3-5 -> 3-8: Biology
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
characteristics of molecules that get through the cell membrane
non-charged, nonpolar, and small
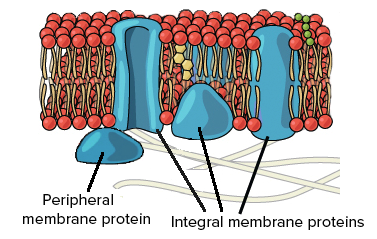
what is this
cell membrane
phospholipid head
hydrophilic
phospholipid tail
hydrophobic
molecules that get through the cell membrane
oxygen and carbon dioxide
aquaporin
get water through the membrane
functions of proteins in the membrane
transportation, cell structure, enzymes (do cell work), cell recognition, intercellular joining, signal transduction
bifacial cell membrane
the inside and outside are different, it saves energy; proteins have specific orientations and carbohydrates are only on the outsides
main macromolecules in cell membranes
phospholipid and proteins
proteins
helps charged, large, polar molecules through the membrane
passive transport
no energy needed (ex. diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis)
active transport
energy needed (ex. endocytosis, exocytosis)
diffusion
passive, moves high to low on the concentration gradient
facilitated diffusion
passive transport, diffusion with a carrier protein
osmosis
the process of water diffusing across a membrane
isotonic
same amount of solute on both sides of the membrane, good for animal cells, bad for plant cells (they become inelastic, or flaccid)
hypertonic
more solute outside, makes animals and plant cells shrink
hypotonic
less solute outside, bad for animal cells (the cell may burst), good for plants cells
active transport
moving molecules against their concentration gradient (low to high) requires energy
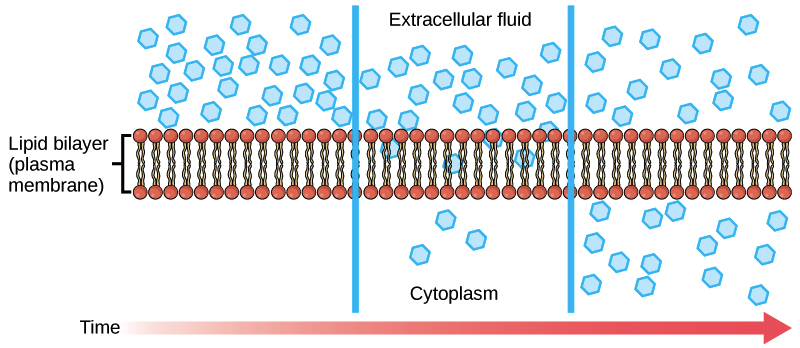
what is this
diffusion
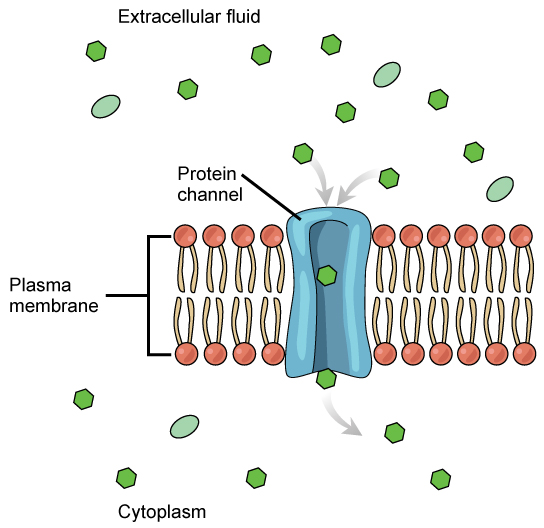
what is this
facilitated diffusion
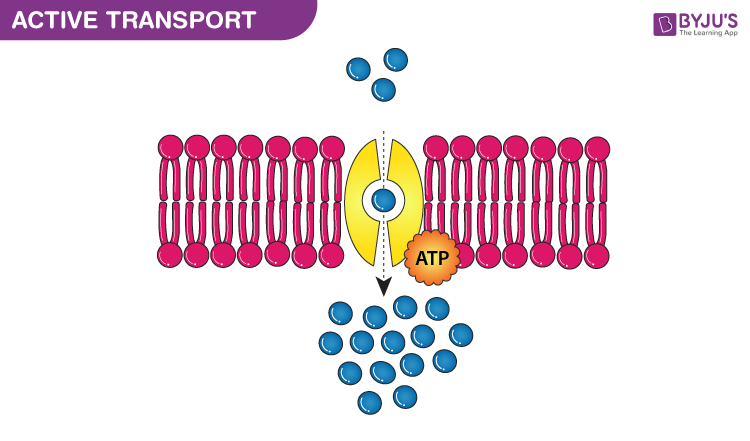
what is this
active transport
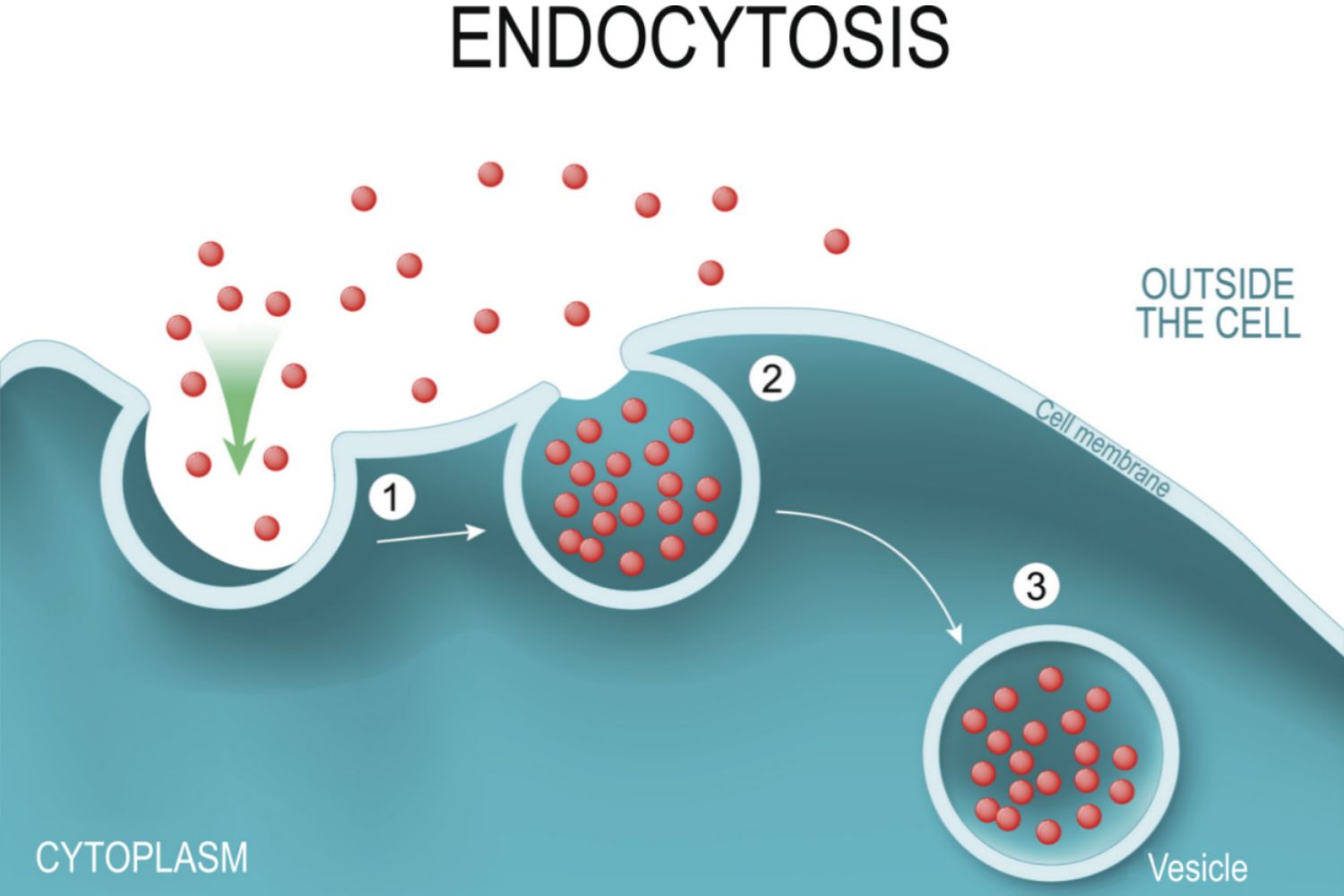
endocytosis
active transport, cell takes in large molecules
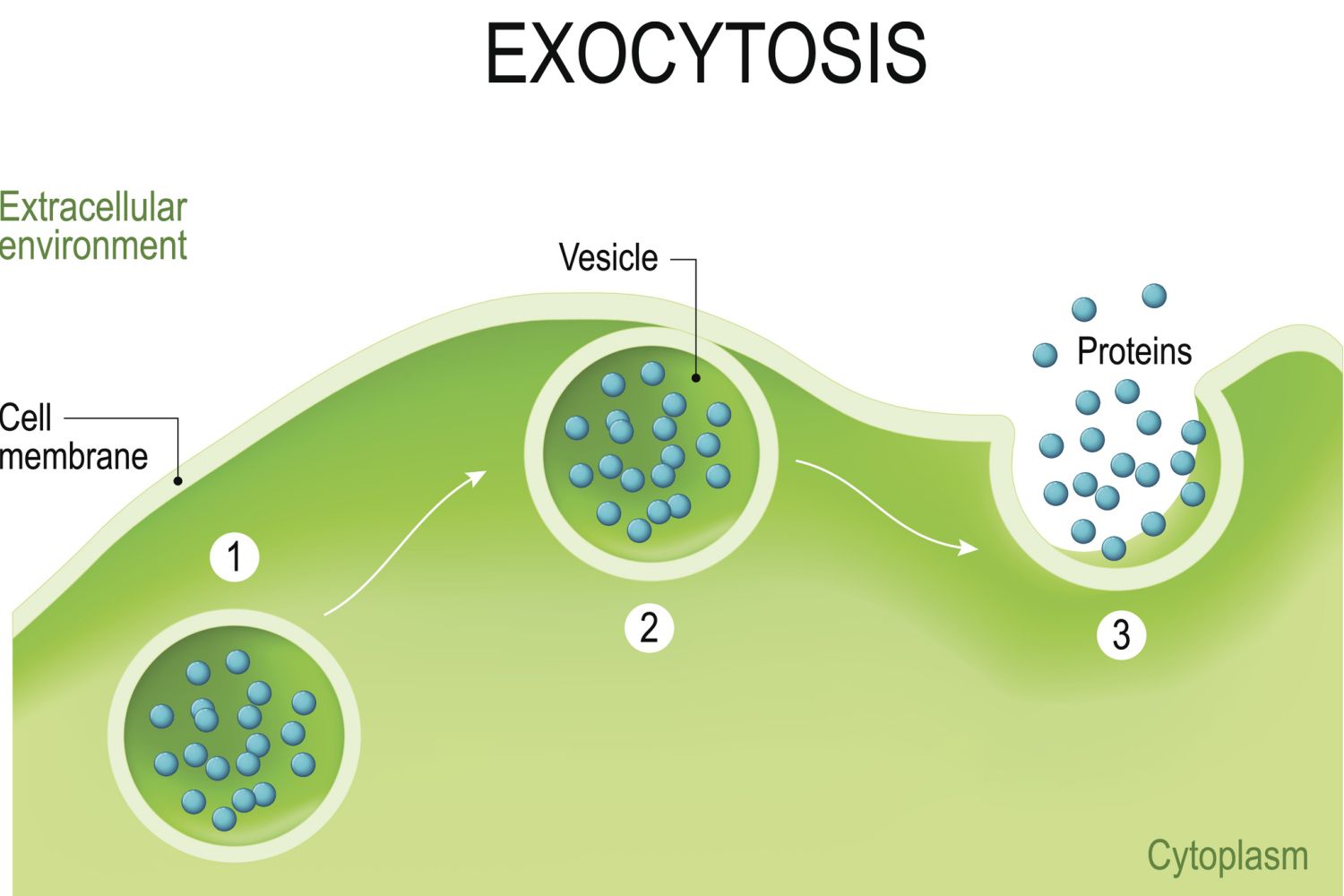
exocytosis
vesicles (membrane sacks sent from the golgi) send large particles out of the cell
stages of c.s
reception (receiving the signal), transduction (passing on the signal), response ( cellular changes because of the signal)
signal molecules
the actual chemical signal that travels from cell to cell; water soluble, and too big to go through the membrane, is usually on the outside
intracellular signals
proteins located in the cytoplasm or nucleus that receive a signal that CAN pass through the cell membrane (ex. steroids (hormones) and nitric oxide)
transduction
the further amplification and movement of a signal in the cytoplasm
celluar responses
production of proteins, production of lipids cell division, apoptosis, increase metabolism
apoptosis
programmed cell death; uses cell signaling pathways, DNA is chopped up, cell shrinks and becomes lobed, pieces are digested by specialized scavenger cells
positive feedback loop
amplifies a response
negative (balancing) feedback loop
returns an organism to its original state
local signaling
paracrine signaling, synaptic signaling (neurons)
synaptic signaling
long distance, fast
long distance (hormonal) signaling
tells what to do and how to respond; long distance, sustained (longer, but slower)