Module 8 Additional Aqueous Equilibria
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Expand your mastery of acid and base equilibria and apply it to calculations and concepts with buffers, titrations, solubility, and selective precipitation. 1. Calculate the pH of a solution containing a weak acid or base and its conjugate base or acid. 2. Prepare a buffer with a desired pH. 3. Evaluate the capacity of a buffer to resist changes in its pH. 4. Calculate and interpret the results of an acid-base titration. 5. Relate the acid strength of hydrated metal ions to the charge on the ions. 6. Relate the solubility of an ionic compound to its solubility product. 7. Separate mixtures of ionic compounds by selective precipitation reactions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Lewis acids and bases
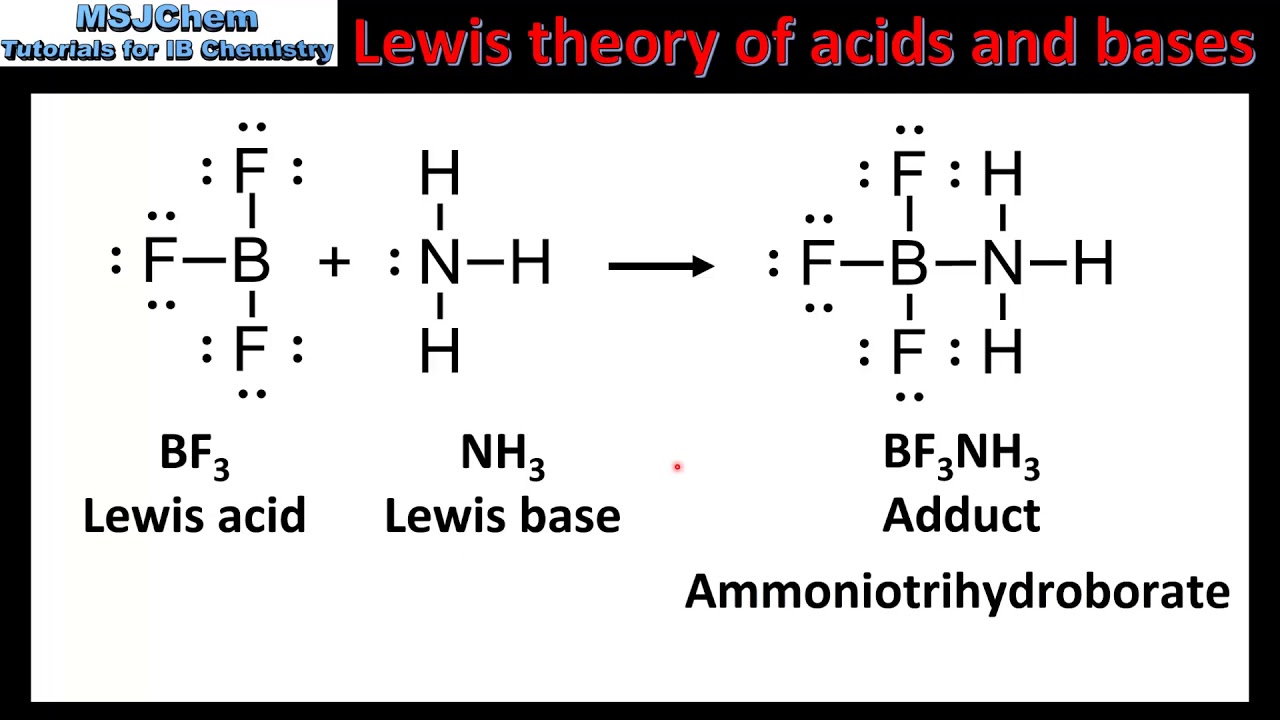
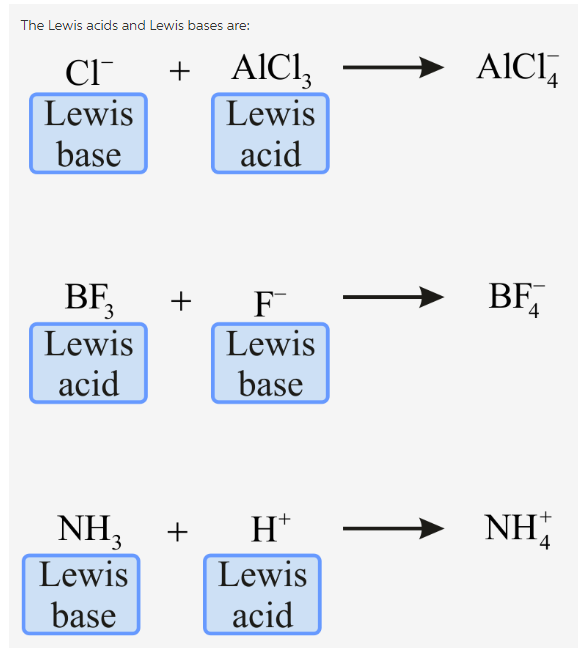
Lewis base DONATES pair of ELECTRONS, lewis acid ACCEPTS a pair of electrons
Common lewis bases
(will donate electrons!!) OH- and O²-
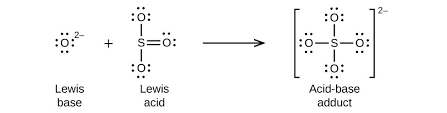
Common lewis acids
(will accept electrons!!) BF3, BCl3, AlF3, AlCl3 (incomplete octets)
Ksp
solubility-product constant…type of equilibrium constant that describes formation of saturated solution of slightly soluble salt
Ex. Mg(OH)2 (milk of magnesia) is the only group 2 element that isnt a strong base b/c its limited solubility in H2O

The smaller the Ksp value…
the less soluable (will ppt out of solution more easily)
selective precipitation
used to separate ions in a solution by adding a reagent (common ion) that selectively precipitates one or more ions as a solid, while leaving others in solution. If
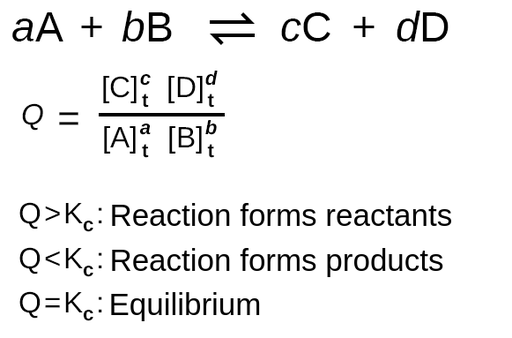
If Q > Ksp
[products] is higher than needed at equilibrium…rxn will favor reactant formation and shift left…compound WILL precipitate (s)
If Q < Ksp
[reactants] is higher than needed at equilibrium…rxn will favor product formation and shift right…compound will NOT precipitate (aq)
Q-value (reaction quotient)
ratio that compares the concentrations of products to reactants at any point in a reaction (NOT JUST AT EQUILIBRIUM!!!). It helps you predict which direction the reaction will shift to reach equilibrium.
neutralization reaction
acid and a base react to form water and a salt
equilibrium
rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal, resulting in constant concentrations of reactants and products.
When is there no equilibrium
when there is a strong acid/base since it dissociates or reacts completely
When is there equilibrium
when there us a weak acid/base since it partially reacts or dissociates…reaction is reversible…establishes (will need to: ICE table, Ka/Kb values) equilibrium —> dynamic balance between reactants and products.
pKa to Ka
10^(-pKa)
Ka to pKa
-log(Ka)