CR1 Intro to Dental Anatomy
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
What are the first set of teeth called?
Primary (deciduous) dentition
When does the primary dentition begin to form
prenatally at around 14 weeks in utero
When is the primary dentition completed
postnatally at 3 years of age
What is the second set of teeth called
permanent (succedaneous) dentition
How long does the transition/mixed dentition period last
between 6 and 12 years old
What are the first to be shed in the primary dentition
the deciduous incisors
What are the first permanent teeth to emerge
The first permanent molars and the permanent incisors
What are the last primary teeth to be shed
the deciduous molars and canines
What are the last permanent teeth to emerge
the permanent canines, premolars, and second molars
When is the permanent dentition complete
around 14-15 years of age
EXCEPTION: third molars usually emerge between 18-25 years old
How many teeth are in both the primary and permanent dentition
20 in the primary
32 in the permanent
What is the dental formula for the mammalian primary dentition
For each half arch:
2 Incisors on the top, 2 on the bottom
1 canine on the top, 1 on the bottom
2 molars on the top 1 on the bottom
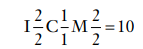
What is the formula for the mammalian permanent dentition
For each half arch:
2 incisors on the top, 2 on the bottom
1 canine on the top, 1 on the bottom
2 premolars on the top, 2 on the bottom
3 molars on the top, 3 on the bottom
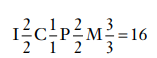
Complete the “universal” system of notation for the primary dentition
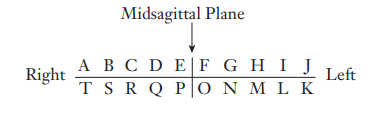
Complete the Zsigmondy/Palmer system notation for the primary dentition
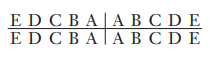
Complete the universal system notation for the permanent dentition
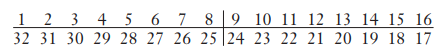
Complete the Zsigmondy/Palmer notation for the permanent dentition
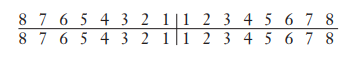
Complete the Federation Dentaire Internationale (FDI) system notation for primary teeth
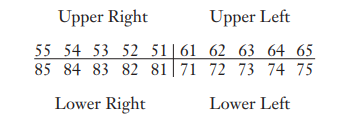
Complete the Federation Dentaire Internationale (FDI) system notation for permanent teeth
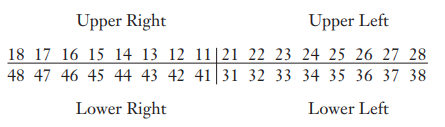
What is the crown covered in
Enamel
What is the root covered in
cementum
Where do the crown and root meet
at the cementoenamel junction (AKA cervical line)
What makes up the main bulk of the tooth
dentin
What makes up the pulp cavity
pulp chamber + pulp canal
pulp chamber is the crown of the tooth
pulp canal is in the root of the tooth
What are the four tissues of the tooth
enamel
dentin
cementum
pulp
Enamel, dentin, and cementum are known as what type of tissues
hard tissues
Pulp is known as what type of tissue
soft tissue
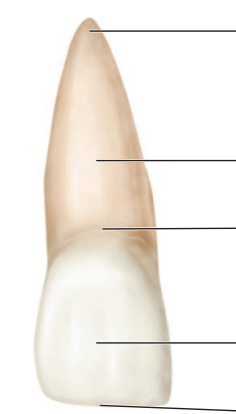
Label the following parts of an incisor
A: apex of root
R: root
CL: cervical line/cementoenamel junction
C: crown
IE: incisal edge/incisal ridge
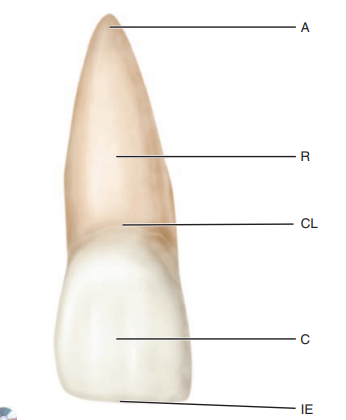
What is the portion of the tooth that support the tooth
the alveolar process
What is the bone of the tooth socket called
alveolus
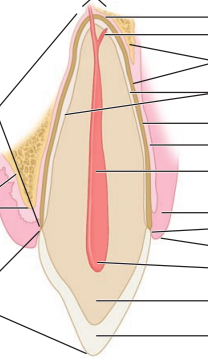
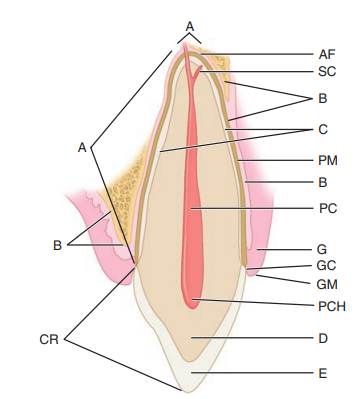
Label the longitudinal section of the anterior tooth
A: Apex
AF: apical foramen
SC: supplementary canal
B: bone
C: cementum
PM: periodontal ligament
PC: pulp canal
G: gingiva
GC: gingival crevice
GM, gingival margin
PCH, pulp chamber
D, dentin
E, enamel
CR, crown
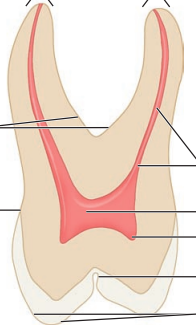
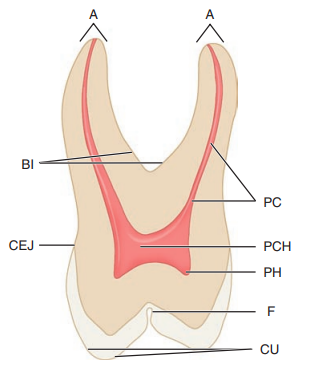
Label the longitudinal section of a posterior tooth
A, Apices
PC, pulp canal
PCH, pulp chamber
PH, pulp horn
F, fissure
CU, cusp
CEJ, cementoenamel junction
BI, bifurcation of roots
How many surfaces do the crowns of incisors and canines have
4 surfaces and 1 ridge
How many surfaces are on the crowns of premolars and molars
5 surfaces
What are the surfaces of the incisors and canines called
labial surface
buccal surface
lingual surface
incisal surface (ridge)
mesial/distal surface
labial+buccal = facial surfaces
mesial/distal = proximal surfaces
What are the surfaces of the premolars and molars called
labial surface
buccal surface
lingual surface
occlusal surfaces
mesial/distal surface
labial+buccal = facial surfaces
mesial/distal = proximal surfaces
Label the sagittal section of the maxillary incisor
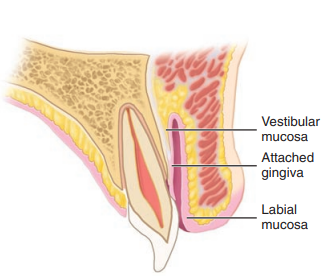
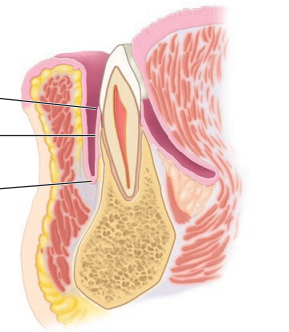
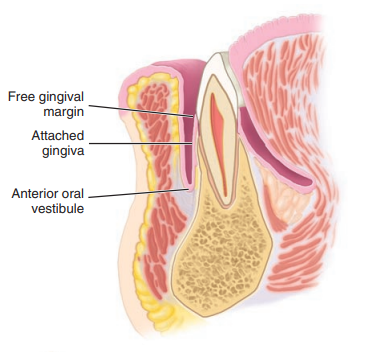
Label the sagittal section of the mandibular incisor
Cusp
an elevation or mound on the crown portion of the tooth
makes up part of the occlusal surface
Tubercle
smaller elevation on a portion of the enamel formed by extra formation of enamel
Cingulum
the lingual lobe of an anterior tooth
makes up the bulk of the cervical third of the tooth
Ridge
any linear elevation on the surface of a tooth
Marginal Ridges
rounded borders of enamel that form the mesial and distal margins of tooth
Triangular ridges
descend form tips of cusps of premolars and molars toward central part of the occlusal surface
Transverse ridge
formed by the joining of a buccal and lingual triangular ridge
Oblique ridge
a ridge crossing obliquely the occlusal surfaces of maxillary molars and formed by the union of the triangular ridge of the distobuccal cusp and the distal cusp ridge of the mesiolingual cusp
Lingual fossa
concavity on the lingual side of an incisor
Central fossae
occlusal surface of molars formed by converging ridges at a central point
Triangular fossae
found on molars and premolars on the occlusal surfaces mesial/distal to the marginal ridges
Sulcus
a long depression between the ridges and cusps of a tooth
Developmental groove
shallow groove between the primary parts of the crown or root
Supplemental groove
shallow depression on the surface of a tooth BUT does not mark the junction of primary parts
Buccal/Lingual grooves
developmental grooves on the buccal and lingual surfaces of posterior teeth

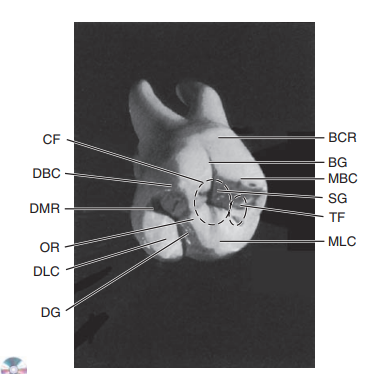
Label the landmarks on the first maxillary molar
BCR, Buccocervical ridge
BG, buccal groove
MBC, mesiobuccal cusp
SG, supplemental groove
TF, triangular fossa
MLC, mesiolingual cusp
DG, developmental groove
DLC, distolingual cusp
OR, oblique ridge
DMR, distal marginal ridge
DBC, distobuccal cusp
CF, central fossa
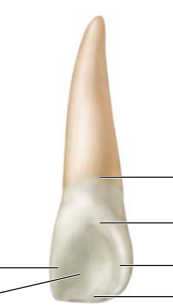
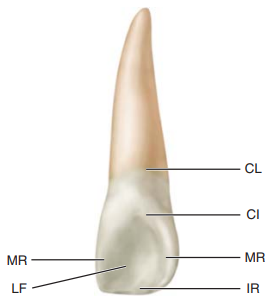
Label the landmarks of the maxillary lateral incisor
CL, Cervical line
CI, cingulum (also called the linguocervical ridge)
MR, marginal ridge
IR, incisal ridge
LF, lingual fossa

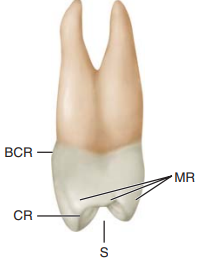
Label the landmarks of the maxillary first premolar
MR, Marginal ridge
S, sulcus traversing occlusal surface
CR, cusp ridge
BCR, buccocervical ridge
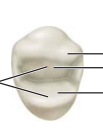
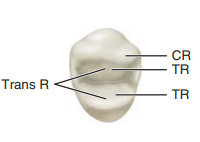
Label the occlusal view of the first premolar
CR, Cusp ridge
TR, triangular ridges
Trans R, transverse ridge
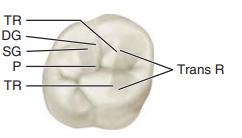
Label the occlusal view of the first molar
Trans R, Transverse ridge
TR, triangular ridge
P, pit formed by junction of developmental grooves
SG, supplemental groove
DG, developmental groove
TR, triangular ridge
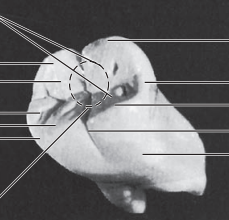
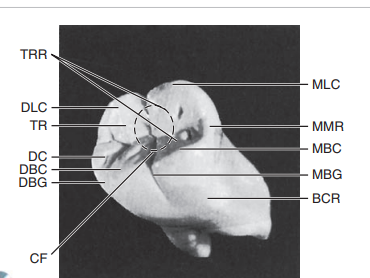
Label the mandibular first molar
MLC, Mesiolingual cusp
MMR, mesial marginal ridge
MBC, mesiobuccal cusp
MBG, mesiobuccal groove
BCR, buccocervical ridge
CF, central fossa
DBG, distobuccal groove
DBC, distobuccal cusp
DC, distal cusp
TR, triangular ridge
DLC, distolingual cusp
TRR, transverse ridge
Pits
pinpoint depressions at the junction of developmental grooves or at terminals of grooves
Central pit
pit in central fossa of molars where developmental grooves join
Lobe
primary formation in the development of the crown
Mamelon
any of the three rounded protuberances on the incisal ridges of newly erupted incisors
How many roots do anterior teeth have
one
Maxillary second premolars and mandibular first and second premolars have how many roots
one
How many roots do maxillary premolars have
two (buccal and lingual)
How many roots do mandibular molars have
two (mesial and distal)
How many roots do maxillary molars have
three (mesiobuccal, distobuccal, lingual)
What are the 3 different ways that a tooth crown can be divided
inciso/occlusocervically
mesiodistally
labio/buccolingually
How is the crown of the molar/premolar divided (occlusocervically)
occlusal third
middle third
cervical third
How is the root of any tooth divided (horizontally)
cervical third
middle third
apical third
How is the crown of the molar/premolar divided (buccolingually)
buccal third
middle third
lingual third
How is the crown of the incisor divided (incisocervically)
incisal third
middle third
cervical third
how is the crown of the incisor divided (labiolingually)
labial third
middle third
lingual third
How are the crowns of all teeth divided (mesiodistally)
mesial third
middle third
distal third
Line angle
the junction of two surfaces of a tooth
What are the line angles of the anterior teeth
mesiolabial
distolabial
mesiolabial
distolabial
labioincisal
linguoincisal
What are the line angle of the posterior teeth
mesiobuccal
distobuccal
mesiolingual
distolingual
mesio-occlusal
disto-occlusal
bucco-occlusal
linguo-occlusal
Point angle
formed by the junction of three surfaces
What are the point angles of the anterior teeth
mesiolabioincisal
distolabioincisal
mesiolinguoincisal
distolinguoincisal
What are the point angles of the posterior teeth
mesiobucco-occlusal
distobucco-occlusal
mesiolinguo-occlusal
distolinguo-occlusal
Summary of Maxillary teeth measurements for drawing/carving teeth
Note: in mm
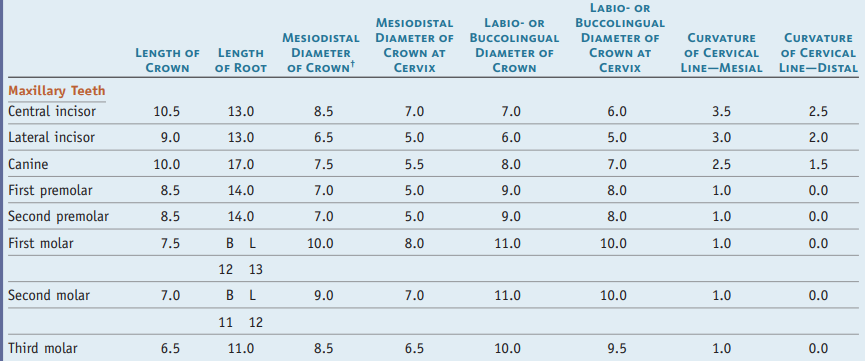
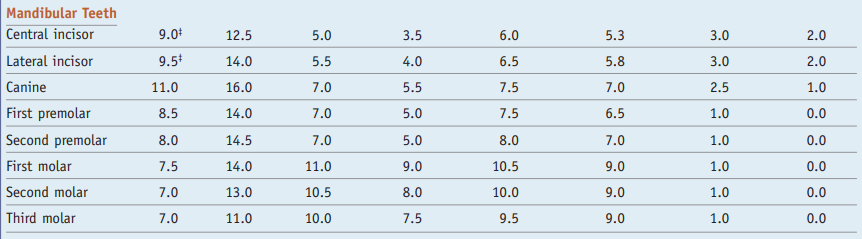
Summary of Mandibular teeth measurements for drawing/carving teeth