Human Physiology - Test 2 Multiple Choice
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Vital capacity is:
A. The amount of air moved in and out of the lungs during normal breathing in the lungs.
B. The maximum amount of air that can be moved in and out of the lungs.
C. The amount of additional air that can be inhaled.
D. The amount of additional air that can be exhaled.
B. The maximum amount of air that can be moved in and out of the lungs.
Internal respiration
A. Moves CO2 out of the blood and O2 into the blood.
B. Is the exchange of gases between the tissues and the blood.
C. Moves CO2 into the blood and O2 out of the blood.
D. A and B are correct.
E. B and C are correct.
C. Moves CO2 into the blood and O2 out of the blood.
External respiration
A. Moves CO2 out of the blood and O2 into the blood.
B. Is the exchange of gases between the tissues and the blood.
C. Moves CO2 into the blood and O2 out of the blood.
D. A and B are correct.
E. B and C are correct.
D. A and B are correct.
The following data were obtained from individuals A and B:
Urine Osmolarity (mOsm/kg H2O) → 200(A) & 400(B)
Urine flow rate (mL/min) → 2.0(A) & 1.0(B)
Plasa Osmolarity (mOsm/kg H2O) → 290(A) & 280(B)
Which of the following statements is true?
A. The osmolar clearance is the same in both subjects but free-water clearances differ.
B. Free water clearance is positive for A and negative for B
C. Free water clearance is negative for A and positive for B
D. Free water clearance is positive for both A and B
E. Free water clearance is negative for both A and B
B. Free water clearance is positive for A and negative for B
Aldosterone would:
A. Enhance K and Na reabsorption
B. Reduce K and Na excretion
C. Enhance K and Na excretion
D. Enhance Na reabsorption and K secretion
E. Enhance Na reabsorption but lower K secretion
D. Enhance Na reabsorption and K secretion
A woman has a respiratory rate of 20, a tidal volume of 350mL, and a dead space of 100mL. What is her alveolar ventilation?
A. 4.0L/min
B. 4.5L/min
C. 5.0L/min
D. 5.5L/min
E. 6.0L/min
C. 5.0L/min
The constriction of a blood vessel to one third of its resting diameter would increase its resistance to blood flow by a factor of
A. 3
B. 6
C. 9
D. 81
E. 16
D. 81
Calculate the cardiac output for a patient that has a stroke volume of 75mL and heart rate of 65 beats/min.
A. 4,875 L/min
B. 4.9 L/min
C. 75 mL
D. 65 beats/min
B. 4.9 L/min
Which of the following theories of autoregulation in the kidney?
A. Myogenic mechanism
B. Tubuloglomerular feedback
C. Starling’s law
D. Both A and B
E. All of the above
D. Both A and B
Autoregulation in the kidney means that the _______ is maintained even though blood pressure may change
A. Renal blood flow
B. Sodium excretion
C. Glomerular filtration rate
D. Urine flow rate
C. Glomerular filtration rate
Constriction of the afferent arteriole will:
A. Decrease glomerular capillary pressure and GFR
B. Increase glomerular capillary pressure and GFR
C. Increase renal blood flow
D. Not affect GFR
A. Decrease glomerular capillary pressure and GFR
The percentage of hemoglobin saturated with oxygen will increase if
A. The arterial PCO2 is increased.
B. The hemoglobin concentration is increased.
C. The temperature is increased.
D. The arterial PO2 is increased.
E. The arterial pH is decreased.
D. The arterial PO2 is increased.
Given a patient’s hemoglobin concentration of 15g/dL, O2 capacity/gm Hb is 1.34 mL O2/gm Hb, solubility of oxygen of 0.003 mL O2/ dL/mmHg, alveolar partial pressure of oxygen of 90mmHg, and 95% O2 saturation:
PaO2:
A. 90mmHg
B. 20.1 mL O2/dL blood
C. 19.1 mL O2/dL blood
D. 0.27 mL O2/dL blood
E. 19.37 mL O2/dL blood
A. 90mmHg
Given a patient’s hemoglobin concentration of 15g/dL, O2 capacity/gm Hb is 1.34 mL O2/gm Hb, solubility of oxygen of 0.003 mL O2/ dL/mmHg, alveolar partial pressure of oxygen of 90mmHg, and 95% O2 saturation:
Arterial hemoglobin carrying capacity:
A. 90mmHg
B. 20.1 mL O2/dL blood
C. 19.1 mL O2/dL blood
D. 0.27 mL O2/dL blood
E. 19.37 mL O2/dL blood
B. 20.1 mL O2/dL blood
Given a patient’s hemoglobin concentration of 15g/dL, O2 capacity/gm Hb is 1.34 mL O2/gm Hb, solubility of oxygen of 0.003 mL O2/ dL/mmHg, alveolar partial pressure of oxygen of 90mmHg, and 95% O2 saturation:
Arterial O2 content:
A. 90mmHg
B. 20.1 mL O2/dL blood
C. 19.1 mL O2/dL blood
D. 0.27 mL O2/dL blood
E. 19.37 mL O2/dL blood
E. 19.37 mL O2/dL blood
Using the data provided calculate

GFR:
A. 161 mL/min
B. 195 mL/min
C. 1.17 mL/min
D. 1.5 mL/in
A. 161 mL/min
Using the data provided calculate

Filtered load of sodium:
A. 29.0 mmoles/min
B. 161 mmoles/in
C. 1.17 mmoles/min
D. 1.5 mmoles/min
A. 29.0 mmoles/min
Using the data provided calculate

Percent filtered sodium reabsorbed:
A. 100%
B. 99.3%
C. 90%
D. 50%
B. 99.3%
Using the data provided calculate

Free water clearance (CH2O):
A. 3.0 mL/min
B. 1.5 mL/min
C. -1.5 mL/min
D. -3.0 mL/min
C. -1.5 mL/min
The pressure-volume loops shown represents?
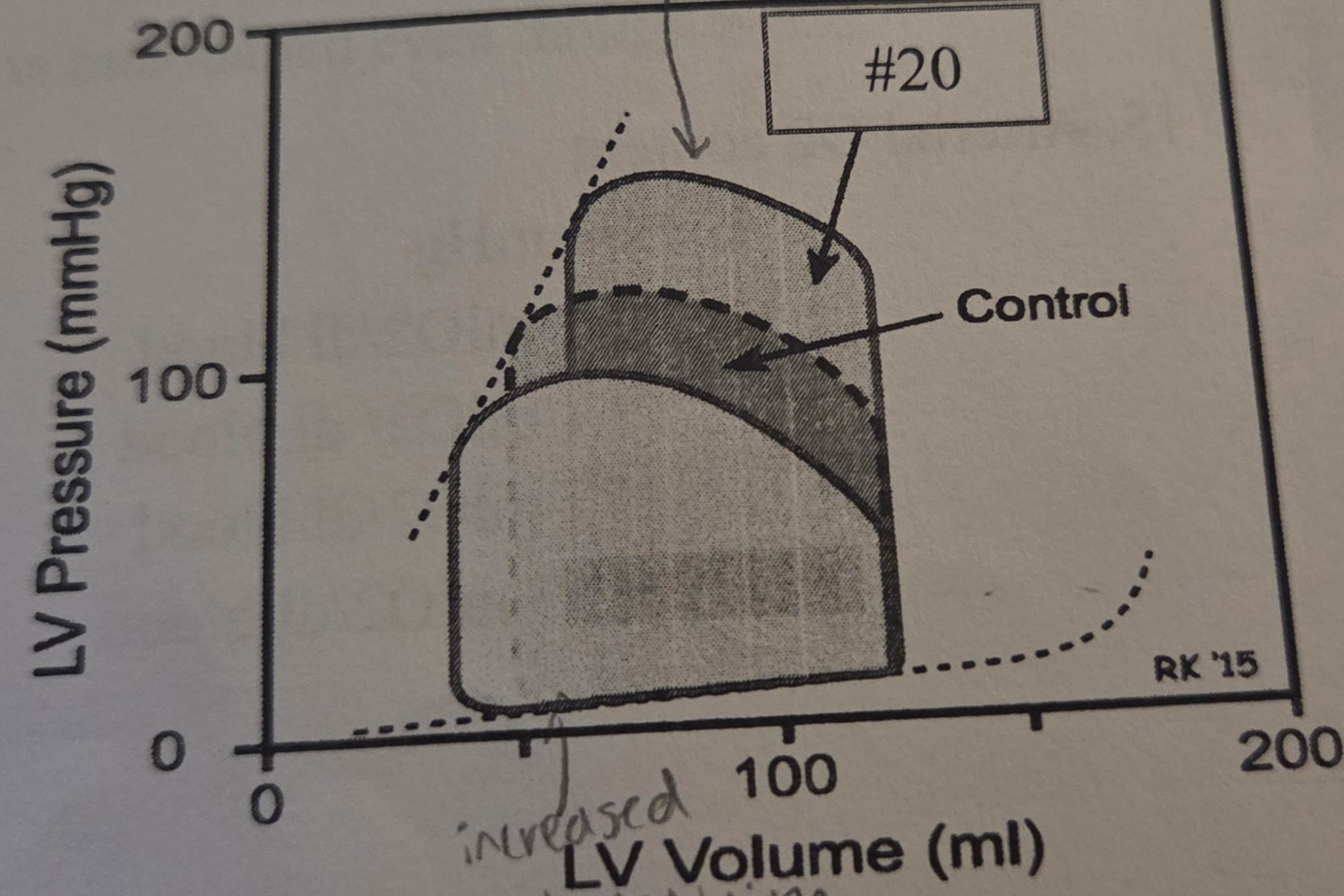
A. Increase afterload
B. Decrease afterload
C. Increase preload
D. Decrease preload
A. Increase afterload
Calculate the compliance for the Aorta with a normal pressure range = 60-120 mmHg and a relative volume change = 0.7.
A. C=0.0117
B. C=85.7
C. C=60
A. C=0.0117
Which of the following will increase GFR:
A. the afferent arteriole is dilated
B. the efferent arteriole is constricted
C. The afferent arteriole is constricted
D. Both A and B
E. Both B and C
D. Both A and B
Increasing preload in left ventricle will:
A. Increases afterload
B. Increases cardiac output
C. Decreases cardiac output
D. Decreases blood flow
B. Increases cardiac output
The cardiac muscle action potential has a plateau phase. Which ion is responsible for the plateau phase?
A. Sodium
B. Potassium
C. Calcium
D. Both A and B
E. All of the above
C. Calcium
The primary pacemaker of the heart is the
A. Purkinje fiber
B. AV bundle (bundle of His)
C. right bundle branch
D. SA node
E. left bundle branch
D. SA node
The QRS complex of the ECG is associated with
A. atrial depolarization
B. ventricular depolarization
C. atrial repolarization
D. ventricular repolarization
E. A and B are correct
B. ventricular depolarization
The ECG can be used to diagnose:
A. heart failure
B. arrythmias
C. respiratory disorder
D. renal failure
B. arrythmias