Prokaryotes and Viruses
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Bacterial Cell: Diagram
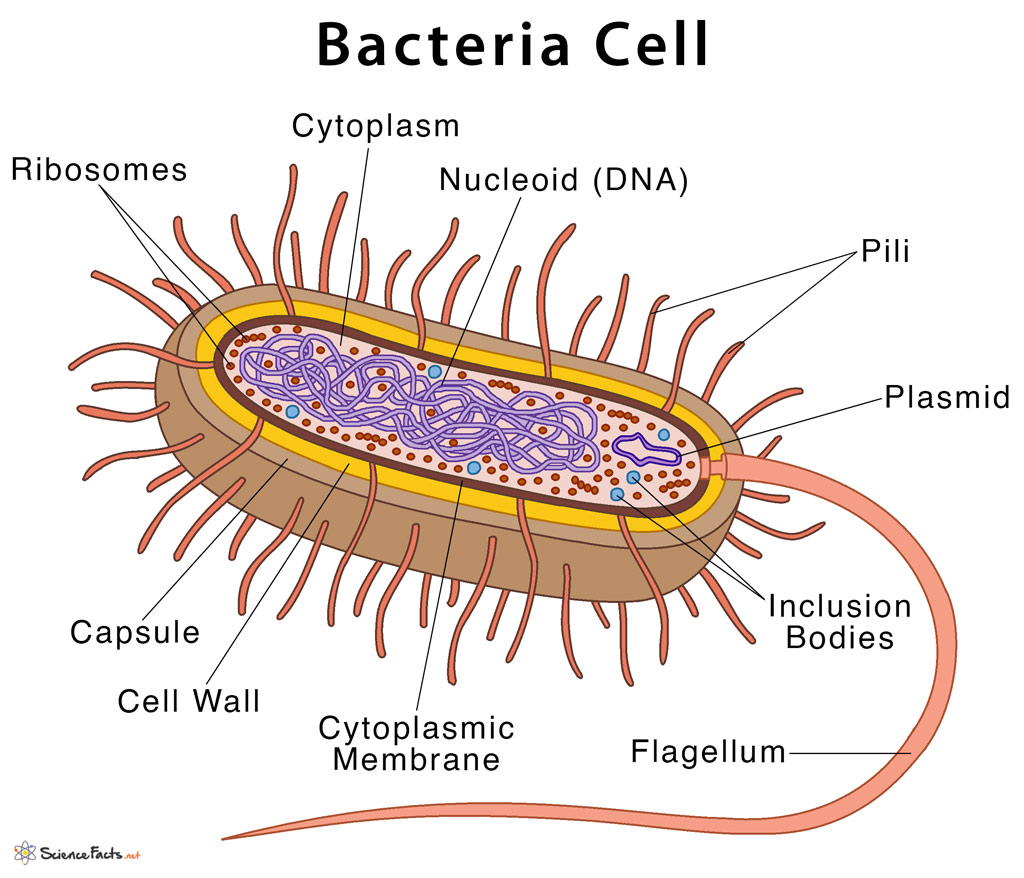
Capsule
Layer of polysaccharides (sometimes proteins), protects the bacterial cell and its often associated with pathogenic bacteria because it serves as a barrier from phagocytosis
Mesosome
Tightly folded region of the cell membrane containing all the membrane bound proteins required for respiration
Pilli
Little hairs to allow the bacteria to stick together
Plasmid
Small circular piece of DNA
Cell Wall
10-80nm thick
Made of murein
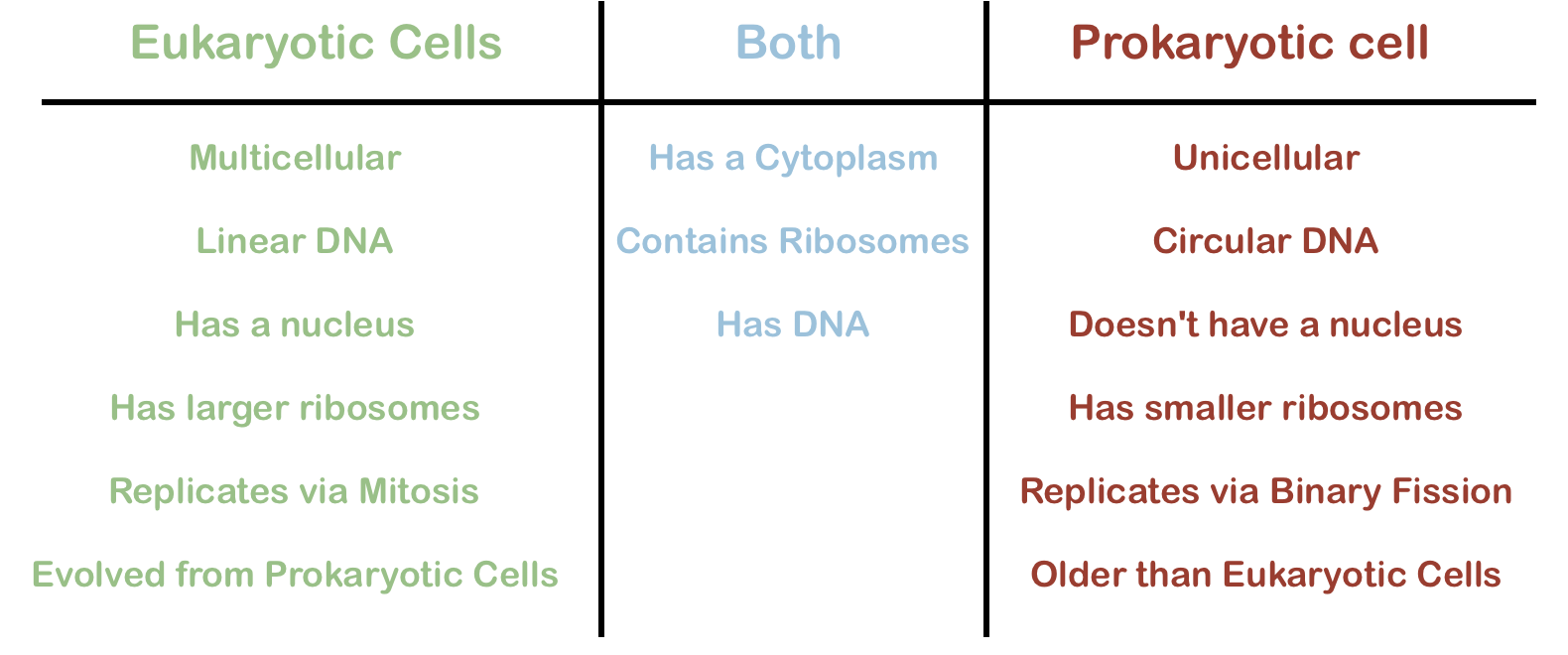
Similarities and Differences between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic cells
Virus (HIV) Diagram
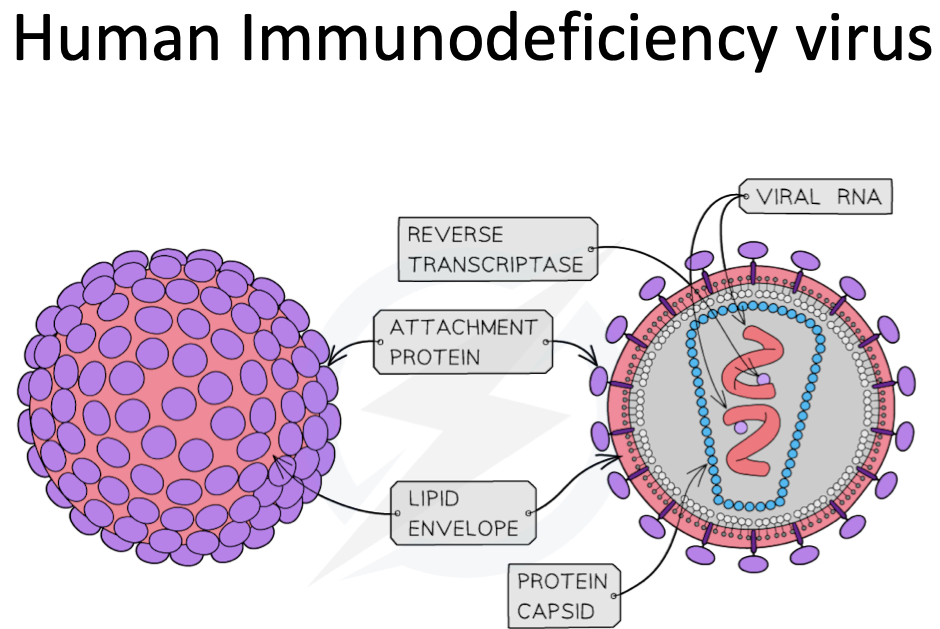
Virus
Acellular
Non-living particles
Smaller than Bacteria ranging from 20-399nm
Contains nucleic acid either as DNA or RNA
Can only replicate inside host cells
Nucleic acid is enclosed inside a protein coat called a capsid
Some viruses have a lipid envelope
Some viruses have attachment protiens on their envelope which allow the virus to attach to a host cell
Name the 2 Virus replication cycles
Lytic cycle
Lysogenic cycle
Lytic Cycle
The virus attaches to the host cell, where it binds to the receptor
The virus can inject either its DNA or RNA, depending on what kind of genetic material it has, into the cell
Some types of viruses are actually taken inside the cell themselves
It takes the genetic material from the virus and it starts following the instructions which tell the cell to make copies of the virus
Cell makes multiple copies of the virus causing the cell membrane to burst - the cell can’t survive without the cell membrane
The viral copies get out of the cell and infect other cells
Viruses assemble
Lysogenic Cycle
Viruses inject their genetic material but it stays hidden in the host’s genetic material
When the host makes new cells, it replicates both its own genetic material and the viral genetic material
May trigger the Lytic cycle
Matrix
Fluid containing enzymes to help the virus survive
Protein Capsid
Encloses the nucleic acid
Lipid envelope
Protects Virus
Attachment Proteins
Helps virus bind to host cell