Coenzymes & Cofactors
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What's a holoenzyme?
Active enzymes with the bound cofactor
Cofactor
- Non-protein, inorganic molecules
- Required for the enzyme's activity to occur to. They produce the specific shape of the active site, but do not take part in the reaction.
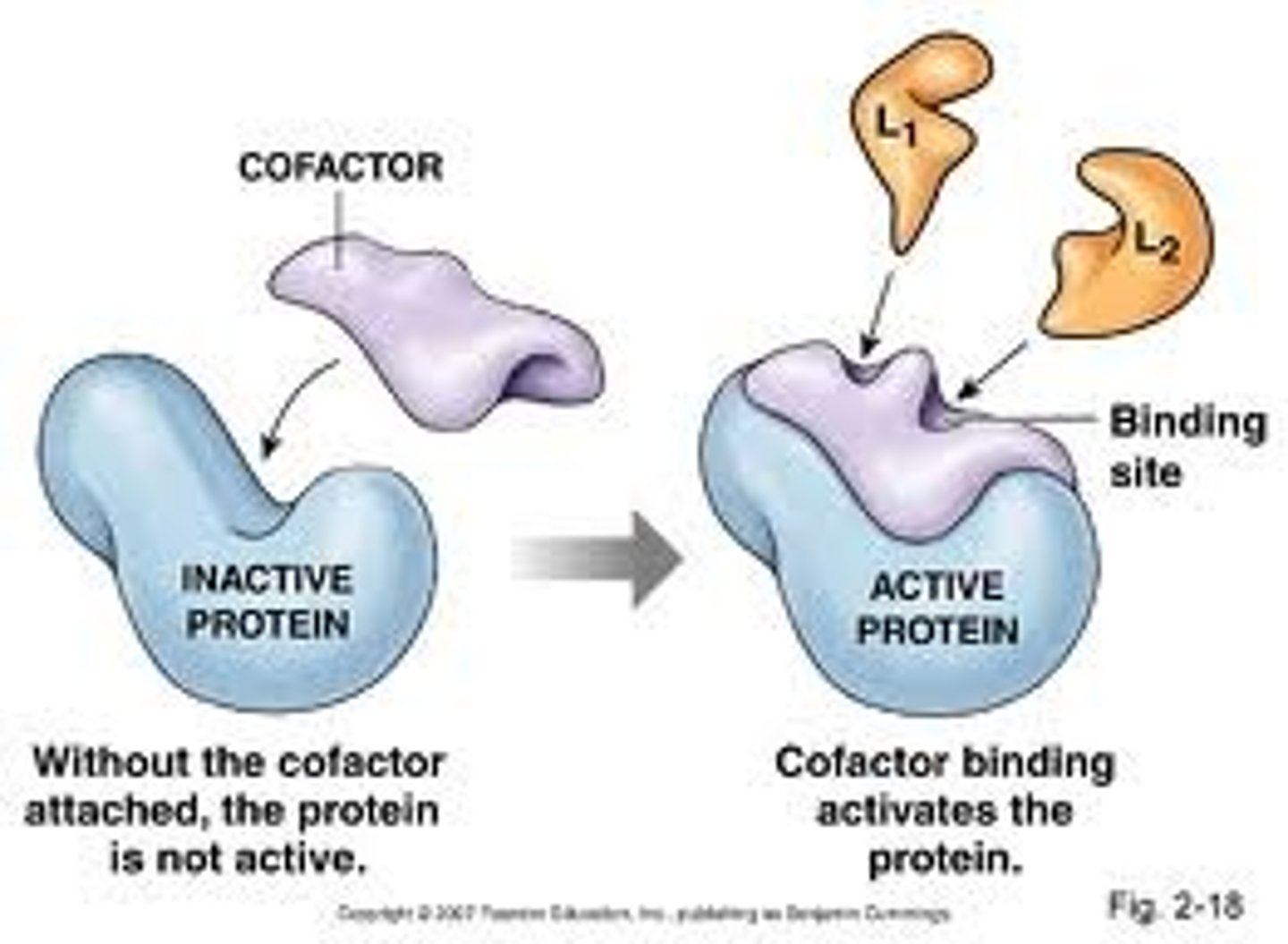
Are cofactors permanently bound to the enzyme?
They are usually temporarily bound. If they are permanently bound, they are a prosthetic group.
Example of a cofactor
Chloride ions (Cl-), which participates in reactions with amylase (amylase is the enzyme that breaks down starch)
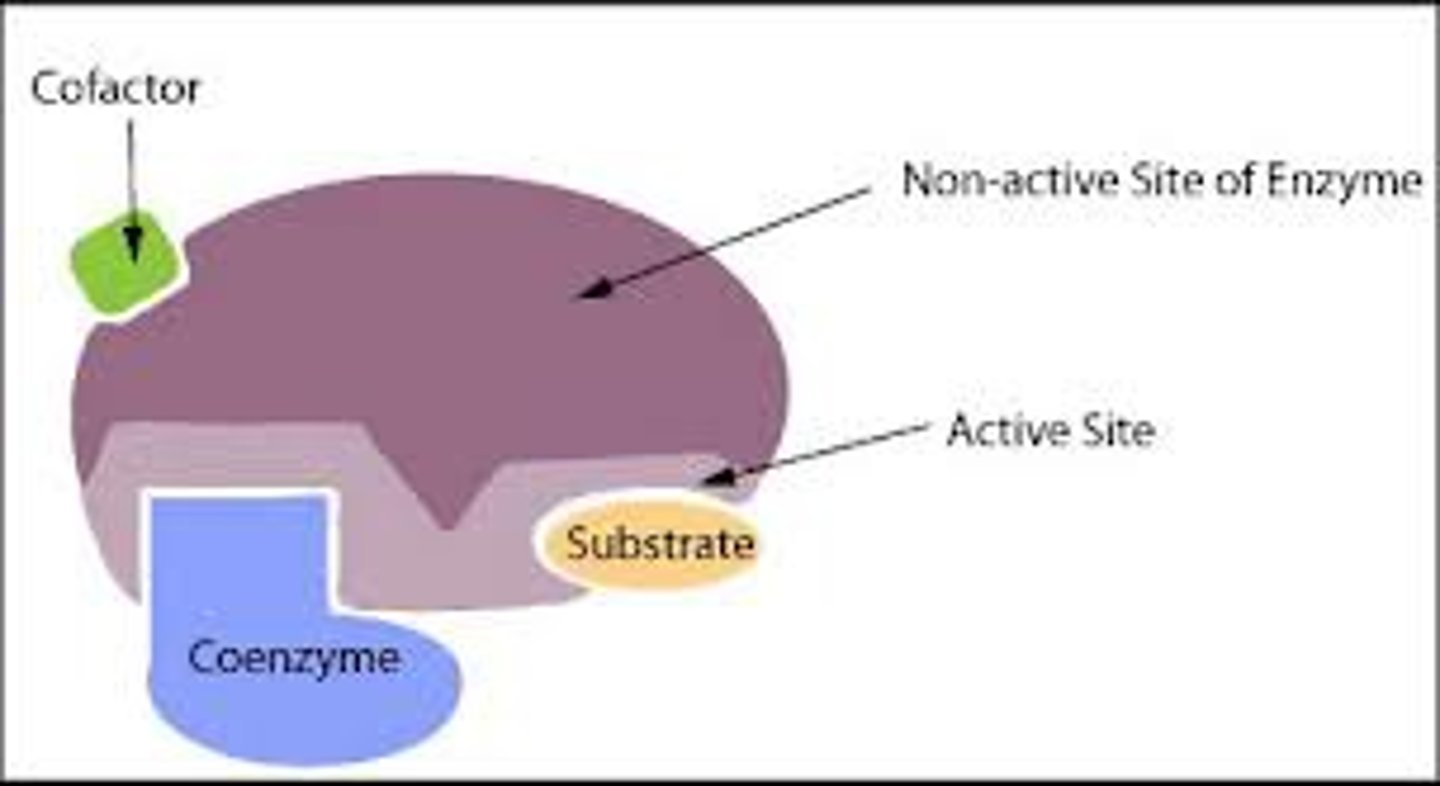
If the cofactor is organic, what is it called?
A coenzyme
Are cofactors directly involved in the reaction?
No.
The role of cofactors is to help bind the substrate and the enzyme. They are not directly involved in the reaction itself therefore they do not change or get used up at the end of the reaction.
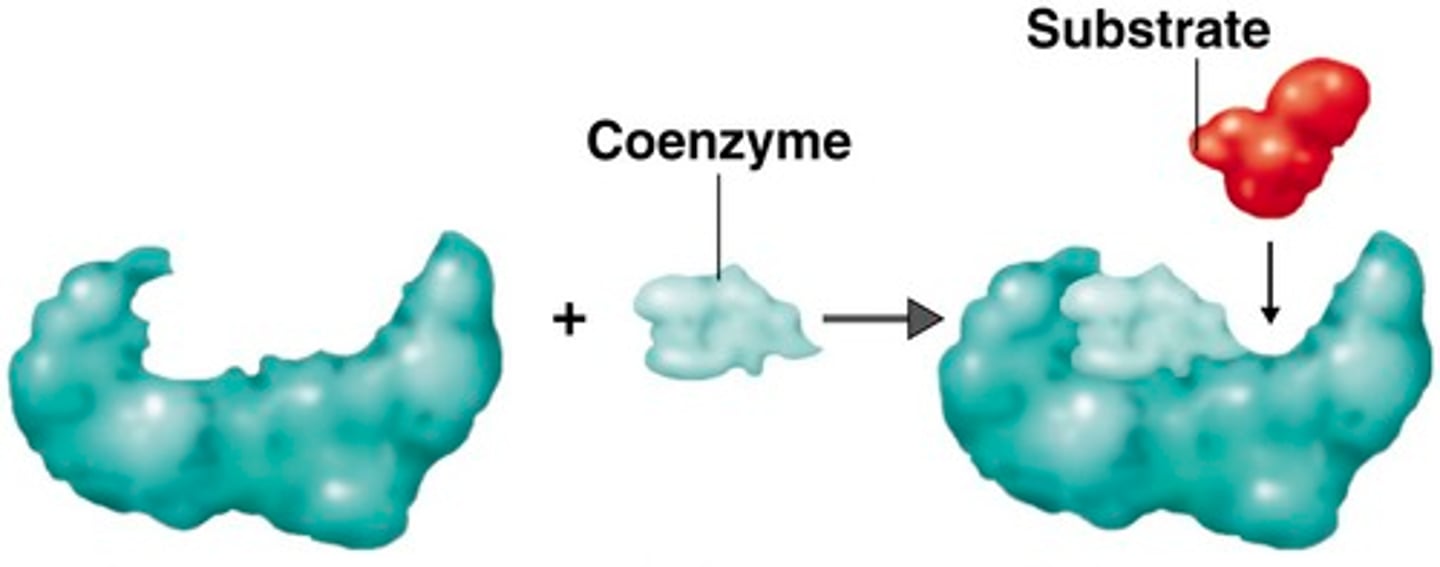
Coenzymes
- Organic molecules
- They facilitate the binding of substrate to enzyme. They are used to activate the enzyme (become a holoenzyme). They produce the specific shape of the active site
- They take part in the reaction
Sources of coenzymes
Vitamins
Vitamin derived coenzymes
NAD is derived from niacin. NAD acts as a hydrogen acceptor.
Prosthetic groups
- A non-protein, inorganic compound
- Unlike cofactors and coenzymes that temporarily participate enzymatic reactions, prosthetic groups are cofactors that are permanently bound the enzyme itself
- Prosthetic groups are a part of the active site. Prosthetic groups are usually a vital component of the active site, and removing the prosthetic group would damage the enzyme and cause it to become denature.
Examples of Prosthetic Groups
Haemoglobin contains te prosthetic haem group, which is Fe²⁺ permanently bound to the molecule, which serves as a means of binding oxygen.