Animal Cells, Neurons, Glia, Blood-brain barrier, Action potential
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
The Reticular Theory
scientific theory in neurobiology that everything in the nervous system including the brain, is one thing (Golgi)
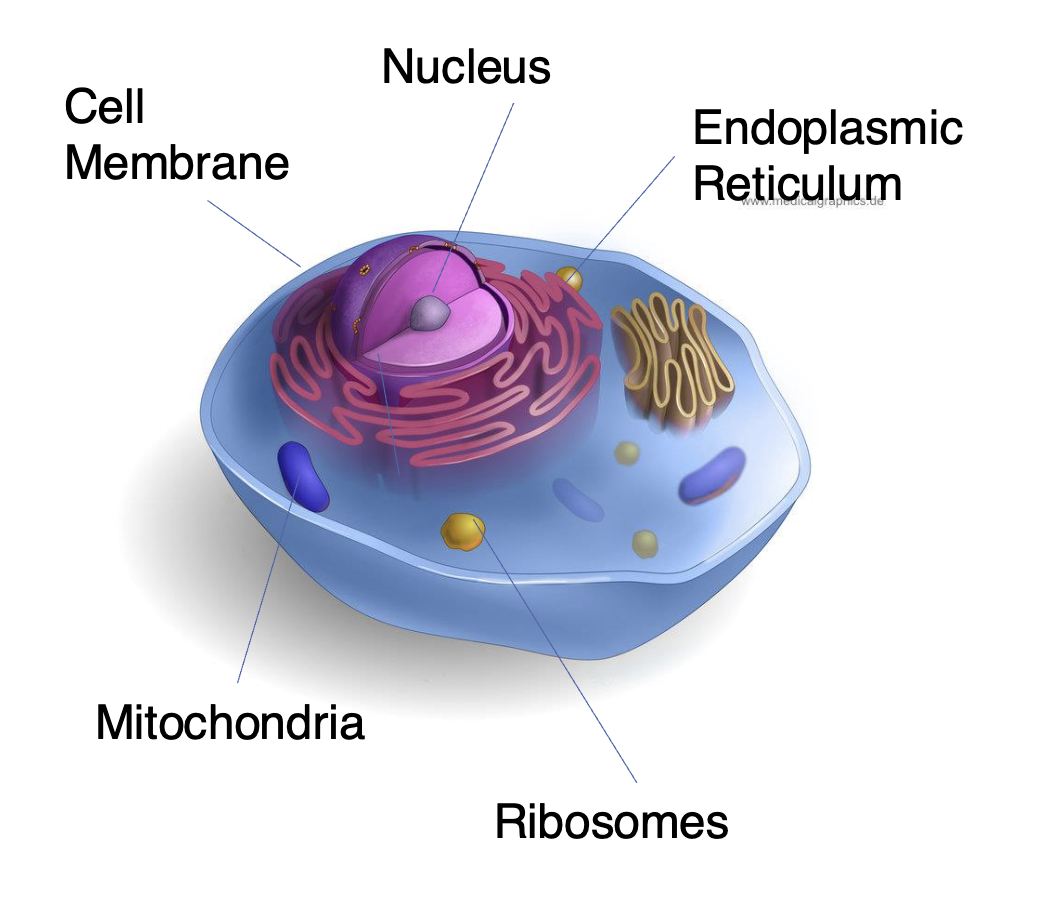
ANIMAL CELLS
Cell Membrane
bilayer that surrounds the cell
Separates the inside of the cell from the outside environment
Nucleus
membrane-bound organelle
Contains the chromosomes / DNA
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Network of thin tubes that transports newly synthesized proteins to their location
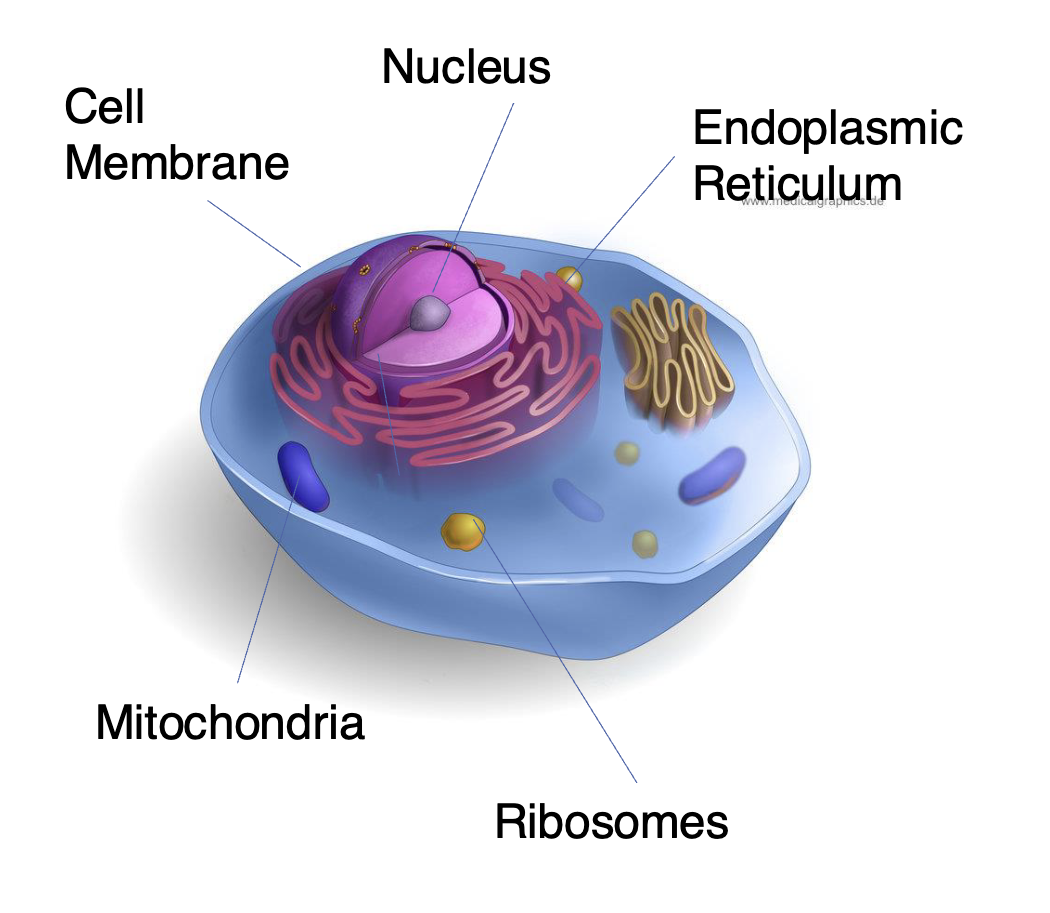
Ribosomes
small, non-membranous organelles
Sites at which the cell synthesizes NEW protein molecules
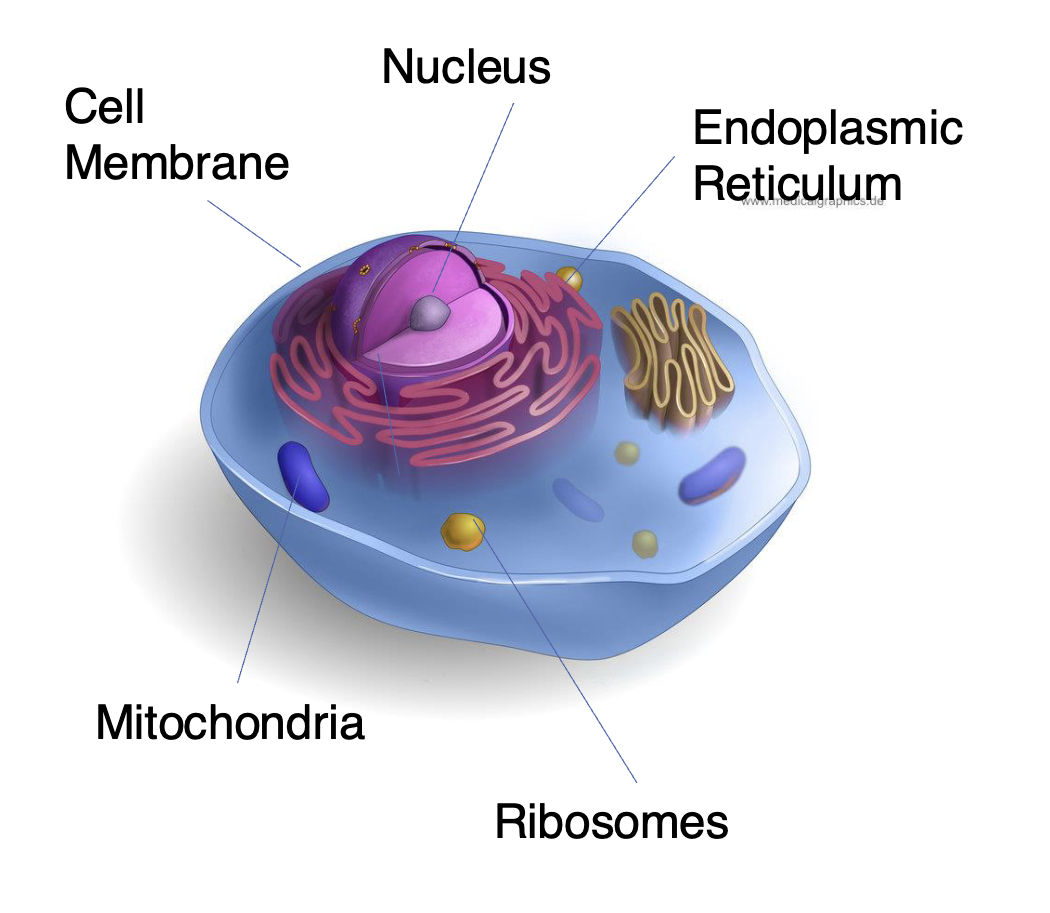
Mitochondria
sausage shape
Performs metabolic activities and provides energy that the cells requires
contains its OWN genes
inherit it from BIOLOGICAL mother
decrease in mitochondria links to higher risk depression
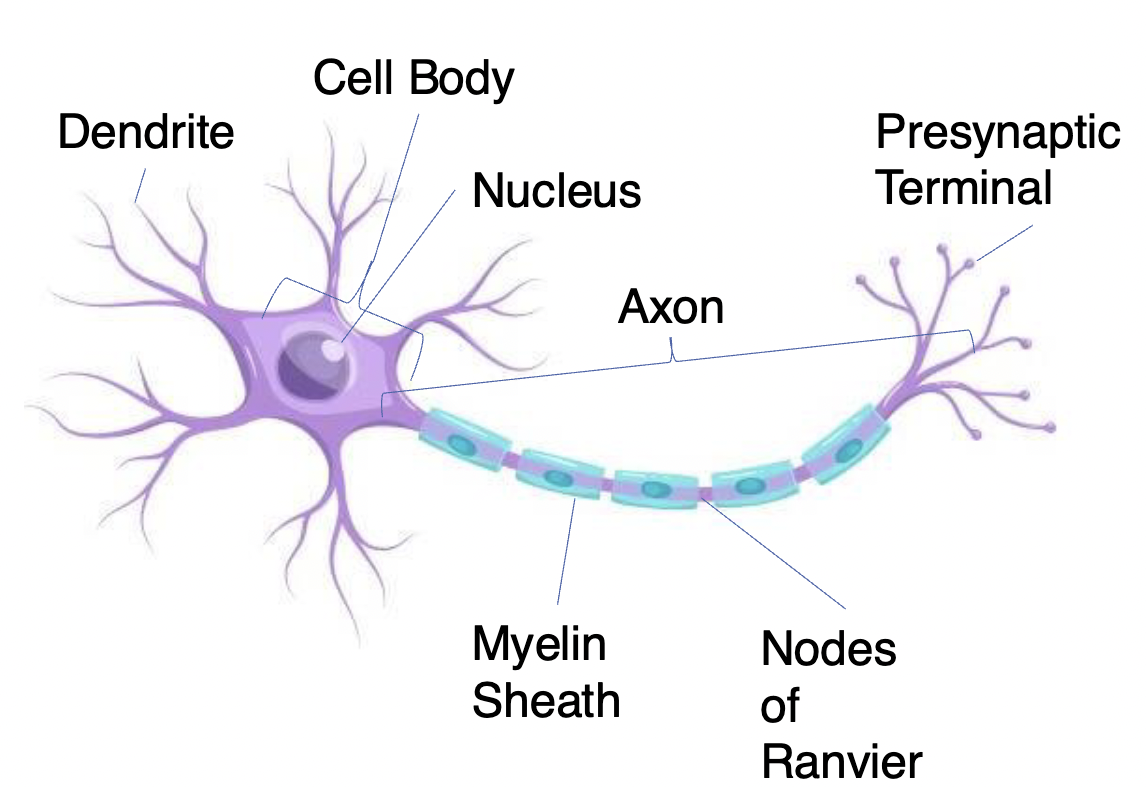
NEURONS
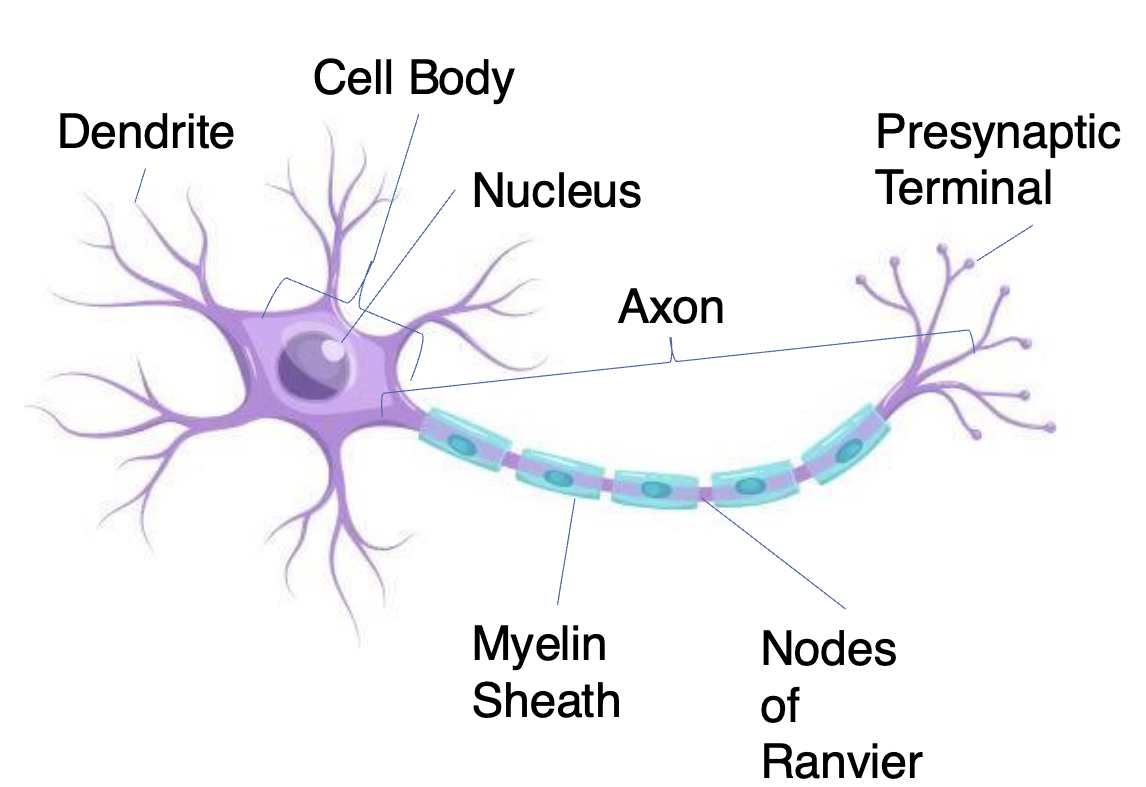
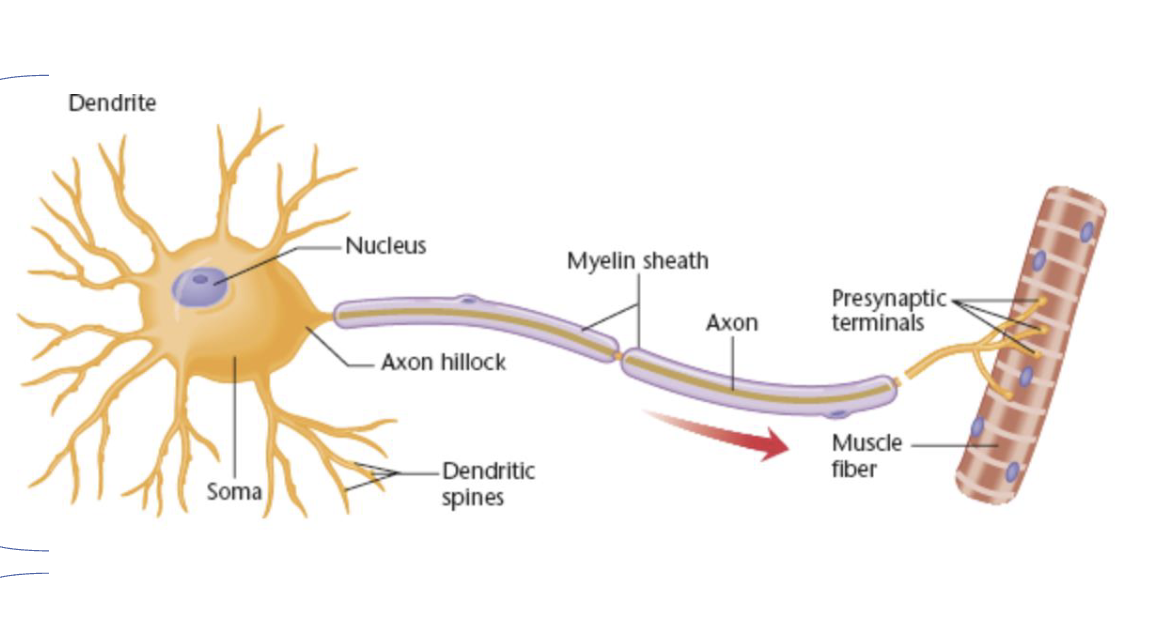
Neurons
Receive information and transmit it to other cells
– have variable shapes
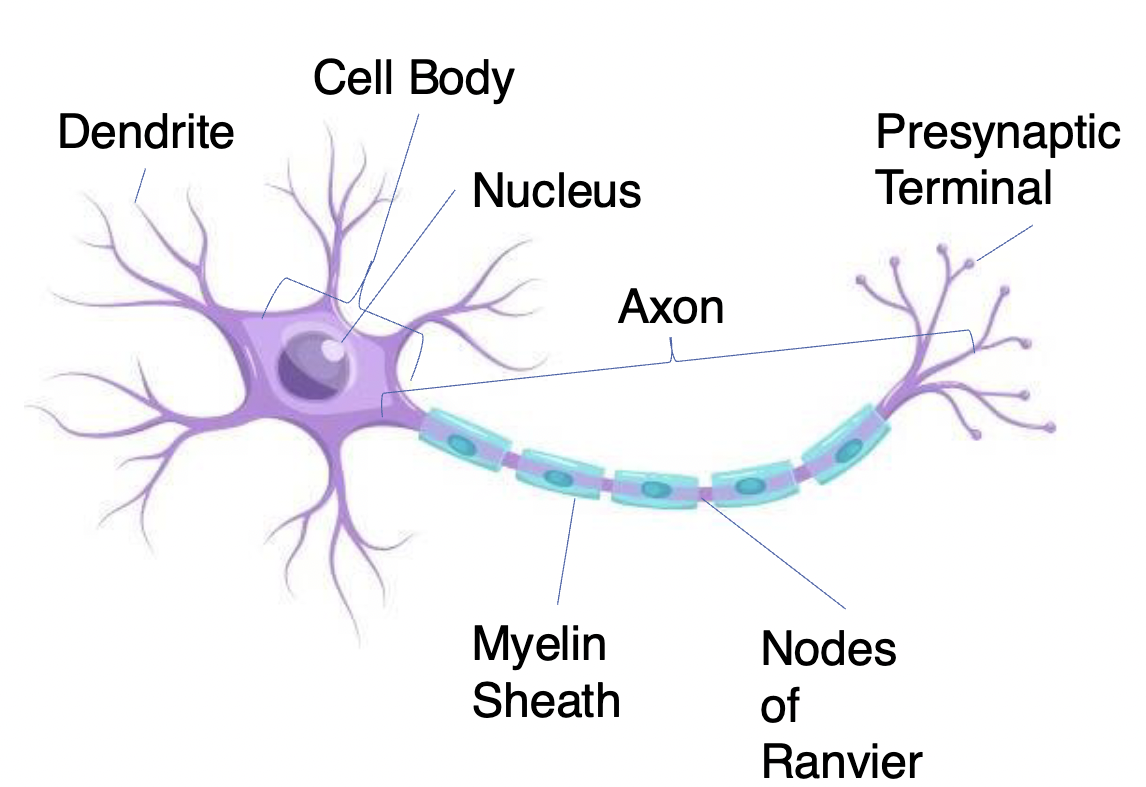
Dendrites
Short high branch extensions that pass nerve impulses toward the cell body
Receives information
covered in synapses receptors
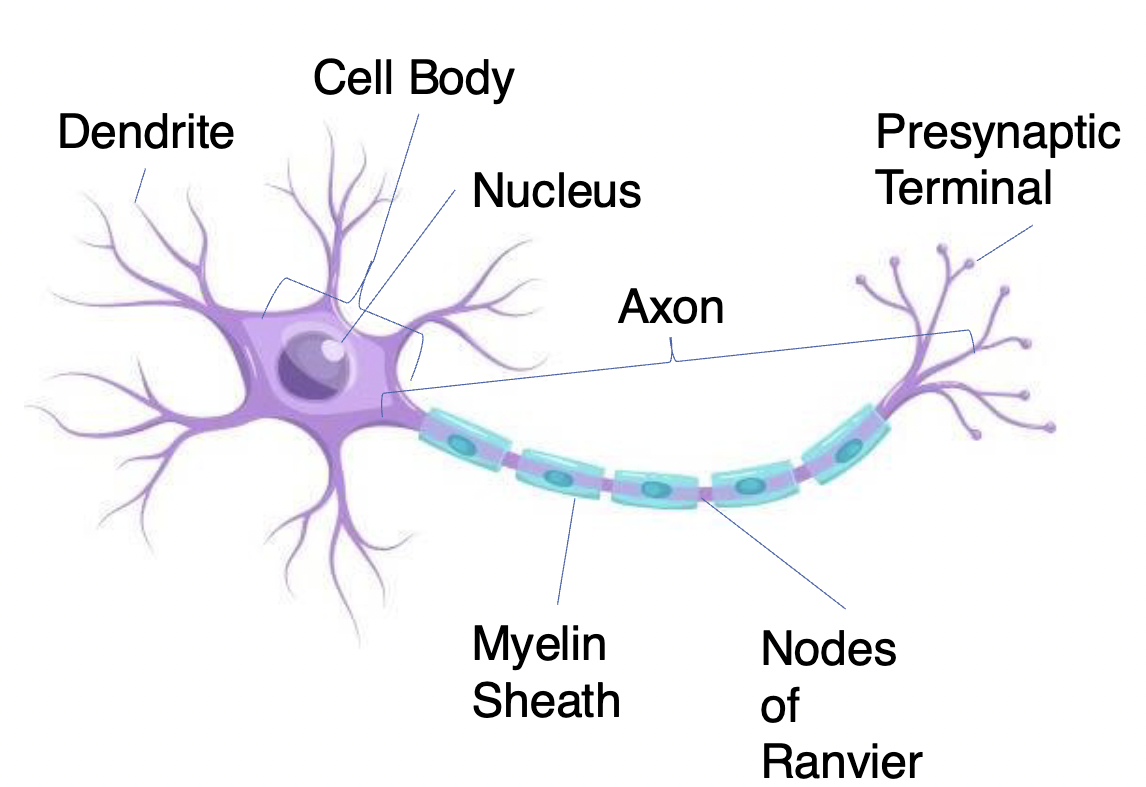
Cell body: (also called the soma)
The spherical part of the neuron that contains the nucleus, ribosomes, and mitochondria
– Processes and integrates information
information
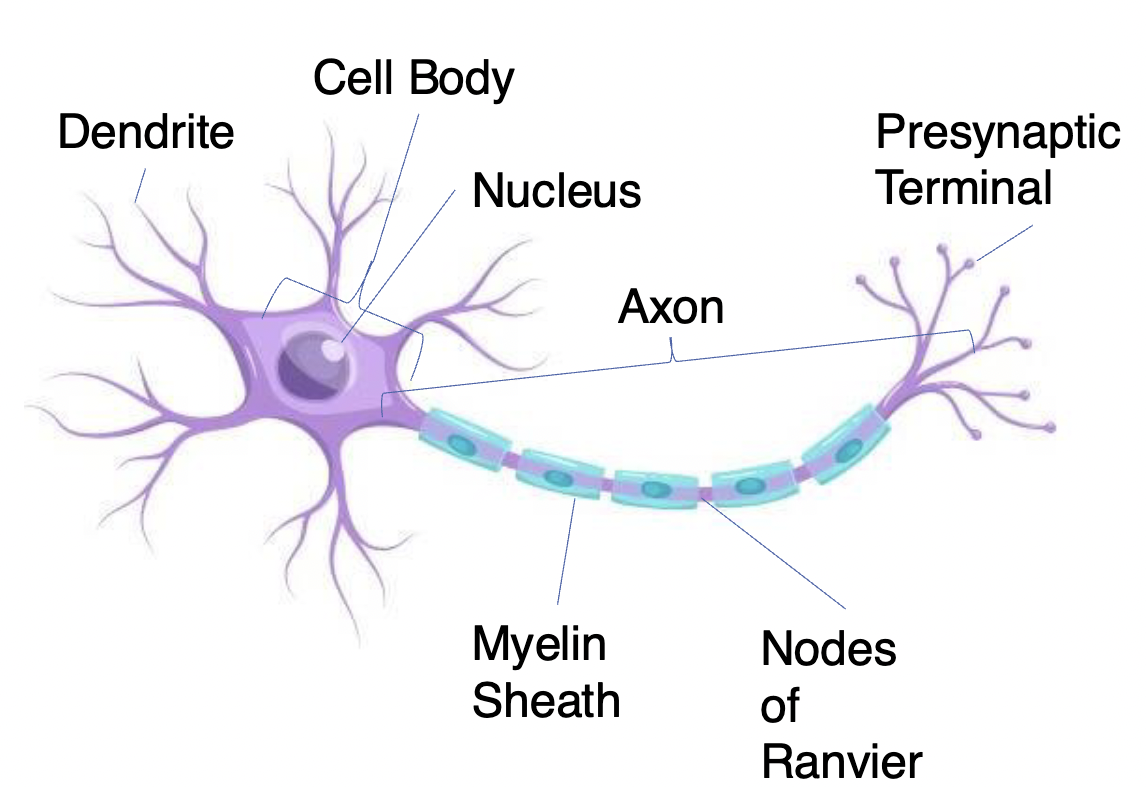
Axon
Long extenion of the neuron that passes nerve impulses away from the cell body
Carries information across long distances from one part of the neuron to another
Afferent Axon
(long extension split into two) brings information into a structure (sensory neuron)

Efferent Axon
(long extension split into two) carries information away from a structure (motor neuron)
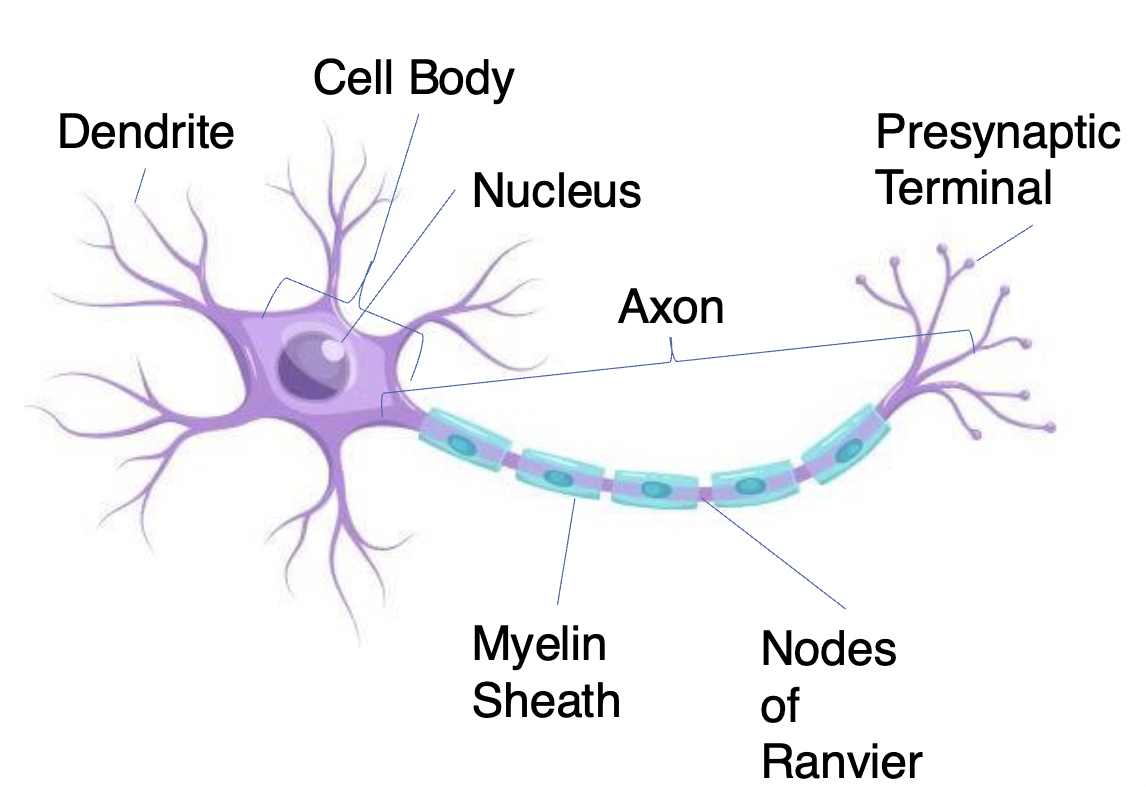
Presynaptic Terminal
( has Synaptic Vesicles) Transmit information to another neuron (only place in THE neuron that can send signals)
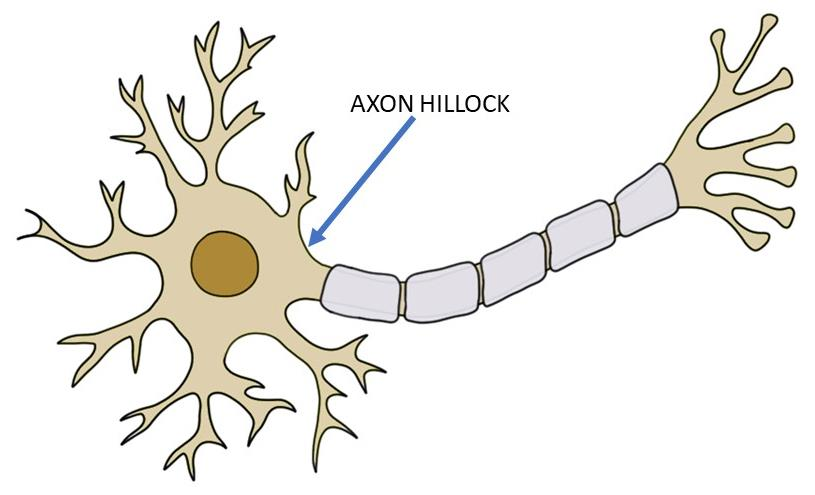
Axon Hillock
The Action Potential starts at the Axon Hillock (Which is where the Axon and Cell body meet) This process only happens when that signal is deemed strong enough ( worth sending through)
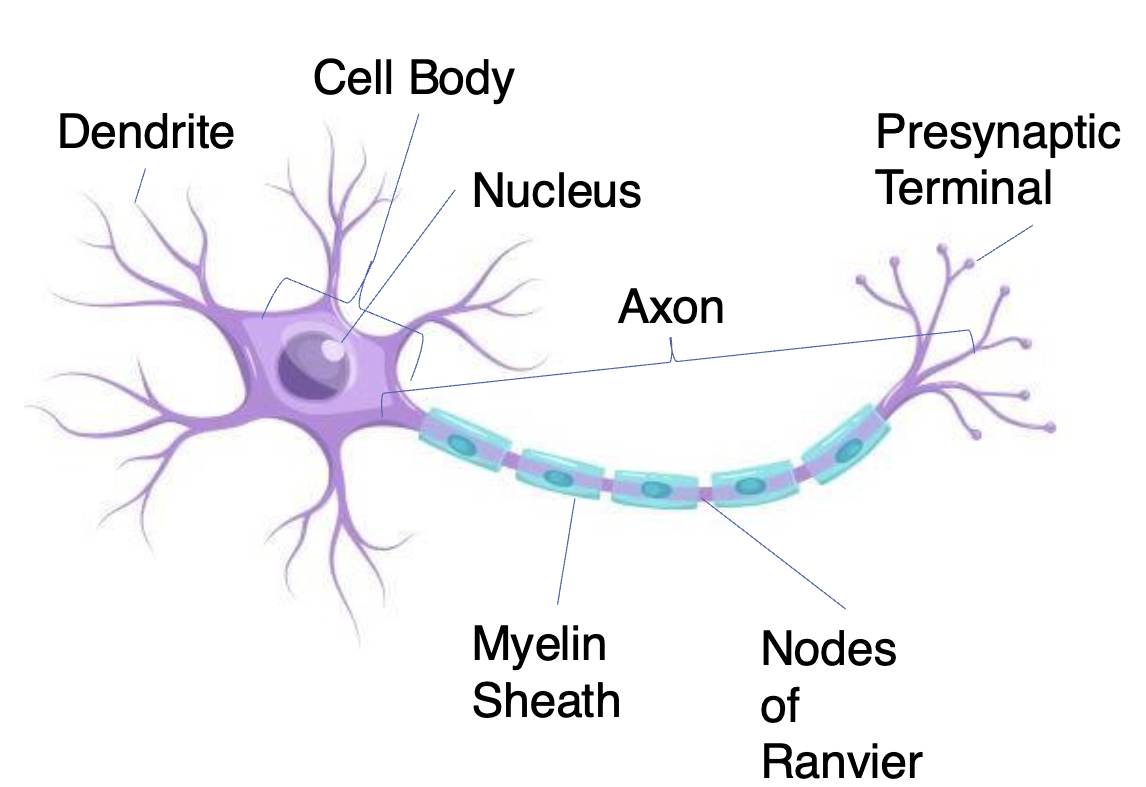
Myelin Sheath
Insulating layer that allows electrical impulses to transmit quickly and efficiently along nerve cells
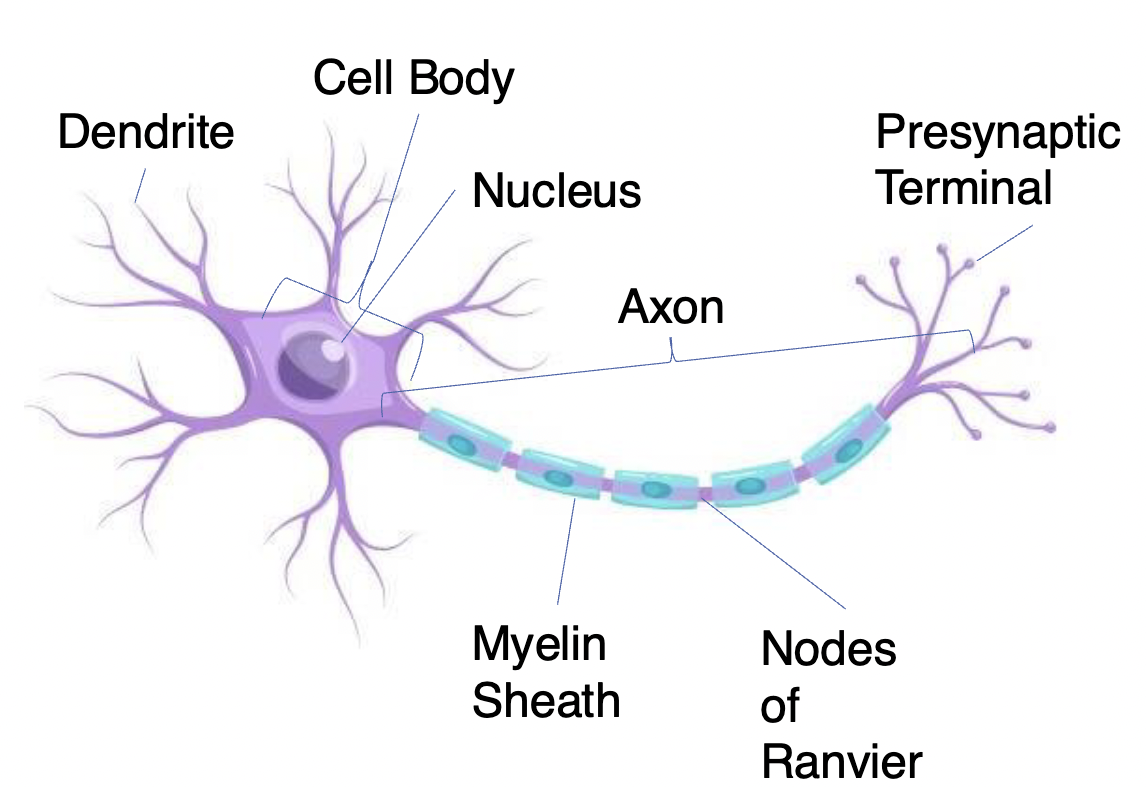
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in myelin sheath (not insulated) that facilitates the rapid conduction of nerve impulses
Motor Neuron
• Has its soma in the spinal cord (part of CNS)
• Receives excitation from other neurons
• Conducts impulses along its axon to a muscle/gland
SENDS SIGNAL
Cell body is massive
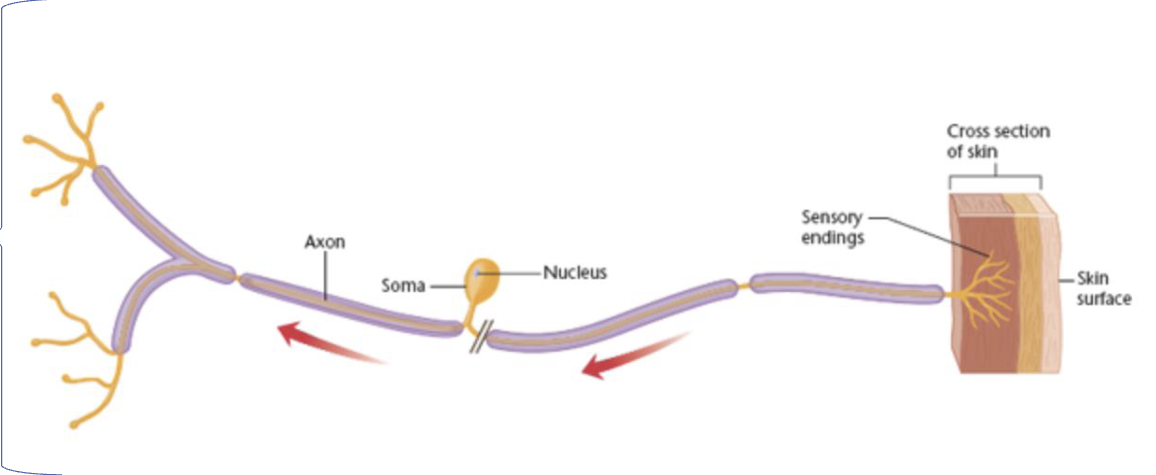
Sensory Neuron
skin to spinal cord
Tiny branches lead directly from the receptors to axon
Cell’s soma is located on a little stalk off the main trunk.
Is specialized at one end to be highly sensitive to a particular type of stimulation (touch, light, sound, etc.)
If a cell’s dendrites and axon are entirely contained within a single structure, the cell is an…..
interneuron or intrinsic neuron of the structure.
Interneuron/ Intrinsic neuron
neuron whose axons and dendrites are all confined within a given structure
Nerves
A bundle of axons travelling together
Nerves can be very long because they often need to transmit information across long distances
GLIA
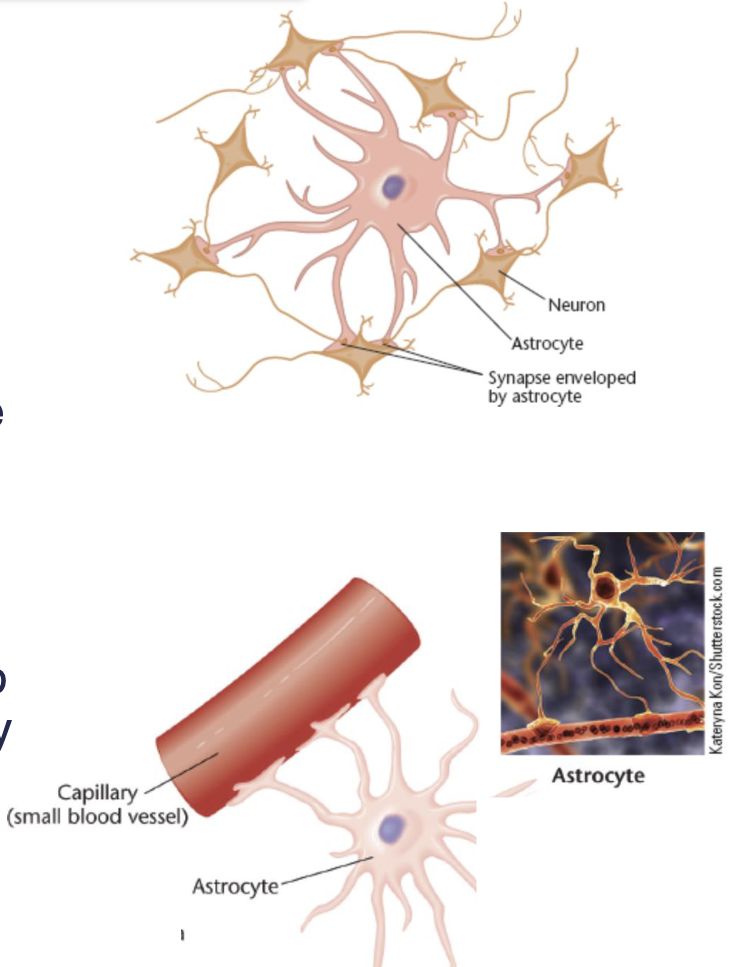
Astrocytes
Help synchronize the activity of the axon by wrapping around the presynaptic terminal and taking up chemicals released by the axon
– Responsible for dilating blood vessels to bring more nutrients into brain areas with heightened activity
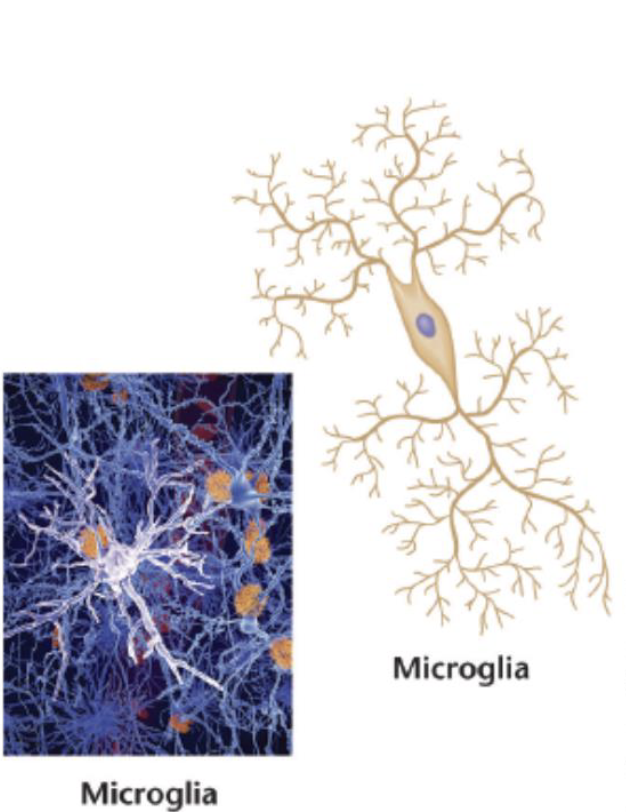
Microglia
Remove waste material, viruses, and fungi from the brain
– Also remove dead, dying, or damaged neurons
Oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells
Build the myelin sheath that surrounds and insulates certain vertebrate axons
– Oligodendrocytes → in the brain and spinal cord
– Schwann cells → in the periphery of the body
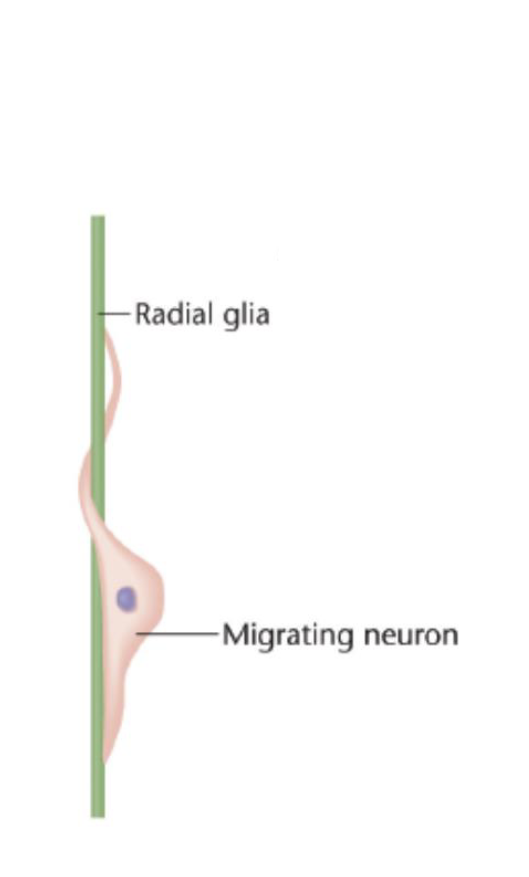
Radial Glia
Neural Progenitor Cells
Help neurons divide and give rise to different types of brain cells
Essential for GENERATING NEW NEURONS during brain development
– Guide the migration of neurons and the growth of their axons/ dendrites during embryonic development
BLOOD BRAIN BARRIER
What is the Blood Brain Barrier?
A mechanism that surrounds the brain and blocks most chemicals from entering
Why do we need a Blood- Brain Barrier?
The immune system destroys damaged or infected cells throughout the body.
Neurons in the brain usually do NOT regenerate
important for the blood– brain barrier to block incoming viruses, bacteria…ect from entering.
How does the Blood- Brain Barrier work?
Outside the brain, endothelial cells (cells that form walls of capillaries) are separated by small gaps
In the brain, endothelial cells join tightly that they block almost anything from coming in
the barrier keeps out useful and harmful chemicals
What happens when a VIRUS crosses over the Blood- Brain Barrier?
Brain’s microglia attack
Mounts an inflammatory response without killing cell
Response controls the virus without eliminating it
Viruses than CAN CROSS the Blood Brain- Barrier
Rabies—> leads to death
Syphilis—> produces fatal consequences
Chicken Pox
Neural Signals
Neural Signals
If axons used electrical conduction the strength of the signal would decay as it travelled
Instead, axons periodically regenerates an impulse

Movement of Ions
For neural signals… Transmission of signal is dependent on the movement of ions
– Ions = charged particles
Presence and movement of ions is important for when a neuron fires or is at rest
ions are unequally distributed inside/ outside of cell
Ion Channels
Open: the ions can pass through in and out
Closed: the ions cannot pass through the channel
Inactivated: regardless of what happened, these signals are not opening
The cell wants an equal amount of positive and negative charged ions
When cells are closed, doesn't allow for positive ions to go through
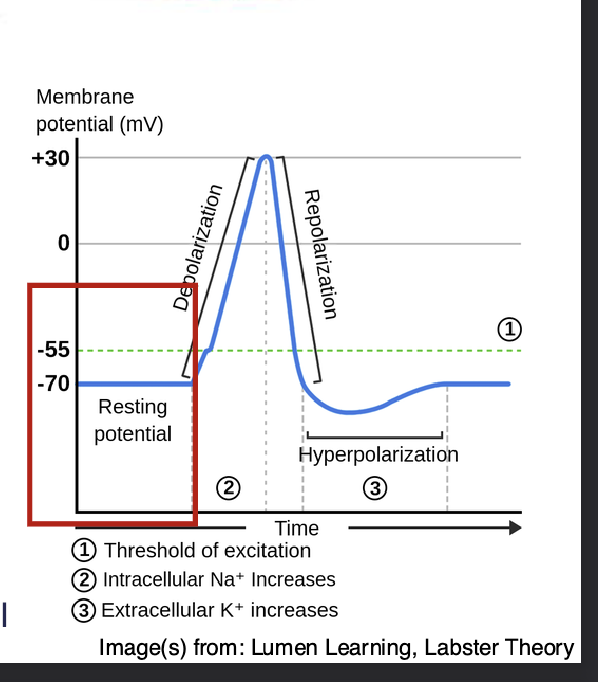
What is Resting Potential
the difference in electrical charge between the inside and the outside of a neuron when the cell is in a non-excited state
How to Measure Resting Potential
Connecting electrodes to a voltmeter
−70 (mV)
Electrical Gradient
RESTING POTENTIAL: When at rest the membrane maintains… electrical gradient:
Concentration Gradient
Difference in distribution of ions (sodium, potassium..) across the membrane
Electrical Gradient + Concentration Gradient
pull sodium ions into the cell
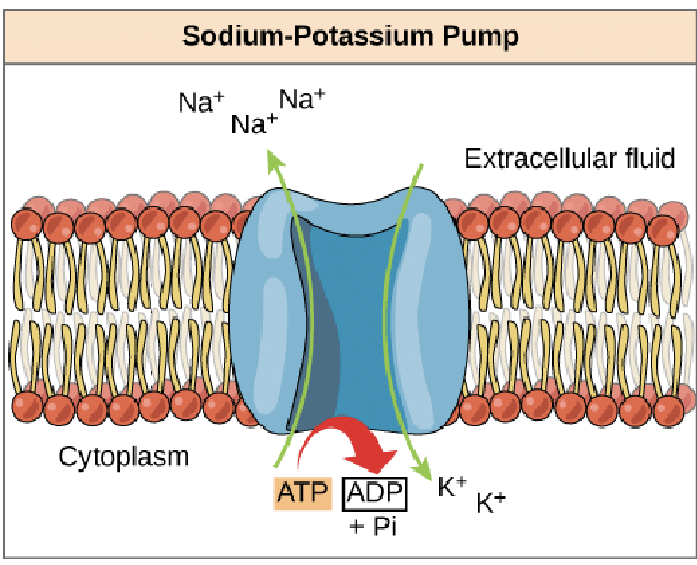
Sodium Potassium Pump
= protein complex
Continually pumps out 3 sodium ions and draws in 2 potassium ions
Helps to maintain electrical gradient
(Potassium keeps the cell at -70)
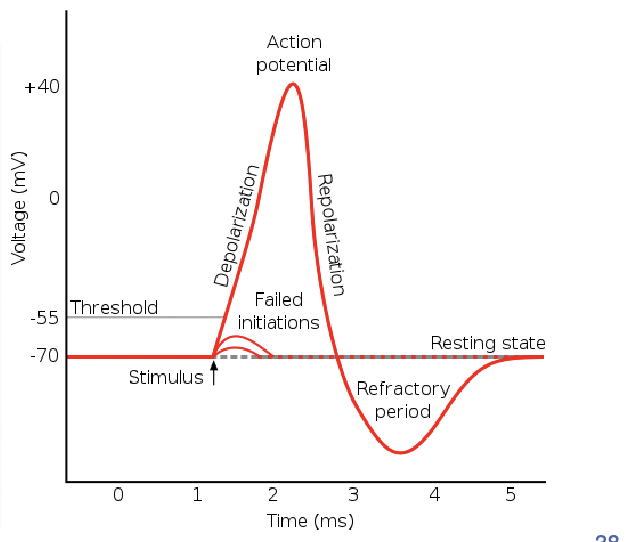
What is the Action Potential
Electrical charge that runs down the axon from the axon hillock to the terminal buttons.
conduction of information along an axon
“neuron fires”
How does the Action Potential Work?
Dendrites – receive signals
Based on signal strength neuron decides whether (or not) to pass information along
If information is strong enough it is transmitted across the full axon—→Action Potential
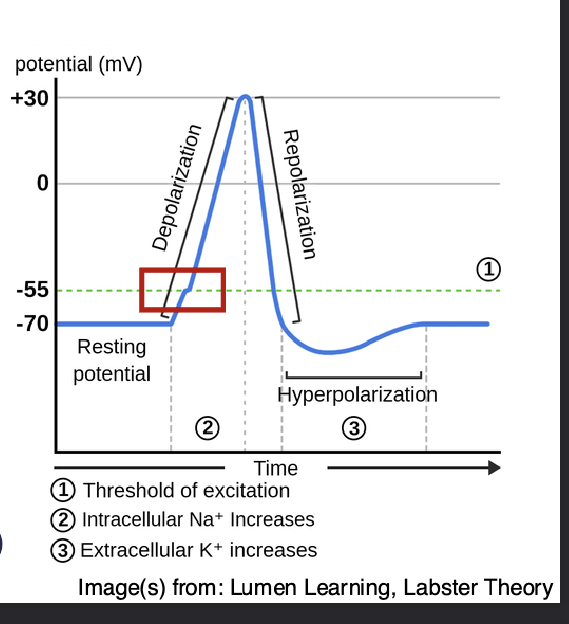
Depolarization (threshold of excitation) RISING STAGE
Some Na+ channels open allowing Na+ ions to enter cell
Membrane starts to depolarize
If threshold of excitation is reached, all Na+ channels open
Resting potential -55
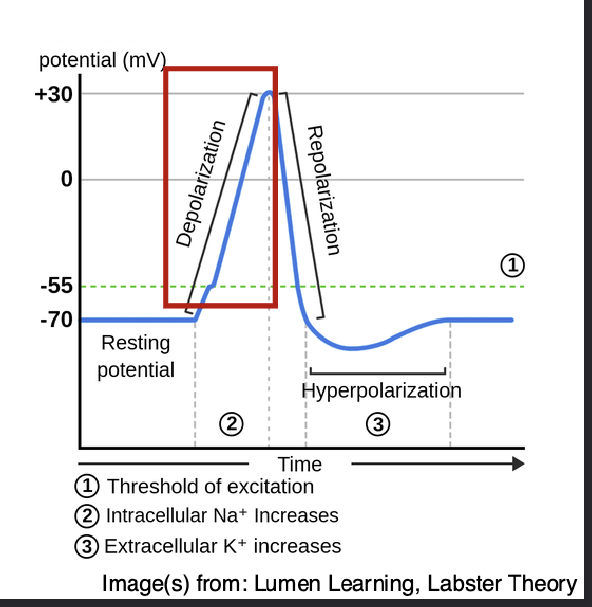
Depolarization PT 2 after THRESHOLD OF EXCITATION—> (peak excitation)
All Na+ channels are open
Na+ floods in +30MV =(peak excitation)
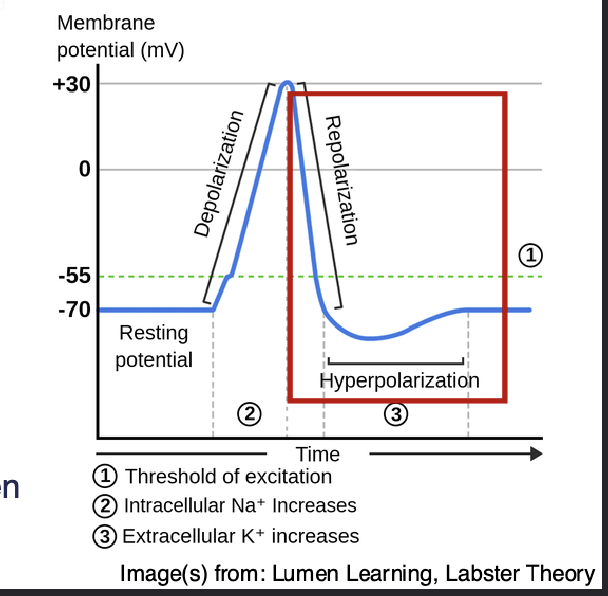
Repolarization FALLING STAGE
At peak action potential, Na+ channels CLOSE, K+ channels OPEN
K+ leaves cell – membrane becomes hyperpolarized
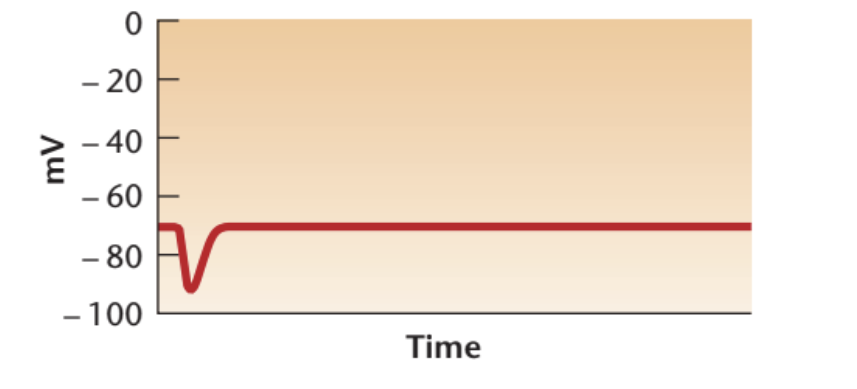
Hyperpolarization
means increased polarization.
neurons membrane becomes more negatively charged in one spot
When stimulation ends, the charge returns resting level.
.
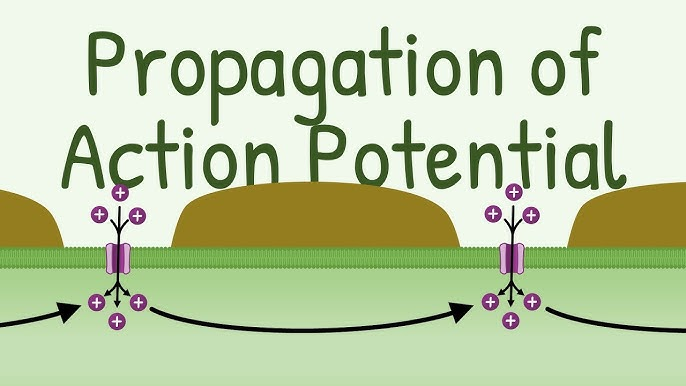
Propagation of an Action Potential
Action potential flows along axon remaining at equal strength
Behind each sodium entry, potassium ions exit, leads to resting potential

Salatory Conduction
“jumping of action potential from node to node”
Activity within a Neuron
All-or-none Law
Once an action potential is initiated in an axon, it travels along the fiber without losing strength until it reaches the end.
Rate Law
Differences in stimulus intensity or transmitted information along an axon are reflected in changes in the firing rate of the axon (i.e., the number of action potentials).