A&P 2 Practical #3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/195
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
196 Terms
1
New cards
Where does fertilization occur?
ampulla of fallopian tube
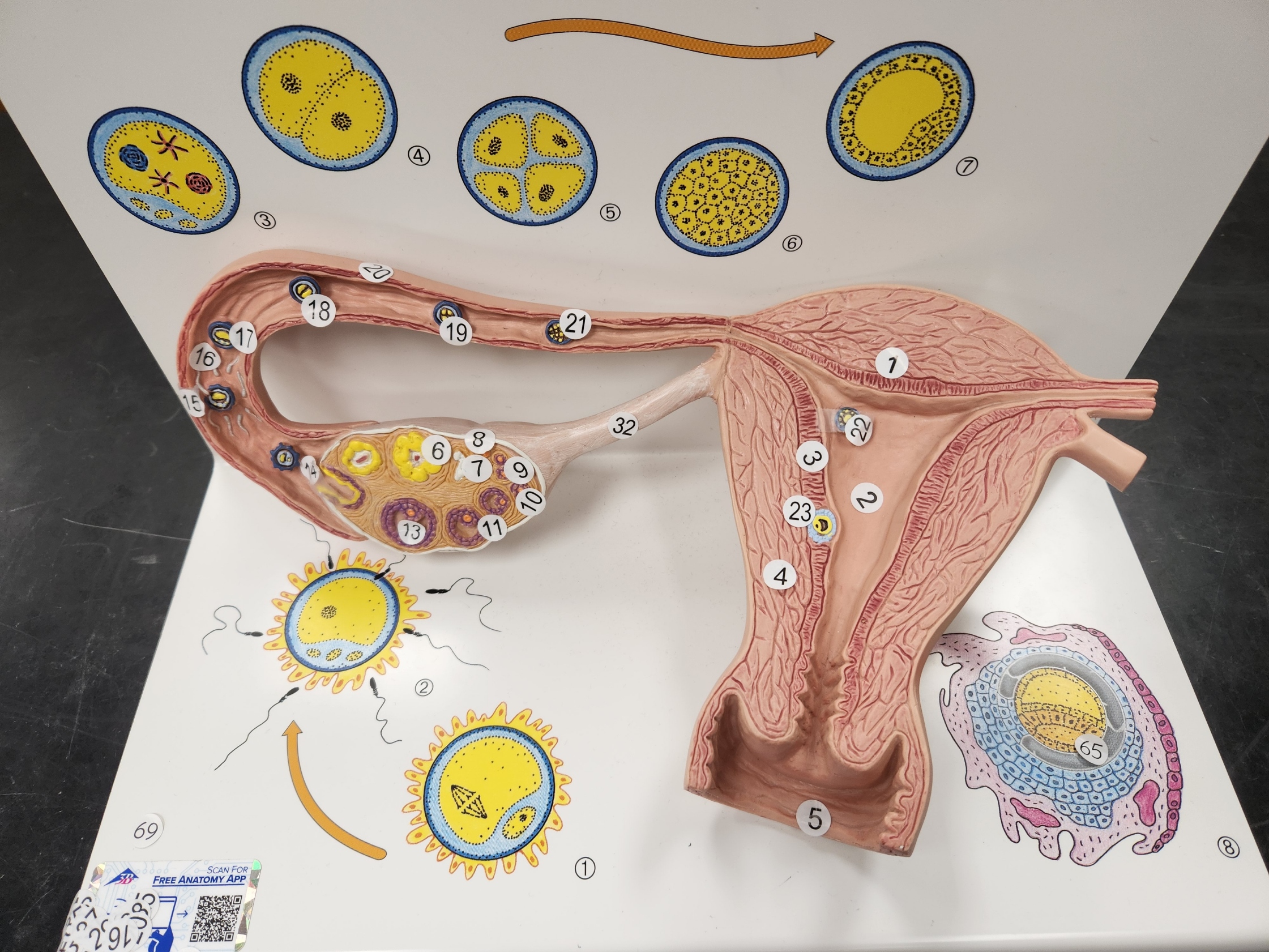
2
New cards
after the spermatozoa unites with the BLANK, it becomes BLANK
secondary oocyte; Ovum
3
New cards
the third stage of fertilization has two what?
pro-nuclei; one from mom and one from dad
4
New cards
blastomeres
two-cell stage
5
New cards
\#5 blastomeres
four-stage cells; each is still a individual blastomere
6
New cards
Morula
a solid ball of cells resulting from the division of a fertilized ovum, and from which a blastula is formed.
7
New cards
Formation of blastocyst
cells are divided into two groups:
8
New cards
the trophoblast is responsible for...
implantation
9
New cards
the embryoblast is responsible for...
forming the embryonic disc
10
New cards
First phase of the menstrual cycle
menstruation; the functional layer sheds; end of the luteal phase
11
New cards
what are the estrogen and progesterone levels in the menstruation phase?
both estrogen and progesterone levels have dropped
12
New cards
the second phase of the menstrual cycle?
proliferation; building up the endometrium in preparation for zygote implantation, during the follicular phase
13
New cards
what happens at the end of the proliferation phase of the menstrual cycle?
ovulation due to the LH surge
14
New cards
what is the third phase of the menstrual cycle?
secretory phase; the endometrium has a high blood supply
15
New cards
during the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle, levels of estrogen and progesterone are BLANK due to....
high; the corpus luteum secreting estrogen and progesterone
16
New cards
follicular phase of ovarian cycle
development of the follicle
17
New cards
what is the function of the follicle?
nourish the oocyte
18
New cards
luteal phase of ovarian cycle
the leftover of when the mature oocytes leave into the fallopian tube
19
New cards
what occurs in order for the early follicle to become a mid. follicle?
selection of the dominant follicle; negative feedback
20
New cards
how is the dominant follicle chosen?
if the follicle has a lot of FSH receptors (high affinity)
21
New cards
when the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary gland detect BLANK, they inhibit BLANK
high estrogen; FSH, LH, and GnRH
22
New cards
Late follicular phase and ovulation
Rising levels of estrogen cause the LH surge.
23
New cards
In the late follicular phase, the LH surge causes what?
a decrease in metalloproteases causing ovulation
24
New cards
in the Luteal phase, the BLANK secretes increased amounts of estrogen, progesterone, and inhibin. WHY?
corpus luteum; inhibit the development of other follicles due to a negative feedback system
25
New cards
the corpus albicans is the result of the corpus luteum being degraded, causing What?
no estrogen/ progesterone secretion; menstruation
26
New cards
LH surge causes
activation of metalloproteases that break apart the mature oocytes
27
New cards
how does the secondary oocytes get into the fallopian tube?
the fimbriae
28
New cards
what needs to take place in order for the fimbriae to sweep the secondary oocytes into the fallopian tube?
the break down of the layers of the follicle; theca cells and granulosa cells
29
New cards
theca cells secrete
androgens that will diffuse into the granulosa cells
30
New cards
granulosa cells use converts BLANK into BLANK
androgens; estrogen
31
New cards
estrogen production
the hypothalamus has GnRH that gets into the Anterior Pituitary gland which causes the release of FSH and LH. they travel to the Ovary and reach their target tissue- ovaries ( theca and granulosa cells); which will then produce estrogen
32
New cards
a primary oocyte is stuck in....
meiosis I (prophase I); still 2n
33
New cards
a primary oocytes has how many layers in the follicle?
just a single layer of granulosa cells
34
New cards
a secondary oocyte is ...
arrested in meiosis II (metaphase II)
35
New cards
the follicle of a secondary oocyte has how many layers?
a layer of granulosa cells and a layer of theca cells
36
New cards
when can a secondary oocyte become a mature oocytes?
when fertilization occurs, completing meiosis II creating a zygote
37
New cards
the mature follicle has how many layers?
it has granulosa cells, theca cells, and an antrum
38
New cards
During a male erection, the cavernous artery fill the BLANK causing the smooth muscles to BLANK, blocking BLANK return.
sinusoids; relax; venous
39
New cards
what nervous system controls the male erection?
parasympathetic; "rest and digest" or "feed and breed"
40
New cards
through the parasympathetic neuron, What neurotransmitter is released?
Acetylcholine (Ach.)
41
New cards
in order for the smooth muscle to relax, what is needed?
NO2 and the inhibition of Ca2+ entry
42
New cards
why do we need to inhibit Ca2+ from entering?
Ca2+ binds to troponin, which initiates the cross-bridge cycle allowing for contraction.
43
New cards
what is the significance of NO2?
it binds to the endothelial cell (lines blood vessels),
44
New cards
How does Viagra (sildenafil) work?
it targets an enzyme that degrades cGMP into 5' GMP (phosphodiesterase)
45
New cards
hormones secreted by anterior pituitary
* FSH
* LH
* ACTH
* TSH
* Prolactin
* GH
* LH
* ACTH
* TSH
* Prolactin
* GH
46
New cards
what is the target tissue of FSH and LH?
gonads; because of GnRH getting into the anterior pituitary through the hypophyseal portal system
47
New cards
site of spermatogenesis
seminiferous tubules
48
New cards
site of sperm maturation and storage
epididymis
49
New cards
LH Binds to which cells in males?
Leydig cells; synthesize testosterone
50
New cards
FSH binds cells in males?
Sertoli cells
51
New cards
how does negative feedback work in testosterone production?
when testosterone is at the optimal level, Sertoli cells secrete inhibin which inhibits GnRH
52
New cards
22/23 pairs of chromosomes are
autosomal chromosomes
53
New cards
the last pair of chromosomes are
sex chromosomes
54
New cards
Mitosis results in
2 diploid daughter cells with the same number and composition of chromosomes
55
New cards
Meiosis results in
4 haploid daughter cells
56
New cards
within the seminiferous tubules, the stem cells divide into...
Type A and Type B daughter cells
57
New cards
spermatozoa develop from..
spermatids
58
New cards
late spermatids have what?
they are connected by the cytoplasmic bridge
59
New cards
early spermatids still have the 4 haploid cells connected together they just dont have.... yet
tails
60
New cards
early spermatids develop from
secondary spermatocytes; completing meiosis II
61
New cards
going from primary to secondary spermatocytes...
a single diploid cell (1- meiosis I complete) into two haploid cells
62
New cards
acrosomes of sperm
Contain enzymes needed to penetrate the egg
63
New cards
midpeice of sperm
metabolic region containing mitochondria that produces ATP to move the tail
64
New cards
tail of sperm
locomotion portion with microtubules
65
New cards
during maturation of the sperm, the midpiece...
acquires Glut receptors, which use Glucose, Mannos, and Fructose from the accessory glands to produce ATP
66
New cards
accessory glands of male reproductive system
seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethral glands
67
New cards
the pathway of sperm to reach the secondary oocyte
Seminiferous Ducts (production), Rete Testes, Epididymis (maturation), vas deferens, ampulla of vas deferens, ejaculatory duct, prostatic urethra, spongey urethra, vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tube, secondary oocyte
68
New cards
glands responsible for the production of semen and function of each secretion
prostatic gland- milky, slightly acidic (part of sperm activation); Seminal gland- alkaline fluid with fructose and glucose; bulbourethral gland- provides lubrication for the glands penis during intercourse
69
New cards
during the male erection, blood flows through the cavernous artery and fills the BLANK with blood
sinusoids
70
New cards
the BLANK Nervous System sends a signal for the release of BLANK
Parasympathetic; Ach.
71
New cards
BLANK and BLANK are both critical to produce estrogen and testosterone
FSH and LH
72
New cards
BLANK binds to the Leydig cell for the synthesis of testosterone
LH
73
New cards
FSH binds to the Sertoli Cells for the synthesis of BLANK
ABP
74
New cards
during the synthesis of estrogen, LH binds to the BLANK to produce androgen that travels to the BLANK cells
theca cells; Granulosa
75
New cards
estrogen is synthesized when BLANK binds to the Granulosa cells
FSH
76
New cards
estrogen and testosterone are both derived from...
cholesterol
77
New cards
BLANK is a chemical messenger synthesized within endothelial cells using BLANK as it's starting material
Nitric Oxide; Arginine
78
New cards
NO2 initiates the male erection by targeting BLANK within the smooth muscle of the corpus cavernosum to prevent the entry of Calcium.
Guanate cyclase
79
New cards
Viagra targets the enzyme BLANK that prevents the degradation of BLANK, maintaining the secondary messenger system that closes calcium channels in trabecular smooth muscle.
phosphodiesterase ; cGMP
80
New cards
during oogenesis, the primary oocyte is a diploid cell that will become a BLANK after the completion of BLANK.
haploid; meiosis I
81
New cards
completion of meiosis I result in the production of \______ and the secondary oocyte
polar body
82
New cards
the secondary oocyte is arrested in \_____ until it is penetrated by a sperm cell that results in an \______ and \______
metaphase II; ovum; 2nd polar body
83
New cards
during spermatogenesis, the completion of meiosis I result in the production of \_____ secondary spermatocytes
haploid
84
New cards
secondary spermatocytes complete meiosis II which results in the production of \_______ early spermatids.
4 haploid
85
New cards
early spermatids become \_______ once they develop their tail.
late spermatids
86
New cards
primary follicle of ovary
two or more layers of cuboidal granulosa cells enclose the oocyte
87
New cards
secondary follicle of ovary
layers of granulosa cells and theca cells
88
New cards
mature follicle of the ovary
granulosa cells, theca cells, and an antrum
89
New cards
the establishment of the dominant follicle is due to \______ feedback mechanism that \______ the release of FSH.
negative; inhibits
90
New cards
increasing levels of estrogen during the late follicular phase results in \______ due to \________ surge that activates \________. this is the result of a \______ feedback system.
ovulation; LH; metalloproteases; positive
91
New cards
the ovary is anchored by.....
the ovarian ligament
92
New cards
Narrow part of fallopian tube near uterus
isthmus
93
New cards
ampulla of uterine tube
site of fertilization
94
New cards
- widest and longest part
95
New cards
infundibulum of uterine tube
between the ampulla and the fimbriae
96
New cards
function of urinary system
filters waste products out of the blood and removes them from the body
97
New cards
Wastes excreted by kidneys
ammonium and urea, creatinine, drugs
98
New cards
ammonium and urea are byproducts of \______
amino acid metabolism
99
New cards
Creatinine is a waste product of:
muscle metabolism
100
New cards
the urinary system regulates
nutrients/ ions, blood pH, and blood volume/pressure