respiration in humans (chap 7) -olevel pure bio
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
what is respiration
the breaking down of food molecules such as glucose to release energy
what is aerobic respiration
the release of energy by the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen
produces carbon dioxide and water as waste products
generates large amount of energy
some of the energy is converted into heat energy circulated around your body to keep warm
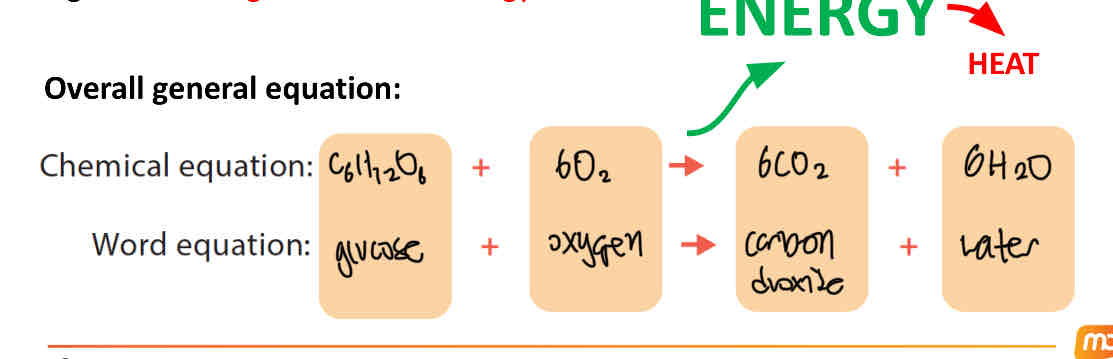
what is the equation for aerobic respiration
examples of energy consuming processes
synthesis of new protoplasm for growth and repair
synthesis of proteins from amino acids
active transport in the absorption of food substances by the small intestine
muscular contractions such as heartbeats and respiratory movements
transmission of nerve impulses
cell division
what is anaerobic respiration
the breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen
generates small amount of energy
word equation for anaerobic respiration
glucose —> lactic acid
what happens during vigorous activity
muscle cells need more energy to contract
aerobic respiration in muscle cells increased
increased breathing rate to remove carbon dioxide and take in oxygen at a faster rate
increased heart rate so that oxygen can be transported to muscles at a faster rate
when vigorous activity continues, muscular contracts are so vigorous that maximum aerobic respiration is not enough to release energy fast enough to meet the demands
muscle cells carry out anaerobic respiration to meet the increased energy demand and lactic acid is formed in the process
what is oxygen debt
when there is insufficient oxygen to meet the demands of the vigorous muscular contractions, an oxygen debt is incurred
oxygen debt is the amount of oxygen required to remove lactic acid
how is oxygen debt removed
continuation of fast heart rate after activity - continuation of fast transport of lactic acid from the muscle cells to the liver and oxygen from the lungs to the liver for removal
continuation of deeper and faster breathing after activity - for fast intake of oxygen by the lungs to obtain oxygen for supply to the liver
once lactic acid is removed, oxygen debt is paid.
adaptations of the nasal passage for respiration
nostrils has a fringe of hairs and is lined with a moist mucous membrane
dust and foreign particles, including bacteria in the air, are trapped by the hairs in the nostrils as well as by the mucus on the mucous membrane
as air passes through the nasal passages, it is warmed and moistened.
harmful chemicals may be detected by small sensory cells in the mucous membrane
adaptations of the trachea for respiration
epithelium of trachea contains 2 types of cells
gland cells: secrete muscles to trap dust particles and bacteria
cillated cells: have hair like particles called cilia on their surfaces. cilia sweep dust-trapped mucus up the trachea towards the pharynx to be coughed out or swallowed.
adaptations of the lungs for efficient gas exchange
numerous alveoli - large surface area
walls of the alveoli is only one cell thick - short diffusion distance for gases for higher rate of diffusion
thin film of moisture covers inner wall of alveolus - allows oxygen to dissolve in it
walls of alveoli are richly supplied with blood capillaries - flow of blood maintains steep concentration gradient of gases
how does gas exchange occur in the alveolus
gas exchange in the lungs occur by diffusion
blood entering the lungs has a lower concentration of oxygen and a higher concentration of carbon dioxide than the atmospheric air entering the alveoli in the lungs
a concentration gradient for oxygen and carbon dioxide is set up between blood and alveolar air
oxygen dissolves into the thin film of moisture on the wall of the alveolus
the dissolved oxygen then diffuses through the wall of the alveolus and the wall of the blood capillary into the red blood cells
the oxygen combines with haemogoblin to form oxyhaemogoblin
carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveolar air
how is the concentration gradient between the alveolus and blood maintained
continuous flow of blood through the blood capillaries
continuous breathing, which causes air in the lungs to be continuously refreshed
what happens during inspiration
diaphragm muscle contracts and the diaphragm flattens
external intercostal muscles contract and internal intercostal muscles relax
ribs and sternum move upwards and outwards
volume of thoracic cavity increases
lungs expand and air pressure decreases as the volume increases
atmospheric pressure is now higher than the pressure within your lungs
air moves into the lungs
what happens during expiration
diaphragm muscles relaxes and the diaphragm arches upwards
internal intercostal muscles contract while the external intercostal muscles relax
ribs and sternum move downwards and inwards
volume of thoracic cavity decreases
lungs are compressed and air pressure increases as the volume decreases
pressure within the lungs is now higher than atmospheric pressure
air is forced out of your lungs to the exterior environment
what effects does nicotine have on health
increases heartbeat rate and blood pressure
increases risk of blood clots in the arteries, which leads to increased risk of coronary heart disease
increases risk of arteries to narrow
in a pregnant mother, narrow arteries decrease the amount of food substances reaching the fetus, affecting fetal development and may cause miscarriage
what effects does carbon monoxide have on health
reduces ability of blood to transport oxygen as carbon monoxide binds permanently with haemogoblin. thus, there will be less haemogoblin available to transport oxygen
in a pregnant mother, less oxygen reaches the fetus through the placenta which may affect fetal development
increases risk of coronary heart disease
effects of tar on health
increases risk of cancer in the lungs as tar can cause uncontrolled cell division
increases risks of chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
tar paralyses cilia lining the air passages. hence, dust particles trapped in the mucus lining cannot be removed
what is chronic bronchitis
prolonged exposure to irritants from smoking
causes inflamed lining of bronchus
excessive mucus secreted by epithelium
cilia on the epithelium become paralysed
dust-trapped mucus cannot be removed
airways become blocked
persistent coughing to clear the air passages
increases risk of lung infection
what is emphysema
persistent and violent coughing due to bronchitis may lead to emphysema
partition walls between the alveoli break down due to persistent and violent coughing
decreased surface area for gaseous exchange
lungs lose elasticity and become inflated with air
breathing becomes difficult, wheezing and severe breathlessness occurs