Nervous System: Neurons, Synapses, and Receptor Signaling
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Neurons
Cells that transmit electrical and chemical signals in the nervous system.
Morphology
The study of the form and structure of neurons.
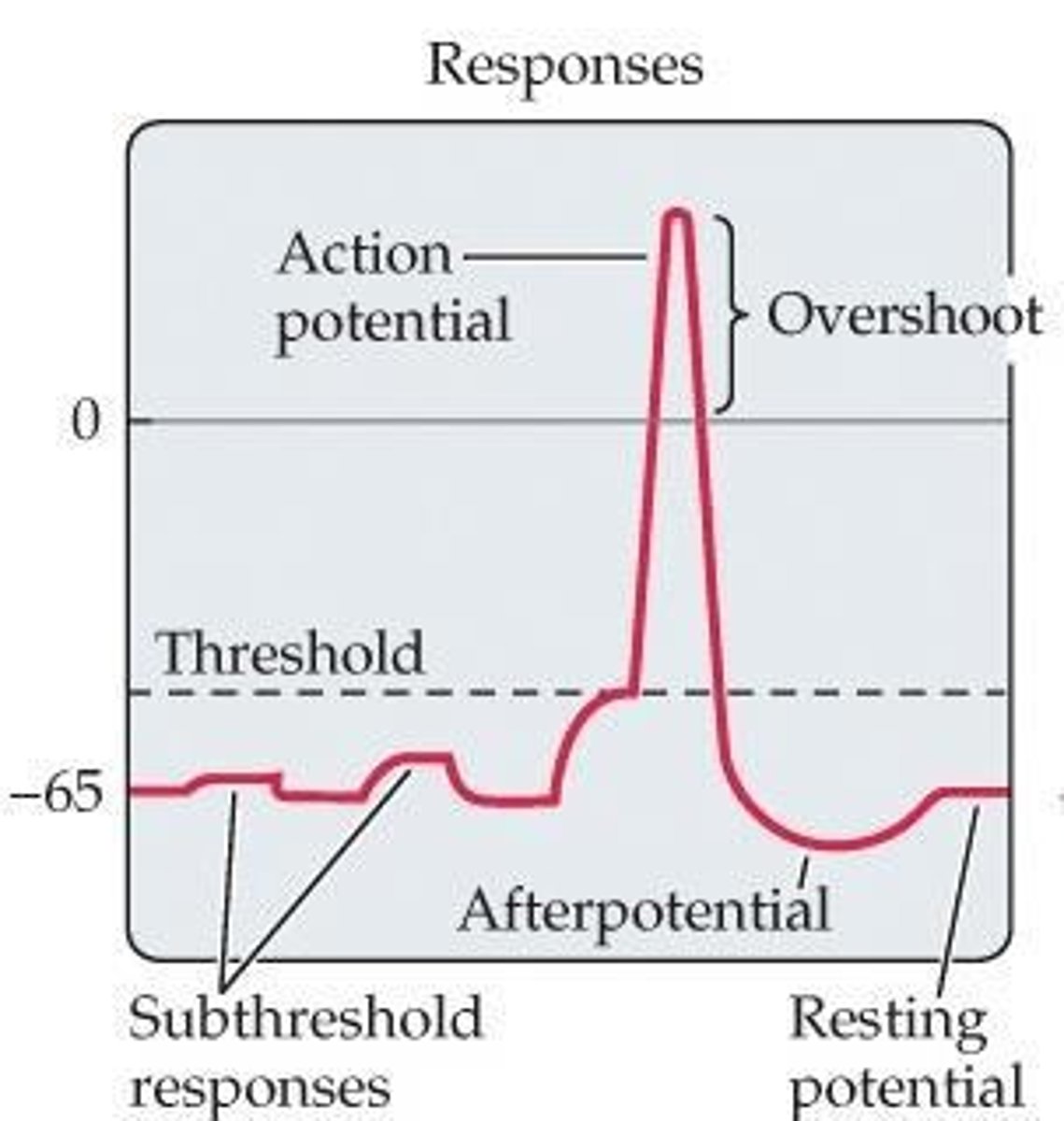
Resting membrane potential
The electrical charge difference across the neuronal membrane when the neuron is not actively transmitting signals, typically around -70 millivolts (mV).
Local potentials
Changes in membrane potential that occur in the dendrites and soma of a neuron, including excitatory post-synaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory post-synaptic potentials (IPSPs).
Action potentials
Rapid changes in membrane potential that propagate along the axon of a neuron when the threshold is reached (approximately -40 mV).
Synapses
Junctions between neurons where neurotransmitters are released and received.
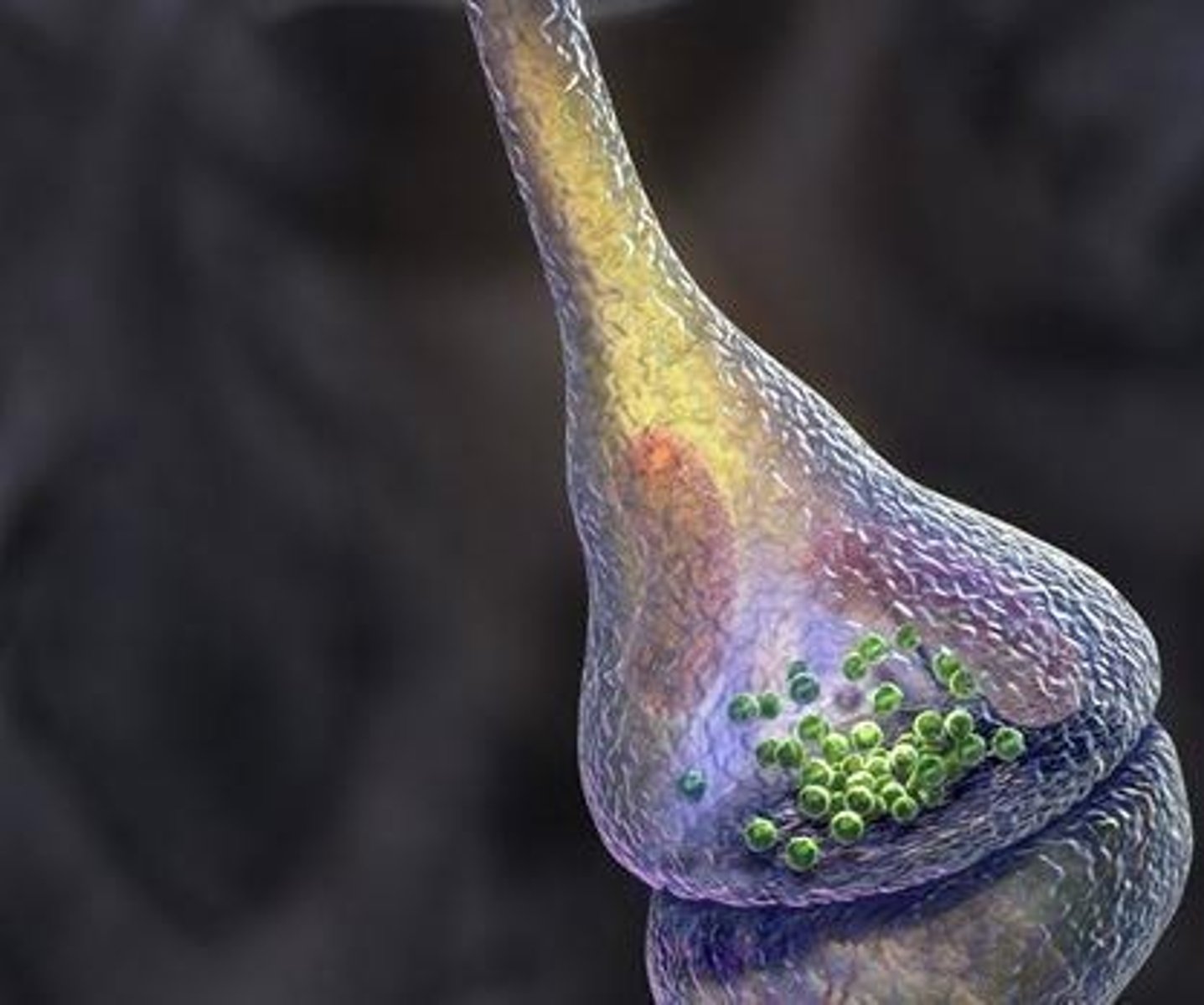
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that transmit signals across a synapse from one neuron to another.
Classical neurotransmitters
Traditional types of neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine, dopamine, and serotonin.
Peptide neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters composed of chains of amino acids, such as endorphins.
Lipid neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters derived from lipids, such as endocannabinoids.
Gas neurotransmitters
Gaseous signaling molecules, such as nitric oxide, that can diffuse across membranes.
Synthesis of neurotransmitters
The process of creating neurotransmitters, including classical NTs and neuropeptides, and storing them in vesicles.
Release of neurotransmitters
The process involving calcium influx, vesicle fusion, and diffusion of neurotransmitters across the synaptic cleft.
Inactivation of neurotransmitters
The process by which neurotransmitters are broken down by enzymes or taken back up by transporters.
Retrograde transmitters
Signaling molecules that travel backward across the synapse, including gases and lipids.
Dendritic spines
Small protrusions on dendrites where synapses are located.
Ion concentrations at resting potential
The distribution of ions such as Na+, K+, Ca++, and Cl- that create the resting membrane potential.
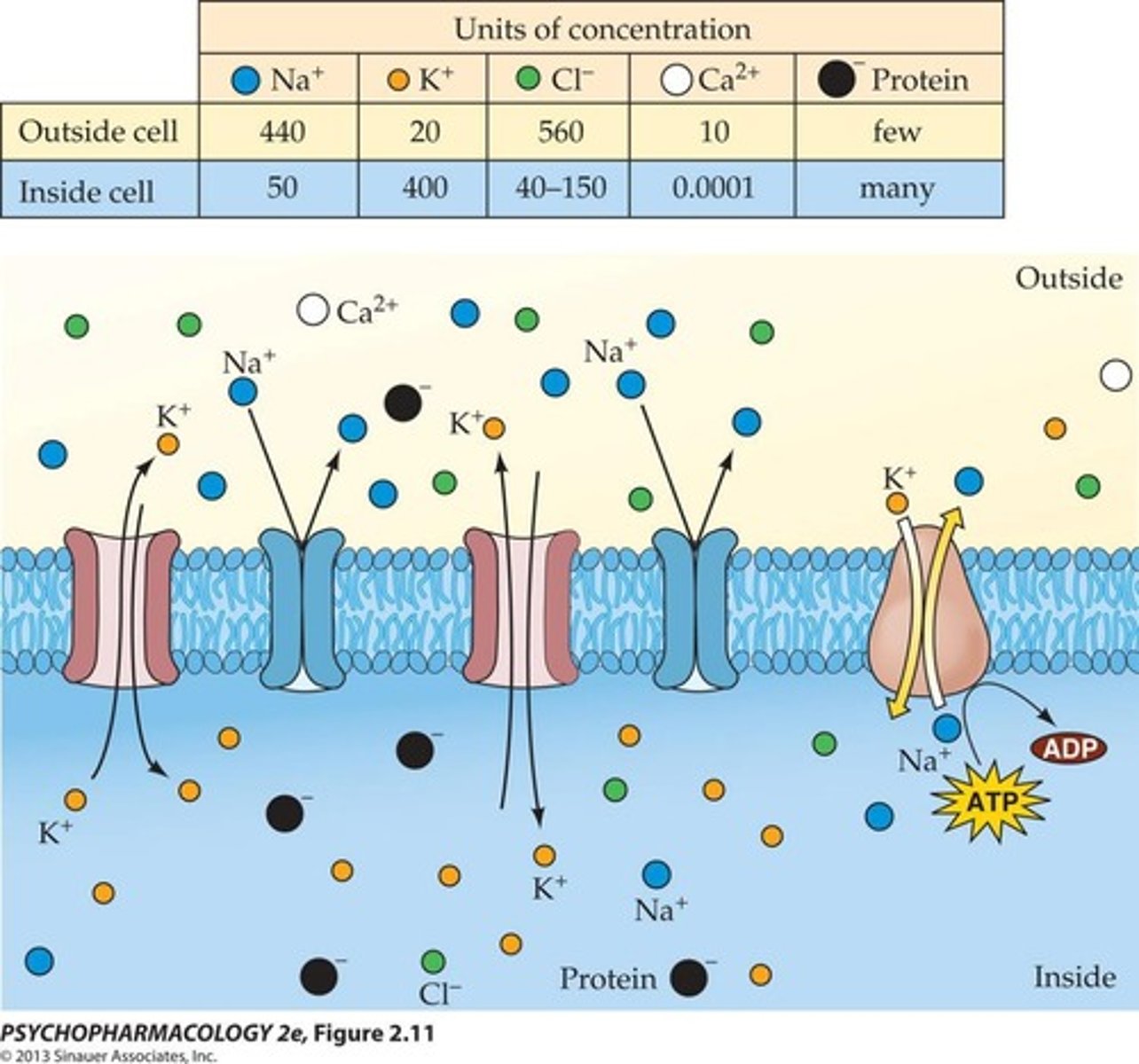
Equilibrium potential
The membrane potential at which the concentration gradient and electrostatic pressure for an ion are balanced.
Ligand-gated ion channels
Ion channels that open in response to the binding of a neurotransmitter.
Voltage-gated ion channels
Ion channels that open in response to changes in membrane potential.
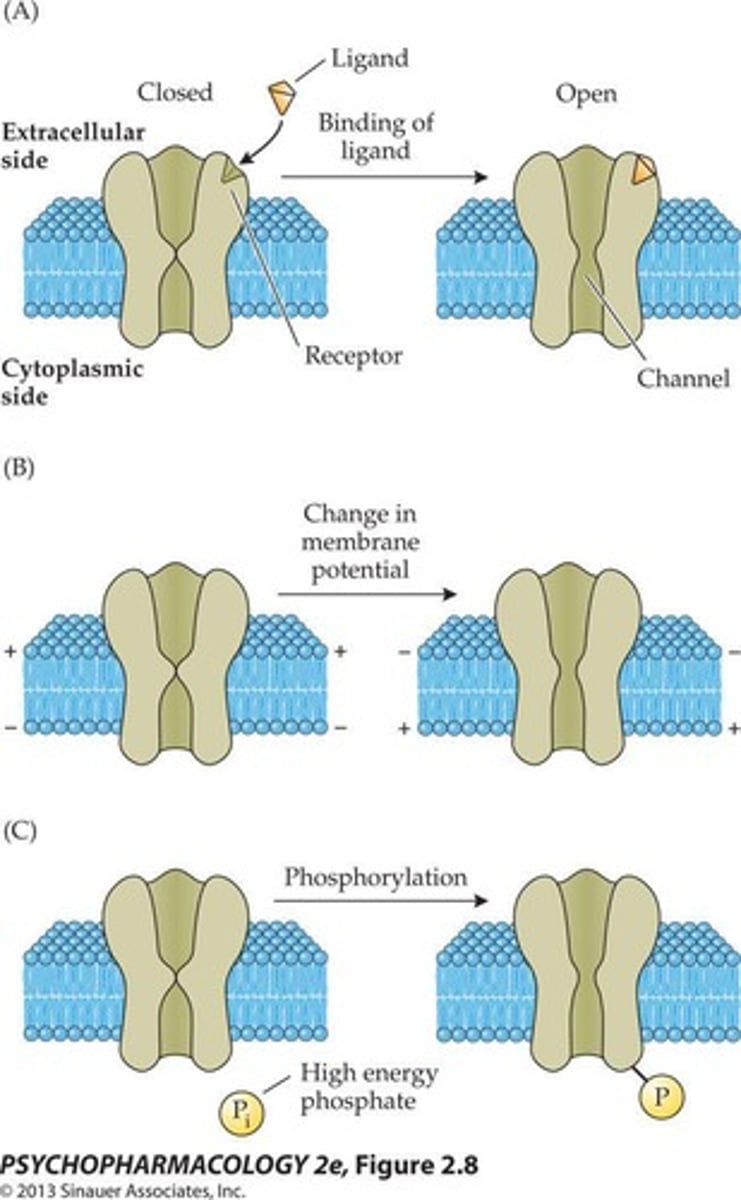
Phosphorylation
The addition of a phosphate group to a molecule, often mediated by second messengers.
Inhibitory post-synaptic potential (IPSP)
A hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane caused by the opening of K+ or Cl- channels.
Excitatory post-synaptic potential (EPSP)
A depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane caused by the opening of Na+ channels.
Threshold
The membrane potential that must be reached to trigger an action potential, approximately -40 mV.
Action potential
Summation of local potentials
IPSP
Inhibitory post-synaptic potential, which involves hyperpolarization.
EPSP
Excitatory post-synaptic potential, which involves depolarization.
Action potential frequency
An action potential can be very rapid - some cells can fire up to 1200 Hz.
Voltage-gated Na+ channels
Conduct the action potential down the axon through saltatory conduction.
Synapse
Site of action for most psychoactive drugs; to clasp or join (Greek).
Neuromuscular junction (NMJ)
Neuronal synapses onto muscle, primarily involving acetylcholine.
Axodendritic synapse
A type of synapse where the axon connects to a dendrite.
Axosomatic synapse
A type of synapse where the axon connects to the soma (cell body).
Axoaxonic synapse
A type of synapse where the axon connects to another axon.
Presynaptic side of synapse
Contains synaptic vesicles that release neurotransmitter upon action potential.
Postsynaptic side of synapse
Contains receptors that respond to neurotransmitters.
Chemical synapses
Involve the release of neurotransmitters (NTs) to transmit signals.
Non-classical neurotransmitters
Include neuropeptides (e.g., opioids), lipids (e.g., endocannabinoids), and gases.
Neurotransmitter synthesis
The process of creating neurotransmitters in the neuron.
Neurotransmitter release
The process by which neurotransmitters are released into the synapse.
Neurotransmitter inactivation
The process by which neurotransmitters are removed or degraded after their action.
Enzymes
Catalyze chemical reactions and typically end in -ase (e.g., hydrolase, transferase).
Catecholamines
Include dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine, synthesized from tyrosine.
Neuropeptide synthesis
Neuropeptides are synthesized in the cell body and transported down the axon.
Vesicular transporters
Move transmitters into vesicles using an electrochemical gradient.
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels
Channels that open in response to membrane depolarization, allowing Ca2+ ions to enter the cell.
Ca2+ influx
The entry of calcium ions into the cell, which triggers neurotransmitter release.
Vesicle fusion
The process by which neurotransmitter-containing vesicles merge with the cell membrane to release their contents.
Exocytosis
The process of releasing neurotransmitters from vesicles into the synaptic cleft.
SNARE proteins
Proteins that mediate the fusion of vesicles with the cell membrane during neurotransmitter release.
Botulinum toxin
A neurotoxin that cleaves SNARE proteins, leading to paralysis at the neuromuscular junction.
LD50 of Botulinum toxin
Approximately 1 ng/kg, indicating the lethal dose for 50% of the population.
Vesicle recycling
The process by which vesicle membrane is retrieved from the terminal membrane and refilled with neurotransmitters.
Diffusion of neurotransmitters
The process by which neurotransmitters spread across the synaptic cleft to bind to receptors.
Post-synaptic neuron
The neuron that receives neurotransmitter signals at the synapse.
Autoreceptors
Receptors located on the presynaptic neuron that provide feedback about neurotransmitter release.
Negative feedback
A regulatory mechanism where autoreceptors modulate neurotransmitter release based on the neuron's activity.
Enzymatic degradation
The breakdown of neurotransmitters by enzymes, such as acetylcholine esterase (AChE).
Plasma membrane transporters
Proteins that remove neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft by reuptake into the presynaptic neuron or glia.
Dopamine transporter (DAT)
A transporter that removes dopamine from the synaptic cleft.
Norepinephrine transporter (NET)
A transporter that removes norepinephrine from the synaptic cleft.
Excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT)
A transporter that removes excitatory amino acids from the synaptic cleft.
Retrograde messengers
Signaling molecules, such as gases and lipids, that transmit signals from the postsynaptic to the presynaptic cell.
Anterograde transmission
Signaling from presynaptic to postsynaptic cells, the typical direction of neurotransmission.
Ionotropic receptors
Receptors that are ligand-gated ion channels, allowing ions to flow through upon neurotransmitter binding.
Metabotropic receptors
G protein-coupled receptors that initiate intracellular signaling cascades upon neurotransmitter binding.
Ionotropic receptors structure
Comprised of 4-5 subunits (separately encoded proteins) bound together to form an ion channel.
Ionotropic receptors properties
Fast and rapidly-reversible.
Ionotropic receptors effects
After ligand is bound, ion channel opens, and ions flow down electrochemical gradient.
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR)
An example of an ionotropic receptor that gates a cation channel; agonists include nicotine.
Antagonists of nAChR
Various poisons such as alpha-bungarotoxin and curare.
GABAA receptor
An ionotropic receptor that gates a chloride ion channel; affected by sedative-hypnotics.
Metabotropic receptors structure
Comprised of 1 subunit with 7 transmembrane domains, coupled to intracellular G protein.
Metabotropic receptors properties
Slower and longer lasting effects compared to ionotropic receptors.
Metabotropic receptors effects
After ligand is bound, the intracellular G protein causes changes via an effector and second messengers.
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs)
A very large family of receptors with over 367 GPCRs in humans that bind endogenous ligands.
G protein signaling
Can alter various cellular processes via an ion channel or a second messenger system.
Second messenger system sequence
1. Activation of G protein; 2. Change in activity of effector enzyme; 3. Change in second messenger levels; 4. Activation of protein kinase; 5. Phosphorylation of a substrate protein.
G protein structure
Includes an α subunit and βγ subunit complex.
Gs protein
A stimulatory G protein that activates adenylyl cyclase and increases cAMP.
Gi protein
An inhibitory G protein that inhibits adenylyl cyclase and decreases cAMP.
Gq protein
A G protein that activates phospholipase C, leading to the production of IP3 and DAG.
Dopamine receptors D1
Coupled to Gs proteins, stimulate adenylyl cyclase, and increase cAMP, resulting in cellular excitation.
Dopamine receptors D2
Coupled to Gi proteins, inhibit adenylyl cyclase, and decrease cAMP, resulting in cellular inhibition.
Glutamate
A neurotransmitter that has both excitatory and inhibitory receptors.
GABA
A neurotransmitter that has both excitatory and inhibitory receptors.
Acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that has both excitatory and inhibitory receptors.
Dopamine
A neurotransmitter that has metabotropic receptors.
Norepinephrine
A neurotransmitter that has metabotropic receptors.
Serotonin
A neurotransmitter that has metabotropic receptors.
Neuropeptides
A class of neurotransmitters that includes opioids and has metabotropic receptors.
Endocannabinoids
A class of neurotransmitters that has metabotropic receptors.
Protein kinases
Modulated by many second messengers and modify other proteins by adding phosphate groups to them.
Protein phosphatases
Enzymes that dephosphorylate proteins.
Transcription factors
A family of proteins that bind to regulatory sites on genes to promote or suppress transcription of DNA to mRNA.
Immediate early genes (IEG)
Genes that are the first to be transcribed into mRNA quickly after neuronal activation.
c-Fos
A transcription factor and an immediate-early gene used as a marker of neuronal activation.
Epigenetics
The study of changes in gene expression that can be passed on to future generations.
Dutch Hongerwinter
A historical event where massive food shortage led to epigenetic changes affecting future generations.
Connectome
A comprehensive map of connections within the nervous system.