Chapter 22 & 23) Dental Hygiene Diagnosis and Care Planning
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
DH process of care
- DH diagnosis statements
- formal written plan integrated with total treatment plan used
dental hygiene diagnosis statements
-Identify significant oral hygiene problems
- Behavioral aspects and deviations from normal oral health (high anxiety)
forma written plan integrated with total treatment plan used:
- Identify interventions based on diagnostic statements
- Educate patient
- Secure informed consent
- Communicate plan with other team members
ethical applications
- Law applies to all dental hygiene professionals
- Dental hygiene practice acts of each state govern the scope of practice and criteria for licensure
- Potential for ethical situations to arise when DHCP interacts with: patient, team members, family/caregiver
Providing Ethical Care To Patients:
- Aware of respect each patient deserves
- Maintains communication among all parties responsible for treatment
- Attains knowledge of current standards of care & legal scope of practice
- Possesses ability to assess and justify reporting of unacceptable practices
informed consent can be:
verbal
DH process of care introduction
- Collect and analyze assessment information
- Establish the diagnosis
- Select treatment and education interventions based on diagnostic findings
- Develop formal plan for care
- DH diagnosis= analysis & synthesis of data and application of clinical judgement and critical thinking skills
- Use evidence-based approach, formalize DH Care Plan &appointment sequence
Assessment Findings
- Chief Complaint (CC): patient's statement on why seeking treatment
- Risk Factors: Anticipatory Guidance, Periodontal Diseases, Systemic Conditions, Dental Caries, Oral Cancer
the oral, systemic, capability, autonomy, and reality planning guide

ASA classification system
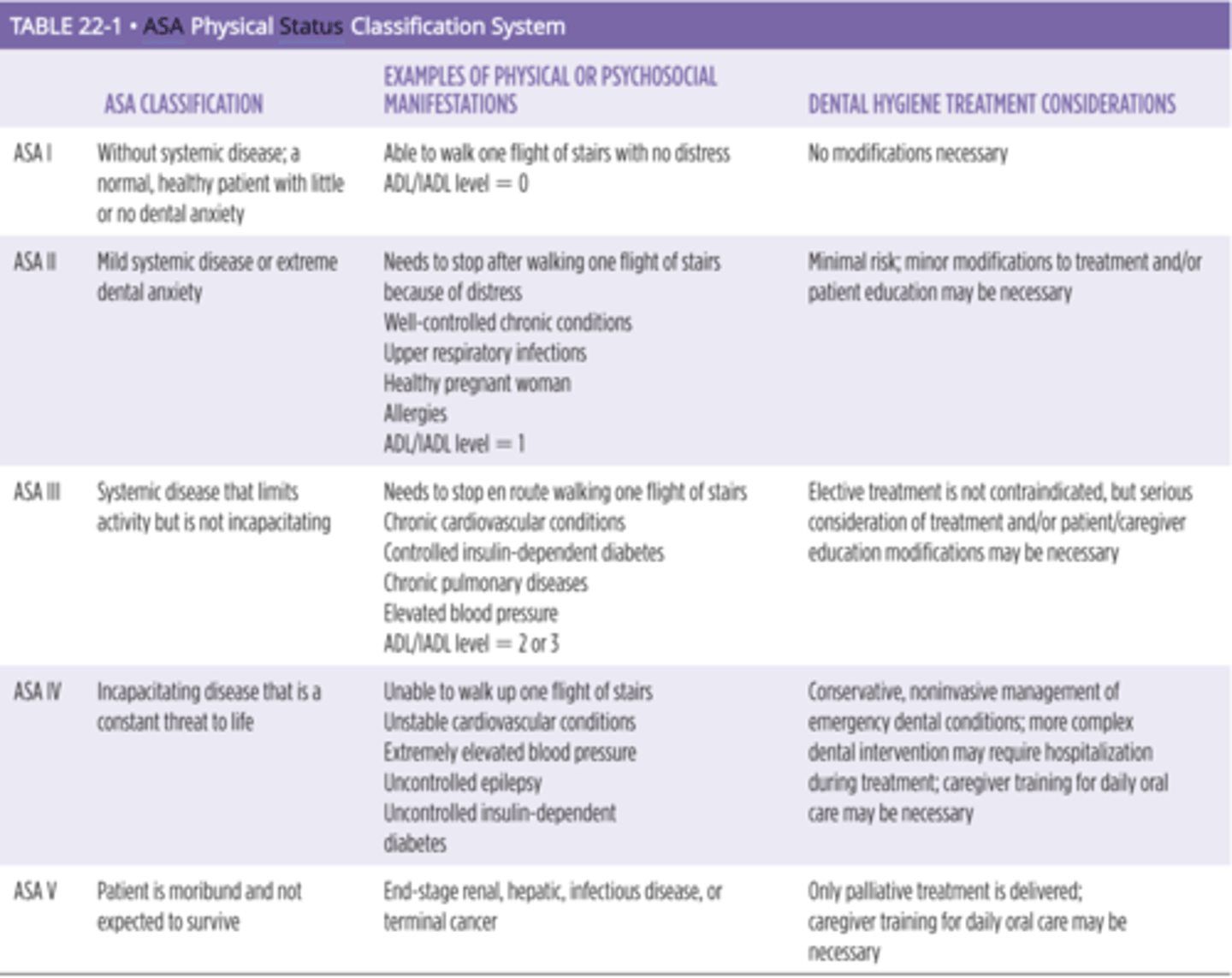
Assessment of Health Literacy
- Oral Healthcare Literacy Level of the Patient: build on current knowledge
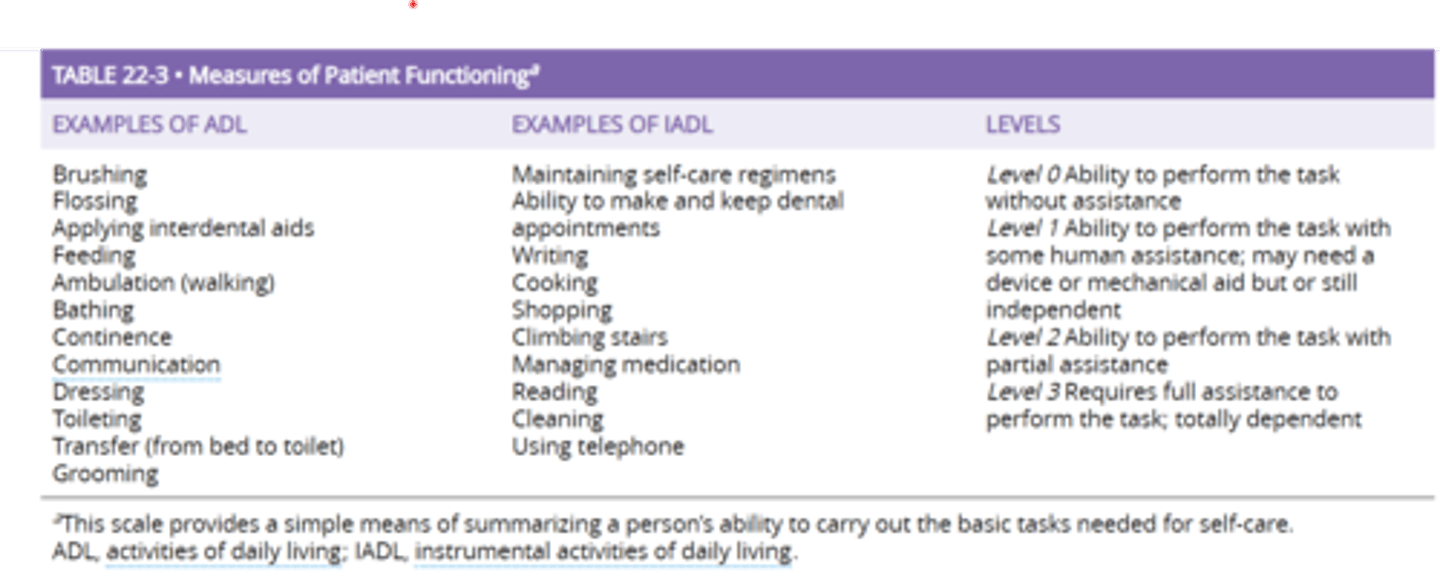
- Patient’s Self-Care Ability: activities of daily living classification; Adaptive or assistive aids, caregiver training needed
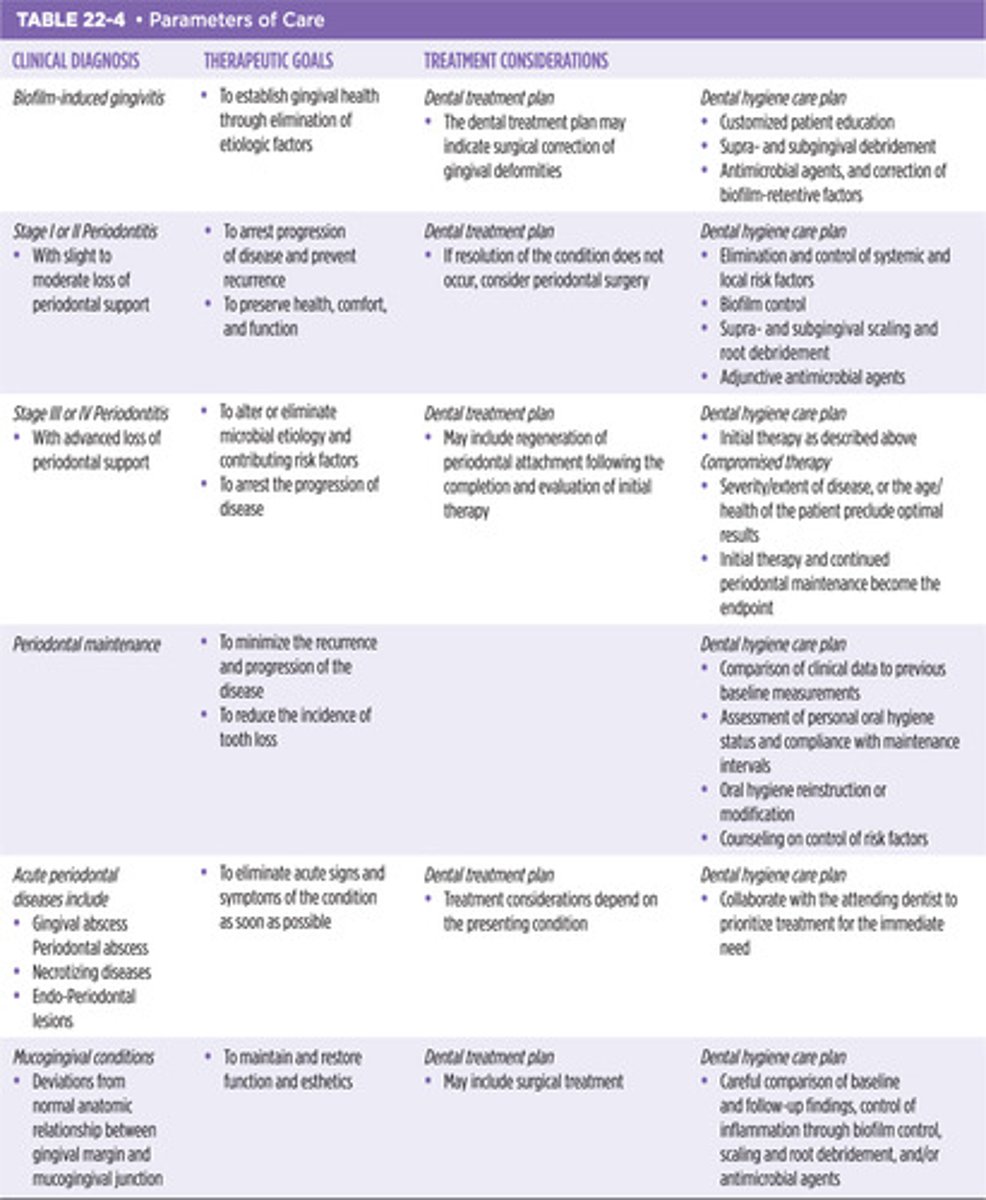
Periodontal Diagnosis & Risk Level
- Plan for # & length of appointments
- Current Periodontal Status
- Classification of Periodontal Diseases
- Parameters of Care
-gingivitis, stage 1 periodontitis, stage II perio, stage III or IV perio
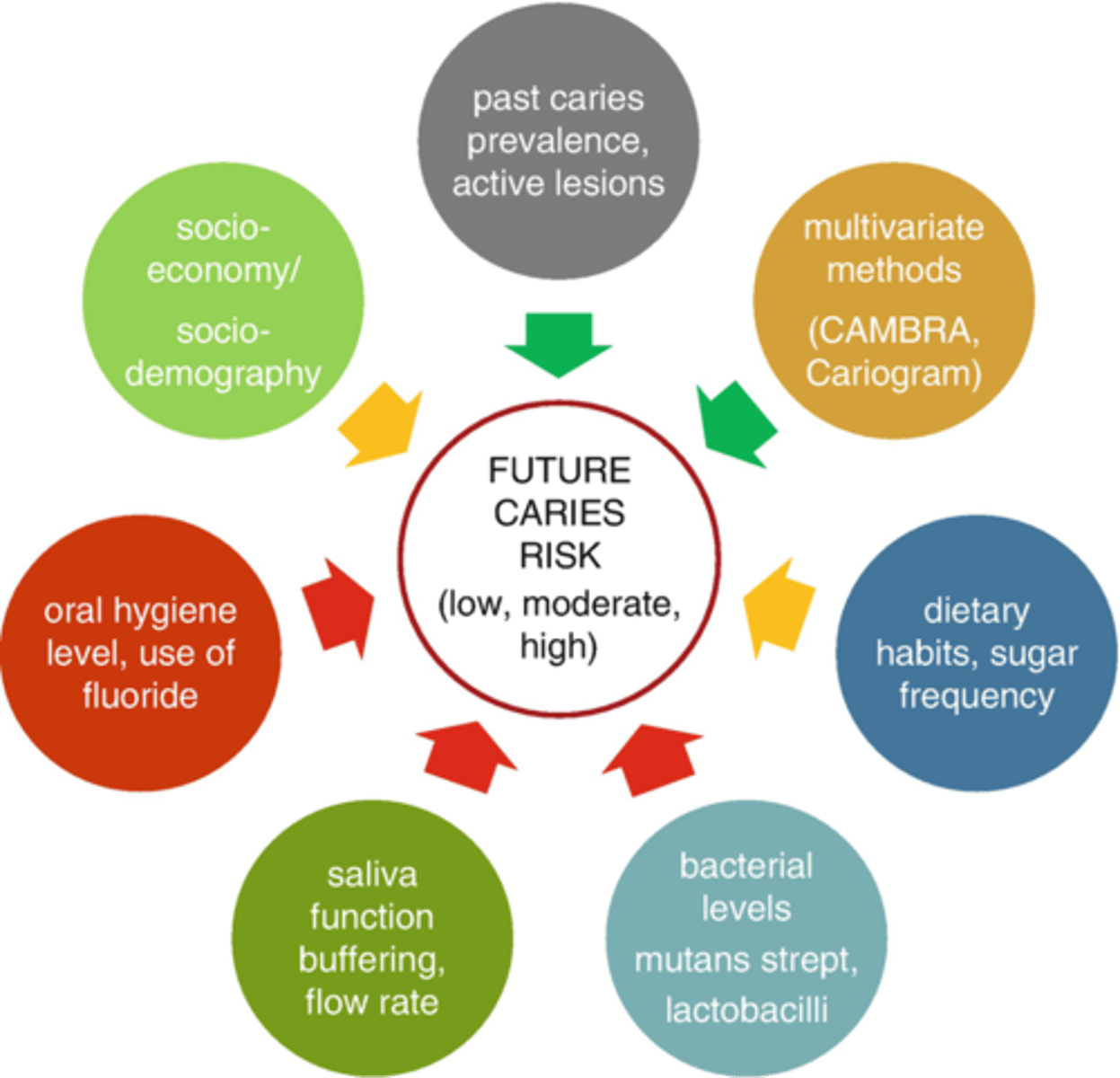
Dental Caries Risk Level
- adults and children different
CRA= Low, moderate or high. Enter on grade sheet for each patient.
dental hygiene diagnosis
- Part of Process of Care
- Provides the Basis for dental hygiene care plan
- Basis for Diagnosis: interview data (chief complaint, social, med/dental history), physical assessment data (perio chart, clinical exam, dental chart), radiographic series
- diagnostic statements: development of care plan focusing on education, oral self-care, prevention, dental hygiene treatment within the scope of DH practice and referral
examples of dental hygiene diagnostic statements
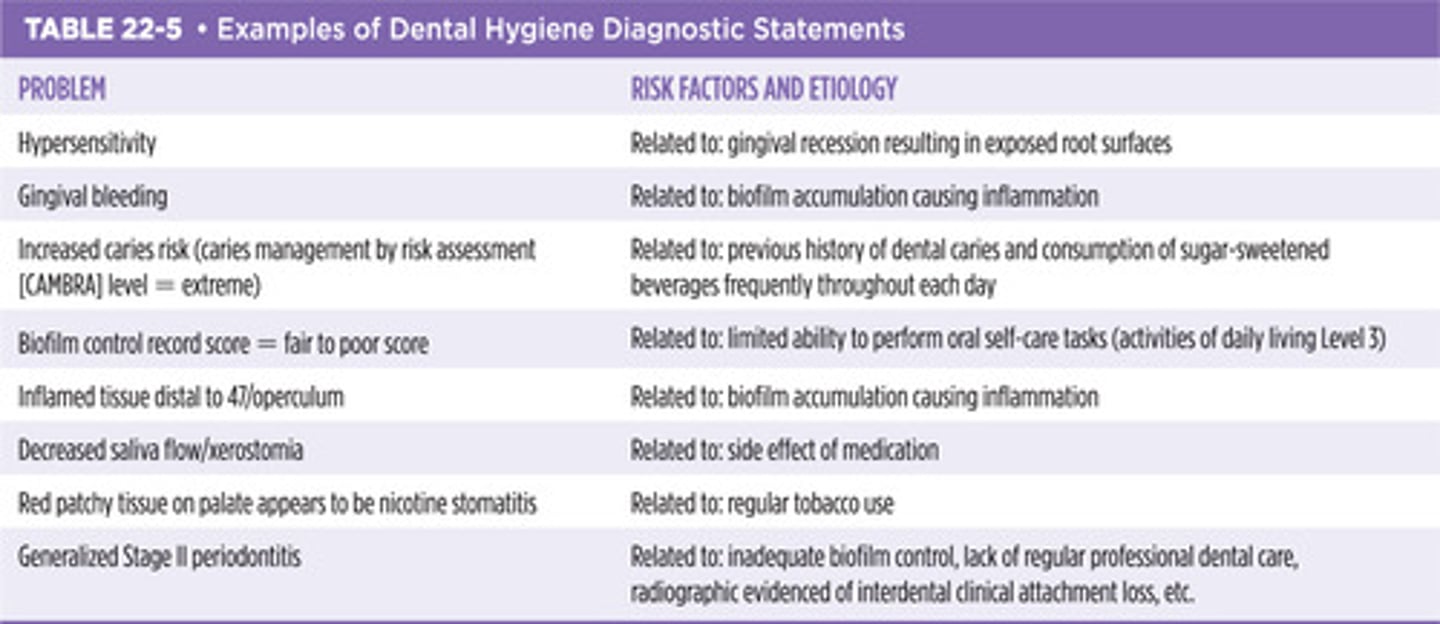
Factors in Assigning Prognosis
- Individual tooth prognosis: good, fair, poor, questionable, hopeless
- Overall prognosis: age, medical status, oral habits, oral health literacy, rate of disease progression
Putting It All Together
- Evaluation of Assessment Data->
- Selection of DH Interventions->
- Dental hygiene care plan->
Documentation
- Computerized or written in ink (black)
- Entries are dated and signed
- Standardized abbreviates
- teaching the patient
documentation: factors to teach the patient:
- Why disease control measures are learned before and monitored throughout dental hygiene care
- Oral disease prevention and oral health promotion relevant to patient's current level of healthcare literacy
- Long-term positive effects of comprehensive continuing care
Preparation of DH Care Plan
- Address needs of entire oral cavity
- Patient’s individual health factors
- Integrates three-part plan (periodontal/ gingival health, Dental Caries control, and other: ex. Modifiable risk factors, nutrition counseling, halitosis)
- Major influence on future oral health of patient
Preparation of DH Care Plan; description
Sequence of interventions
Preparation of DH Care Plan; rationale
Focus on individualized patient needs & risk factors
Preparation of DH Care Plan; objectives
- Addresses patient needs
- Flexible & realistic
- Treatment & OH goals in collaboration with patient
- Referrals
Preparation of DH Care Plan; Parts of care plan
1. Periodontal/Gingival health
2. Dental Caries Control
3. Other: Personal daily oral biofilm control, Eliminate modifiable risk factors, Desensitizing exposed dentin, Resolving halitosis, Nutritional counseling
Components of a Written Care Plan
- Demographic Data
- Assessment Findings & RiskFactors
- Periodontal Diagnosis & Status
- Caries Risk Status
- Diagnostic Statements
- Patient-Centered Oral HealthGoals
- Planned Interventions
- Expected Outcomes
- Evaluation Methods
- The Appointment Plan
- Re-evaluation
Role of the Patient
- Purpose: Willingness and ability of patient
- Procedure: Determine level of understanding of diseases, risk factors or OH behaviors
Pain & Anxiety Control; procedures
- Treat areas of pain/discomfort 1st
- If no Anxiety -Treat most severe area 1st
- Treat right, then left side
Sequencing & Prioritizing Patient Care
- Provide Evidence-Based, Individualized Patient Care
- Eliminate or Control Etiologic & Predisposing Disease Factors & Prevent Recurrence of Disease
- Eliminate Signs & Symptoms of Disease
Factors Affecting Sequence of Care
- Identify overall treatment & educate patient
- Outline series of appointments: urgency, existing etiologic factors, severity & extent of condition, individual patient requirements
Presenting Dental Hygiene Care Plan; to collaborating dentist
- purpose: Comprehensive treatment plan & Provide coordinated dental & dental hygiene statement to patient
- procedure: follow sequence & summarize demographic data, major systemic and dental health assessment findings, and risk factors
- Indicate suggested intervention strategies, goals, expected outcomes, and referrals
- Outline suggested appointment sequence & services
- Be prepared to give detail and answer questions
Explaining Plan to Patient
- Use radiographs, intraoral camera, motivational interviewing
- Purpose
- Informed consent patient’s role
- Reinforce
- Procedure
- Face-to-face
- Appropriate terminology
- educate patient on: systemic link & oral disease, and recommended DH services, appt. sequence, expected outcomes, referrals
- visual aids
- Engage patient in planning and setting goals
- Give detail & answer questions
- Obtained signed informed consent
Informed Consent
- Provide relevant information
- Aid in making optimal decisions for OH
- Allow shared decision making
- Can exist w/o written documentation
- Lacking even with signed document
- Informed of all treatment options, chooses Tx option, and consents to follow recommendations
- Provide written documentation
- informed refusal: autonomy & informed refusal of care
- additional considerations: cultural differences & age/disability
-documentation