Skeletal System
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Composition of skeleton
Bone and cartilage
2 parts of the skeleton
Axial
Appendicular
Axial skeleton
Central, middle
Includes: skull, vertebral column, and ribcage
Function: protection of organs: heart, lungs, brain, spine
Appendicular skeleton
Everything attached to the axial skeleton
Includes: limb bones, upper and lower
Function: movement
Girdles
Set of bones that connect limbs to axial skeleton
2 types of girdles
pectoral girdle
Pelvis girdle : hip where lower limbs attach
Classification of bones
4 classifications based on shape
Long bone
Short bone
Flat bone
Irregular bone
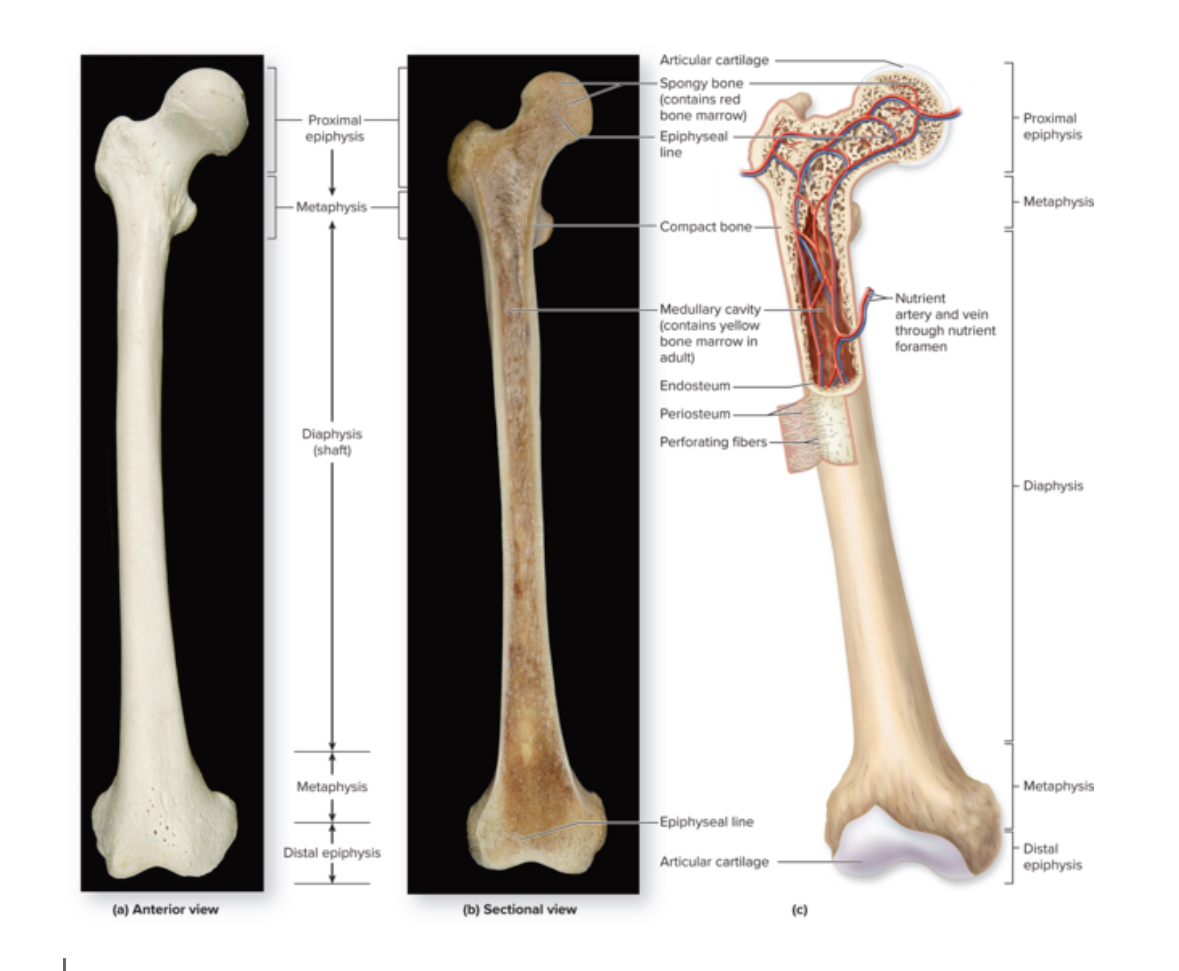
Long bone
Structure: Shaft and 2 bone ends. Longer than wide. Central shaft = diaphysis. Ends = epiphysis. Periosteum covers surface of the bone. Sharpies aka perforating fibers attach bone to periosteum.
Location: femur, fibula, tibia humerus, radius, ulna.
Function: leverage and movement
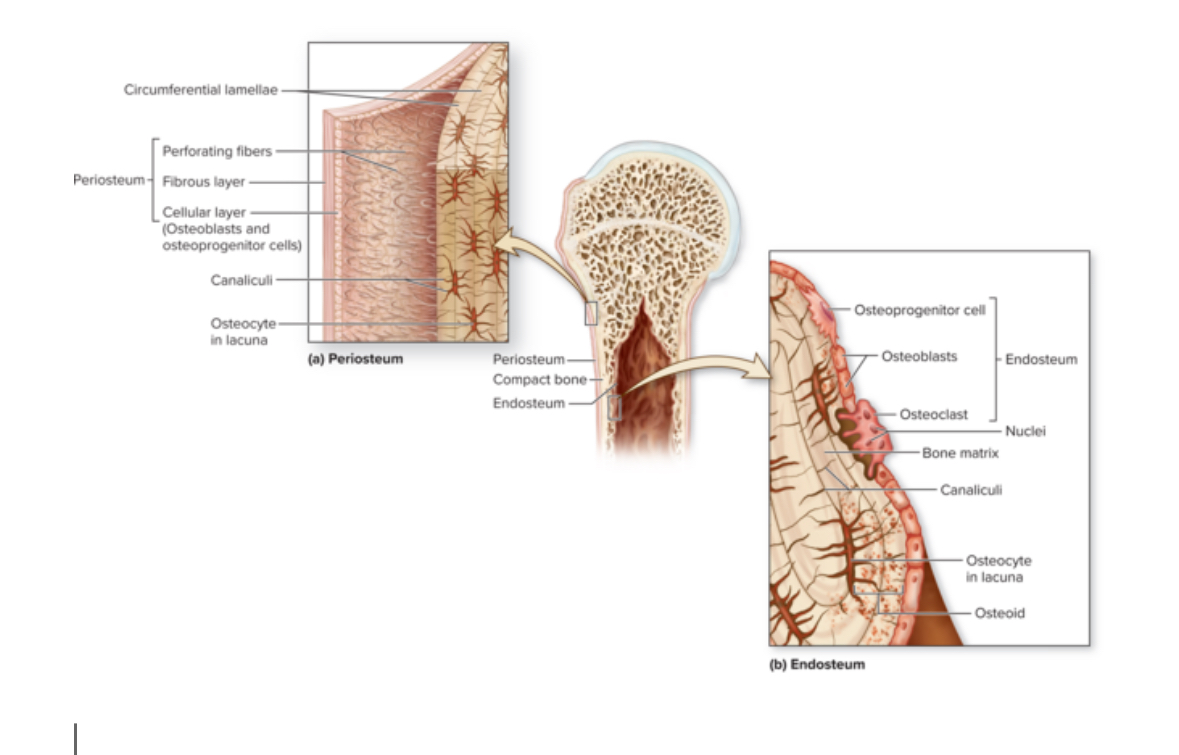
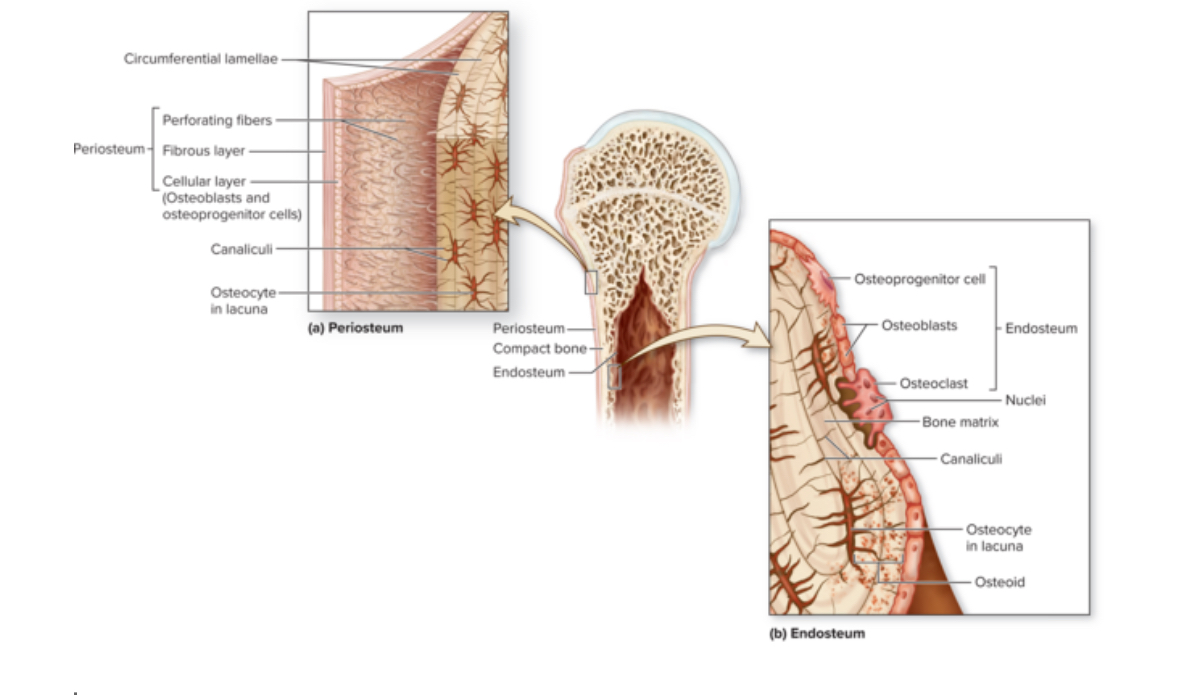
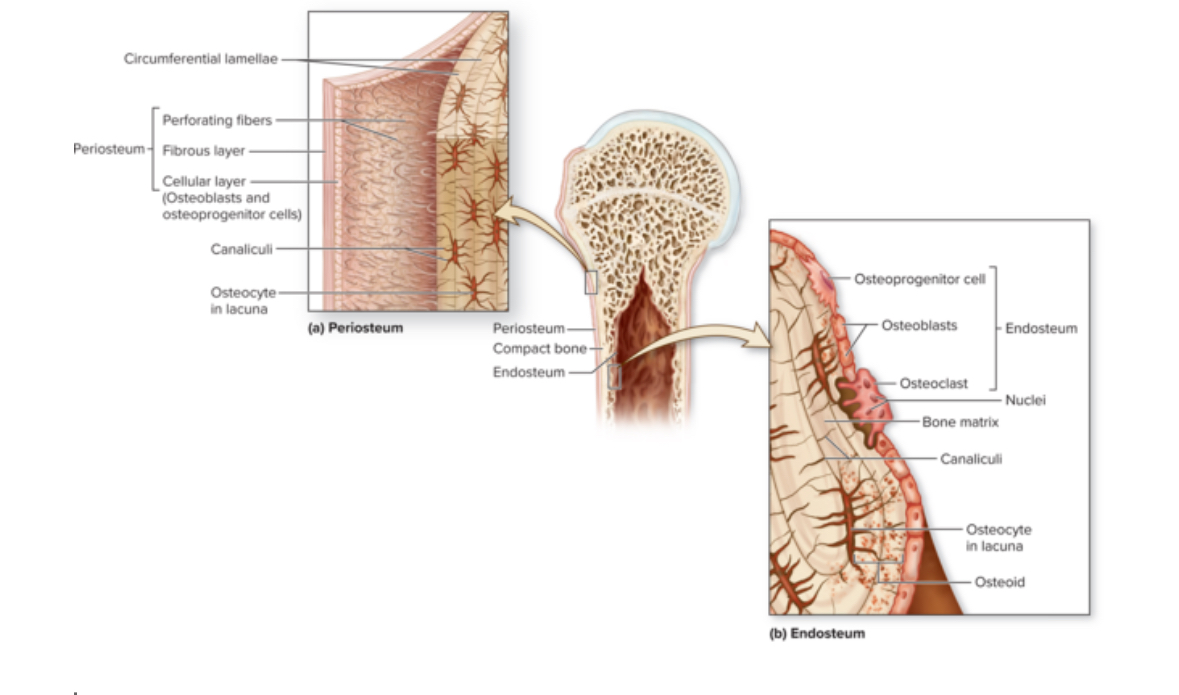
Periosteum
Structure: DICT. Membrane. Contains stem cells and osteoblasts.
Location: covers bone surface
Function: protects the bone, anchor blood vessels and nerves to the surface of the bone
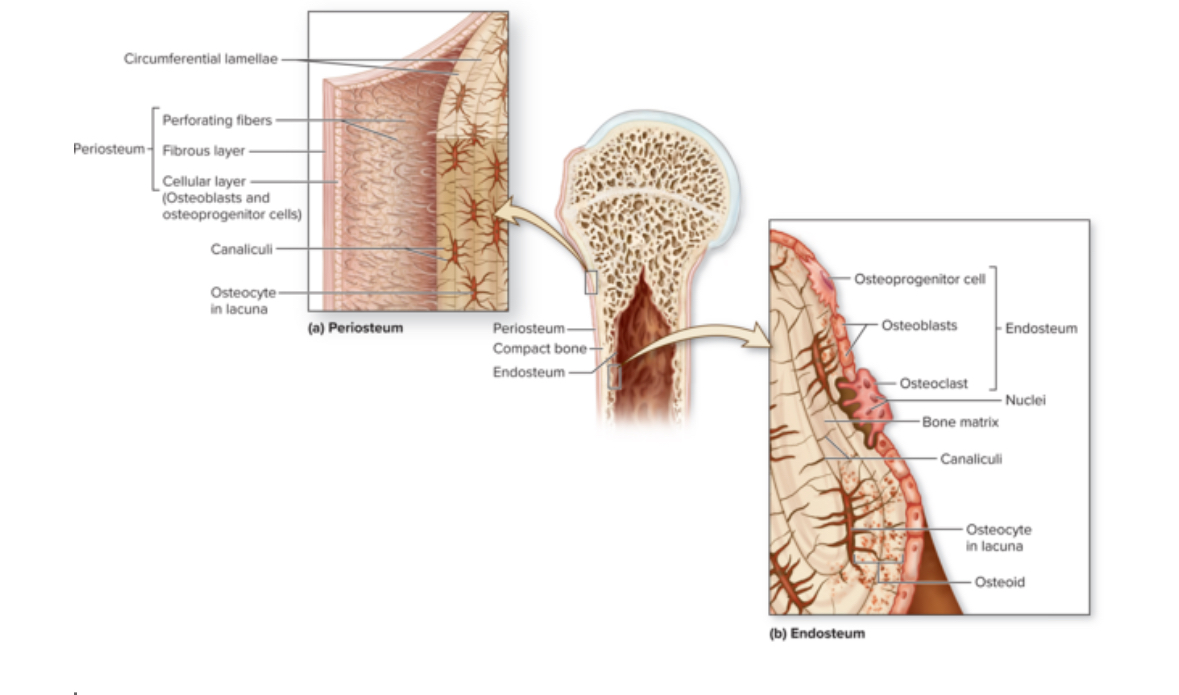
Endosteum
Structure: Thin membrane of cells and reticular fibers. Contains osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts
Location: Covers all internal surfaces of the bone
Function: Active during bone growth, repair, and remodeling.
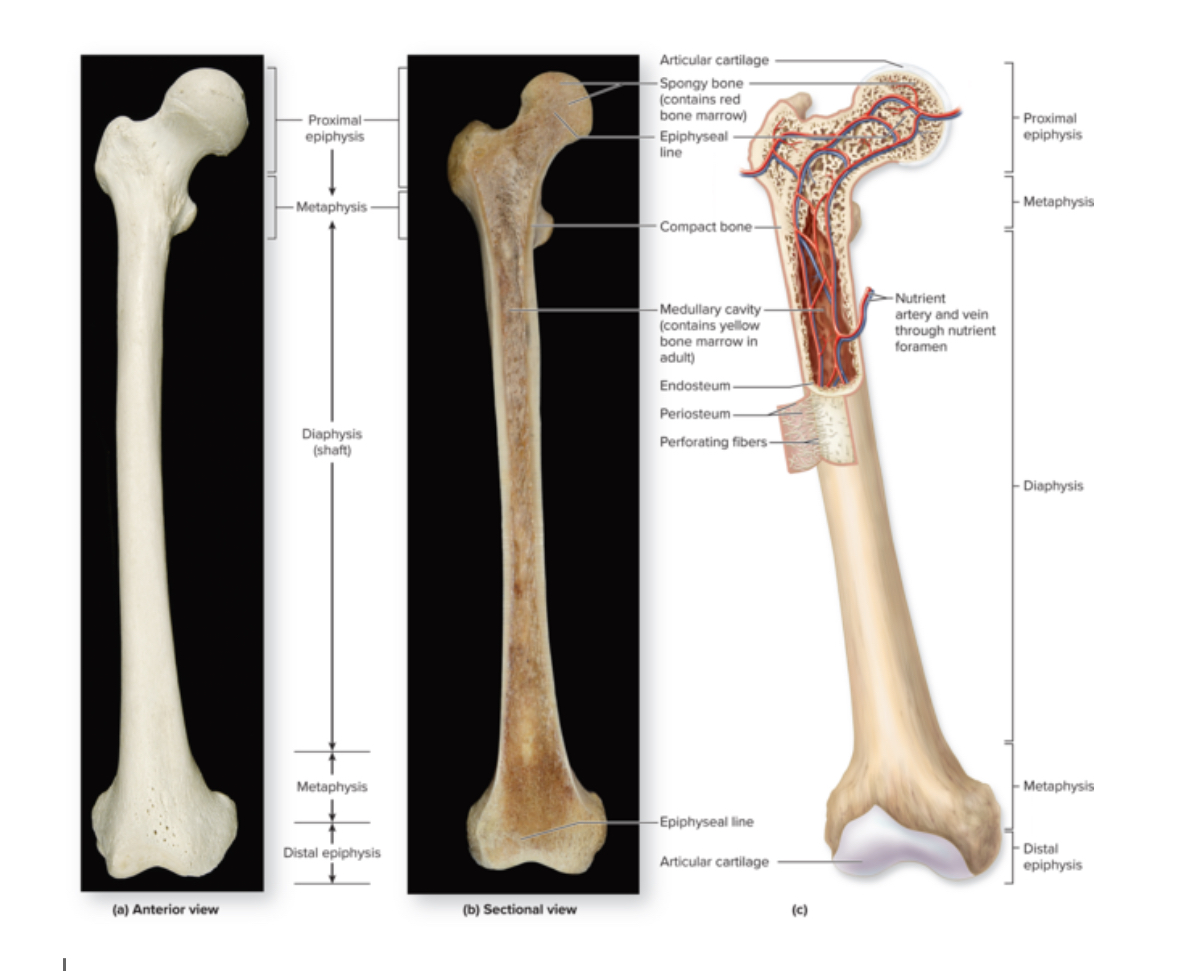
Medullary cavity
Structure: Hollow space within the diaphysis.
Location: long bones
Function: in adults contains yellow bone marrow. In infants, contains red bone marrow.
Yellow bone marrow
Adipose tissue
Red bone marrow
Function: make cells
Nutrient foramen
Openings for blood vessels.
Can be multiple.
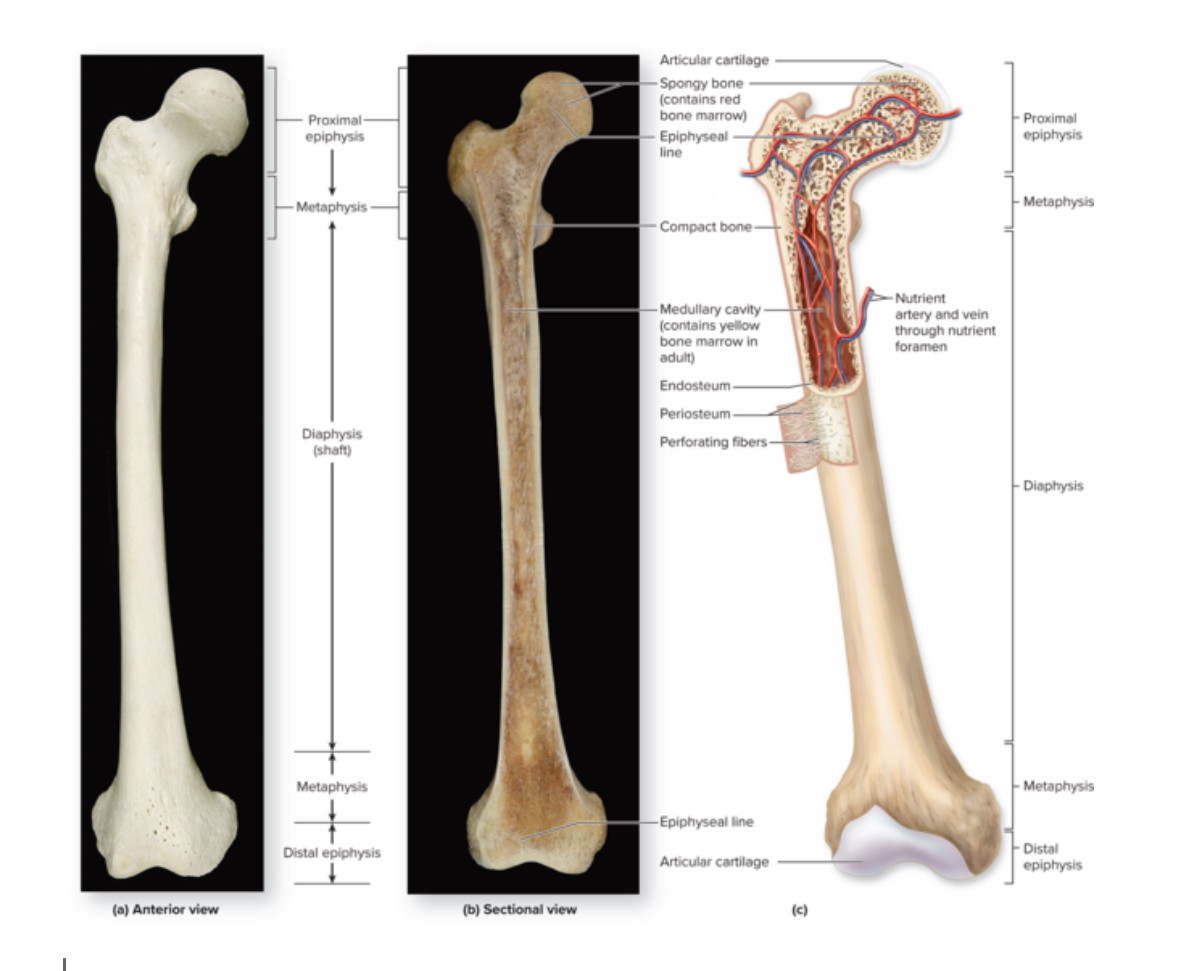
Epiphysis
Structure: Inside= spongy bone. Outside = compact bone. No medullary cavity.
Location: 2 in each long bone. One proximal and one distal.
Function: Form a joint with another bone. Articulation.
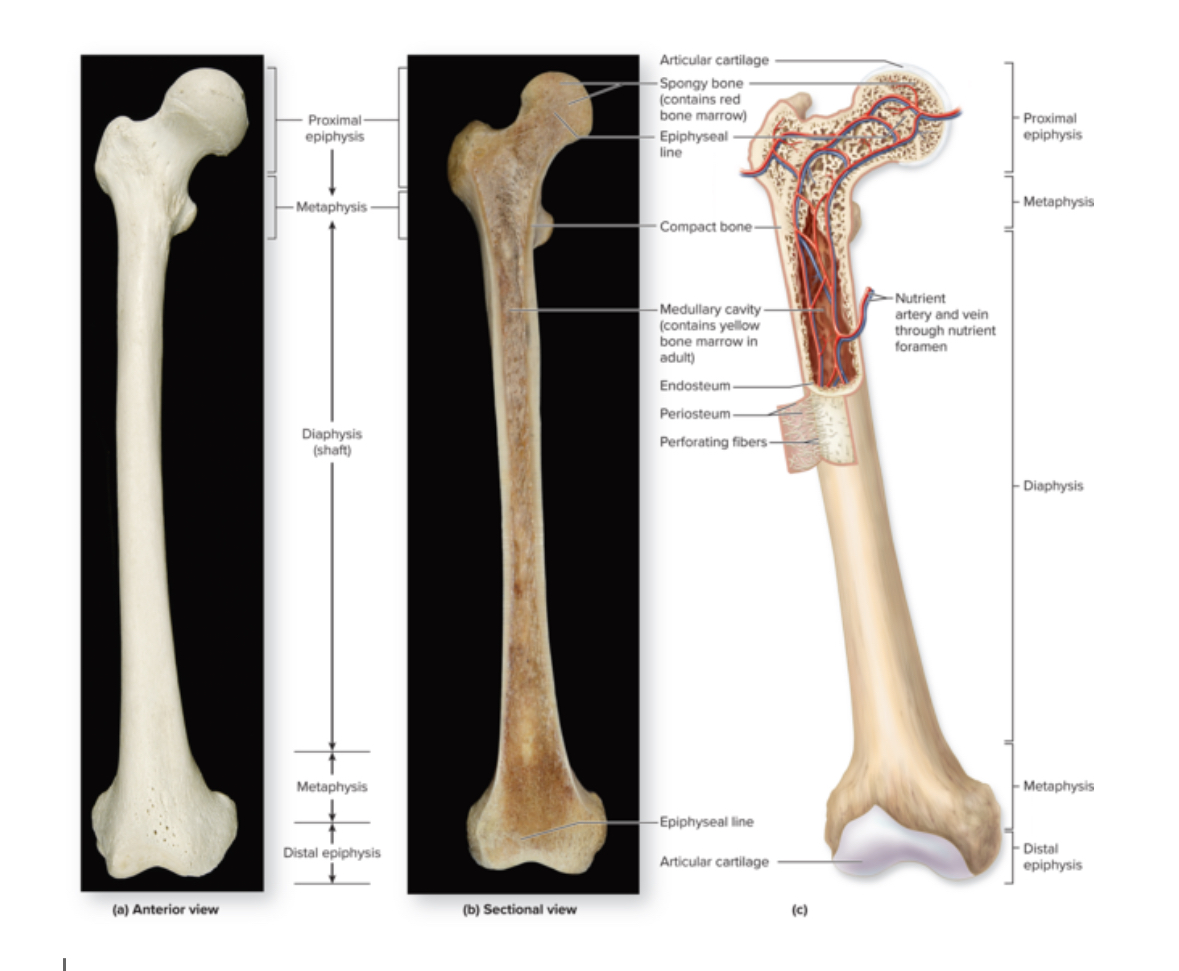
Articular cartilage
Structure: Layer of hyalin cartilage tissue
Location: Around the epiphysis
Function: Prevent friction at joints
Epiphyseal plate
Structure: thin layer of hyaline cartilage
Location: Region of the long bone between the epiphyseal and diaphysis
Function: Provide for the continued lengthwise growth of the diaphysis
Epiphyseal line
Structure: thin layer of compact bone
Location: the region between the epiphysis and the diaphysis
Function: Remnants of the epiphyseal plate
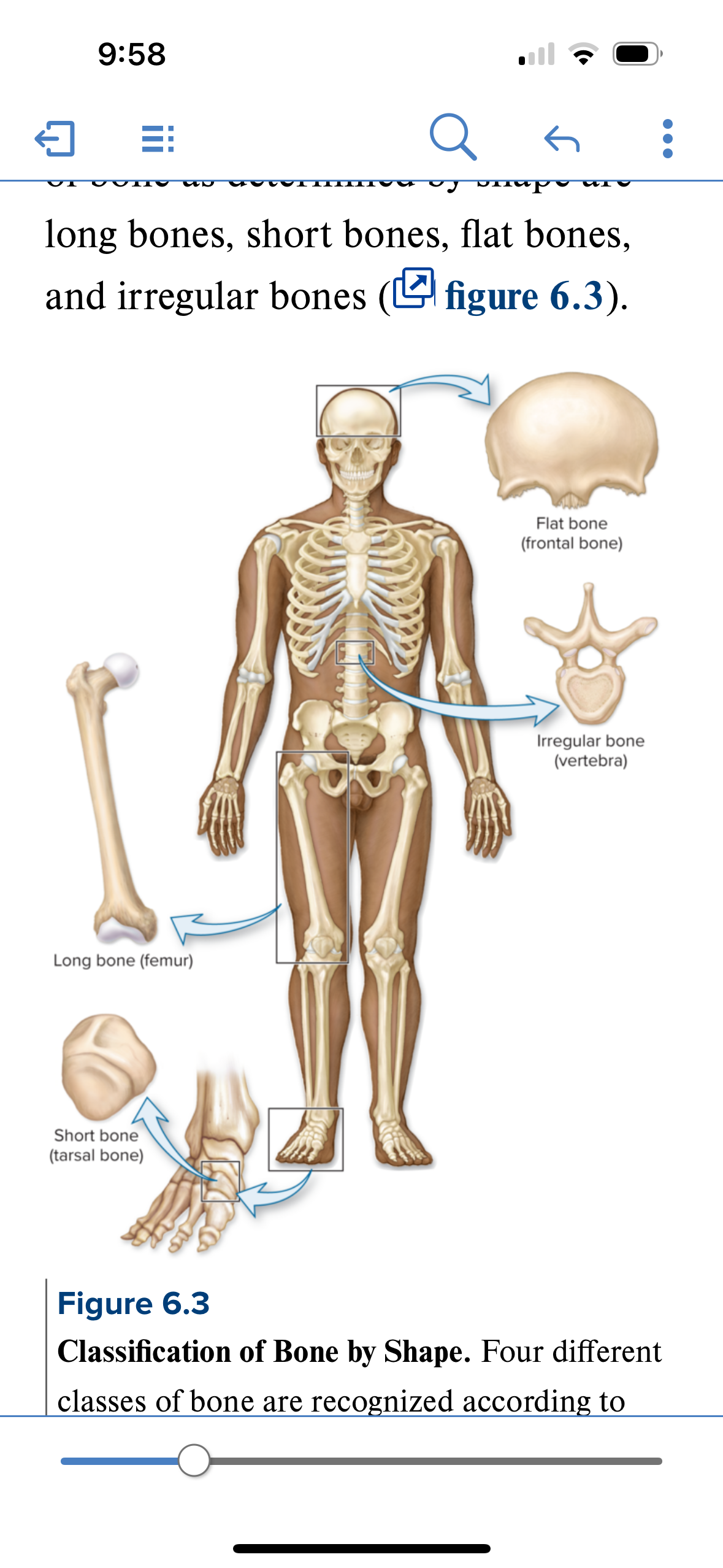
Short bone
Structure: roughly cube shaped bones. Primarily spongy bone with a thin layer of compact bone. Sandwich architecture. Compact bone on either side of spongy bone.
Location: areas where movement is limited and stability is required: carpals (wrist) and tarsals (ankle)
Function: stability and support, shock absorption
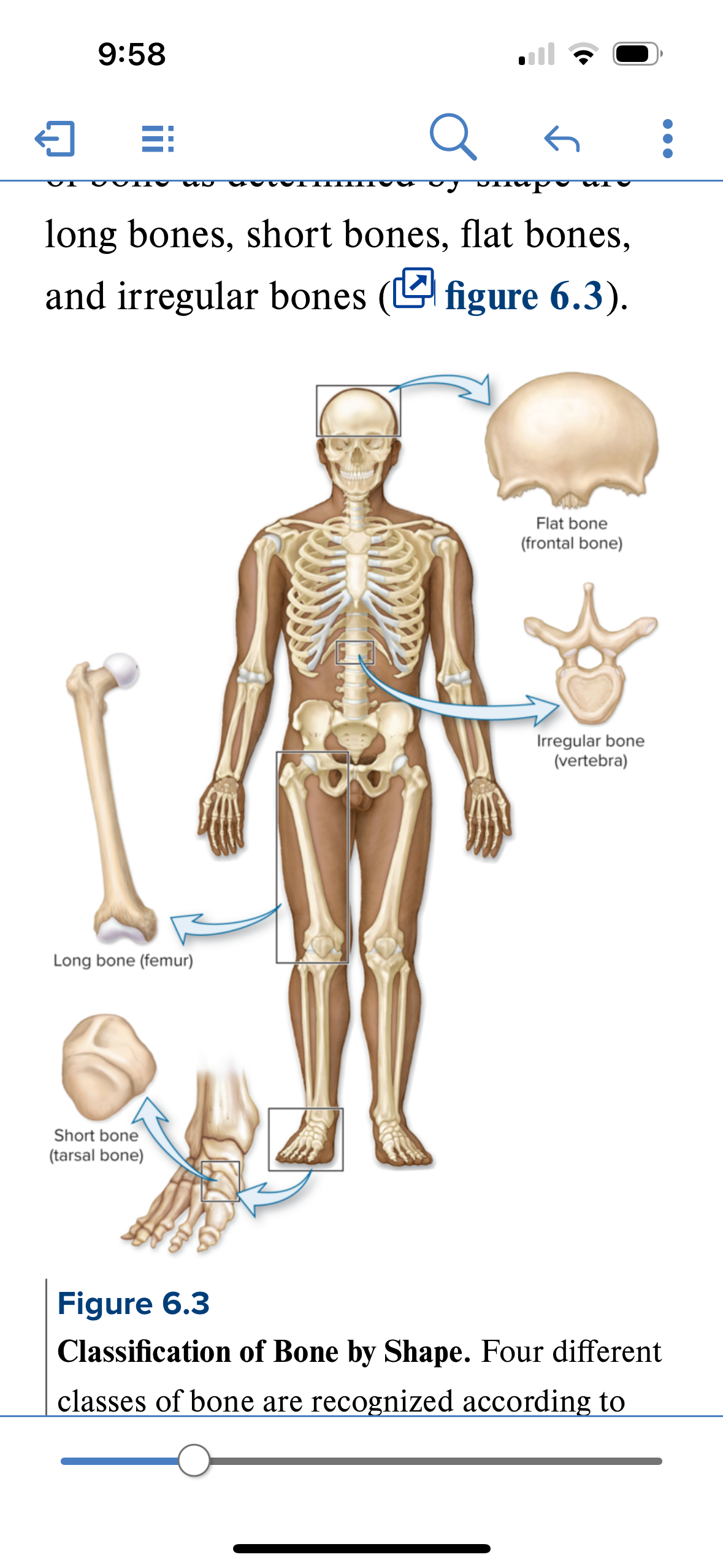
Flat bones
Structure: thin, flattened, often slightly curved. Composed of 2 layers of compact bone enclosing a layer of spongy bone
Location: Sternum, skull, ribs, scapulae
Function: Protection and muscle attachment.
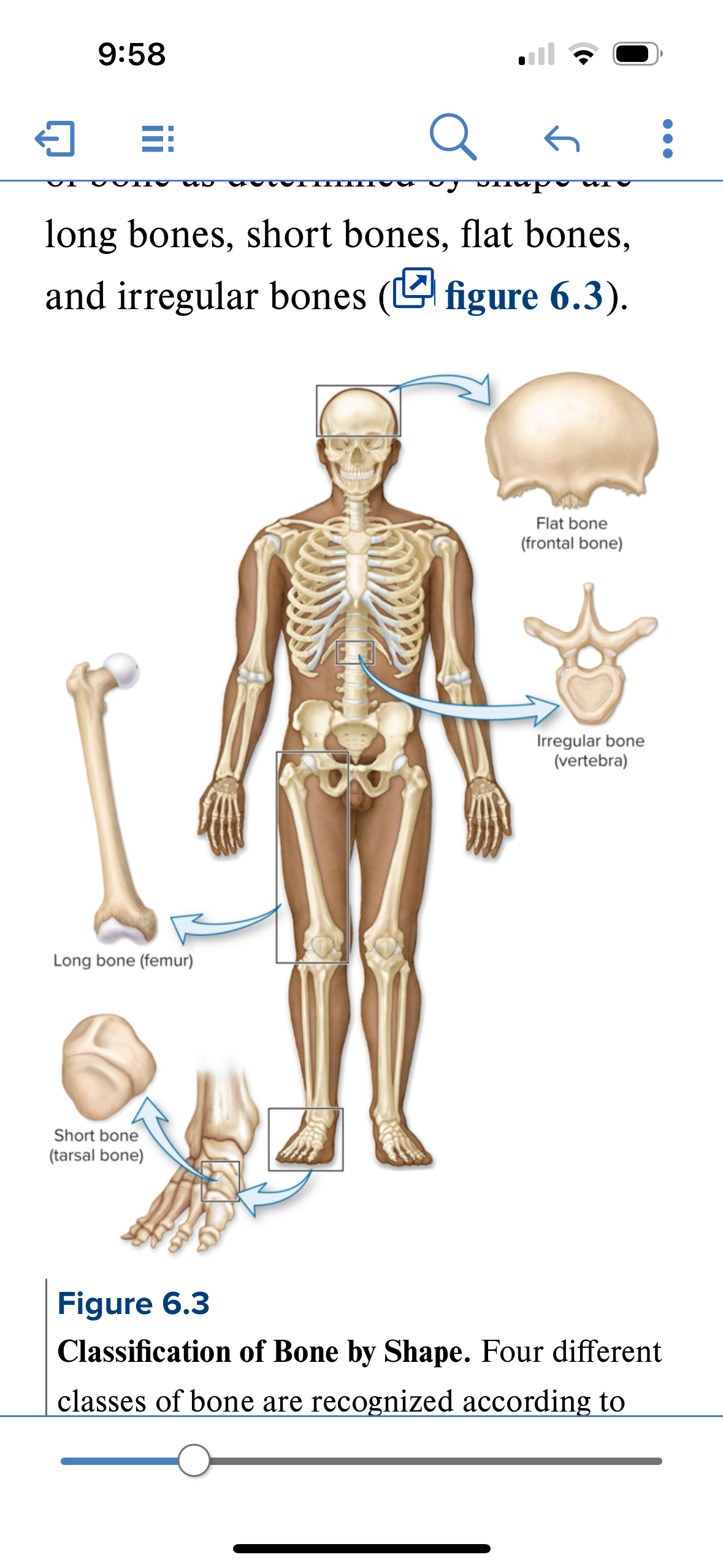
Irregular bones
Structure: bone is not long, not short, and not flat. Odd shaped. Sandwich composition = compact bone on either side of spongy bone. Spongy bone composed of trabeaculae
Location: Ethmoid, vertebrae, sphenoid
Function: Protection, articulation, muscle attachment, support
Spongy bone
Structure: composed of an open lattice of narrow plates of bone called trabeculae. Space between trabeculae contains red bone marrow. Porous. No central canals. Osteocytes within lamellae. Canaliculi house bone extensions for communication between osteocytes.
Location: internal layers of bone and ends of long bones.
Function:
Bone development
AKA ossification
Turning soft CT into bone
2 types of bone development
Intramembraneous
Endocardral
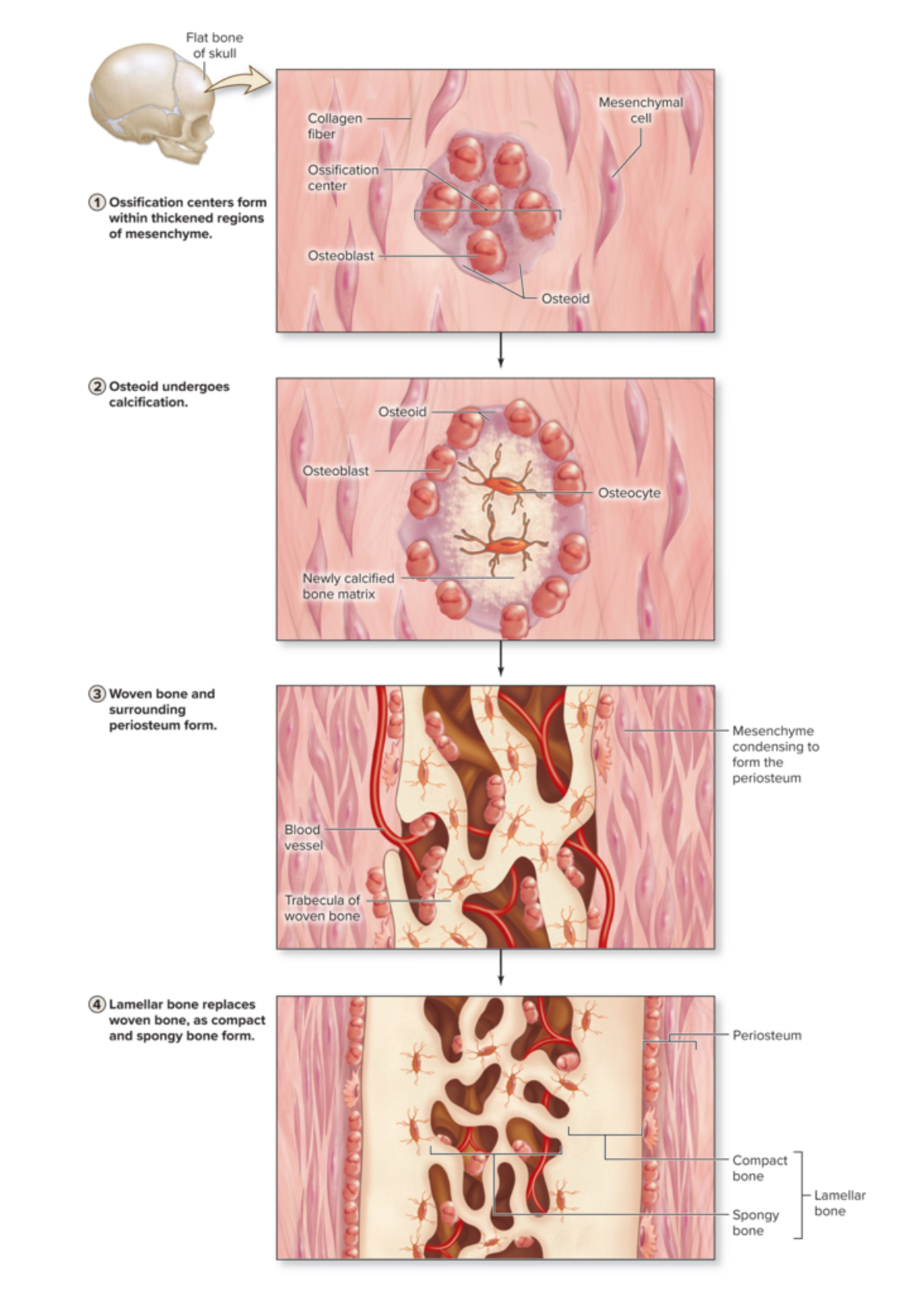
Intramembraneous ossification
Means: bone growth with a membrane
The thin layer of mesenchyme is sometimes referred to as a membrane
Mesenchyme source of these bones is an embryonic CT turns into bone tissue
Produces flat bones
Location: the cranial vault, zygomatic, maxilla, mandible, and central part of the clavicle.
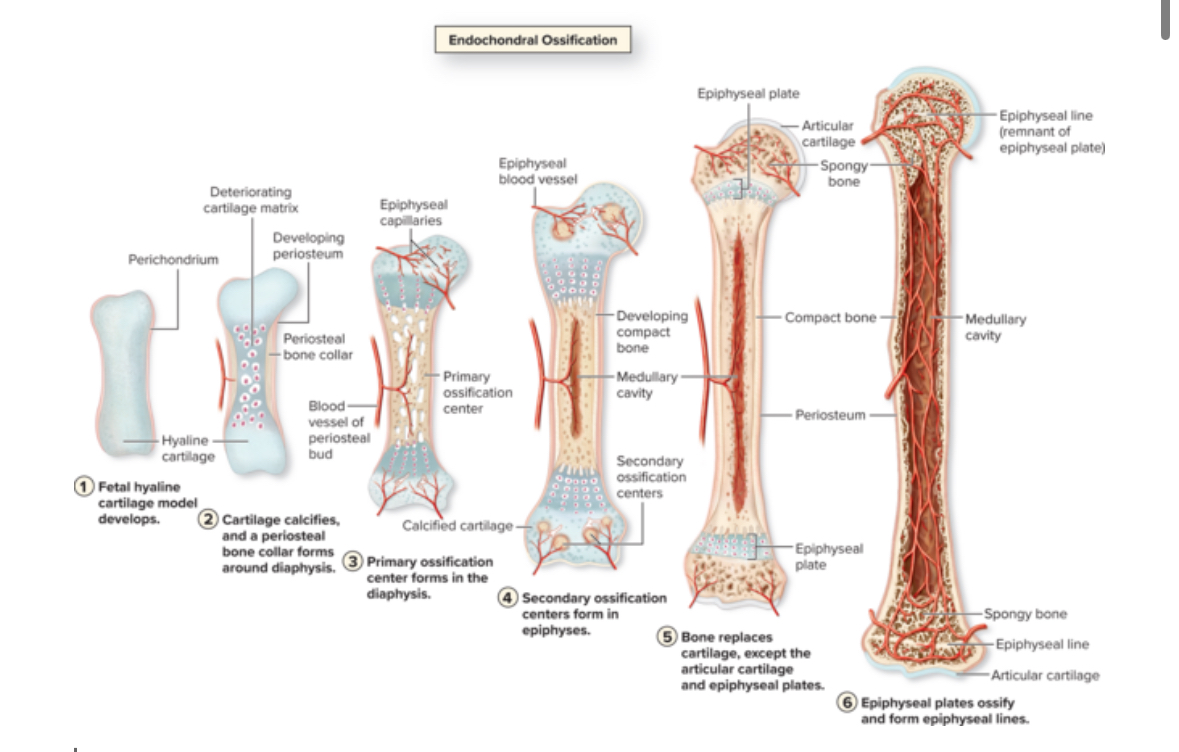
Endochondral ossification
Hyaline cartilage into bone tissue.
Location: skull base, vertebrae, long bones, pelvis
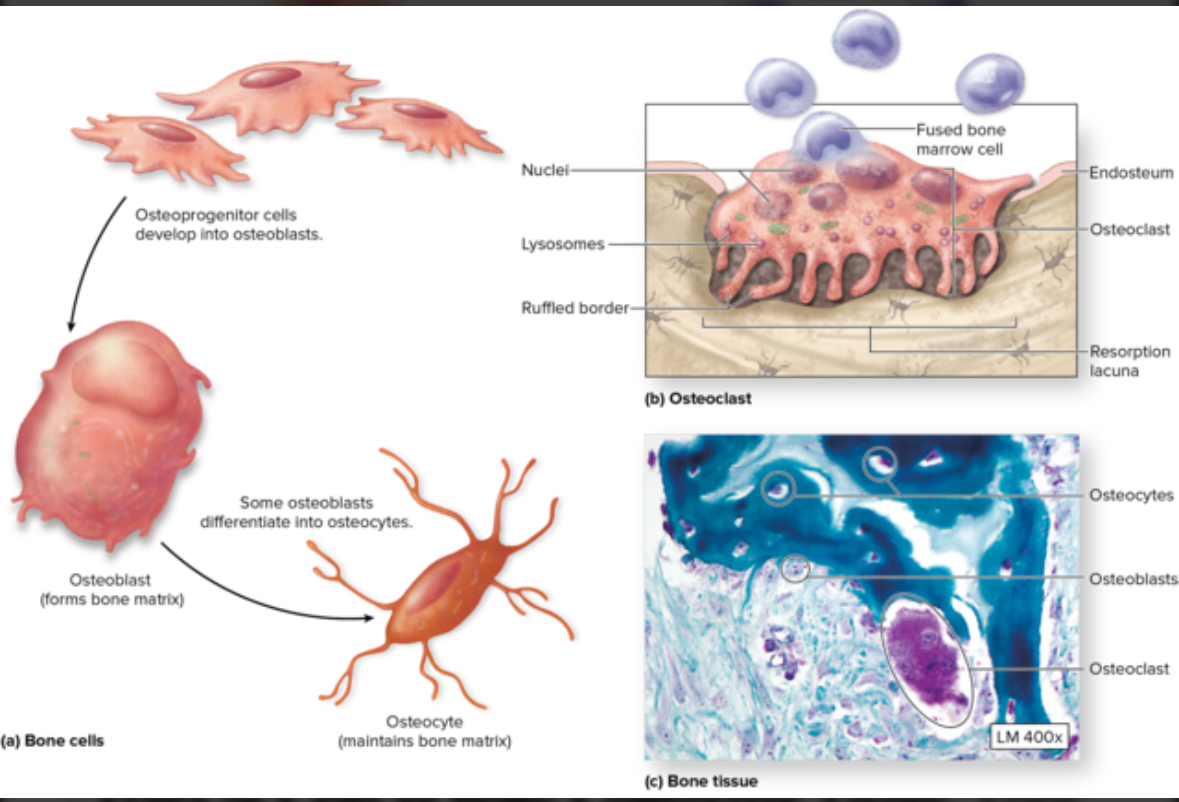
Cell types used in bone development
Osteoblasts
Osteocytes
Oateoclasts
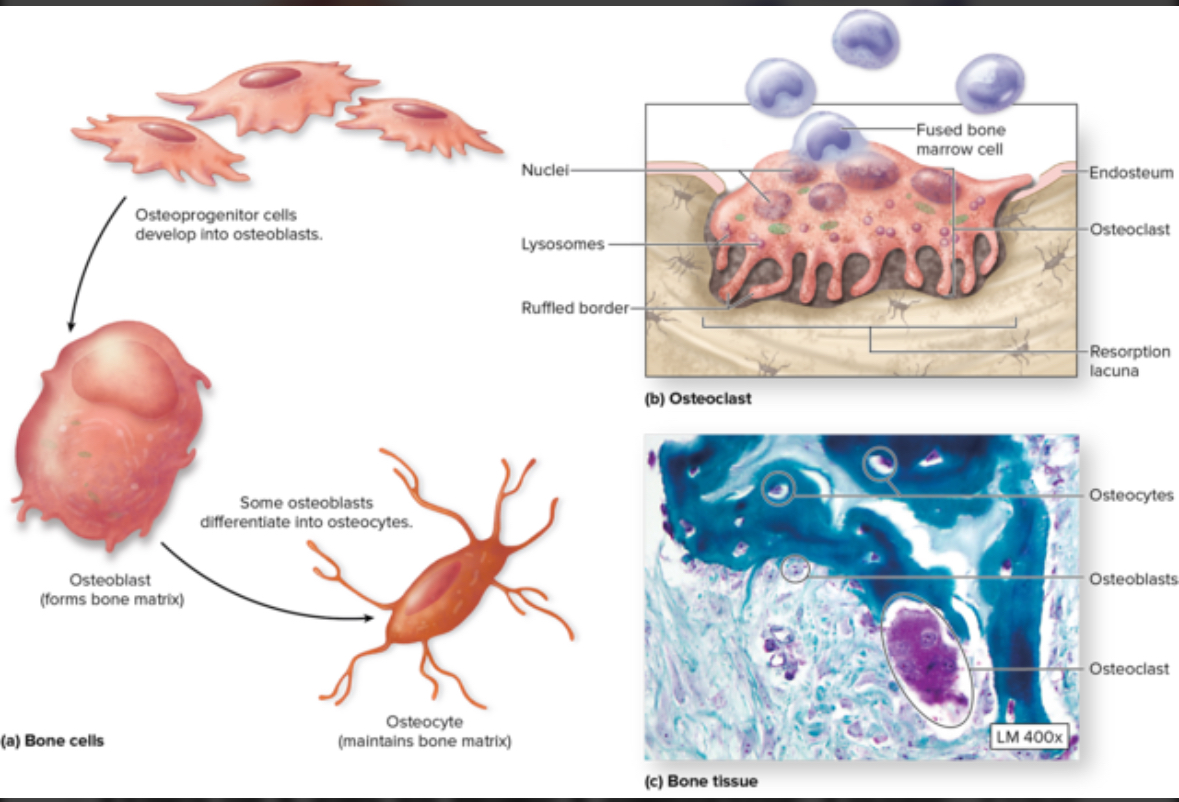
Osteoblasts
Structure: Come from stem cells = osteogenis cells. Cuboidal.
Function: Form bone ECM
Osteogenic cells
AKA osteoprogenitor
Structure: Stem cells
Location: Found in fibrous CT
Function: Turn into osteoblasts
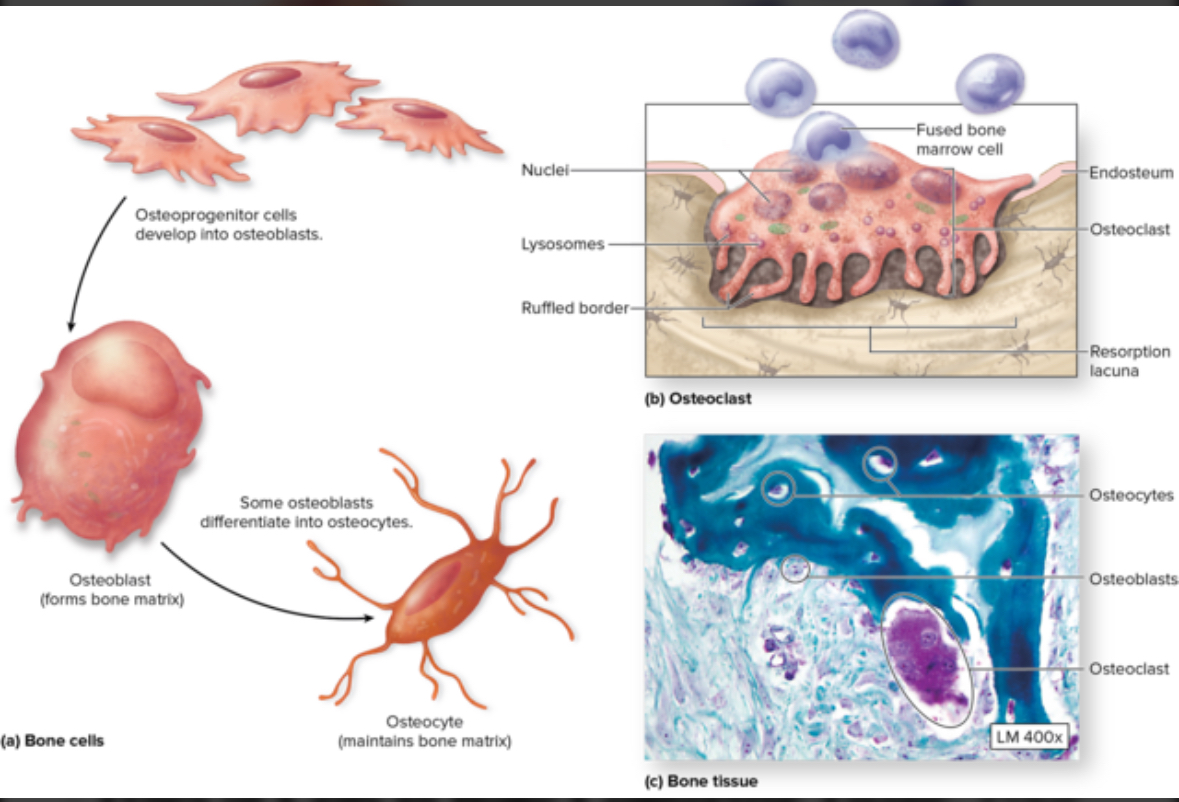
Osteocytes
Structure: Mature osteocytes
Location: Within the matrix of the lacunae in bone tissue
Function: monitor bone ECM, can sense mechanical stress such as exercise and convert back to osteocytes to create new bone tissue
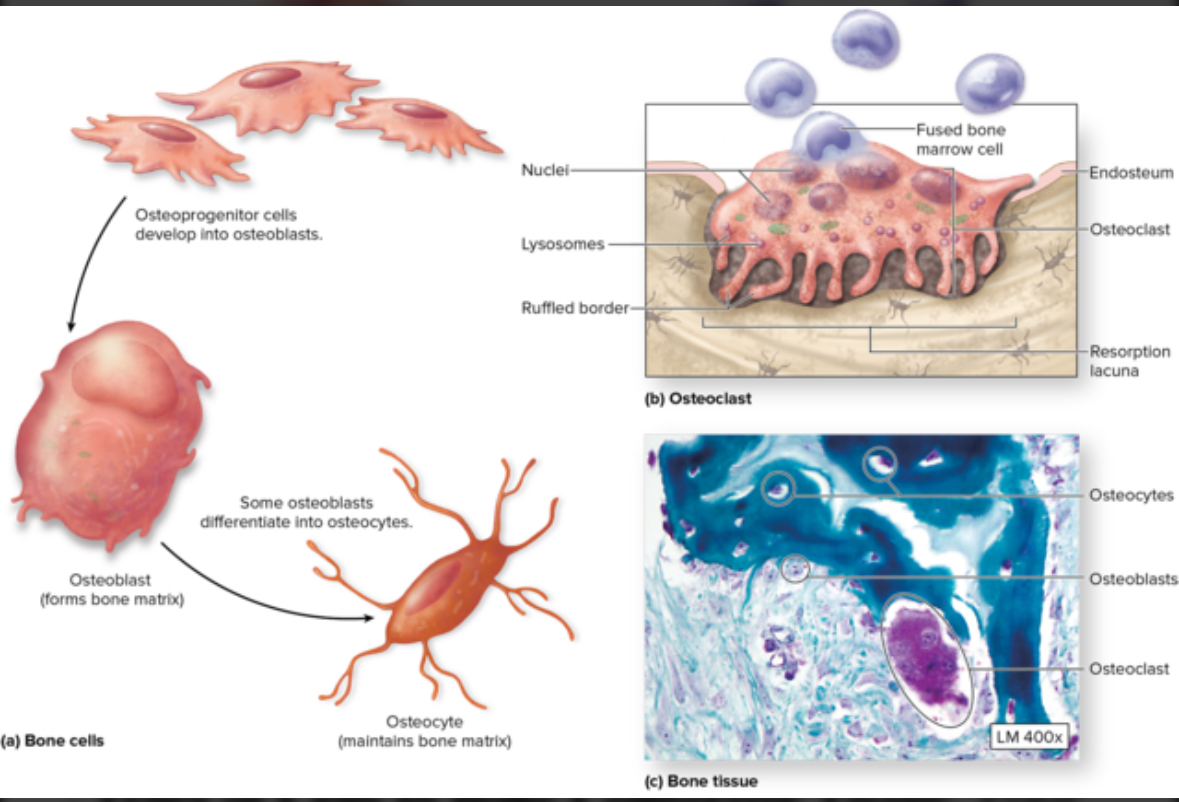
Osteoclasts
Structure: Come from macrophages stem cells. Large multinuclear phagocytic cells.
Location: Within or adjacent to a depression or pit on the bone surface.
Function: Dissolve bone ECM. Eat up bone tissue. Bone respiration.
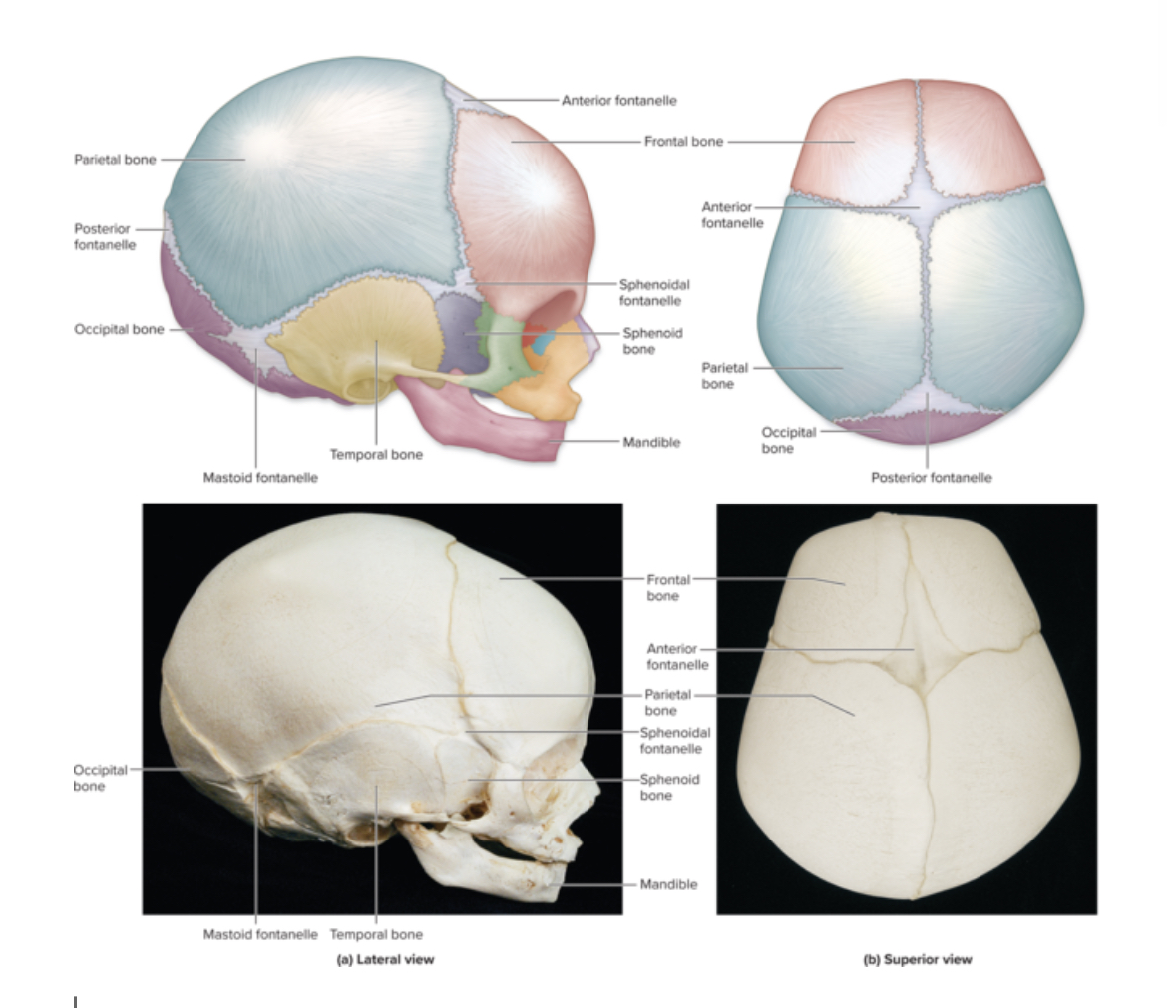
Fontanels
Structure: soft spot. Fibrous CT that has not formed into bone yet in an infant.
Location: skull
Function: flexibility during birth and brain growth
Sutures
Structure: Immovable joints. DRCT. Turn into bone tissue around age 50 = ossification.
Location: Skull
Function: connects cranial bones together
Bone remodeling
Replacement of bone tissue with new bone tissue
2 processes of bone remodeling
Bone deposition by osteoblasts
Bone resorption by ostroclasts
2 main purposes of bone remodeling
Maintaining blood Ca²+ levels. Increase Ca = bone resorption. Decrease Ca = bone deposition.
Accommodate mechanical stress. Increase weight training = more bone deposition. Immobility = weaker bones = less bone density.
Osteoporosis
Trabeculae more porous. More bone resorption. Related to hormones, estrogen. After menopause bone density decreases. Build strong skeleton before menopause.
Bone repair
Break bone to heal bone
Bone break steps
Form hematoma = blood clot
Form soft callus. Tissue = cartilage and collagen. Fibroblast create collagen fibers. Chondroblasts create cartilage fibers. Bridge gap between broken ends. Fibrocartilaginous cells.
Form hard callus = bone tissue.
Bone remodeling. Continued to deposit new bone tissue from osteoblasts