Health Education
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Cognitive Learning Theory
Learner thought process
Allows for understanding of mental processes
Encourages self-reflection
Behavioral Learning Theory
Learning influenced by external forces
Positive reinforcement - learner more likely to complete task
Incentives offered improve behavior
Social Learning Theory
Learning by observing others
Depends on consequences, learner imitates/avoid that
behavior
Cognitive and environmental factors into consideration
Experiential Learning Theory
Learning from experiences
Retain and recall information when hands-on
Participation in real-world experiences
Transformative Learning Theory
Learners change thinking after gaining new information
Reflects on previous experiences
Critical evaluation of perspectives occurs
-Results in transformation of thinking
Humanistic Learning Theory
Learning is a holistic process
Educator is facilitator
-makes environment conducive to learning
Freedom for students to learn what they’re interested in
Retention of knowledge used to evaluate learner
Learning Styles
• Visual
—See content
—Photos, models, videos
• Auditory
—Hear content
—Podcasts, recorded lectures
• Tactile-kinesthetic
—Hands-on experiences
Cognitive
• How learner thinks
• Development of knowledge and skill
Affective
• How learner’s values/beliefs evolve (emotional)
Psychomotor
• Application of knowledge (doing)
• Use of sensory-motor skills
Health Belief Model
• Determines internal motivation to make health changes
• Includes
—Perception of risk of getting illness
—Modifying factors
—Likelihood/Cues to take action
Health Promotion Model
• Determines factors that influence motivation to change
• Disease prevention, health promotion (primary)
• Categories
—Individual characteristics
—Behavior-specific cognitions and affect
—Behavioral outcome
Transtheoretical Model
• Stages of change
Stages
• Precontemplation (no consideration)
• Contemplation
• Preparation
• Action
• Maintenance
Cultural Care Theory
Provide culturally congruent care
Consider culture when providing care and education
Make effort to learn about other cultures
Health Literacy
• Ability to obtain, understand, make health-related decisions
• Risk factors for poor health literacy
—Older adults
—Low socioeconomic status
—Medically underserved
Strategies to Improve Health Literacy
Plain language
Identify clients who have low literacy levels.
Supplemental teaching methods.
Teach Back method
Barriers to Learning
• Education
• Language
Strategies to improve Barriers
• Health literacy universal precautions
• Plain language
• Slower speech
• Limit content
• Repeat vital points
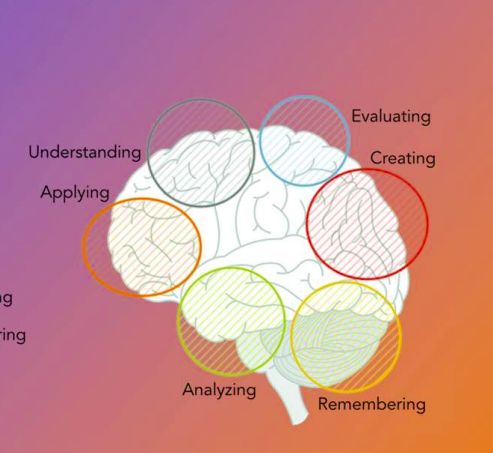
Hierarchy and brain placement of domains of learning
6 Parts