblasts
Adipocytes
Mast cells
Phagocytes
Other immune system cells
3 type of muscle tissues
Skeletal muscle- striated/ voluntary
Cardiac muscle- striated/ involuntary
Smooth muscle- involuntary
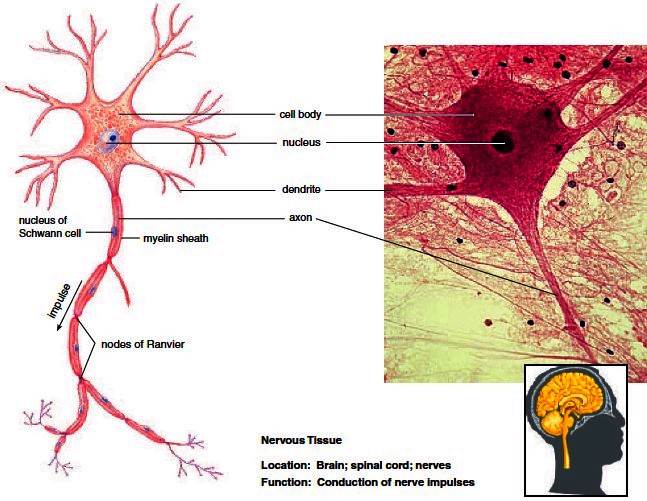
neurons
Solitary axon extends from one end of soma; responsible for
moving a nerve impulse from soma to a target cell (may be
another neuron, muscle cell, or gland); axons illustrate Cell-Cell
Communication Core Principle
type of membranes
true membrane
membrane like structure
serous membrane
tissue repair
process of wound healing; dead and
damaged cells are removed and replaced with new
cells or tissues to fill in gap for maintenance of
homeostasis; process differs with different tissues
skin layers
– Epidermis – superficial layer; keratinized stratified squamous epithelium resting
on basement membrane
– Dermis – deep to epidermis and basement membrane; loose connective tissue
and dense irregular connective tissue
layers of epidermis
Stratum basale – (stratum germinativum) single layer of stem cells resting on basement membrane.
• Stratum spinosum – thickest layer; on top of stratum basale; still close to blood supply.
metabolically and mitotically active
• Stratum granulosum
• Stratum lucidum – narrow layer of clear, dead keratinocytes; only in thick skin
• Stratum corneum – outermost layer; several layers of dead, flattened keratinocytes with thickened plasma membranes
thick skin
about as thick as paper towel; all five epidermal layers and very thick stratum corneum; no hair follicles; many sweat glands.
thin skin
covers areas of body not subjected to as much mechanical stress; about as thick as sheet of printer paper; only four layers (no stratum) lucidum)
skin marking
small visible lines in epidermis created by interaction between dermis and epidermis; best seen in thick skin
rule of 9
• Method for estimating how much of body
has been affected by burn
• Body is divided into 11 areas; each
represents 9% of total body area
• Useful clinical tool for grading extent of
burn; severity and extent of burn are
used to direct treatment options
2nd degree burns
Second-degree (partial thickness)
– Involve epidermis and part or all of dermis
– Can result in pain, blistering, and scarring
3rd degree burn
Third-degree (full thickness)
– Most damaging wounds
– Involve epidermis, dermis,
hypodermis, potentially even deeper
tissue (muscle or bone)
– Not generally painful at first because
nerves too are destroyed
– Typically major tissue damage and
significant scarring; loss of hair
follicles; diminished or absent keratin
production
– Problems with dehydration due to
massive fluid loss from swelling; also
great risk for infection