Microbiology, Bio 221, BYUI
1/229
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
230 Terms
cell membrane
lipid bilayer, proteins, carb, and lack steroids in plasma membrane of prokaryotic cells
Prokaryotes
lack membrane bound organelles, and DNA are single circular with no histones; no sterols in plasma membrane
Eukaryotes
have membrane bound organelles, and DNA are linear
Shapes of bacteria
Cocci, Baccilli, Spiral (Vibrio, Spirilla, Spirochete)
Vibrio
form a bow shape
Spirilla
helical shape that is rigid; 2-3 curves
Spinochete
helical shape that is flexible; 3-4+ curves
Four basic types of flagella arrangements:
Peritrichous, Monotrichous, Lophotrichous, and Amphitrichous
Monotrichous (& Polar)
One flagellum at one pole
Peritrichous
flagella all over cell
Lophotrichous (& Polar)
tuft of flagella at one pole
Amphitrichous (& Polar)
flagella at both poles of the cell
Atrichous
bacteria that lack flagella
Axial Filaments
- Only found in spirochetes
- Rotation causes cell to move like a corkscrew
- Axial filament located between the outer sheath and the cell wall
Fimbriae (fimbra1)
hairlike appendages made of pilin; used for attachment and colonization of host
Pili
Made of pilin and form a single long shaft connecting two bacteria together; to exchange DNA between bacteria
Glycocalyx
-Capsule when substance is composed, organized, and attached to cell wall and thick
-Slime layer if only loosely attached to cell wall and thin
-Polymer of polysaccharide and protein found on outside of cell wall
Cell Wall
2 Types - Gram+ and Gram-
Components include:
-peptidoglycans
-peptides and proteins
-phospholipids
-polysaccharides
Plasma membrane is under cell wall
Gram positive
-Describing the group of bacteria that have a cell wall that is structurally less complex and contains more peptidoglycan than the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. Gram-positive bacteria are usually less toxic than gram-negative bacteria.
-Contain Teichoic Acid which is the main antigenic determinate for Gram+
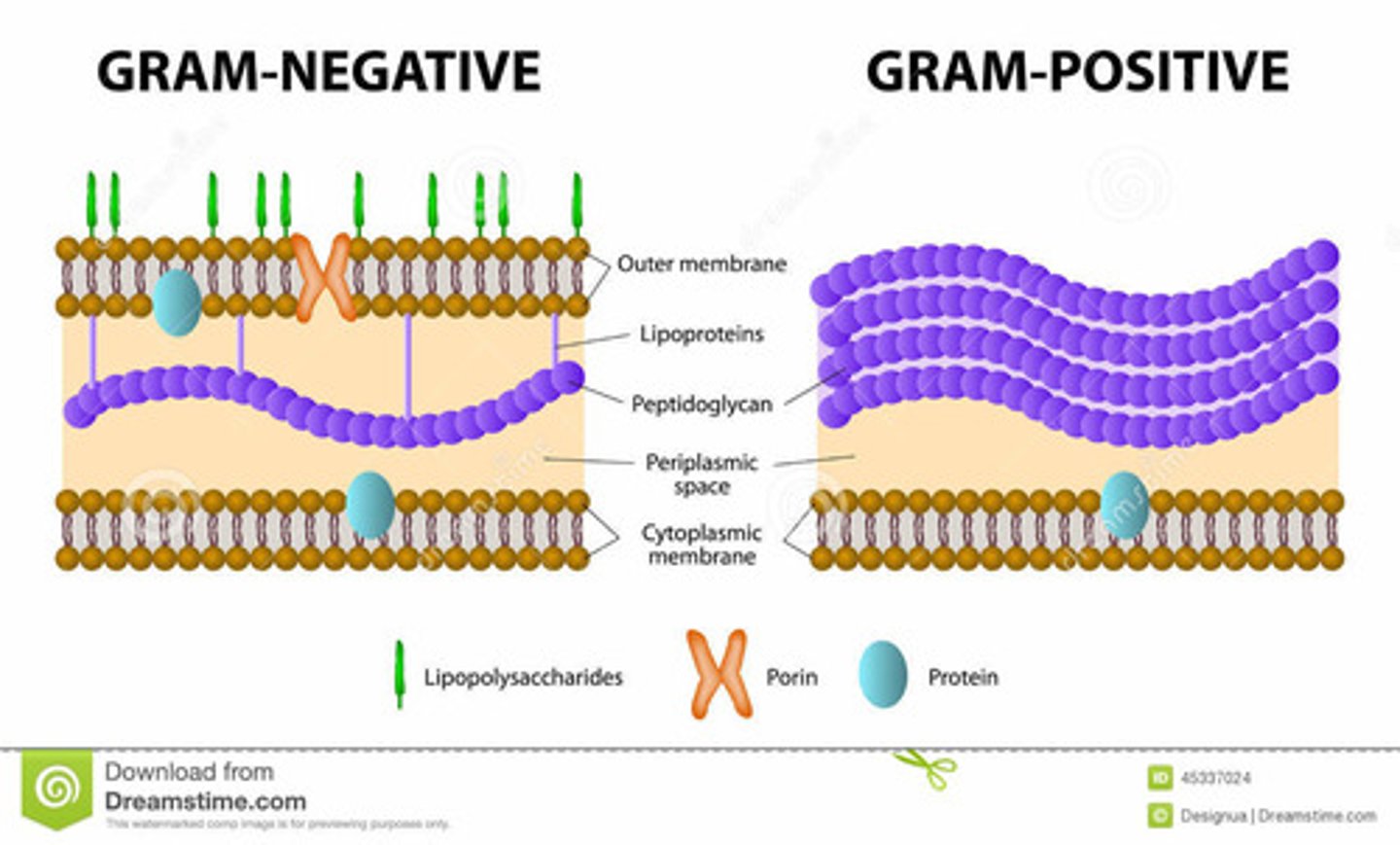
Gram Negative
Describing the group of bacteria that have a cell wall that is structurally more complex and contains less peptidoglycan than the cell wall of gram-positive bacteria. Gram-negative bacteria are often more toxic than gram-positive bacteria
-NO Teichoic Acid
-Contain O Polysaccharide-main antigenic determinate (tail of mouse-behind)
-Contain LipidA - an endotoxin - very toxic (mouse behind imbedded in outer membrane)
How does penicillin work?
Interferes with final linking of peptidoglycan rows by peptide cross bridges.

Carbohydrate Backbone
NAG/NAM; Cross bridges bind to NAM
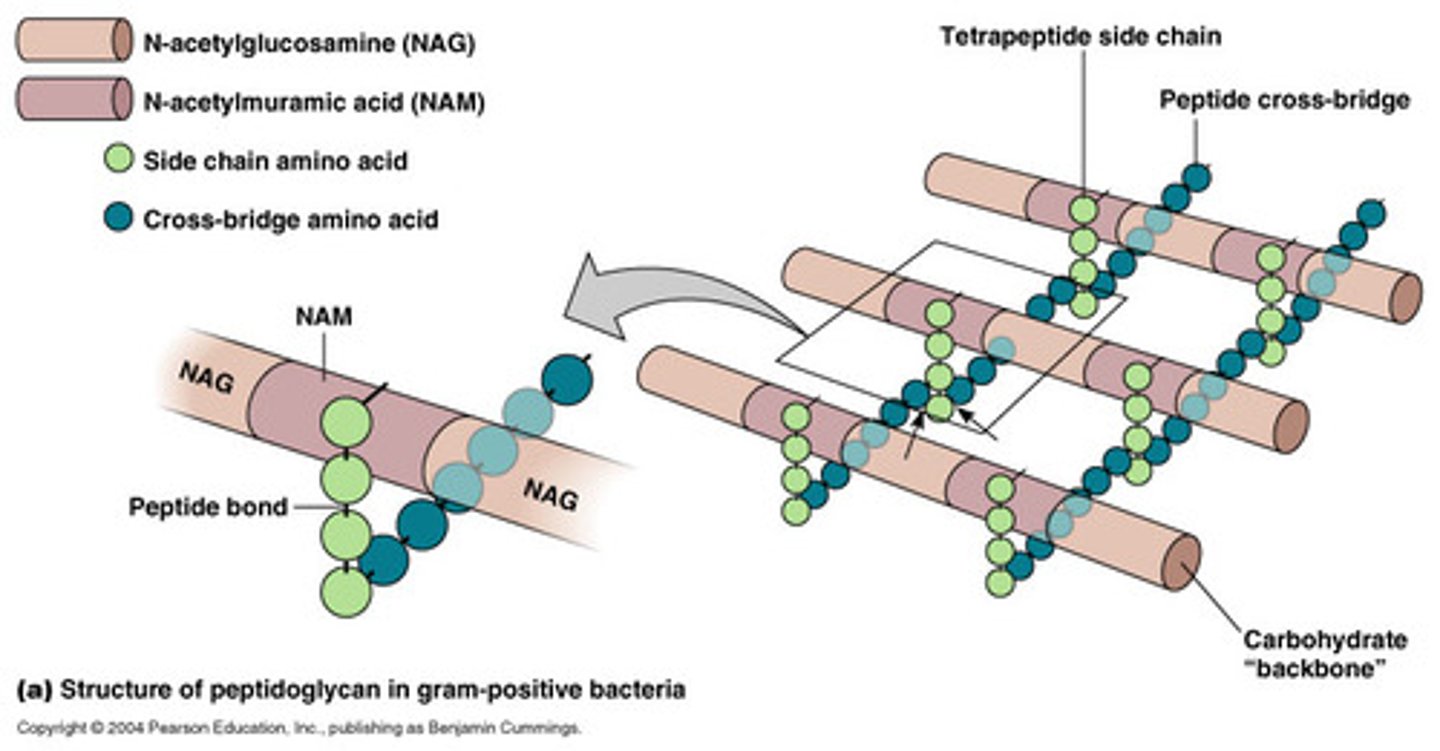
These antibiotics kill by binding the transpeptidase enzyme which attaches to the cross bridge, instead attaches to ___________ and causes the disruption of cellular intergrity.
Penicillin and Beta Lactam antibiotics
Where does lysozyme attack bacteria cell walls?
It attacks the peptidoglycans found in the cell walls, especially gram-positive bacteria.
What's teichoic acid doing in gram + cell walls?
It's an antigenic determinant; Helps provide structure
-composed of alcohol and phosphate
Gram Negative outer membrane function
Strong negative charge is an important factor in evading phagocytosis and the actions of complement, two components of the defenses of the host. The outer membrane also provides a barrier to certain antibiotics, digestive enzymes such as lysozyme, detergents, heavy metals, bile salts, and certain dyes.
periplasmic space
The space between the inner and outer cell membranes in Gram-negative bactera. The peptidoglycan cell wall is found in the periplasmic space, and this space sometimes contains enzymes to degrade antibiotics.
Porin Protein
-A type of protein in the outer membrane of gram-negative cell walls that permits the passage of small molecules; nutrients and waste pass through
2 TYPES
1) Integral - span and go whole way through plasma membrane; allow nutrients and waste products out
2) Peripheral Protein - only attach to one surface of plasma membrane; either inside or outside; act as an enzyme to speed up chemical reaction in cell
Lipoproteins
-connect outer membrane and plasma membrane
-make periplasmic space possible
Tetrapeptide Sidechains
-4 Amino Acids attached to NAM 's in the backbone
-Parellel tetrapeptide side chains may be directly bonded to each other or linked by a peptide crossbridge
Prokaryotic Flagella
-Filament- Composed of proteins called flagellin; form the long hairlike structure that sticks out of the cell (Not enclosed within the plasma membrane)
-Hook - wide structure that holds the filament and turns it like apropellar
-Basal Body - anchors flagellum to the cell wall and plasma membrane
Eukaryotic flagella
Membrane covering present on filament of flagella
Hook and only two rings attached to the plasma membrane
Wave-like motion
vacuole
stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
cilia
Only found in euks, are hairlike projections that extend from the plasma membrane and are used for locomotion
lysosomes
contains digestive enzymes
Mitochondria
ATP, Double membrane system, carry out the most efficient energy-releasing reactions, reactions require O2
Golgi complex
Put finishing touches on proteins and lipids that arrive from ER
Package for shipment to final destinations outside of cell - "Post office" - "Shipping and Receiving"
Material arrives and leaves in vesicles
nucleus
Keeps DNA separated from cytoplasm, Makes it easier to organize DNA, copy, before parent cells divide into daughter cells
Endoplasmic Reticulum
In animal cells, continous with nuclear membrane, extends throughout cytoplasm, rough one and smooth one
Smooth ER - Lipid synthesis
Rough ER - Protein synthesis
Chemotaxis
movement of a motile cell or organism, or part of one, in a direction corresponding to a gradient of increasing or decreasing concentration of a particular substance.
run and tumble
movement of flagelar bacteria; short runs interrupted by tumbles
Capsule
Thick, highly organized, and solidly fixed to the cell wall, these prevent the use of penicillin
pilin
-protein that makes up pili, which forms a single long shaft connecting two bacs together to exchange DNA
-Fimbriae are also composed of this
hypotonic
-Solution with lower solute concentration than inside of cell - water follows solutes
-Most bacteria are happy in hypotonic solution
lysozyme
an enzyme found in saliva and sweat and tears that destroys the cell walls of certain bacteria
active transport
the movement of materials through a cell membrane using energy
CV-I complex
the __ is too large to pass through the thick cell wall of gram positive cells
Steptococcus Pyogenes
Cocci
Positive
Strep throat
Staphlyoccus aureus
Cocci
Positive
Food poisoning
Escherichia coli
Bacilli
Negative
Urinary tract infection
Clostridium botulinum
Bacilli
Positive
Food poisoning
Bacillus anthracis
Bacilli
Positive
Anthrax
Neisseria meningitidis
Cocci
Negative
Meningitidis
Vibrio cholerae
Vibrio
Negative
Cholera
Borrelia burgdorferi
Spirochete
Negative
Lyme Disease
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Bacilli
Positive
Tuberculosis
Yersihia pestis
Bacilli
Negative
Bubonic plague
Salmonella typhi
Bacilli
Negative
Typhoid fever
Troponema pallidum
Spiral
Negative
Syphilis
bacterial growth
increase in number of cells, not cell size; fission
bacterial growth requirements
physical and chemical
Simple Diffusion
Passive;
movement of molecules from areas of high concentration to low concentration
Facilitated diffusion
Passive;
Molecules combines with a plasma membrane proteins called transporter protein
Osmosis
passive
movement of WATER across a selectively permeable membrane
high concentration to low concentration
Plasmolysis
lysing of bacteria because water is drawn out in a hypertonic solution
isotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is essentially equal to that of the cell which resides in the solution
No net movement
Hypertonic solution
water moves out of cell, causing its plasma membrane to shrink (plasmolysis)
Hypotonic solution
Water moves into a cell and may cause cell to burst if wall is weak or damaged (osmotic lysis)
Active Transport
cell uses energy (ATP) to move substance across plasma membrane
-moves substance from low concentration to high concentration
Group Translocation
Active process, occurring in some prokaryotes, by which a substance being actively transported across a cell membrane is chemically changed during transport.
-once substance is across the membrane, it is impermeable to the membrane
-Only in prokaryotes
Inclusion
Storage areas fro cells to store molecules and particles that they need (1-Gas vacuoles, 2-lipid inclusion, 3-polysaccharide granules, 4-metachromic granules which contain phosphate to be able to produce ATP in future, diptheria have metachromic inclusions)
Endospore
-"Resting cells"
-When an environment becomes unlivable, certain GRAM+ bacteria can form these resting structures
-Cell puts DNA inside endospore and thr est of the cell dies.
-Can survive for 10,000+ years; resistent to heat and toxins
2 Generra of endospore forming bacteria
1) Clostridium (tetanus and botulism)
2) Bacillus (Anthrax)
Vegatative cell
metabolically active form of bacterium in which reproduction can occur; NOT ENDOSPORE
Nuclear envelope (nuclear membrane)
-a lipid bilayer that surrounds the nucleus in eukaryotic cells
-Innermost surface has DNA attachment sites
-Pores span bilayer
Chromatin
-Cell's collection of DNA and associated proteins
-Chromosome is one DNA molecule and its associated proteins
-Appearance changes as cell divides
-DNA molecules are not wound up and are loose floating inside nucleas
Components of Cytomembrane System
1) Endoplasmic Reticulum- attached to nuclear envelope
2) Golgi Bodies
3) Vesicles - "bubble" off of ER and travel over to Golgi Bodies
Endoplasmic Reticulum
-continuous with nuclear membrane
-extends throughout cytoplasm
-two regions - Rough and Smooth
Rough ER
-ER that is dotted with ribosomes
-Purpose is protein synthesis
Smooth ER
3 Functions:
1- Lipids assembled
2-Lipid synthesis
3-Inactivate toxic chemicals (liver cells have a lot of this=alcohol and tylenol are deactivated by smooth ER in liver
vesicles
-membranous sacs that move through the cytoplasm
-Lysosomes - contain digestive enzymes= break down old depleted parts of cells to components and then they are recycled
-Peroxisomes - Store things
Mitochondria
ATP producing "powerhouse"
require oxygen
Cytoskeleton
-Present in all eukaryotic cells
-Basis for cell shape and internal organization
-Allows organelle movement within cells and in some cases, cell motility
Cytoskeleton Elements
1) Microtubule- Thickest component; push and pull on membrane
2) Intermediate Filament - Next thickest; Not very flexible but is very STRONG
3) Microfilament - Smallest; extremely flexible; Not very strong
Psychophile
Cold Loving
Optimal Growth 15C
-Too cold to be pathogens
Psychotroph
Cold Loving
Optimal Growth 25C (which is room termperature)
-Can grow in body, but immune system will clear them out
Mesophile
Moderate temp loving
Optimal Growth 37C (which is body temperature)
-Include pathogens which are optimized for body temperature
Thermophile
Heat Loving
Optimal Growth 55C
-Can't grow inside body; "Hot Pots in Yellowstone"
Acidophiles
Grow in acidic environment less than 6.5
-linked to stomach ulcers
-Very few bacteria can grow below 4.0
=Many foods such as sauerkraut, pickles, and cheeses are preserved from spoilage by acids produced during fermentation
Osmotic Pressure Range
Low osmotic pressure kills many prokaryotes by plasmyolysis= Hypertonic solution
Halophiles
Microbes that can survive in salty environments
-bacteria function with Na pumps
Obligate Halophiles
Microbes that need salty environments to survive
Obligate Aerobes
must have free oxygen for aerobic respiration
-Neutralize O2
-living forms had to evolve to use O2
facultative anaerobes
Have both aerobic and anaerobic growth
-Growth is greater in the presence of oxygen because full respiration occurs
Aerotolerant anaerobes
Only anaerobic grown, but can tolerate the presence of oxygen
-Growth occurs evenly throughout media as oxygen as no effect
Halophiles
"salt-loving" archaea that live in environments that have very high salt concentrations
Microaerophiles
Only aerobic growth
-Oxygen is required in low concentrations
-Growth occurs only where a low concentration of oxygen has diffused into the medium
-growth is in center of medium
Obligate Anaerobes
Killed by free oxygen.
Growth only occurs where there is no oxygen
Nutritional Requirements for Growth
1) Carbon- all living things need a carbon source (usually a sugar-glucose, sucrose, fructose)
2) Nitrogen- used in protein and nucleic acid synthesis (Amino Acids are made because their is nitrogen)
3) Sulfur- Used in protein synthesis
4) Phosphorus- Used in ATP and nucleic acids
5) Trace Elements- (Fe, Zn, Cu, etc.) Co-factors and co-enzymes to activate enzymes
-Bind to enzymes to turn enzyme on or off
-Bacteria are "mining" for iron (Fe)
6) Organic Grown Factors- organic compounds that are essential to the organism but the organism is unable to synthesize it itself (EX: Vitamins ,amino acids, nucleotides)
Neutrophiles
Neutral environment pH 6.5-7.5
-Most pathogens are neutrophiles as human body is mostly within this pH range
-most bacteria that cause food spoilage grow between pH 6.5-7.5