PSYCH EXAM II
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
extinction
conditioned response declines and disappears over trials without the unconditioned stimulus
conditioned response
behavior that does not come naturally, but is learned by the individual by pairing a neutral stimulus with potent stimulus
example of conditioned response
Pavlov’s dog experiment
unconditioned stimulus
automatic, involuntary and unleared reaction to a stimulus like salivating at the sight of food
spontaneous recovery
after a rest interval, the extinguished conditioned response reappears at almost its previous strength and then extinguishes faster the next time
why does spontaneous recovey occur
corpus callosum
allows info to be passed to left and right hemispheres- important for communication between hemispheres
left visual field goes to
right hemisphere
right visual field goes to
left hemisphere
language hemisphere
left
if i am a split brain patient and i have something shown in my right visual field will I be able to vocalize what I saw?
yes
if i am a split brain patient and i have something shown in my left vidual field will i be able to vocalize what i saw?
no
if i am a split brain patient and i was shwon something in my left visual field will I be able to correctly choose the object iwth my left hand
yes
classical conditioning- voluntary or involuntary?
voluntary
US- unconditioned stimulus
input to a reflex (food in mouth)- you dont need to learn this
UR- unconditioned response
output to a reflex- salivation for food -do not need to learn this
CS- conditioned stimulus
bell-tone- initially results in investigatory response, then habituation after conditioning, results in CR
CR (conditioned response)
response to CS; measure amplitude, probability, latency (this is learned)
measures of conditioned response: amplitude
the strength of the conditioned response (can see how much saliva is produced in the tube)
measures of conditioned response: probability
how often the conditioned response occurs (eye blinks due to a bell)
measures of conditioned response: latency period
time for CR to occur (how long till heartbeat is beating fast due to tone)
aquisition
period time of learning when pairing the CS with the US (bell with food): more reinforcement (trials) make the CR stronger
extinstion:
if you dont provide the CS with the US (bell without food), the strength of the CR deceased and goes away
due to the buildup of inhabitation- the learned idea that bell leads to no food inhibits the idea that bell leads to food
the bell with no food learning is not permanent
spontaneous recovery
after 24 hours, the CR is recovered without any further training (its spontaneous)- NOT AS STRONG AS PREVIOUS STRENGTH; extinction happens faster from now on
contiguity
time in between presenting the CS (bell) and the US (food)
optimal time interval
best time (right time) between presenting the CS and the US to get the strongest CR
stronger CS creates stronger CR example
louder bell (CS) creates more salivation (CR)
second (higher) order conditioning
first create the CR (salivation) from the CS (electric can opener) that was paired with the US (food)- first order conditioning
Now because you have the CR (salivation) to the CS (electric can opener) you can USE THAT CS (can opener) to pair with another stimulus (new CS- cabernet door squeak)
NOW after the pairing of the first order CS and the second roder CS (the new CS)= can opener with squaeaky door sound over and over now… the dog salivates to the cabinet door squeak!!!!
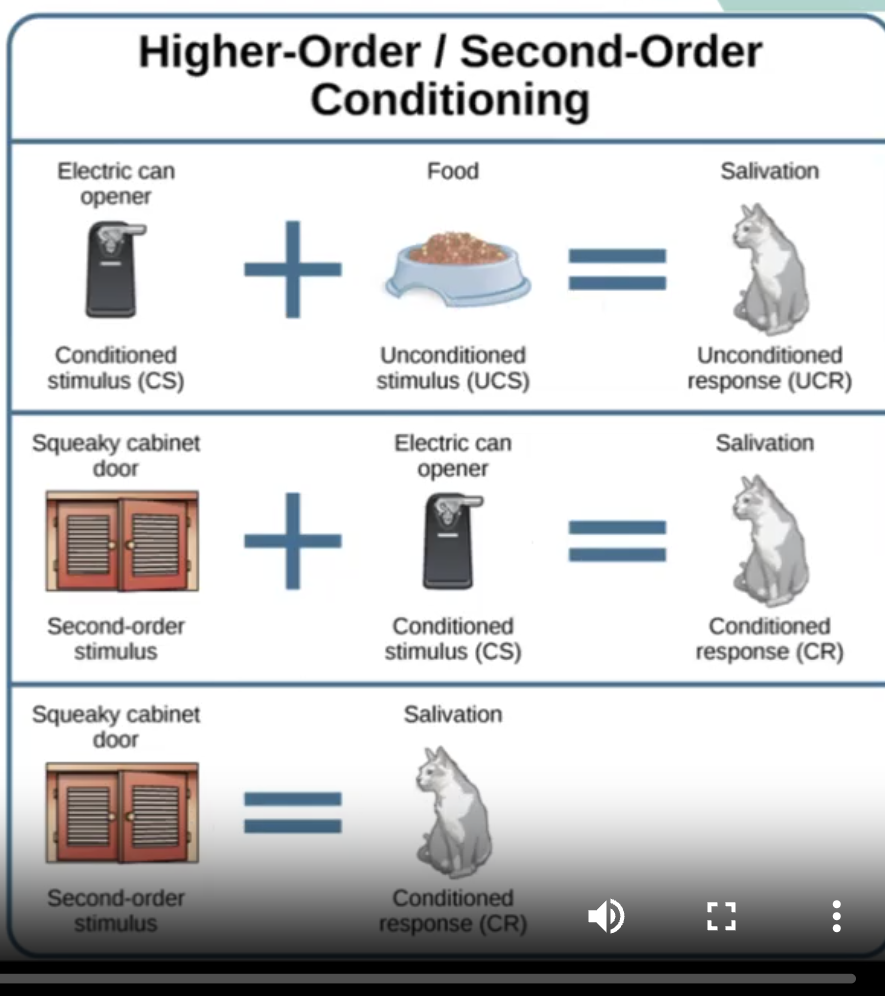
second order (higher order) conditioning
look at image
Generalization
similar stimuli create similar responses
discrimination
different stimuli create different responses
CS “tone” allows for prepartion of the US (shock)
rabbit received a shock (US) with a tone (CS)
heart rate now increases (UR)
NOW because it could be dangerous- the tone (CS) tells the body “WAIT, slow down your heart rate to protect itself”
so now, after learning, the tone (CS) informs the body to prepare for the shock (US) so the CS actually makes the heart rate (CR) decrease (compensation)
Thorndike’s cat puzzle box
learning is incremental/ bit by bit/ gradual
Law of Effect: response is strengthens when followed by reinforcement. (satisfying state of affairs)
response is weakened when followed by punishment (annoying state of affairs)
operant conditioning
voluntary
reinforcement operant conditioning- voluntary
reinforcement depends on response (cat has to push paddle- in order to get out of the box, which is the reinforcement
operant conditioning example
a rat presses a bar and when the light is ON the rat receives reinforcement of food, the rat presses the bar and when the light is off, the rat does NOT RECEIVE REINFORCEMENT
discriminative stimulus: light on (does not cause the response, just says when to press the bar to be reinforced
schedules of reinforcement for operant conditioning: partial reinforement effect:
continuous reinforcement: if you reinforce therat every time for the response—> does not lead to that strong of a response
partial reinforcement: if you reinforce the rat sometimes (some of the time)
schedules of reinforcement for operant conditioning: interval
reinforce a response after a period of time
fixed interval
time is fixed- when rat presses bar- every 30 seconds the rat will receive reinforcement when it presses bar- every 30 seconds the rat will receive reinforcement when it presses bar (times is reset every time); scallop design on graph
variable ratio
ratio is averaged- on average it will be every 10 responses it receives a reinfocement- this makes it unpredictable (could be 8 responses, 12 responses, 5 responses, 15 responses)
makes the rat press bar continuously because it is unpredictable- straight slope on graph
continuous reinforcement: all response receive reinforcement
shaping- operant conditioning
trying to get a subject to do ONE behavior- shaping can make the subject do a response the animal would have never done spontaneously on its own
example of shaping-operant conditioning
we want a rat to press a bar
left hemisphere
language
right hemisphere
spacial abilities
steps for answering a split brain question
which side of the visual field was the info presented on?
which hemisphere did that info go to?
what abilities does that hemisphere control?
extinction
conditioned response declines and disappears over trials without unconditioned stimulus
extinction due to
buildup of inhibition
spontaneous recovery
after rest interval, extinguished condition response reappears at almost previous strength and extinguishes faster next time
spontaneous recovery due to
dissipation of inhibition
pavlov’s view
conditioned stimulus- conditioned reflex
modern view
conditioned stimulus and unconditioned stimulus association, such that conditioned stimulus provides info about unconditioned stimulus
forward pairing
conditioned stimulus is presented before the unconditioned stimulus
simultaneous pairing
conditioned stimulus comes at the same time as the unconditioned stimulus
backward pairing
conditioned stimulus comes after the unconditioned stimulus
law of effect
response is automatically strengthened when followed by reinforcement (“satisfying state of affairs”): automatically weakened when followed by punishment “annoying state of affairs”
skinner “skinner box”
many responses; little time and effort; easily recorded- RESPONSE RATE IS THE DEPENDENT VARIABLE
positive reinforcement
delivers appetitive stimulus (food, approval)
negative reinforcement
removes aversive stimulus (shock, alarm clock noise)
(pos or negative reinforcement/ punishment) increases behavior and presents stimulus
positive reinforcement
(pos or negative reinforcement/punishment) decreases behavior, presents stimulus
positive punishment
(pos or negative reinforcement/punishment) increases behavior and removes stimulus
negative reinforcement
(pos or negative reinforcement/punishment) decreases behavior and removes stimulus
negative punishment
discrimitnative stimulus
indicates under what circumstances response will be reinforced
example of discriminative stimulus
rat presses bar but only gets food when LIGHT in box is ON; eventually doesnt press unless light is ON
stimulus does not CAUSE response, or SIGNAL reinforcement, it ____ for response
sets occasion
how does something get to be a conditioned reinforcement?
through CLASSICAL conditioning
partial reinforcement effect
reinforcing ONLY SOME TRIALS produces even STRONGER response than reinforcing ALL TRIALS
interval schedule
reinforce next response after some time interval
fixed interval
time is fixed; rat gets food pellet for next bar press, say, 30 seconds after last pellet (checking mail, delivered daily)
varia ble interval
time is average; rat gets food pellet for next bar press 20, 40, 25, 35 seconds after last pellet- 30 seconds on average
ratio schedule
reinforcement after some number of responses
fixed ratio
ratio is fixed; rat gets food pellet for every 10th bar press (factory piecework)
“variable ratio”
average; rat gets food pellet after 8, 12, 5 ,15 responses- 10th response on average
behaviorist view
response is learned automatically due to reinforcement- we know response is learned when rat performs it
cognitive view says
“cognitive map” of maze is learned (even without reinforcement)- used later when animal has purpose or motivation
short term memory=
working memory
human memory: stage theory:
long term and short term memory
duration: long term memory
relatively permanent
short term memory: duration
seconds to minutes
storage capacity long term memory-
infinite
short term memory storage capcity
7±2 “chunks” organized packets of information
flow of information in memory
stimulus → STm → rehersal *→ Long term memory
two kinds of rehersal
maintenance- holds info in STM
elaborative- moves info to LTM
primacy effect in free recall
early part of list recalled better than middle: recalled from LTM
recency effect
last part of list recalled better than middle: recalled from short term memory
delay between 20th word and recall
reduce recency
present words faster
reduce primacy
short term phonological- based on
speech sounds: confuse “boat” with “coat”
long term memory: semantic
based on meaning: confuse boat with ship
neural code short term memory
dynamic- pattern of activity among a group of cells
neural code long term memory
pattern of connections within a group of cells
amnesia
interruption of consolidation process; retrograde anmesia for events BEFORE trauma; anterograde amnesia for events AFTER trauma
forgetting in short term memory
STM: Displacement and or decay
forgetting in short term memory
LTM: MISplacement and or retrieval failure
proactive interference: old affects new
retroactive interference: new info affects old
STM not just storage box- more like
“cognitive workbench”
used in all processing of information: mental calcuation, reading, (16 × 31=?)
working memory
describes the idea that the unconditioned stimulus and conditioned stimulus should be presented within a close time interval for acquisition to occur
contiguity
after being conditioned to salivate at the sound of a metorone, pavlov’s dogs were shown a black square before the metronome sound was played- what is the black square considered?
second order stimulus
food is presented and then a metronome sounds- would conditioning occur?
no, because unconditioned stimulus is followed by conditioned stimulus