Flashcards for Exam
1/52
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
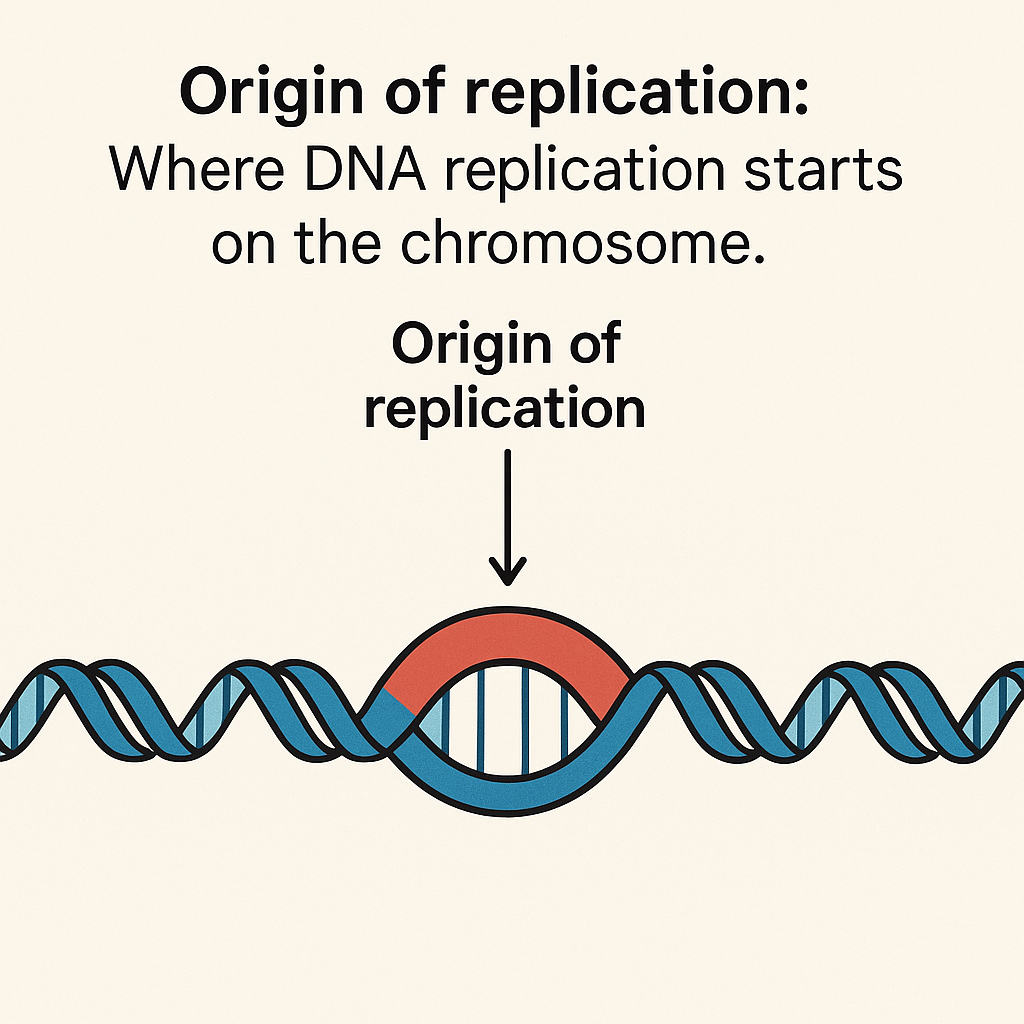
Origin of replication
Where DNA replication starts on the chromosome.
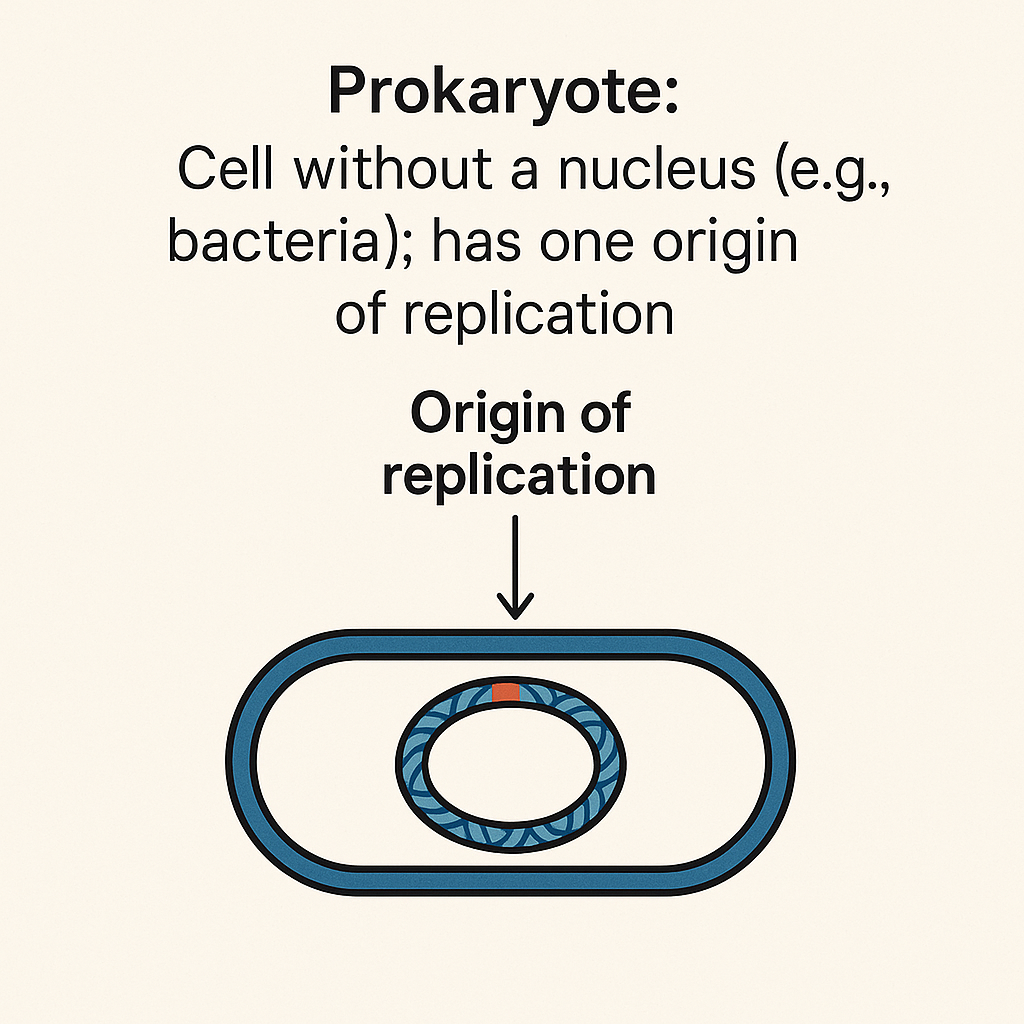
Prokaryote
Cell without a nucleus; has one origin of replication.
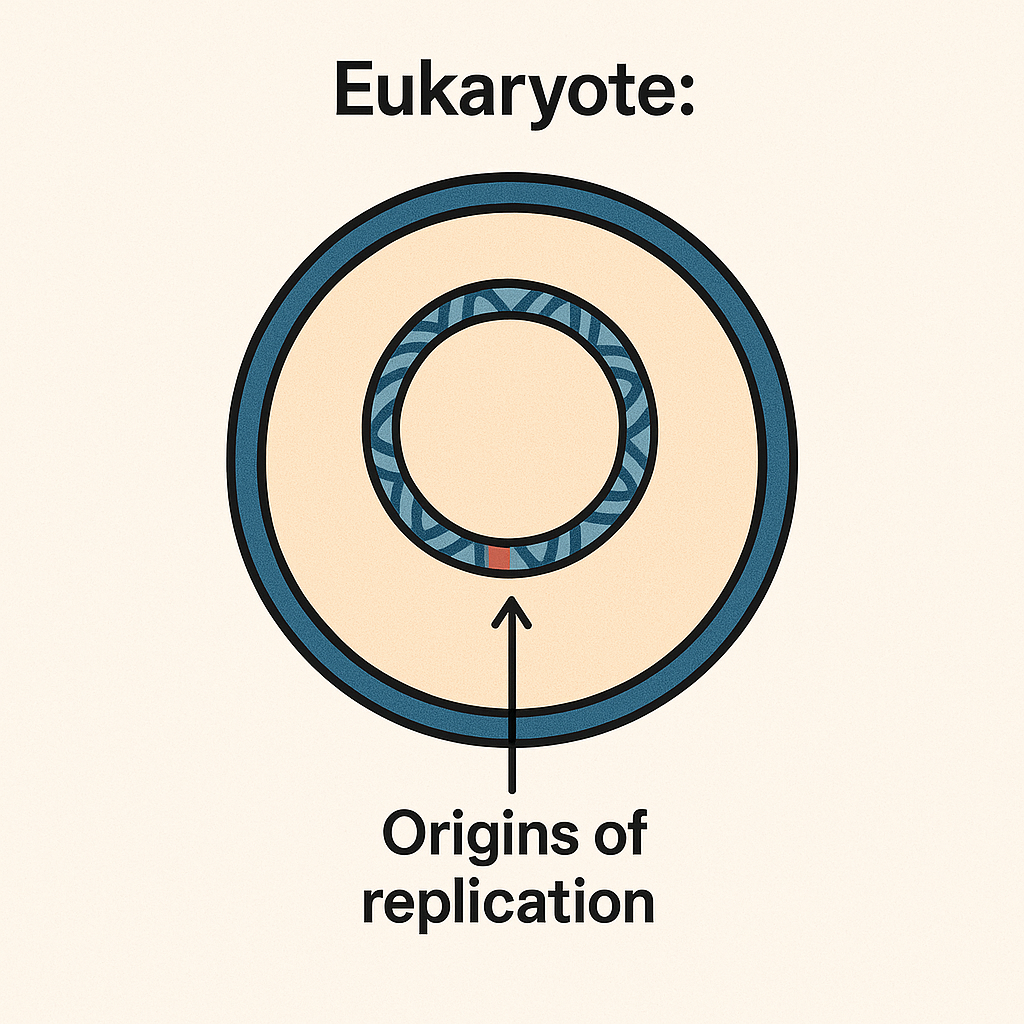
Eukaryote
Cell with a nucleus; has many origins of replication.
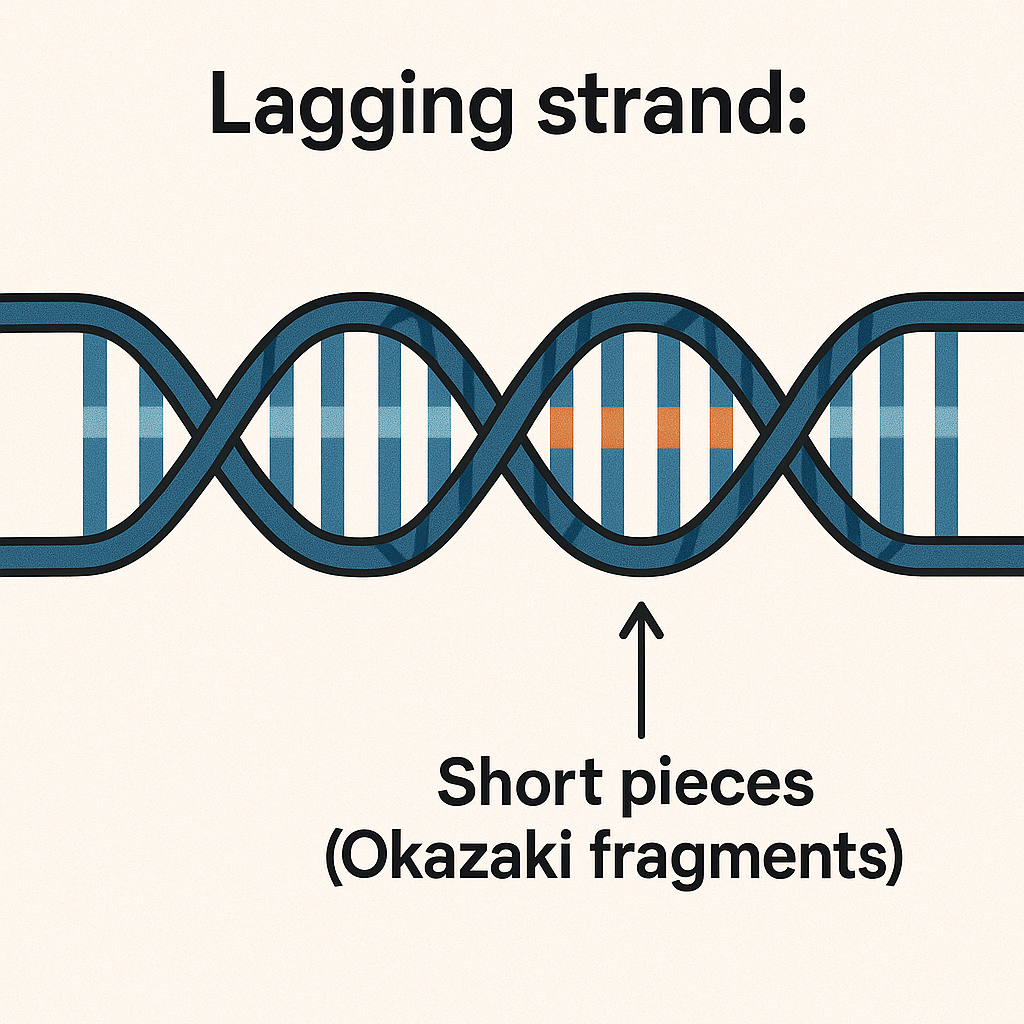
Lagging strand
DNA strand made in short pieces (Okazaki fragments).
Okazaki fragments
Short DNA pieces made on the lagging strand.
Primase
Enzyme that makes a short RNA primer to start DNA synthesis.

DNA Polymerase I
Removes RNA primers and fills in DNA on lagging strand.
DNA Polymerase III
Main enzyme for making new DNA in prokaryotes.
Ligase
Enzyme that joins DNA fragments together.
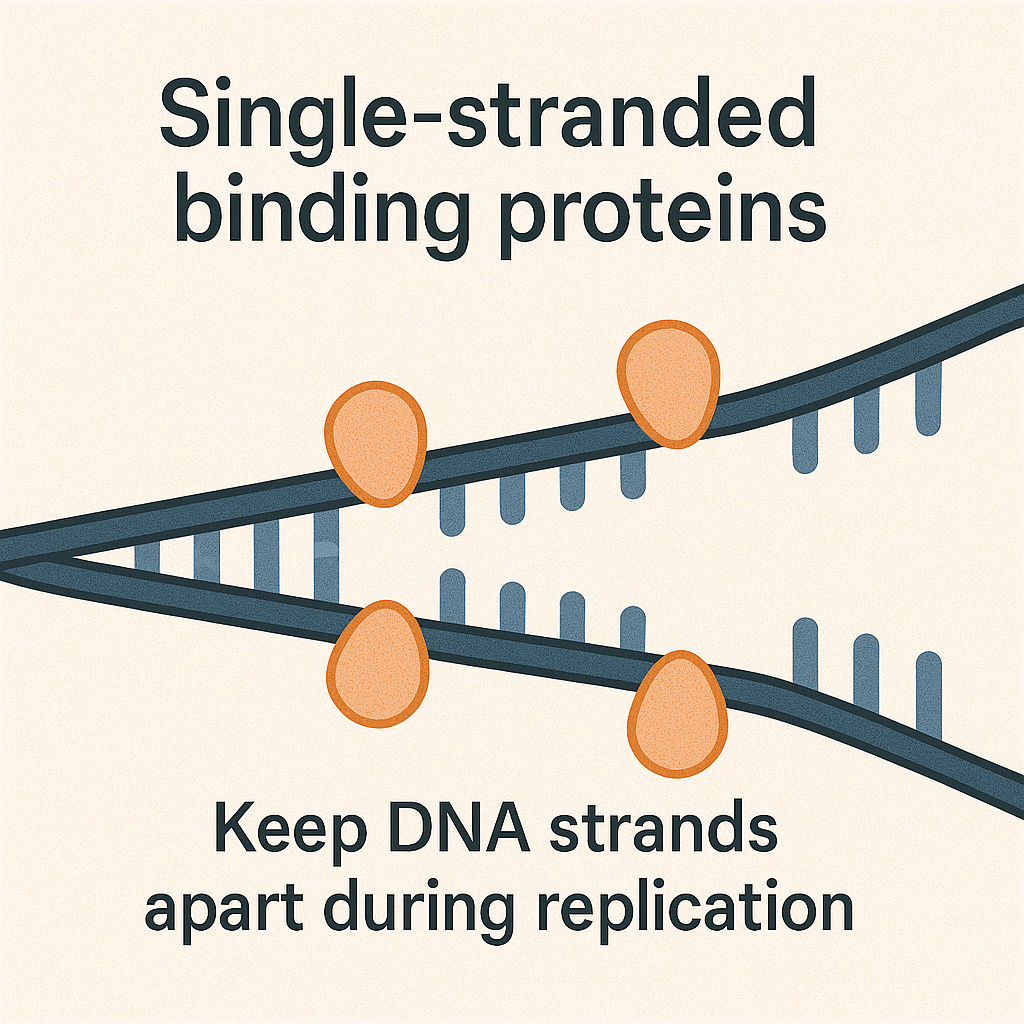
Single-stranded binding proteins (SSB)
Keep DNA strands apart during replication.
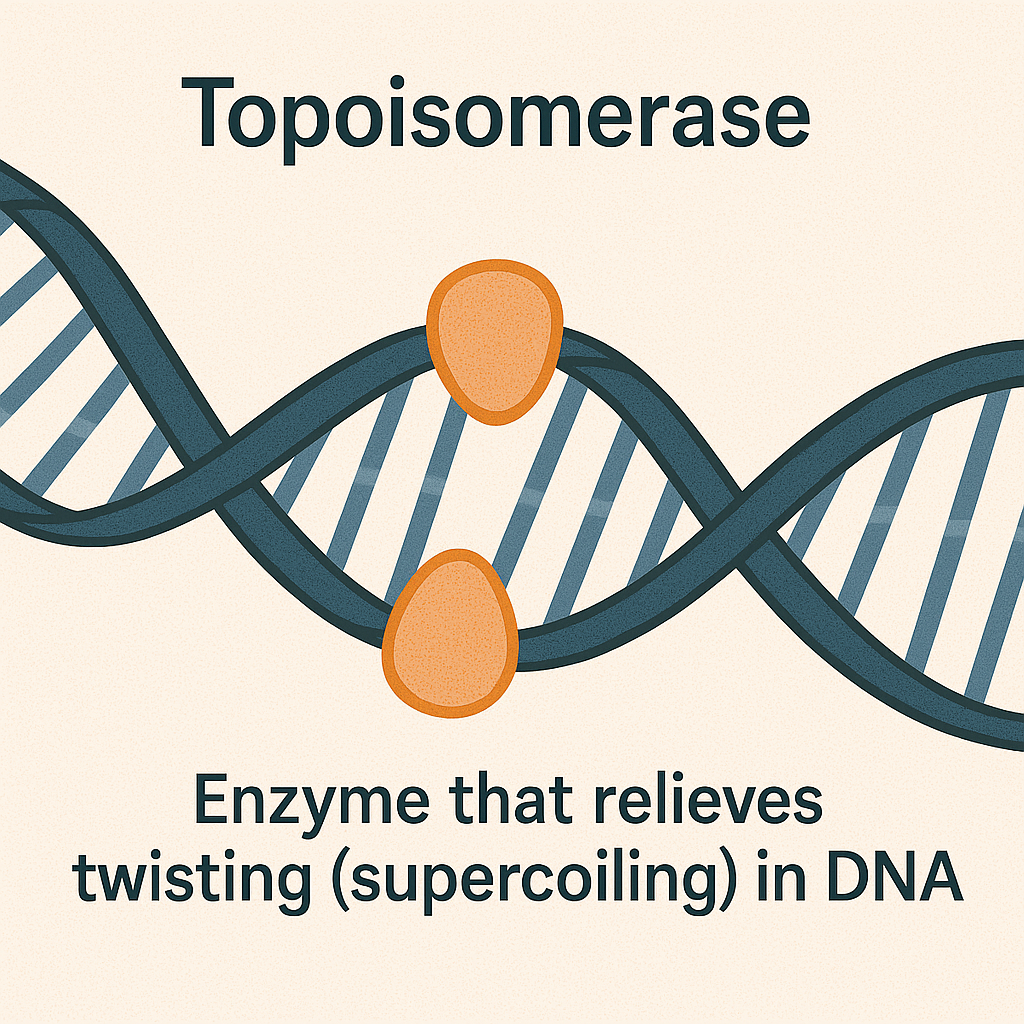
Topoisomerase
Enzyme that relieves twisting in DNA.
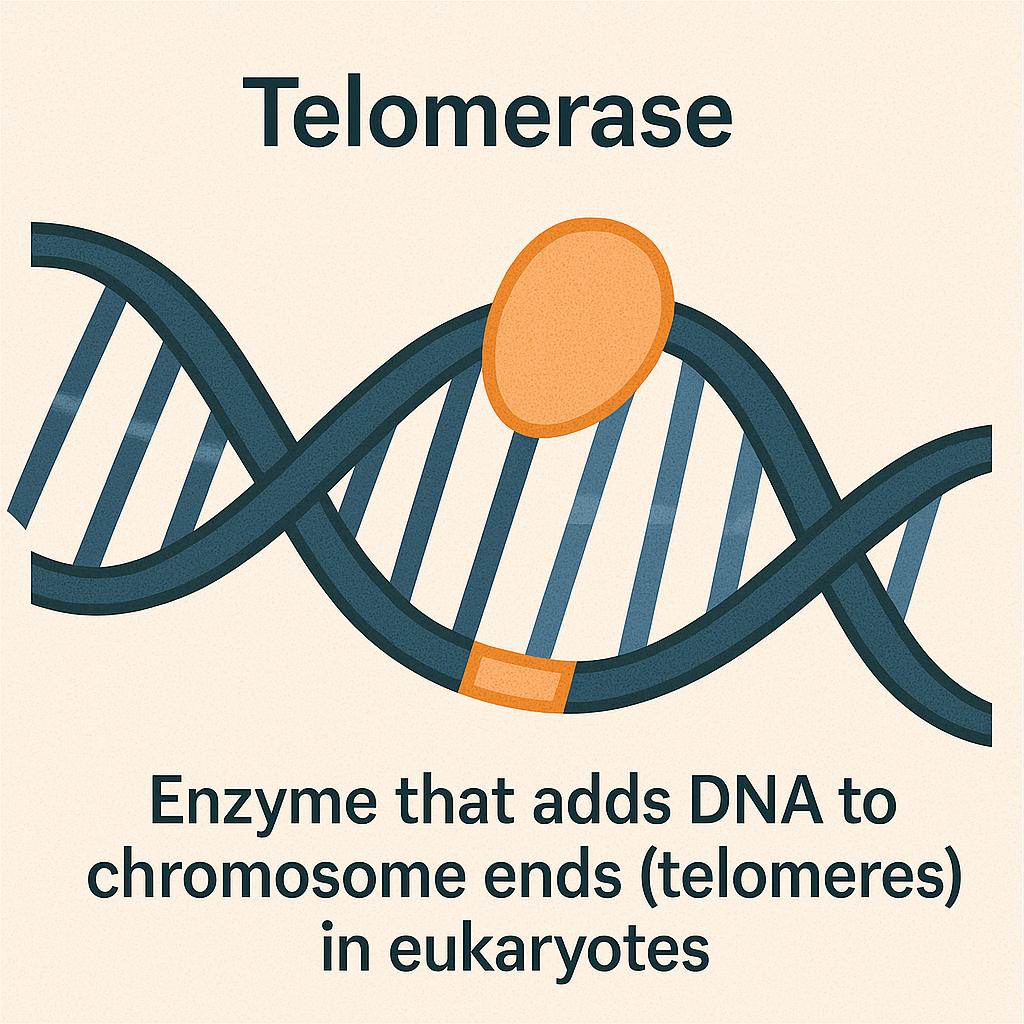
Telomerase
Enzyme that adds DNA to chromosome ends in eukaryotes.
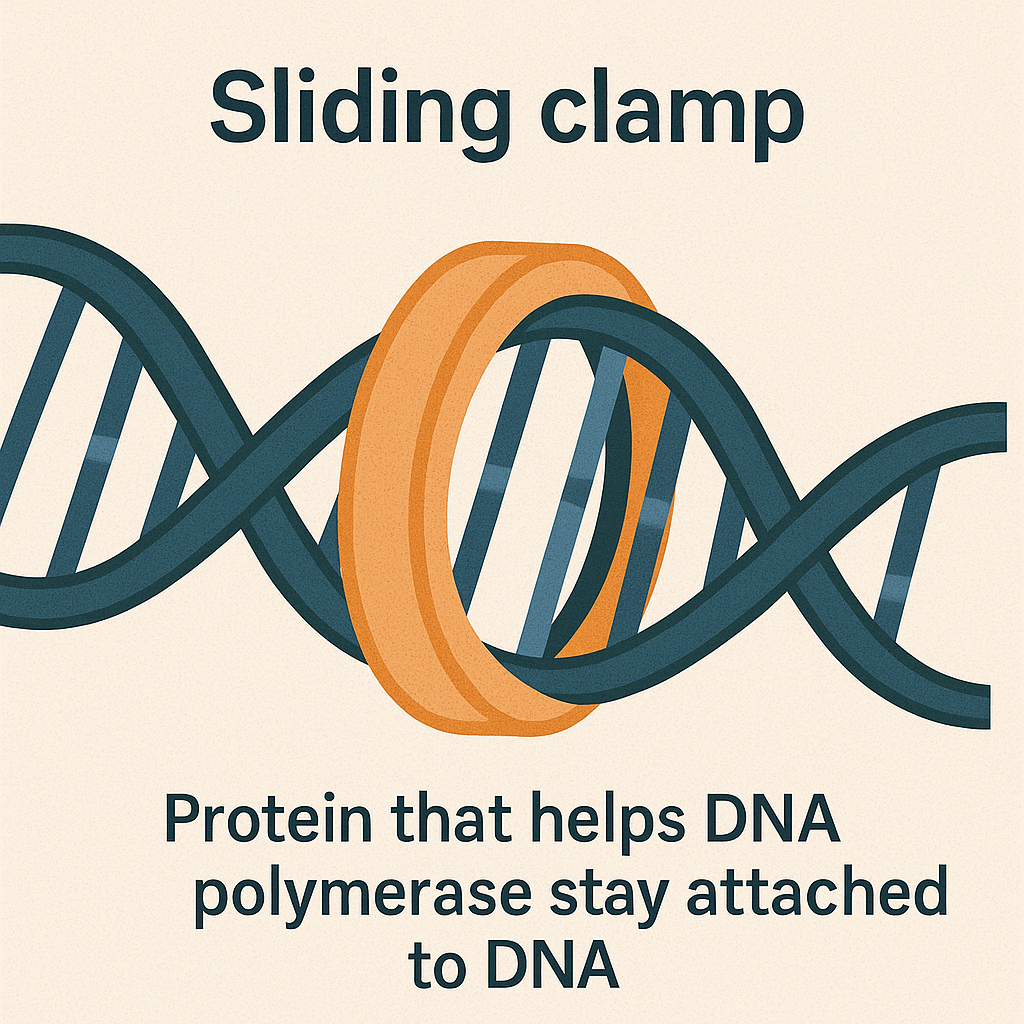
Sliding clamp
Protein that helps DNA polymerase stay attached to DNA.
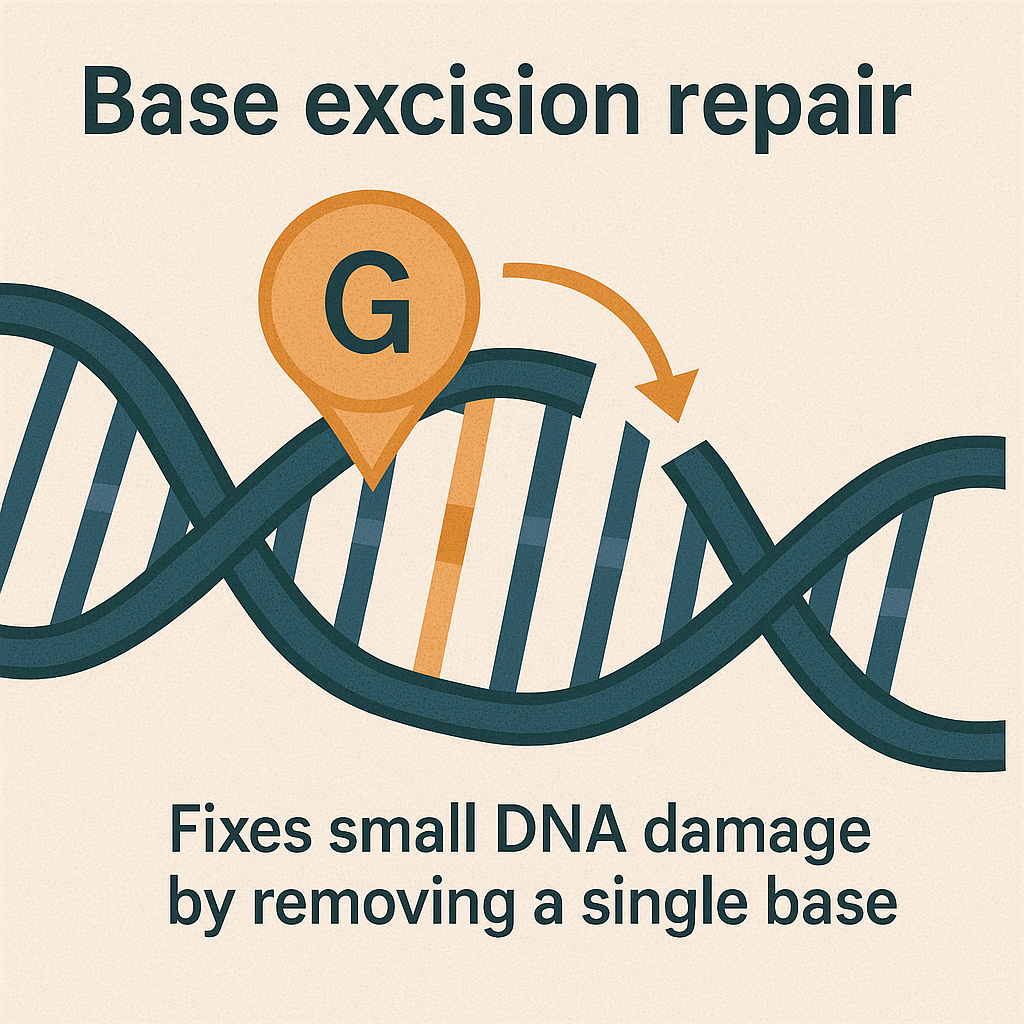
Base excision repair (BER)
Fixes small DNA damage by removing a single base.
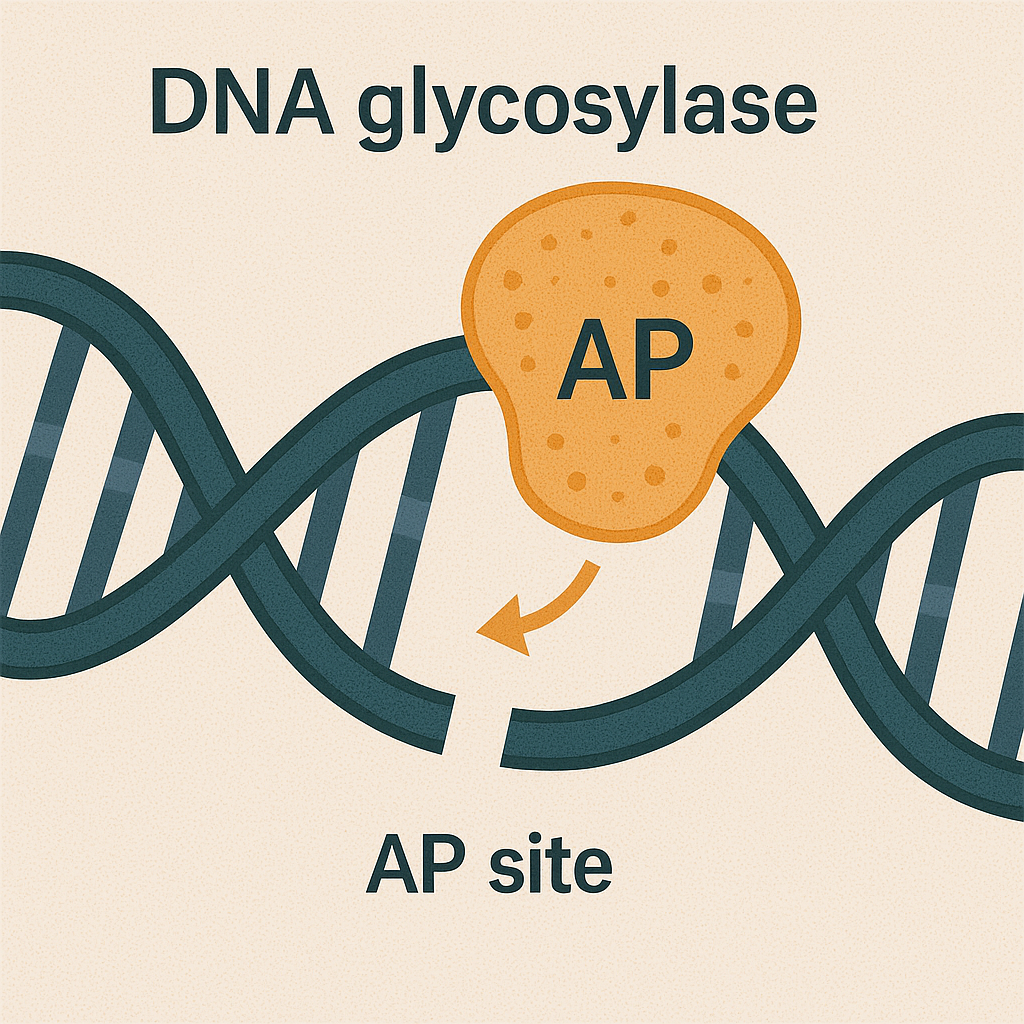
DNA glycosylase
Enzyme that removes damaged bases in BER.
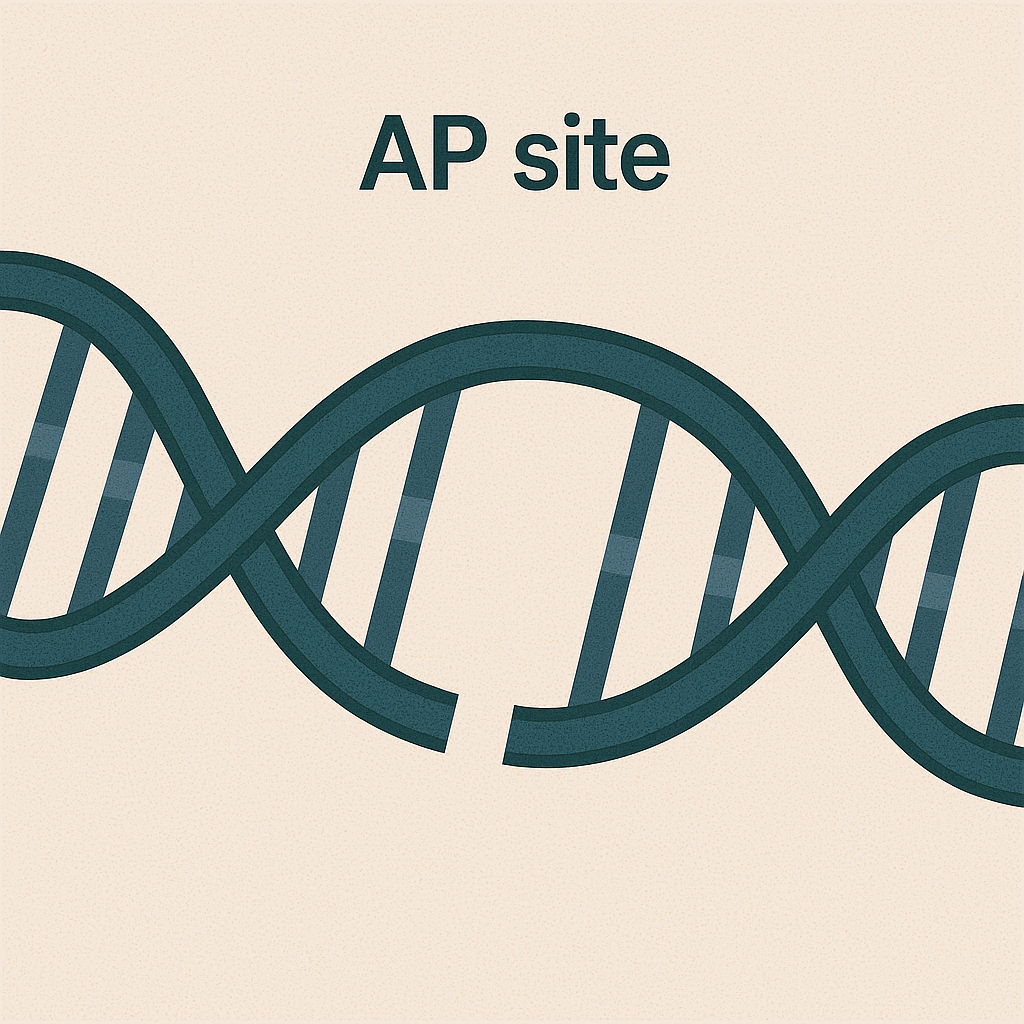

AP site
Place in DNA missing a base (after glycosylase action).
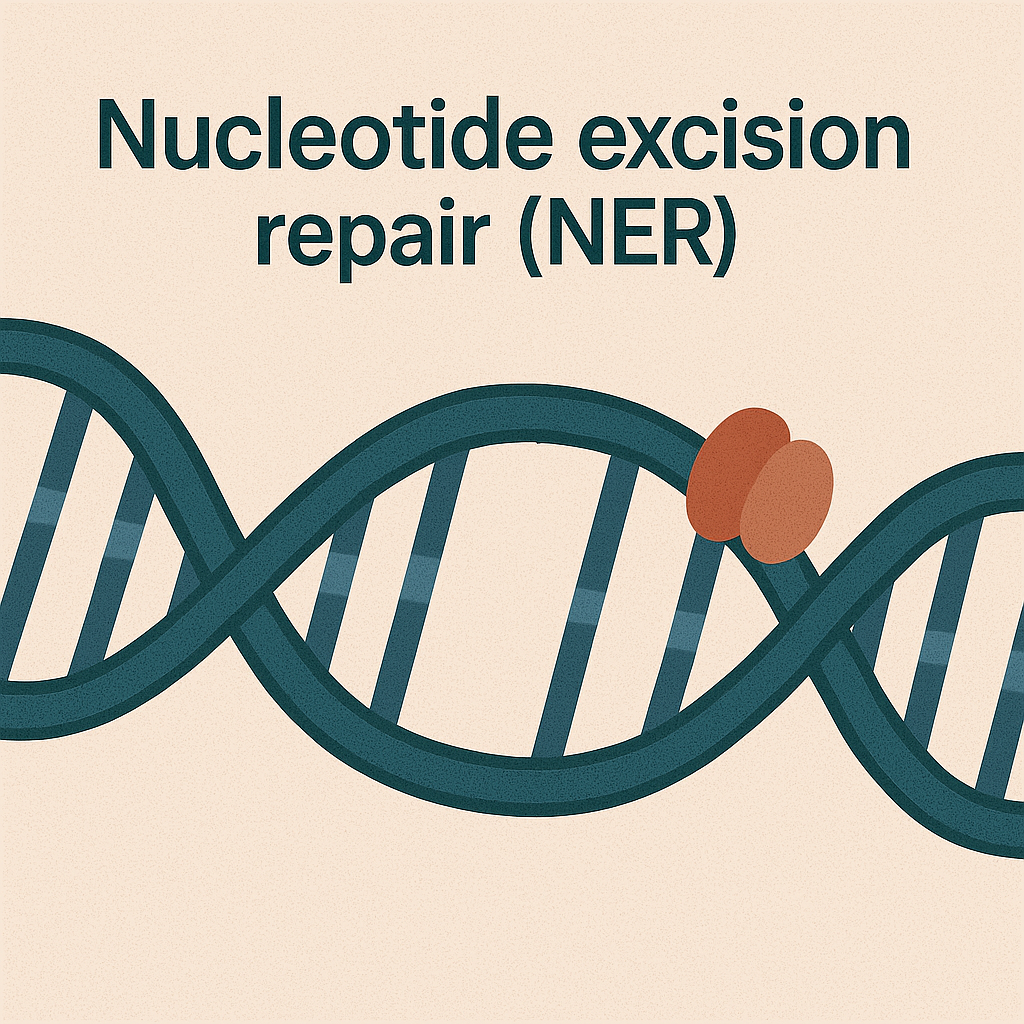
Nucleotide excision repair (NER)
Removes bulky DNA damage.
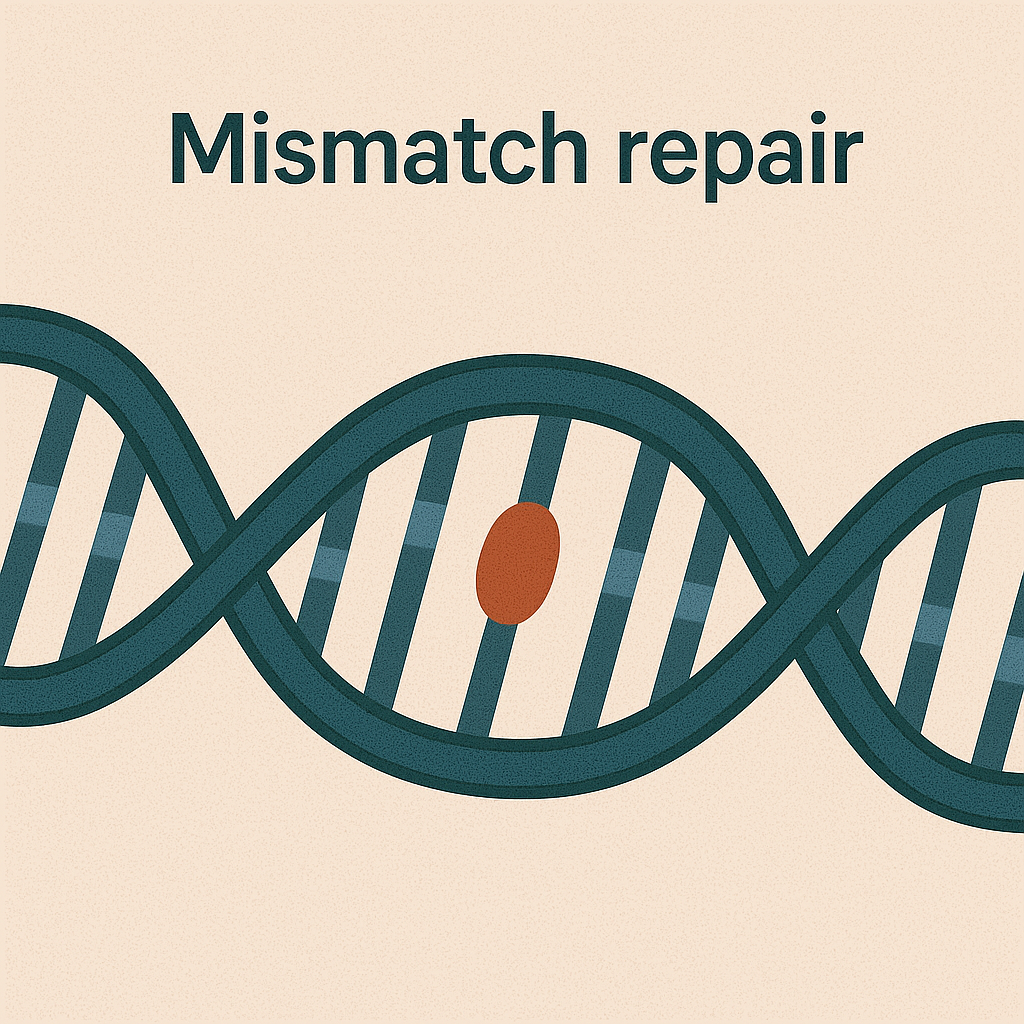
Mismatch repair
Fixes mistakes made during DNA replication.
MutL/MutH
Proteins involved in mismatch repair.
Direct repair
Fixes DNA damage directly, without removing bases.

Homologous recombination
Repairs DNA breaks using a similar DNA molecule.
Holliday junction
Four-stranded DNA structure formed during recombination.
Transcription
Making RNA from a DNA template.
Promoter
DNA sequence where RNA polymerase binds to start transcription.
TATA box
DNA sequence in eukaryotic promoters, helps start transcription.
Sigma factor
Protein in prokaryotes that helps RNA polymerase find the promoter.
RNA polymerase
Enzyme that makes RNA from DNA.
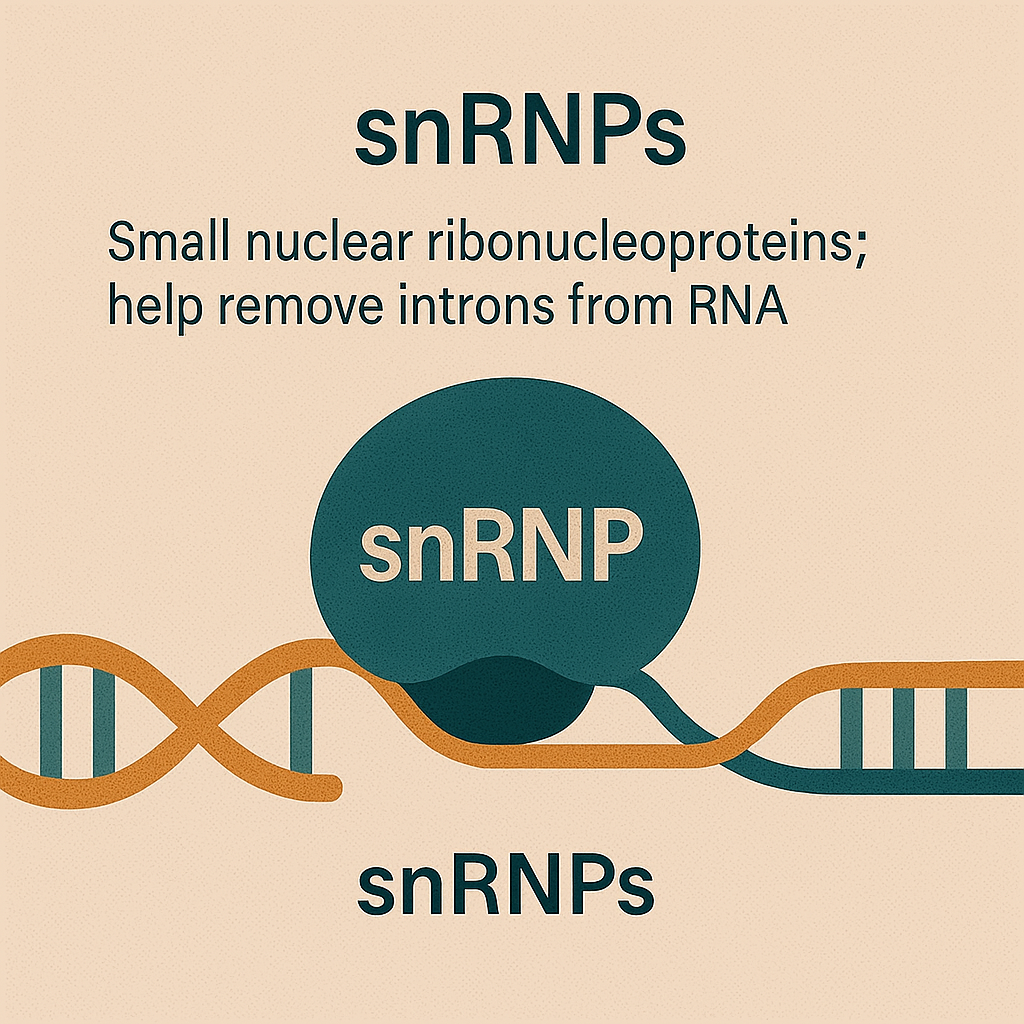
snRNPs
Help remove introns from RNA.
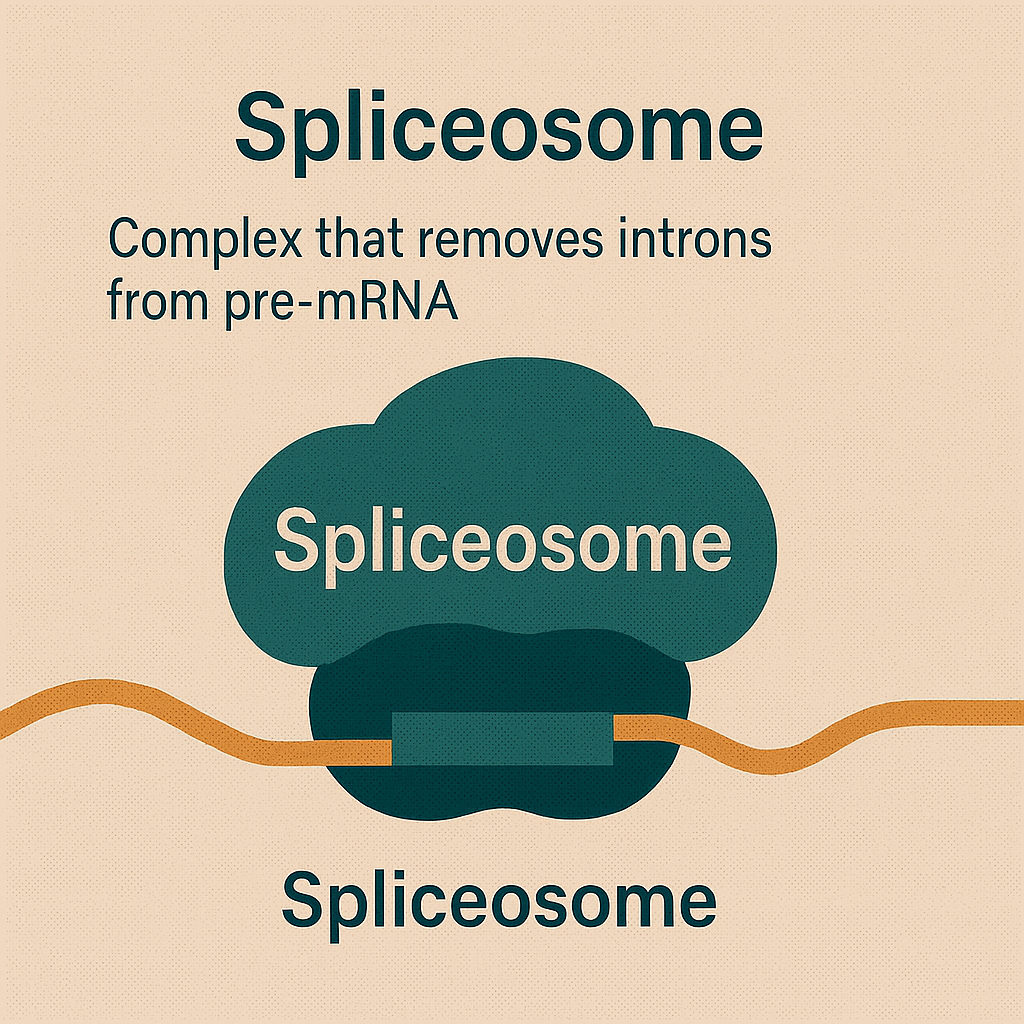
Spliceosome
Complex that removes introns from pre-mRNA.
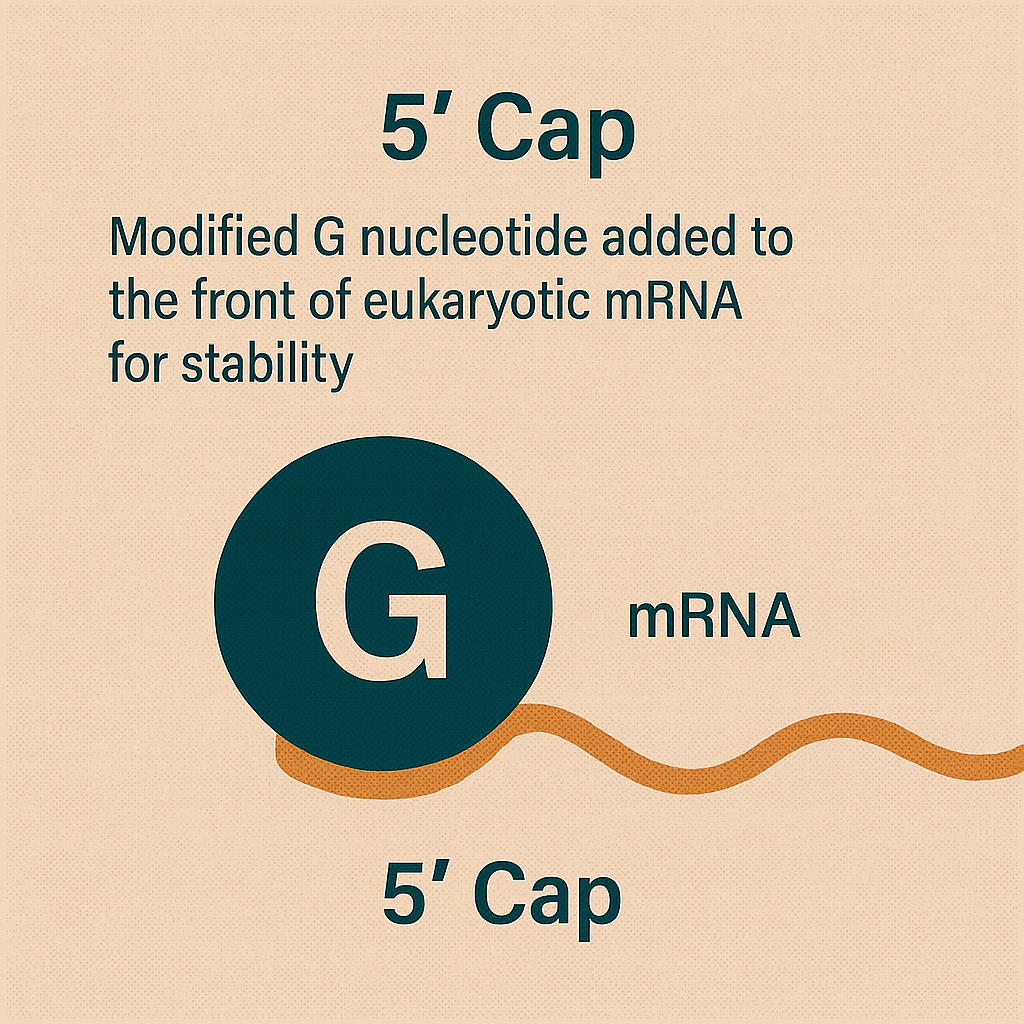
5' cap
Modified G nucleotide added to the front of eukaryotic mRNA for stability.
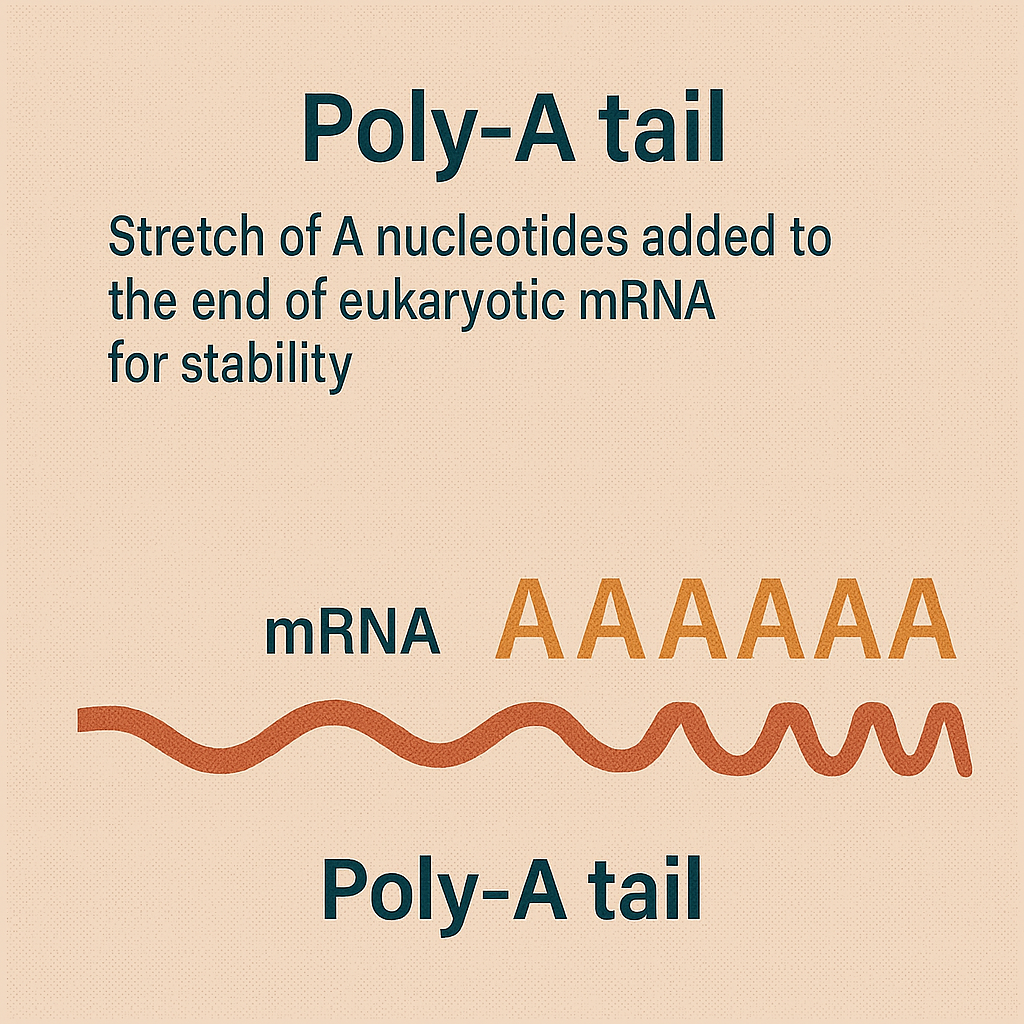
Poly-A tail
Stretch of A nucleotides added to the end of eukaryotic mRNA for stability.
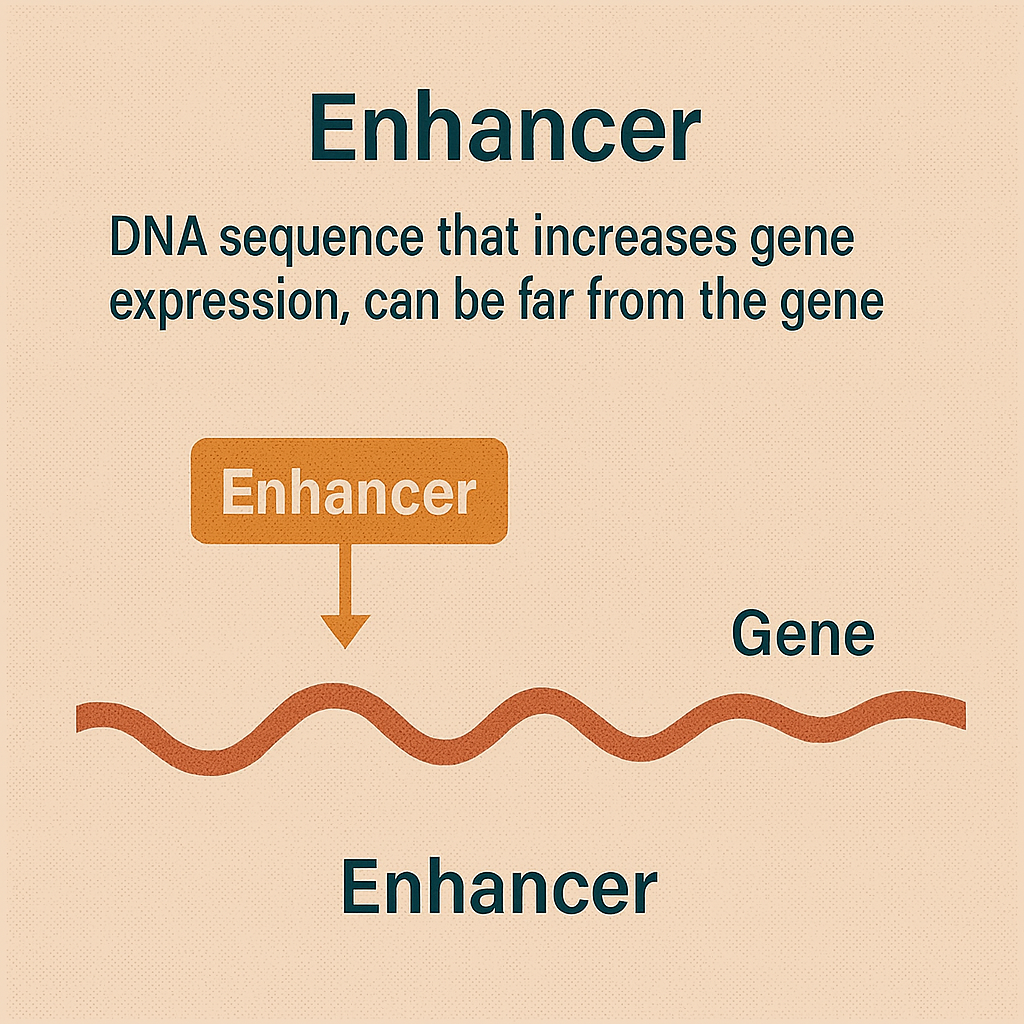
Enhancer
DNA sequence that increases gene expression, can be far from the gene.
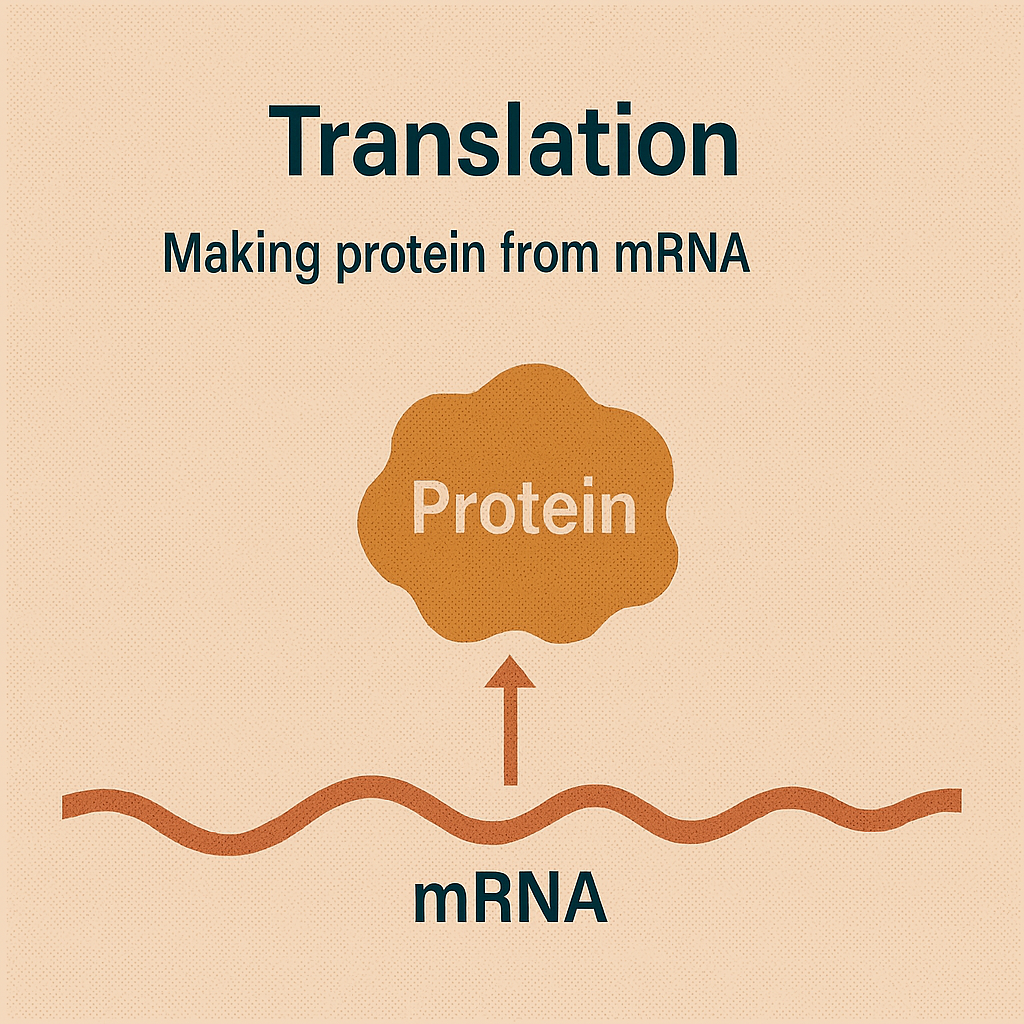
Translation
Making protein from mRNA.
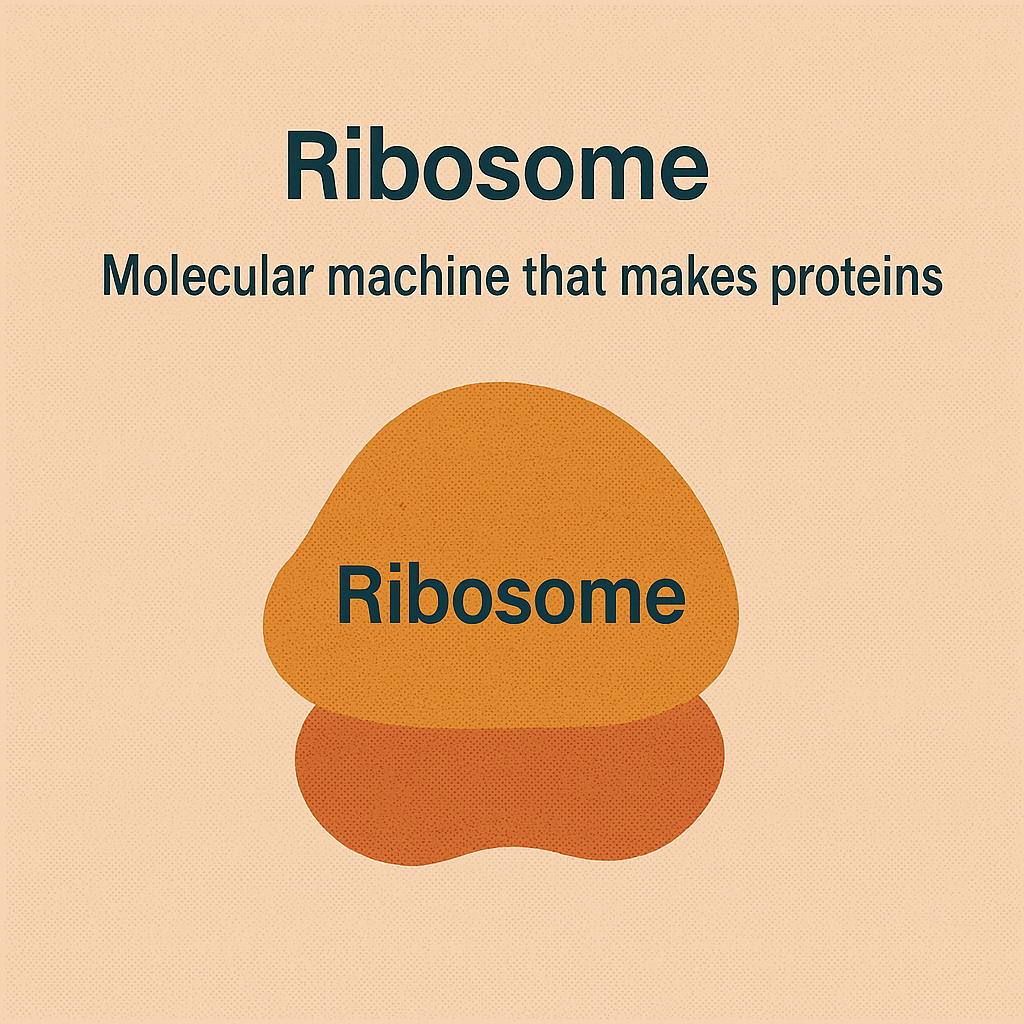
Ribosome
Molecular machine that makes proteins.

tRNA
Transfer RNA; brings amino acids to the ribosome.

Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
Enzyme that attaches amino acids to tRNA.

Codon
Three-base sequence in mRNA that codes for an amino acid.

Anticodon
Three-base sequence in tRNA that pairs with mRNA codon.

Start codon
First codon in mRNA (usually AUG, codes for methionine).

Stop codon
Codon that signals the end of translation (UAA, UAG, UGA).

Shine-Dalgarno sequence
Sequence in prokaryotic mRNA that helps ribosome find the start codon.
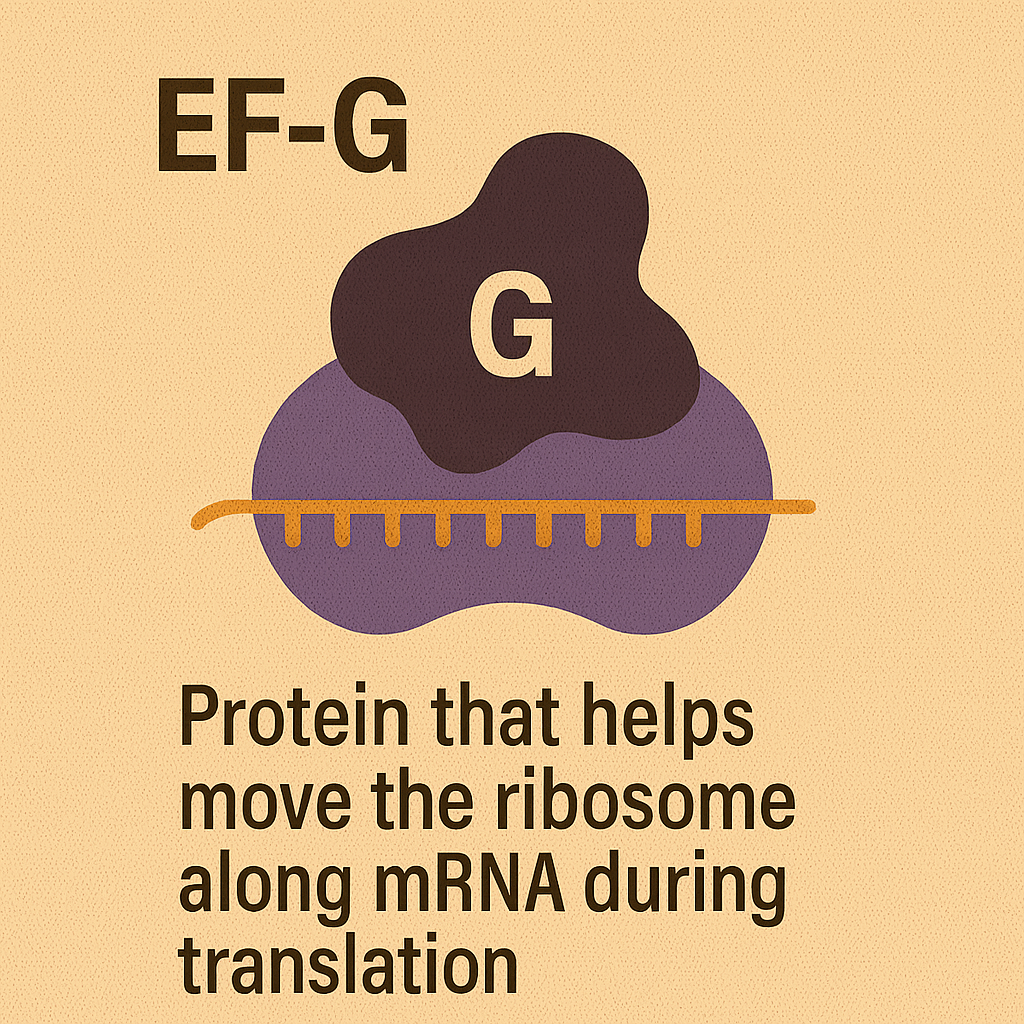
EF-G
Protein that helps move the ribosome along mRNA during translation.
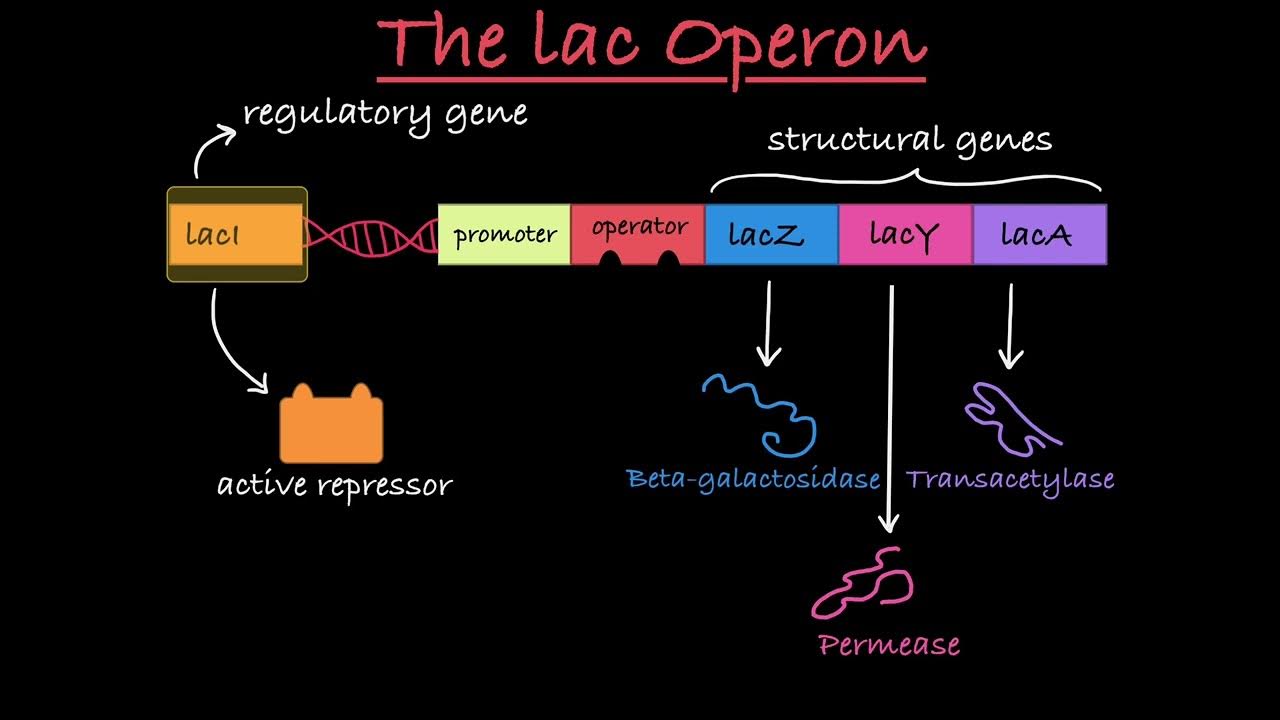
Lac operon
Group of genes in bacteria for lactose metabolism.
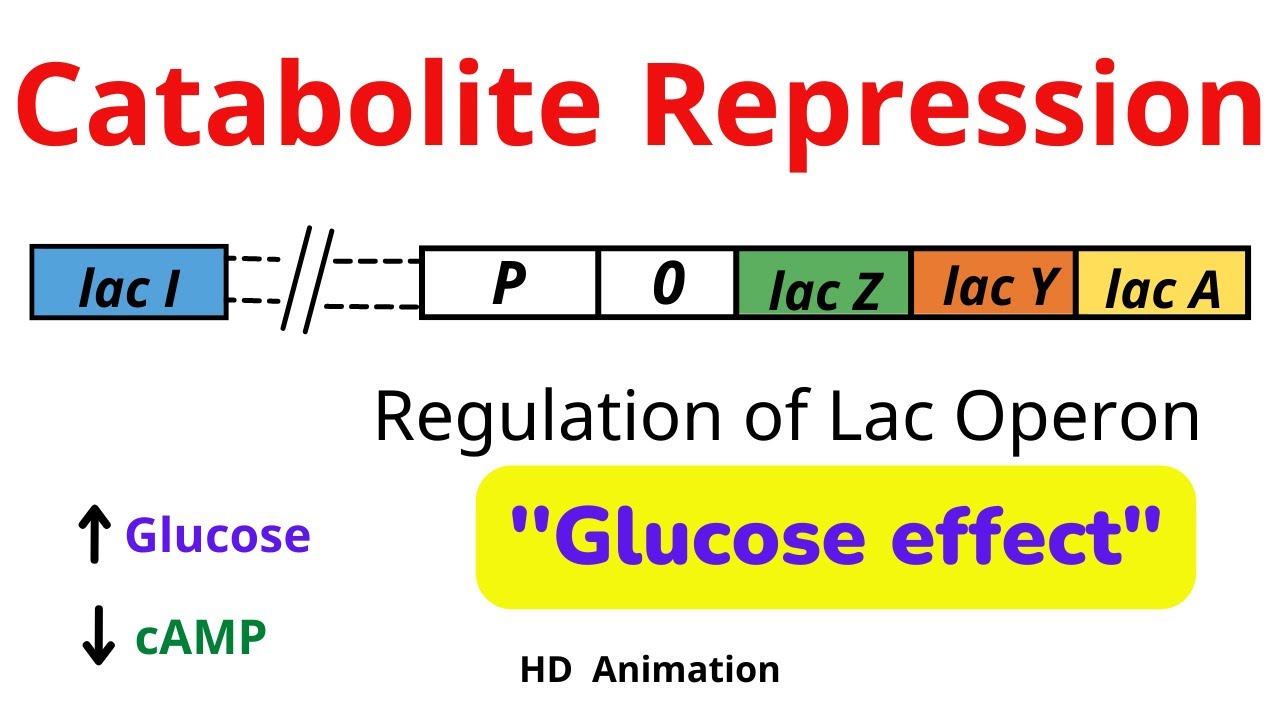
Catabolite repression
When glucose prevents the lac operon from being active.
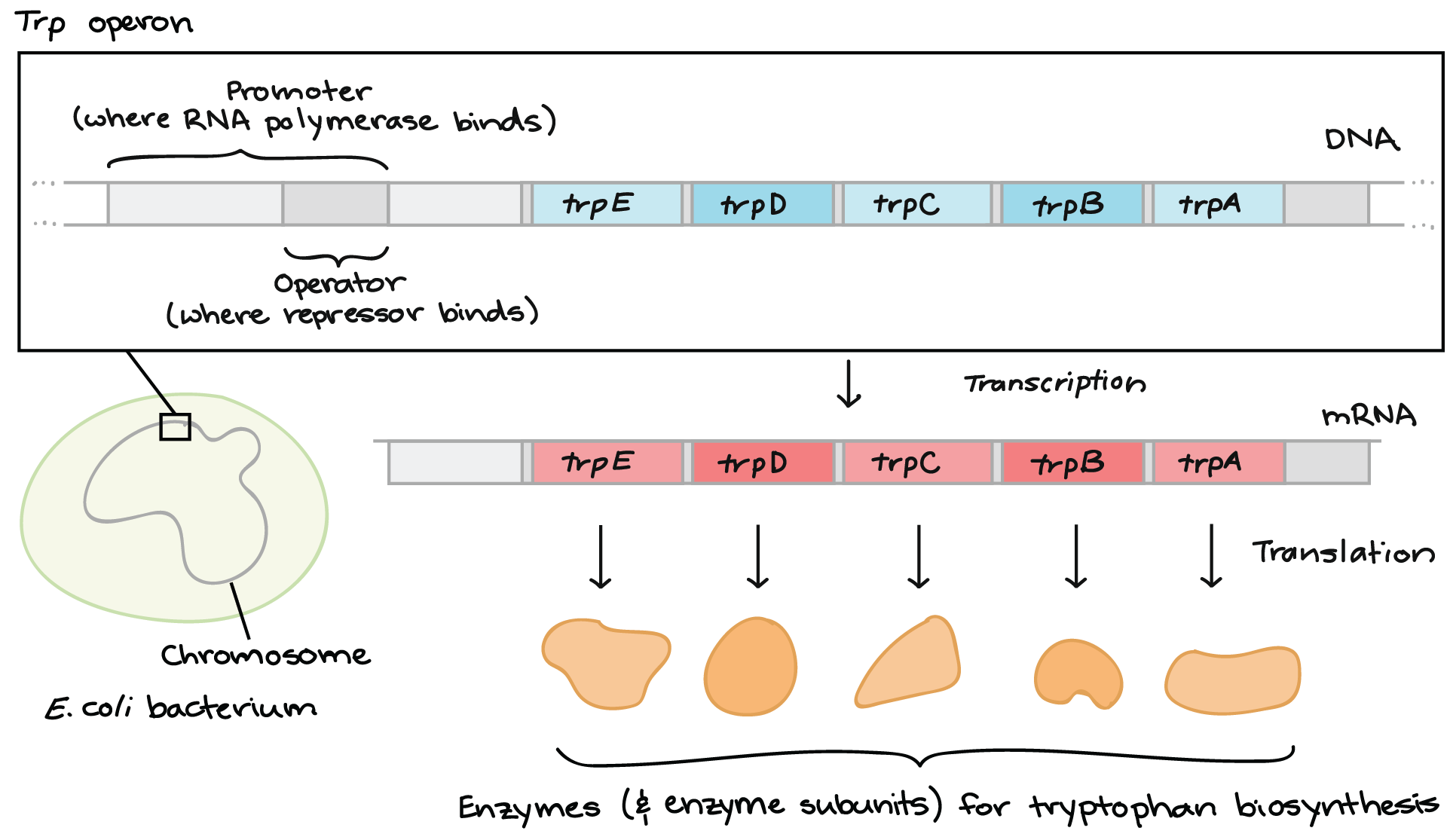
Trp operon
Group of genes for tryptophan synthesis.
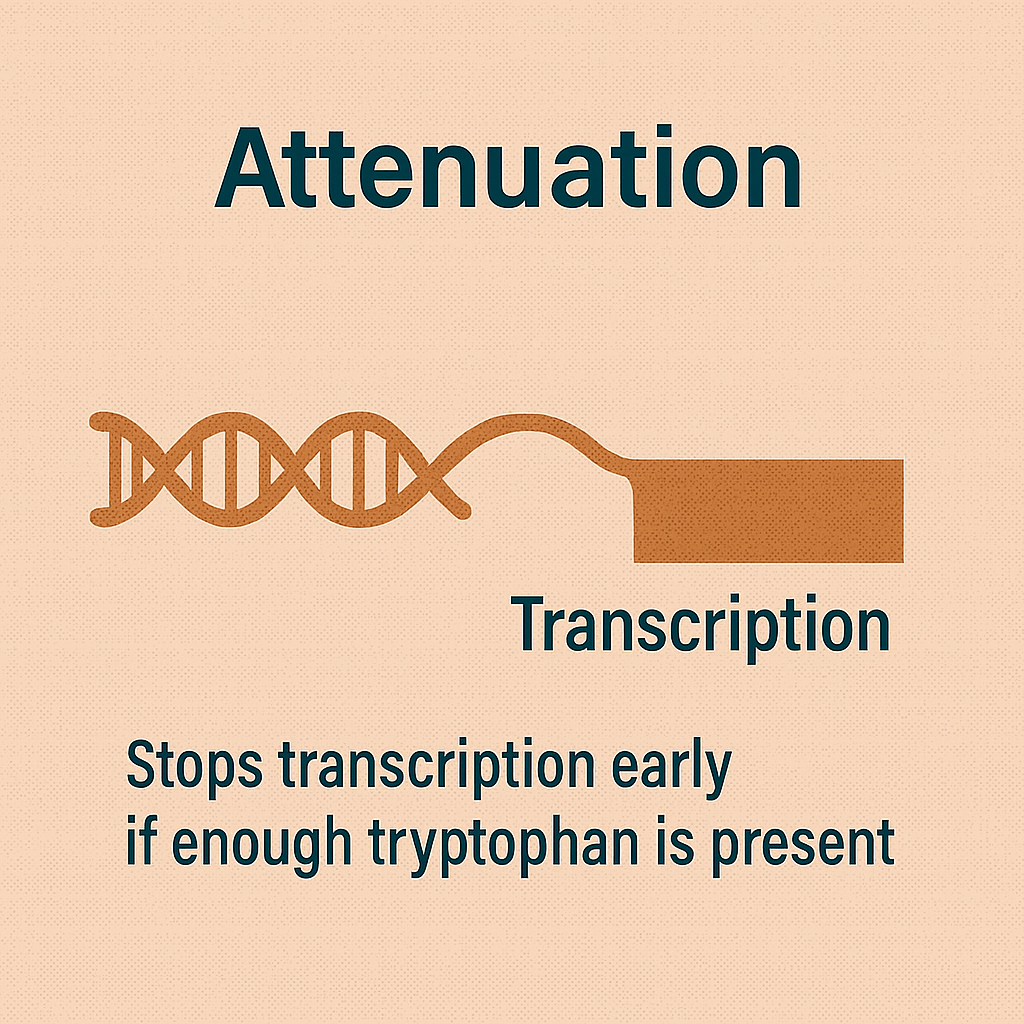
Attenuation
Stops transcription early if enough tryptophan is present.

Chromatin remodeling
Changing how tightly DNA is wrapped around histones.
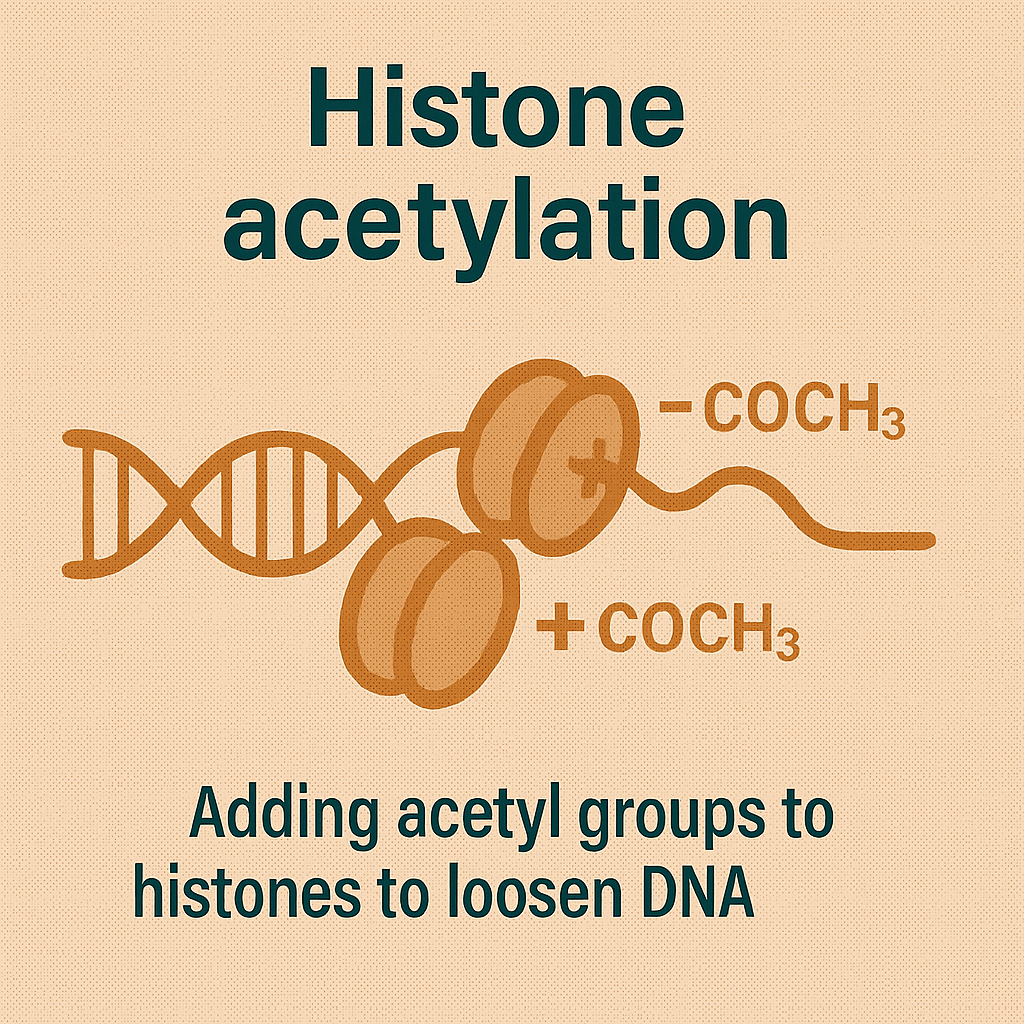
Histone acetylation
Adding acetyl groups to histones to loosen DNA.

Point mutation
Change in a single DNA base.

Nonsense mutation
Mutation that changes a codon to a stop codon.
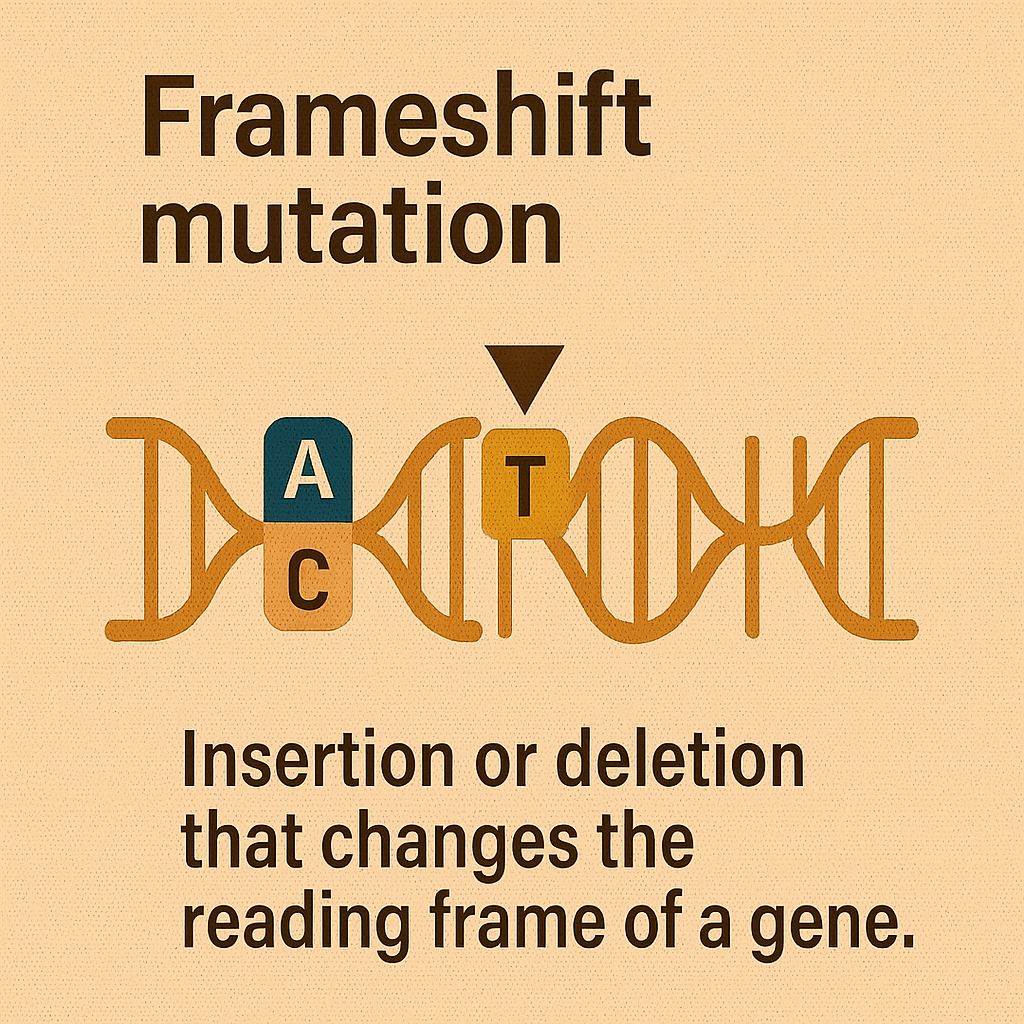
Frameshift mutation
Insertion or deletion that changes the reading frame of a gene.
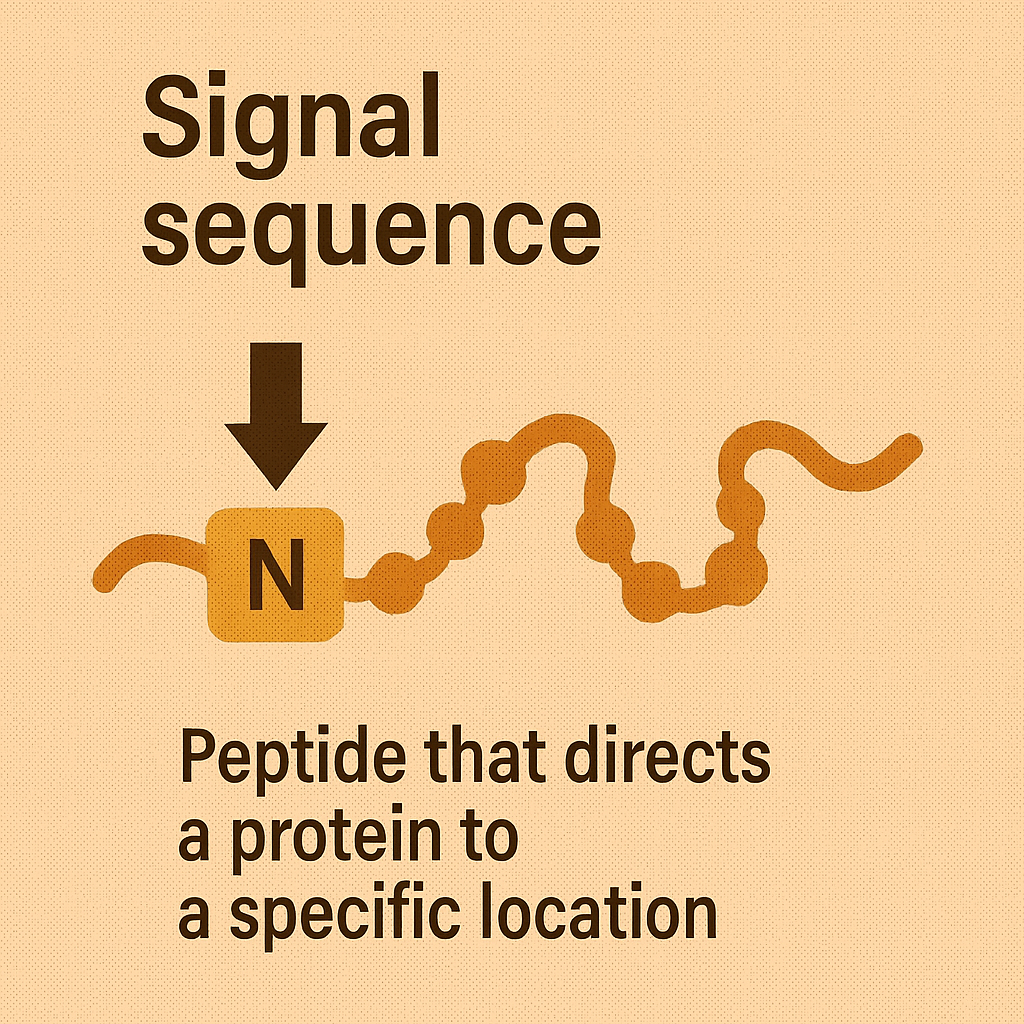
Signal sequence
Peptide that directs a protein to a specific location.
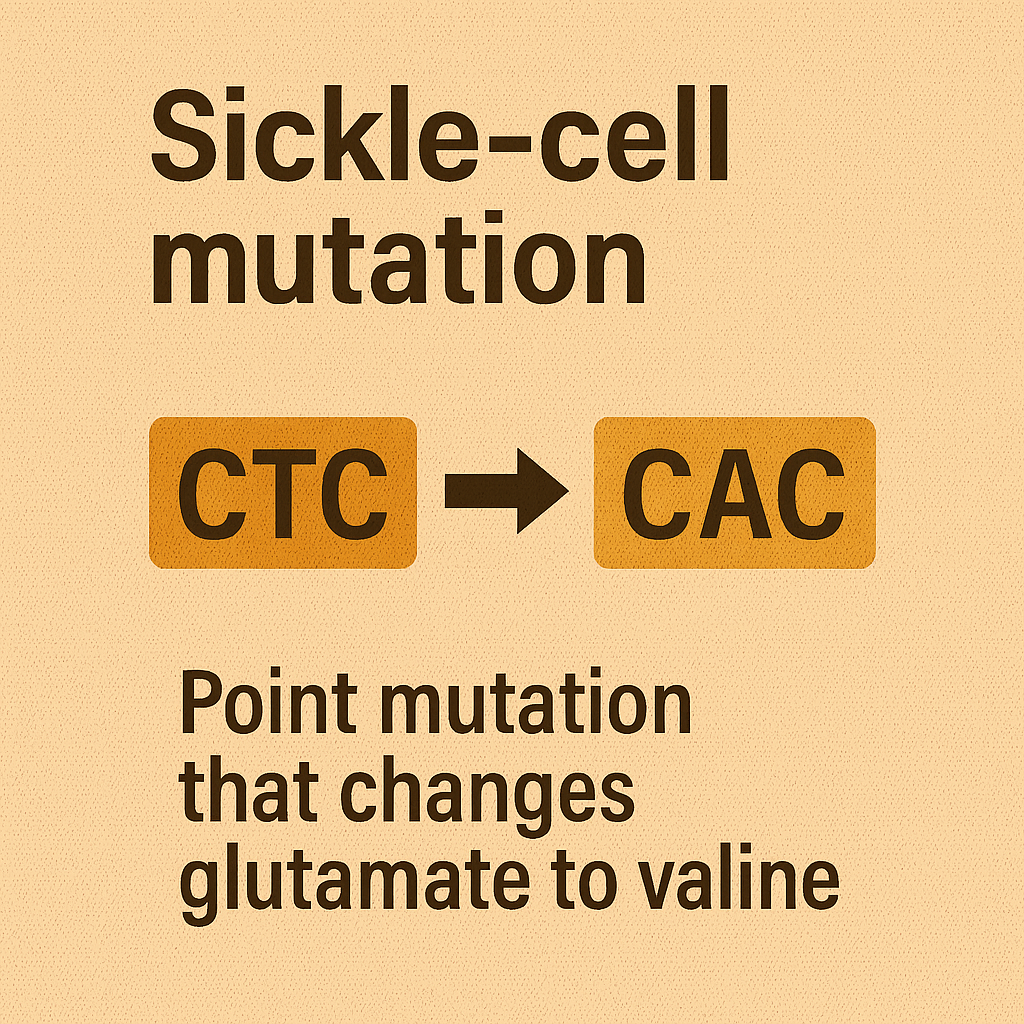
Sickle-cell mutation
Point mutation that changes glutamate to valine.