Topic 4- Fungi
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What type of organisms are fungi?
Heterotrophic eukaryotes.
What is the closest known relative (sister group) to fungi?
Nucleariids, a group of single-celled protists.
From what type of ancestor did fungi evolve?
A unicellular, aquatic ancestor.
When did fungi colonize land?
~470 million years ago, before plants.
How many major fungal groups (phyla) exist?
Five.
How do fungi obtain nutrients?
By absorbing them from the environment (heterotrophic).
What type of digestion do fungi use?
External digestion – They secrete enzymes (hydrolases) to break down organic material.
Do fungi perform photosynthesis?
No, they do not produce their own food.
What is the main structural component of fungal cell walls?
Chitin.
Do fungi primarily have a haploid or diploid life cycle?
Mostly haploid, with brief diploid stages.
What are the two major forms of fungi?
Single-celled fungi – Yeasts. Multicellular fungi – Mycelium (network of hyphae).
What is mycelium?
The fungal body, consisting of a network of hyphae.
What are hyphae?
Long, branching filaments that grow in and around food sources.
What are the three main types of specialized hyphae?
Predatory Hyphae – Capture and digest small organisms. Mutualistic Hyphae – Symbiotic fungi that benefit hosts. Reproductive Hyphae – Aid in spore dispersal.
What are haustoria?
Specialized hyphae that penetrate host tissues and extract nutrients.
What are mycorrhizae?
Symbiotic fungi that help plant roots absorb nutrients.
What are fruiting bodies?
Large, multicellular reproductive structures (e.g., mushrooms).
What are fungal spores?
Haploid (n) reproductive cells that develop into a new organism.
How are spores dispersed?
Wind, water, or animals.
Why is sexual reproduction important for fungi?
It increases genetic diversity.
How do fungi determine compatibility for mating?
By releasing pheromones.
What are the main steps of sexual reproduction in fungi?
Plasmogamy – Fusion of cell membranes forms a heterokaryon (n + n). Karyogamy – Fusion of nuclei produces a diploid (2n) zygote. Meiosis – Produces haploid (n) spores.
What percentage of fungal species reproduce only asexually?
~20,000 species.
What are molds?
Filamentous fungi that produce spores via mitosis.
How do yeasts reproduce?
Mitosis (equal division) and budding (new cell grows off parent).
What are the five major fungal phyla?
Chytridiomycota (Chytrids), Zygomycota (Zygomycetes), Glomeromycota (Glomeromycetes), Ascomycota (Ascomycetes - "Sac Fungi"), Basidiomycota (Basidiomycetes - "Club Fungi").
"Crazy Zebras Gallop Across Bridges."
Crazy → Chytridiomycota (Chytrids)
Zebras → Zygomycota (Zygomycetes)
Gallop → Glomeromycota (Glomeromycetes)
Across → Ascomycota (Ascomycetes - "Sac Fungi")
Bridges → Basidiomycota (Basidiomycetes - "Club Fungi")
What is the role of fungi as decomposers?
They break down organic matter and recycle nutrients.
What are mycorrhizal fungi?
Fungi that help plants absorb water and nutrients.
What are lichens?
Symbiotic associations between fungi and algae/cyanobacteria.
What are some fungal pathogens?
Athlete’s foot, ringworm (dermatophytes), Chytridiomycosis – Deadly fungal disease in amphibians.
What are predatory fungi?
Fungi that trap and digest small organisms (e.g., nematodes).
What antibiotic is produced by fungi?
Penicillin, from Penicillium.
How are fungi used in medicine?
Cyclosporine, an immunosuppressant used in organ transplants, comes from fungi.
What are some examples of edible fungi?
Mushrooms, truffles, and morels.
How do fungi contribute to food production?
Used in cheese production (e.g., blue cheese). Yeasts ferment sugars to make alcohol (beer, wine).
How is Saccharomyces cerevisiae used in research?
It is a model organism in genetics and biotechnology.
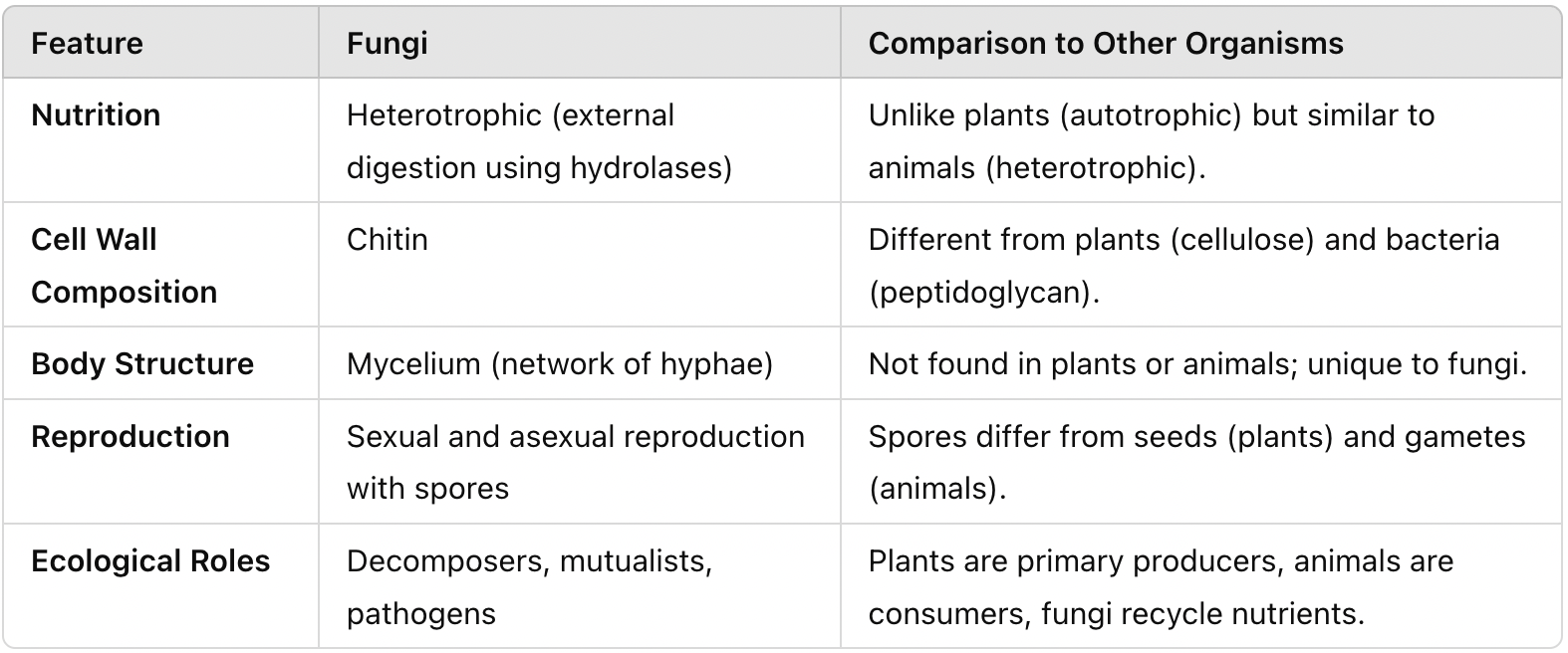
Sequence the evolution of fungi
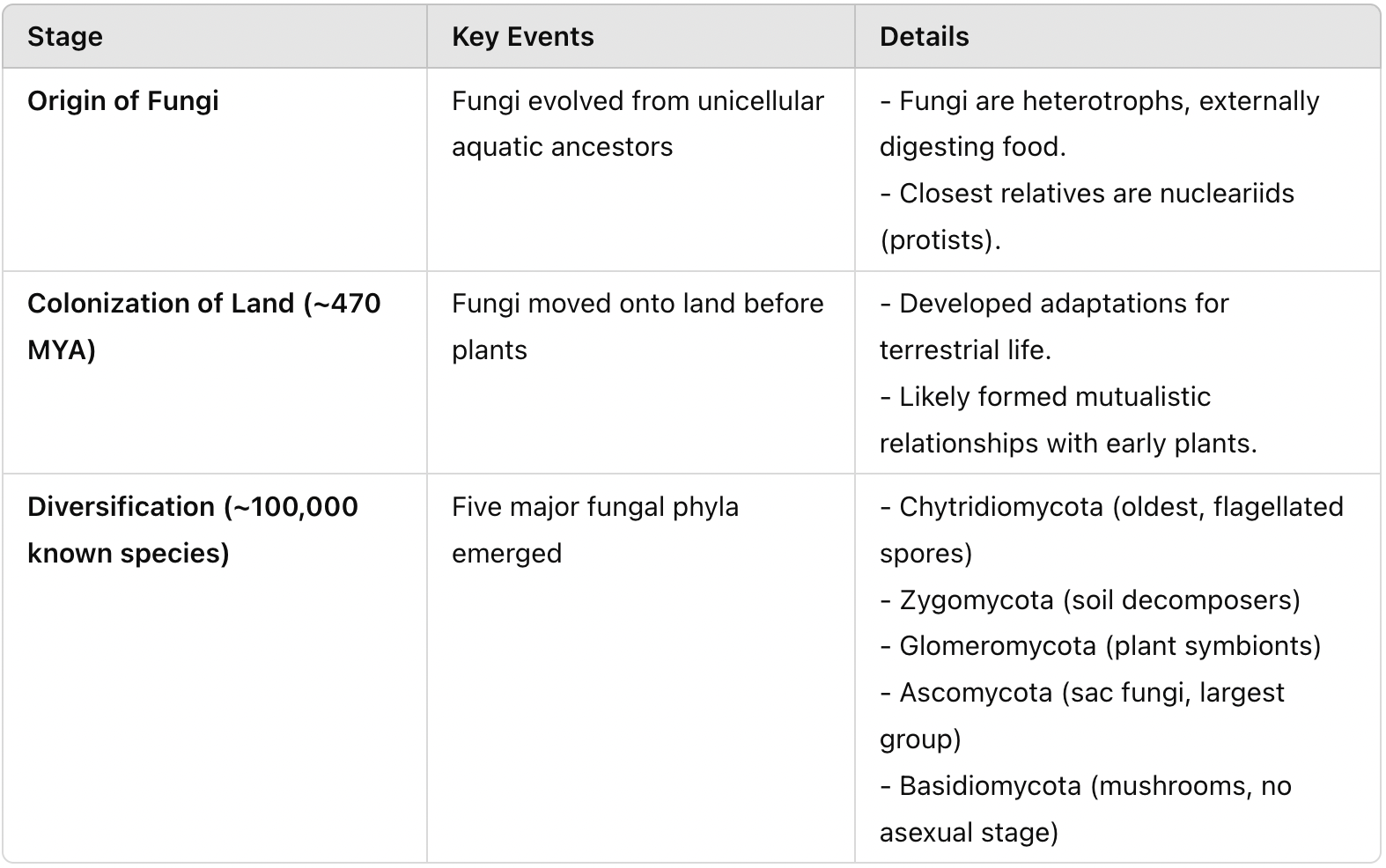
Compare and contrast the characteristics of fungi and other organisms (nutrition, cell wall, body structure, reproduction, ecological roles)
Sequence the general fungal life cycle (asexual and sexual reproduction)

Compare and contrast the major groups of fungi
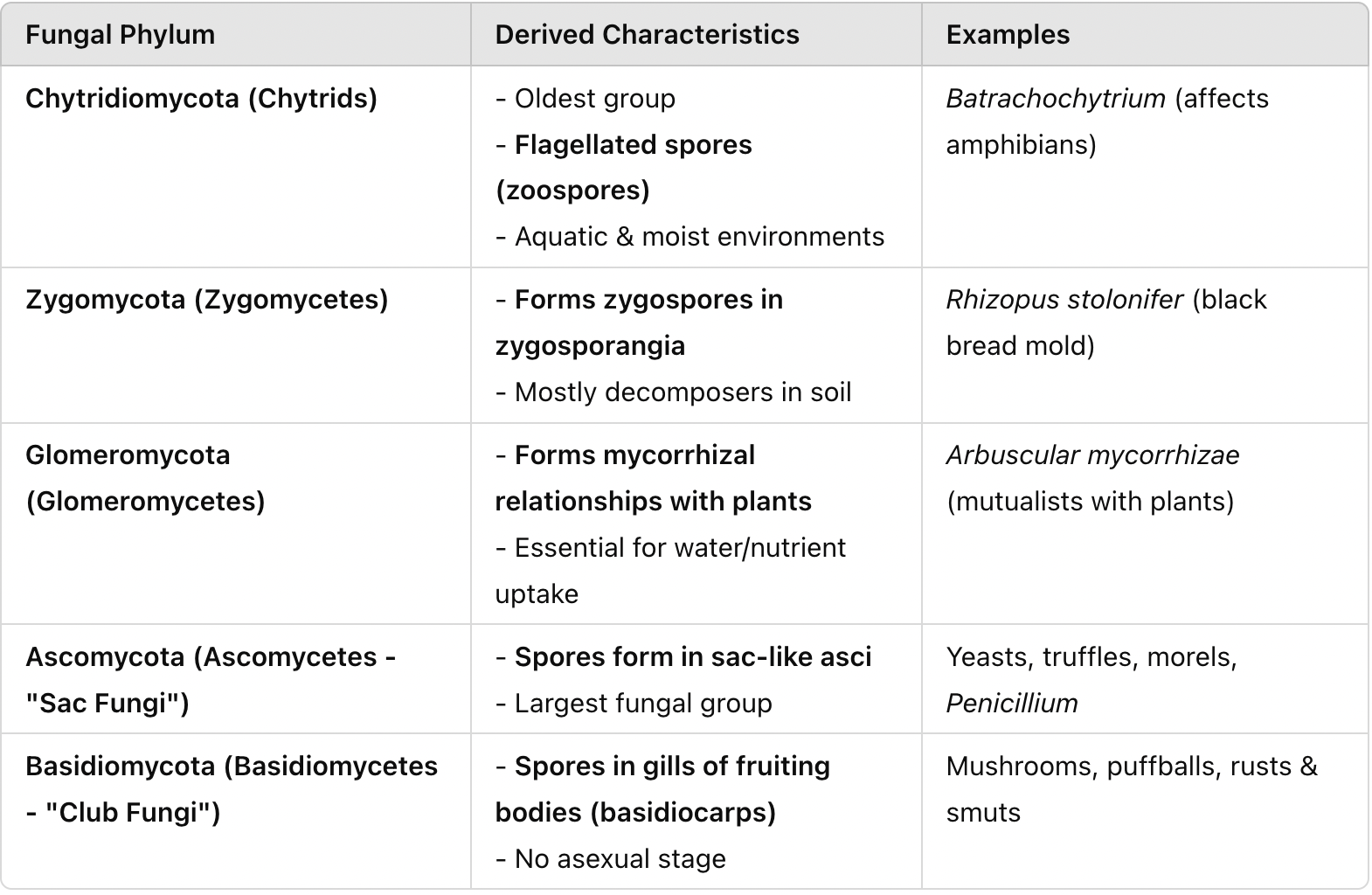
Compare and contrast ecological relevance of fungi