APES chapter 3 (enviornmental interactions)
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Ecosystem
a biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment. ex) a cave
biosphere
combination of all ecosystems on earth
what are the boundaries of ecosystems?
Ecosystem boundaries distinguish one ecosystem from another. Although boundaries can be well-defined, often they are not. Boundaries are commonly defined either by topographic features, such as mountain ranges, or are subjectively set by administrative criteria such as Yellowstone.

Photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
cellular respiration equation
C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 --> 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + ATP
heterotroph
consumer, eats other organisms for energy
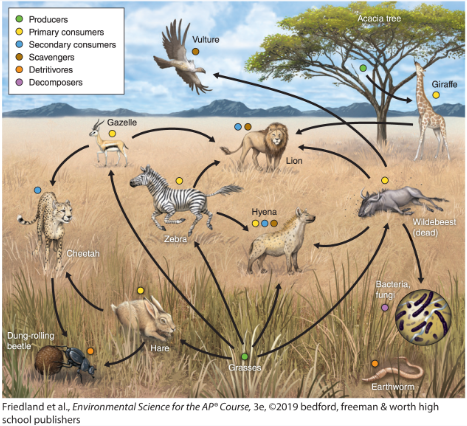
autotroph
producer, makes its own enregy
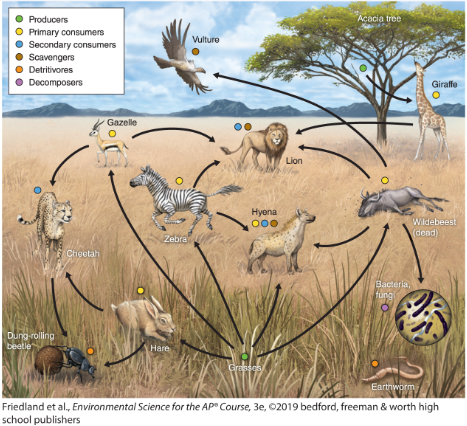
primary producers
produce their own food ex) plants
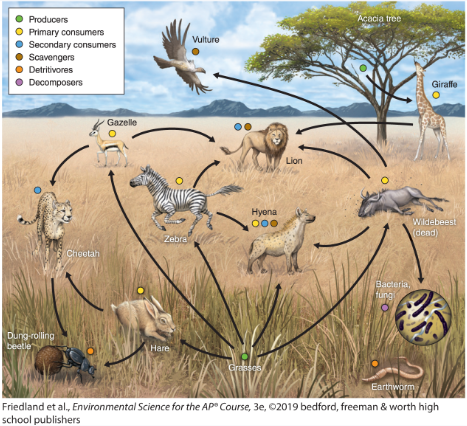
primary consumers
animals that eat plants ex) butterflies
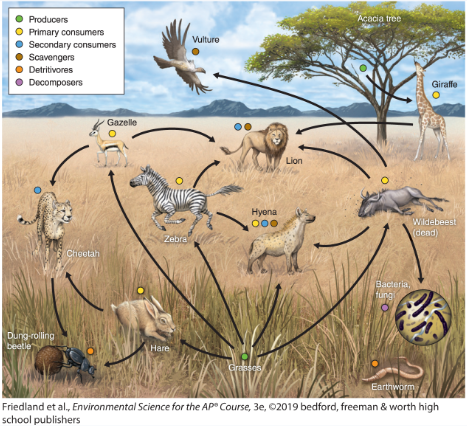
herbivore
ONLY eats plants (a section of primary consumers)

Secondary consumer
Any animal that consumes an primary consumer ex) a snake
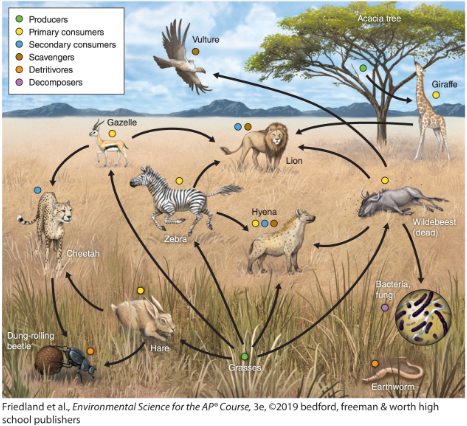
Tertiary consumers
an animal that obtains its nutrition by eating primary consumers and secondary consumers ex) a lion

scavengers
an animal that feeds on carrion, dead plant material, or refuse. ex) vulture

detritivores
an animal which feeds on dead organic material ex) earthworm
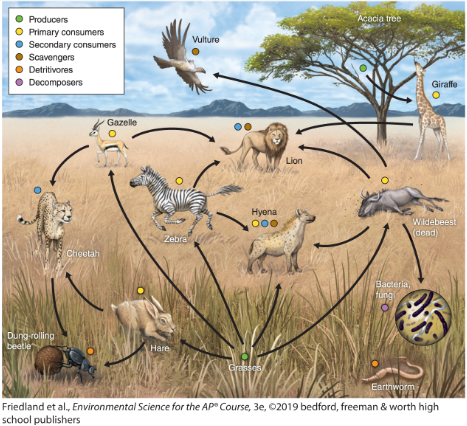
decomposers
feeds on and breaks down dead plant or animal matter ex) fungus

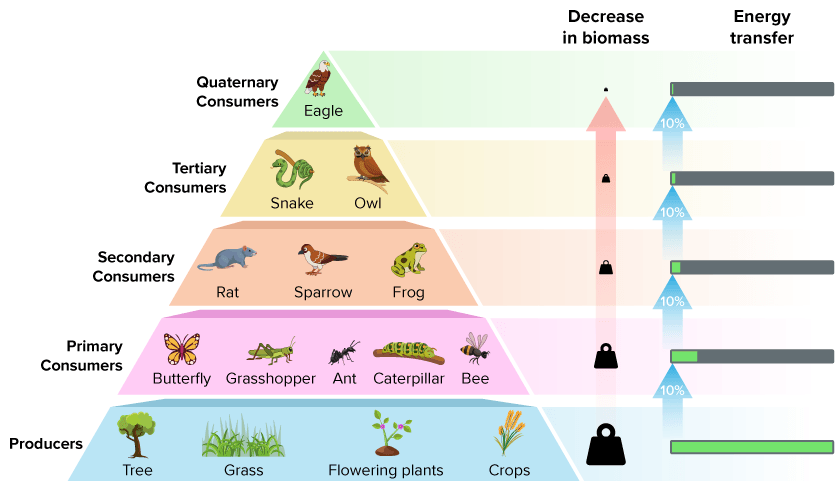
Energy is _____ as it goes up the tropic levels
lost
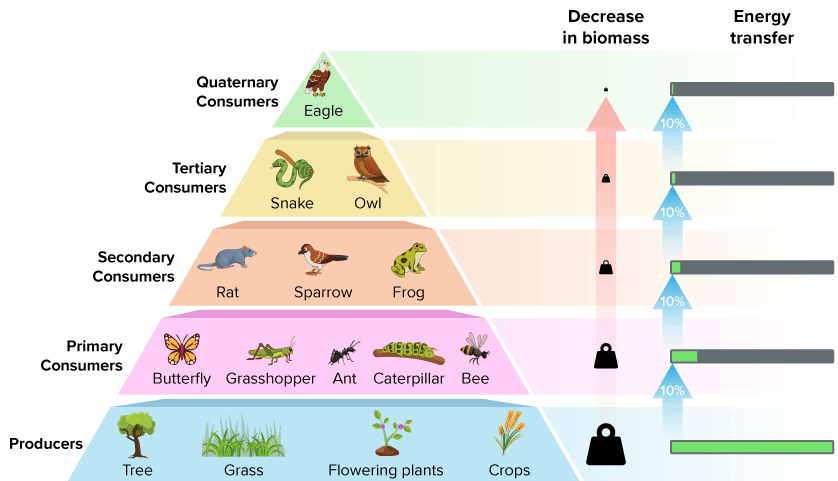
what does the “productivity” of an ecosystem measure
energy
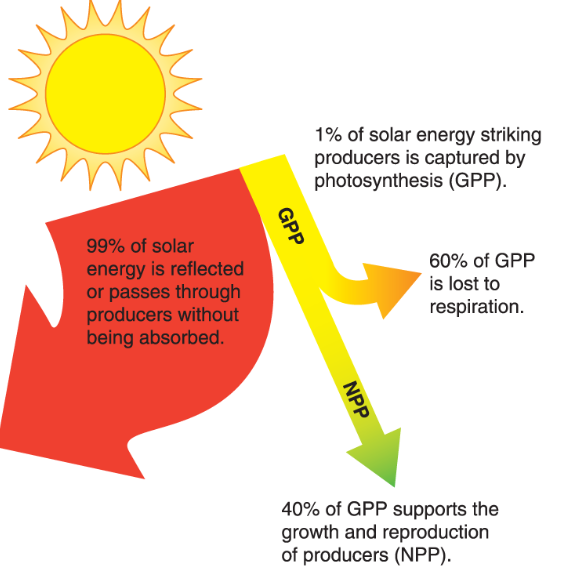
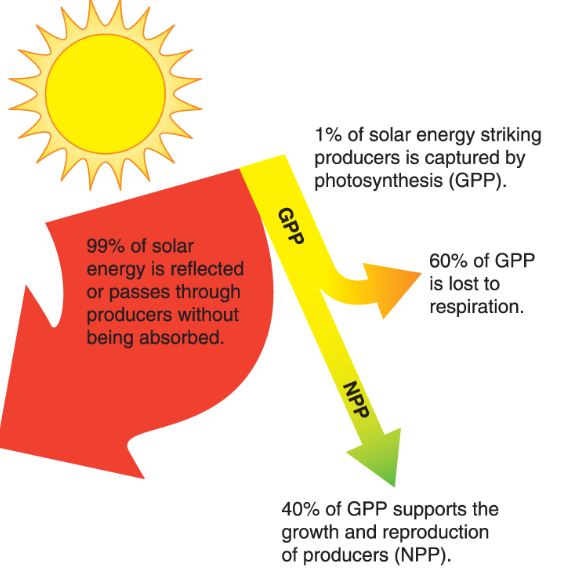
what is GPP (gross primary productivity)
total amount of solar energy captured over a given period of time
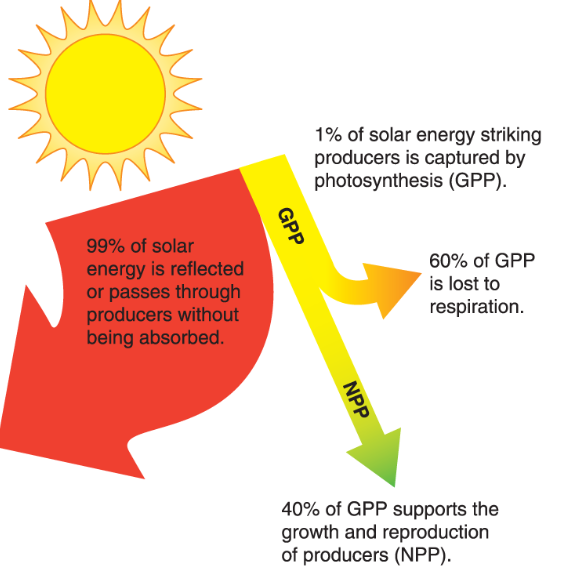
What is NPP (Net primary productivity)
Energy used by producers (respiration)
explain the 10% rule
the average amount of energy remaining going up each trophic level

What percentage of incoming solar energy do plants capture during photosynthesis?
1%
flora
pants
fauna
animals
What defines an ecosystem?
temperature and precipitation

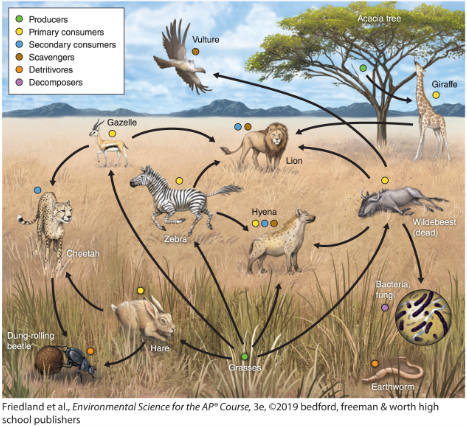
tropic cascade
When you remove something it messes up the food web (ex. mice population goes extinct so an owl eats more moles and the mole population depletes)
NPP=
GPP- respiration by producers
what are the most productive ecosystems?
Tropical rainforest, seasonal forest, temperate rainforest, swamps, coral reefs, salt marsh
What are the least productive ecosystems?
extreme desert, desert scrub, tundra, open ocean
where do we find carbon that sits for a long period of time?
In the ocean (or hydrosphere)
Lithosphere
the earth
Transpiration
plants release water from their leaves.
plants like _____
nitrogen, but cant use it in its original form
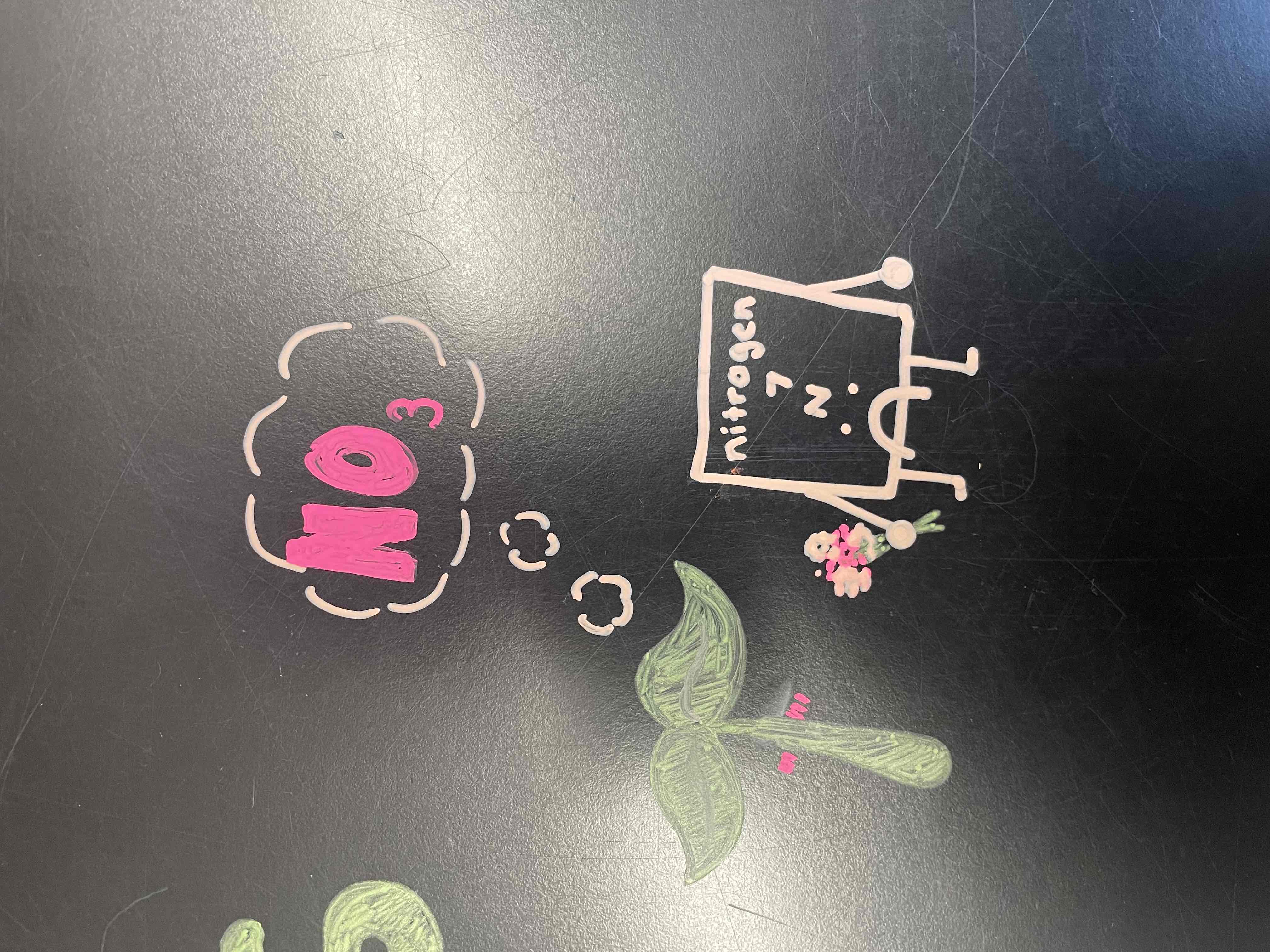
The atmosphere is made of….
78% nitrogen 28% oxygen 1% everything else
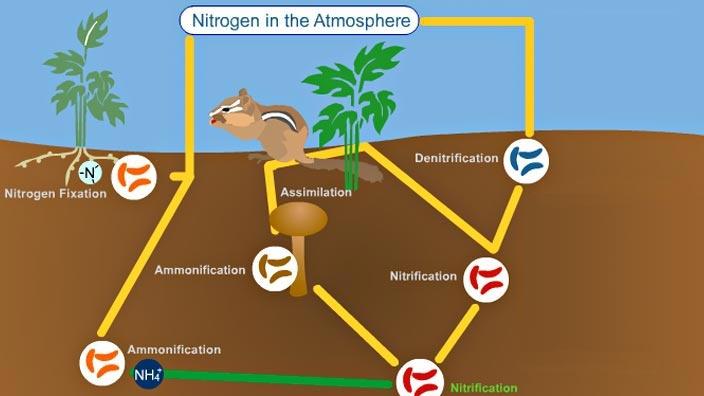
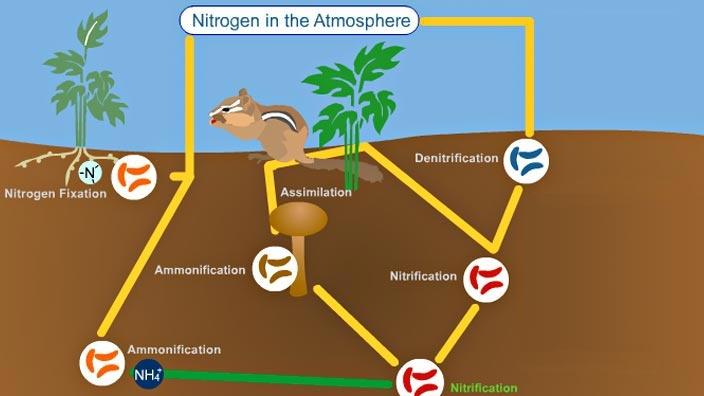
What are the steps of the Nitrogen Cycle?
1) Fixation 2) Nitrification 3) Assimilation 4) Ammonification 5) Denitrification
Abiotic fixation
“zaps” through lightning or fire and turns N Into N03
Biotic fixation
Bacteria take N2 and transform it into Ammonium NH4 which is how plants can be high in protein
Evaporation
solar energy heats the Earth and evaporates rivers, lakes, streams, and oceans.
precipatation
rain, snow, hail
condensation
the process where water vapor becomes liquid - reverse action of evaporation
percolation
the process of a liquid slowly passing through a filter- ex coffee

“pools” store____
matter
NH3
Ammonia
NH4
amonium
NO3
nitrates
N2
nitrogen gas
N2O
Nitrous oxide
Nitrogen fixation
Puts Nitrogen into the soil in a usable form
Biotic (bacteria)- N2 → NH3
Abiotic (lightning, fires, fertilizer)- N2 → NO3
Phosphorus dose not have a _________ phase
gassus
Phosphorus forms ________ and ___________ compounds
stable
insoluble
Eutrophication
to much phosphorous and too much nutrients in a system

Nitrification
Bacteria makes the change, now it is nitrate which is useable for plants
NH4 → NO3
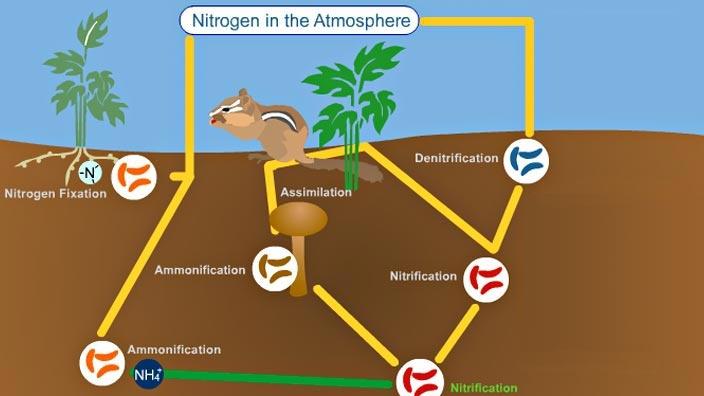
Assimilation
NO3 is absorbed, gives the plants Nitrogen and protein
Volcanisim
eruption of volcainos
Phosporous is…..
Natural!
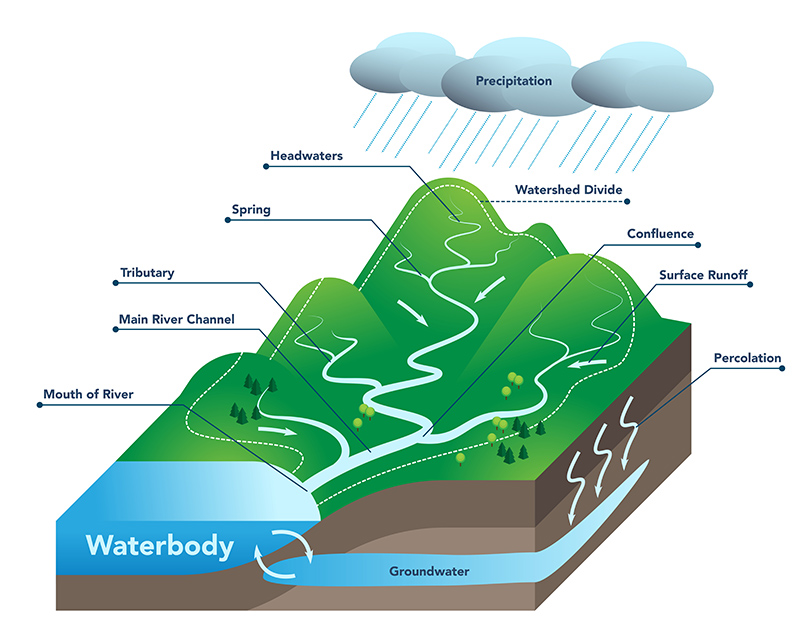
watershed
an area or ridge of land that separates waters flowing to different rivers (ex. Pine flows into Allegheny River)
biological/chemical/physical disturbance
Disturbances caused naturally ex) hurricanes, tsunamis, forest fires

anthropocentric disturbances
disturbances caused by humans ex) pollution, housing developments, overuse pesticides
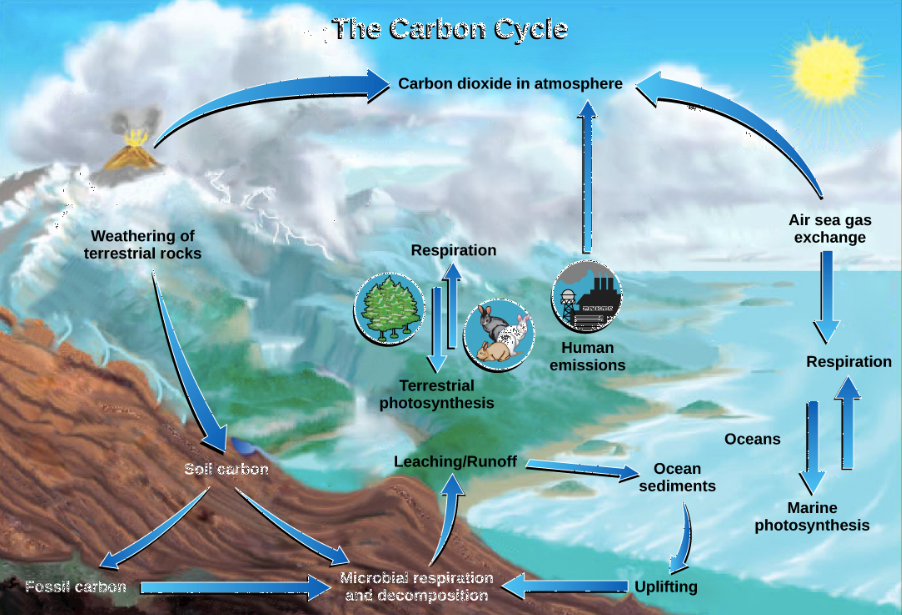
What are some examples of carbon pools?
the ocean, rocks, living organisms, the atmosphere
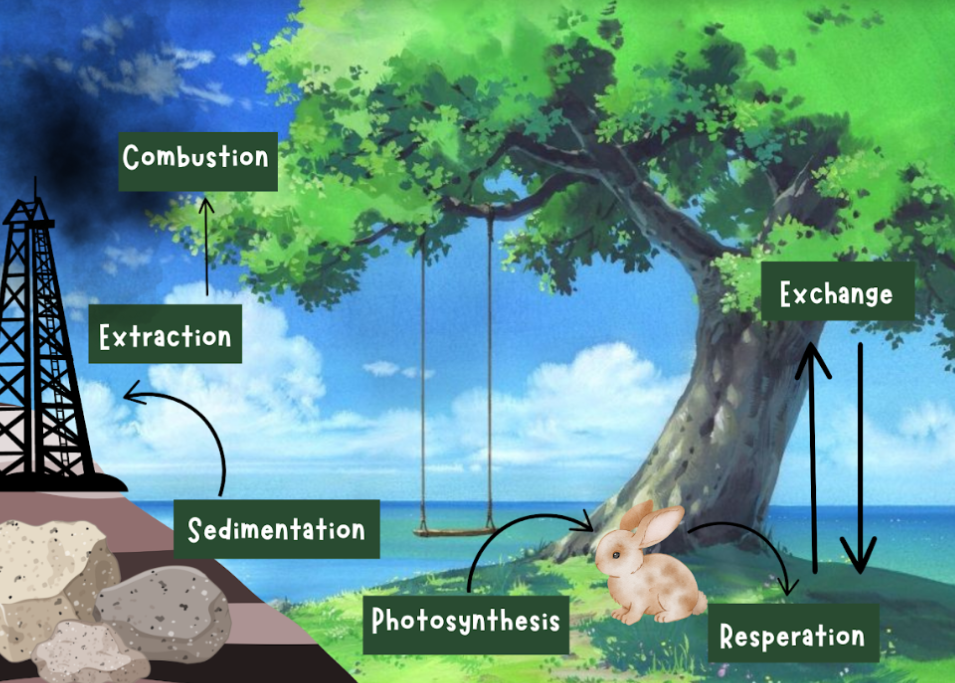
what are the 6 steps of the carbon cycle?
1) Photosynthesis
2) Resperation
3) Exchange
4) Sedimentation
5) Extraction
6) Combustion
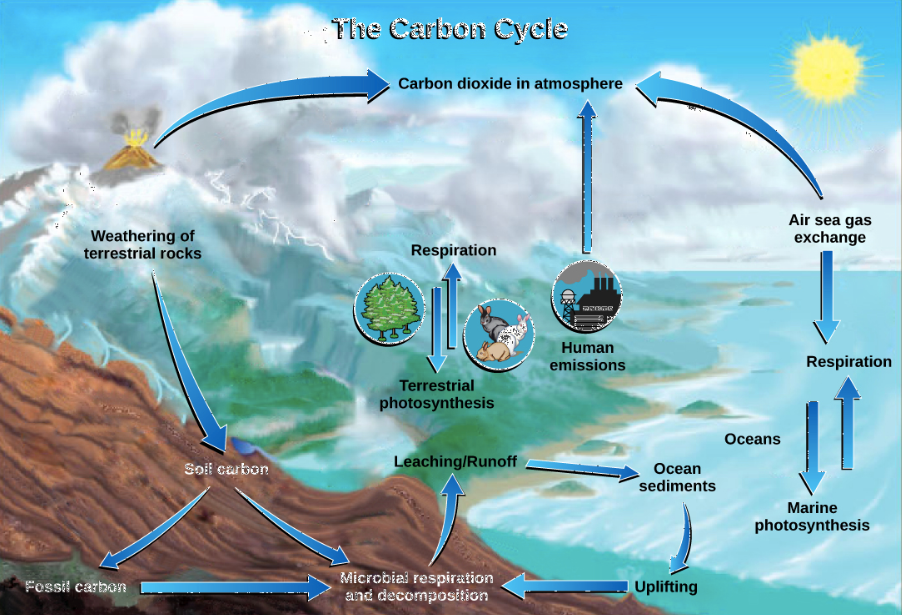
Long Term/SLOW Carbon Cycling and Pools
-Ocean/Hydrosphere
-Lithosphere
-Atmosphere
Fast Carbon Cycling…
-Photosynthesis
-respiration
-Flora/Fauna
are disturbances good or bad?
not necessarily, fires can turn over soil. Disturbances can help the flow of energy.
What is the importance of the “Hubbard Brook” watersheads
It was found that when trees are no longer present to take up nitrogen, nitrate drains into the watershed.
What are the 5 steps of the nitrogen cycle?
1) Nitrogen fixation
2) nitrification
3) assimilation
4) ammonification
5) denitrification
What is exchange in the carbon cycle?
Carbon dioxide is transferred from one reservoir to another
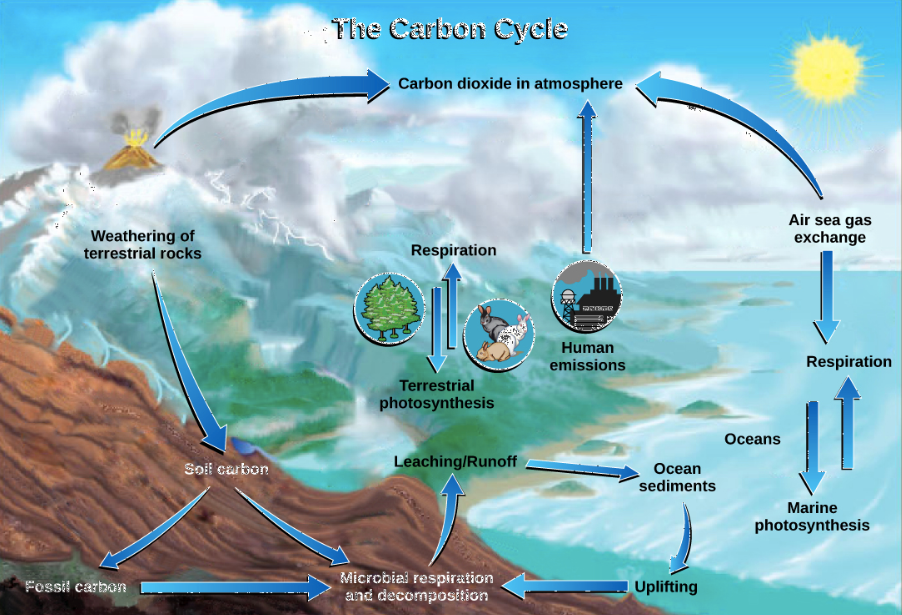
What is Sedimentation in the carbon cycle?
Carbon Carbonate precipitates out of the water as sediments through heat and pressure. An example of this is limestone and this provides a long term pool for the carbon.
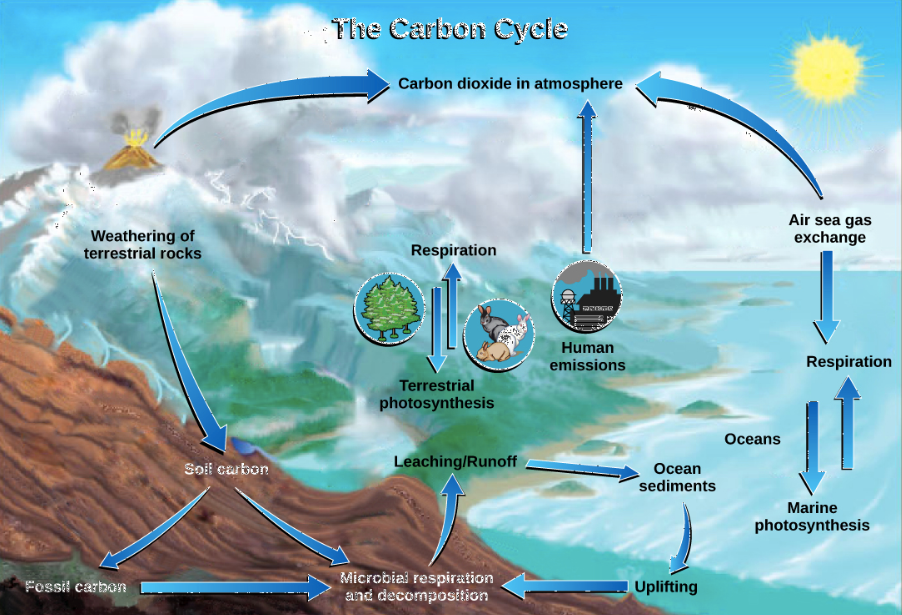
What is extraction in the carbon cycle?
Humans extract fossil fuels bringing carbon to earth’s surface where it can be combusted.
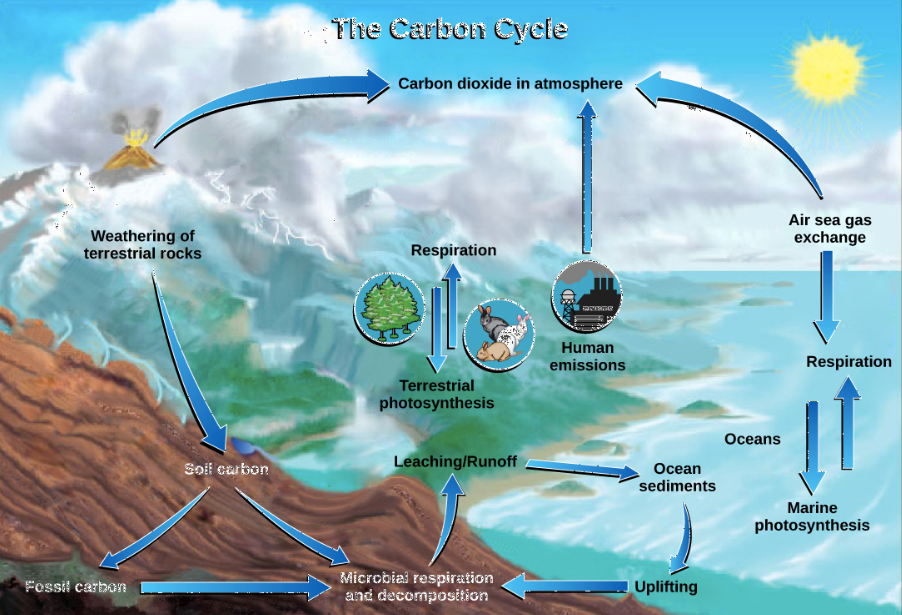
What is combustion in the carbon cycle?
Fossil fules and plant matter are converted into co2 (transfers from biosphere to the atmosphere)