FOOD SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Section 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What is the primary function of a raising agent in a flour mixture?
Raising/Leavening agents are substances that cause dough to rise and to become light and porous.
What are the THREE main raising agents?
Air
Steam
Carbon Dioxide
State 3 ways to incorporate air during the preparation of food (mechanical)
Whipping or beating (egg whites/yolks)
Sifting dry ingredients
Folding in ingredients
Rolling ough
Creaming fat and sugar
List 2 examples of chemical raising agents
Baking soda 2. Baking powder
Briefly explain how Baking soda causes leavening
Baking soda, when combined with an acid and moisture, produces carbon dioxide gas, which expands and creates bubbles, leading to the rising of the dough or batter.
State 1 common acid ingredient that is commonly used with baking soda in leavening batters and doughs
Buttermilk/Sour Milk
All baking powders include ______, an ______ or _________________ and ____
soda, acid or acid-forming ingredient, starch
What is the SAS-phosphate baking powder?
A specific type of baking powder that contains sodium aluminum sulfate (SAS) as an acid component, which reacts with baking soda to produce carbon dioxide gas upon hydration and heating. It also contains phosphate which reacts with liquids during the mixing process and causes the lightening of the batter before baking.
In order to act as a leavening agent, yeast must produce _____ and ________
carbon dioxide and alcohol
Describe the process of yeast leavening bread
Yeast leavening bread involves the fermentation of sugars by yeast, resulting in the production of carbon dioxide and alcohol. Invertase converts sucrose to glucose and fructose. Maltase which changes maltose to glucose and zymase which turns fructose and glucose into carbon dioxide and alcohol. The carbon dioxide causes the dough to rise, creating a light and airy texture in the final baked product.
Precautions to observe during mixing when using yeast as a raising agent
Ensure the temperature of water is optimal
Avoid excessive salt
Allow proper fermentation time.
Precautions to observe during cooking when using baking powder as a raising agent
Use fresh baking powder
Maintain appropriate moisture levels
Avoid overmixing the batter.
What is dextrinization?
Dextrinization is the process where complex carbohydrates in starchy foods, like grains, break down into simpler, more digestible forms called dextrins when subjected to heat. This breakdown results in changes to the food's color, texture, and taste, often causing browning.
Carmelization is?
The process of heating sugar until it melts and turns brown, resulting in a distinctive (sweet/buttery) flavor and color.
Define the term ‘gelatinization’.
Starch gelatinization is the process where starch and water are subjected to heat, causing the starch granules to swell and burst open
What is ‘crystallization’?
Crystallization in cooking, particularly in candy making, is the process where sugar, after being dissolved in water, cools and forms crystals.
What is dextrin?
The more soluble carbohydrate formed when starch grains are exposed to dry heat.
State 3 effects of heat on meat
Collagen is softened - tenderization
Loss of nutrients (Vitamin B)
Meat shrinks due to water loss
Redness decreases (colour change) as temp increases
______ and ________ are the TWO terms used to describe the effect of heat on eggs.
Gelation and Coagulation
Differentiate between coagulation and gelation
Gelation is the formation of a gel like structure with no specific structure
Coagulation is the change from liquid to solid state with no specific structure (occurs during the frying/boiling of an egg)
Describe the effect of heat on fish
When fish is heated, the connective tissue that contains collagen is quickly converted to gelatin. This causes the fish to break apart into flakes.
What is denaturation?
Denaturation ("changing the nature") happens when protein molecules unravel from their naturally coiled state.
Define coagulation
Coagulation refers to the process where protein molecules, when exposed to heat, acids, or enzymes, change from a liquid to a solid or semi-solid state
What is the maillard reaction?
The Maillard reaction is many small, simultaneous chemical reactions that occur when proteins and sugars in and on your food are transformed by heat, producing new flavors, aromas, and colors.
Describe the term ‘syneresis’
Syneresis in cookery, especially with proteins, refers to the release of liquid (often water) from a gel or protein-rich mixture. This occurs when proteins coagulate and release trapped moisture, leading to a watery or curdled texture. It's often caused by overcooking or improper handling of protein-rich foods like eggs, custards, or meat.
What is meant by the ‘flash point’ of an oil?
It's essentially the point where the oil's vapors become flammable. [When the temperature is raised so high that the vapour spontaneously ignites.]
The _____ _____ is essentially the temperature when an oil starts to burns and produce smoke
smoking point
What are the 3 principles of heat transfer?
Conduction
Convection
Radiation
What is conduction?
Conduction is the method of heat transfer from one molecule to another by mans of direct contact.
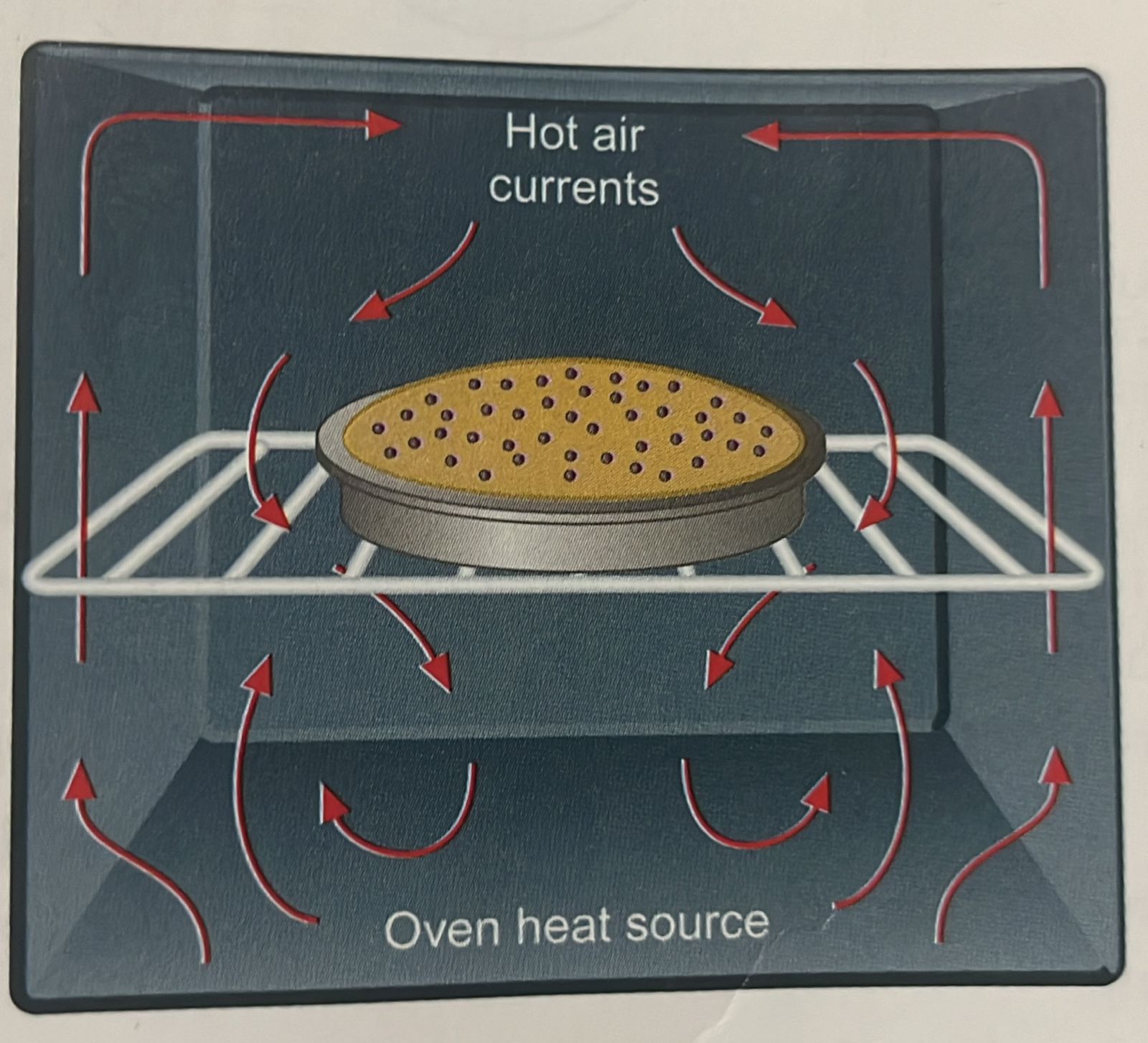
Identify the principle of heat transfer displayed
Convection
What is convection?
Convection is the transfer of heat through air or liquid currents. It is the natural movement of molecules in a fluid - hot air rises and cool air falls.
List 2 sources of radiant energy used in cooking
Toaster, The Broiler on the Range/Cooker, Coals from a BBQ
What is radiation?
Radiation heat transfer in cooking is the process where heat is transferred through electromagnetic waves, like infrared and microwaves, without requiring direct contact between the heat source and the food
What is a ‘food additive’?
Any substance other than the usual ingredients, that is added to food for a specific purpose
List 4 reasons why food additives are used in food
Flavouring - to enhance flavour
Appearance - to create a more appealing appearance
Preserving - to prevent spoilage and maintain freshness
Stabilizing
Thickening
Differentiate between natural and synthetic/artificial additives.
Natural additives are produced by plants and animals and are extracted directly from natural products while artificial additives are produced in the laboratory
List 3 chemical preservatives
Vinegar, Salt and Sugar
Discuss the scientific principle that explains the removal of excess water from cucumber during pickling
The spiced vinegar is more concentrated than the solution inside the cell of the cucumber therefore, the water will pass out of the cell through the process of Osmosis. Osmosis is the movement of water from a high to a low concentration through a semi-permeable membrane’
List 4 underlying principles of preservation
Removal of moisture - water activity is reduced (heat and evaporation) OR adding sugar or salt has the same effect (osmosis causes dehydration)
Altering the temperature - Either decreasing or increasing temperature can prevent microbial growth
Altering the pH - The pH can be lowered to make the environment too acidic for microorganisms to grow
Exclusion of oxygen - This ONLY prevents the growth of MOULD and aerobic bacteria.
Use of chemicals - A number of chemicals can be used to halt the growth of microorganisms [antibiotics, antioxidants, preservatives, disinfectants)
Irradiation - Used to reduce food borne pathogens and increase shelf life
Define the term ‘water activity’
The extent to which water is available in foods.
State 3 methods of drying used in preserving foods
Solar Drying (grapes, prunes, cocoa
Spray Drying (milk, instant tea, instant coffee)
Drum Drying (tomato paste)
Freeze Drying ( pharmaceuticals and coffee)
Baking (crackers)
Why is quick freezing important when preserving foods?
Quick freezing prevents the formation of large ice crystals. These large ice crystals spoil the texture of the food, During thawing the ice crystals puncture the cell walls and rupture tissues which causes a loss of juices.
State 3 guidelines to follow when selecting foods for preservation
Fruits should be at the optimal stage of ripeness for best flavour, colour and texture
Vegetables should be young and tender, full of flavour
Fish should be freshly caught
Meats and poultry should be of top quality
Outline the steps for freezing green beans
Wah green beans thoroughly to remove dirt and other visible contaminants
Blanching - denatures enzymes that cause deterioration, helps maintain better quality, removes some air and shrinks tissues to facilitate packaging
Dry beans before packaging
Place in sealed and suitable packaging (ensure there are no tears to allow freezer burns to form)
Rapid freezing
Describe suitable packaging for freezing fish,meats and poultry
Packaging should exclude air and moisture. It should not change upon exposure to low temp, should not crack or become brittle, should not absorb water, fat or blood.
Define sterlization
The complete destruction of microorganisms by heat
Define the term ‘pasteurization’
Pasteurization is the heating of milk etc. below its boiling point but at a temperature sufficient to kill pathogenic organisms. This can be the HTST (High Temperature Short Time) process.
State 3 reasons for preserving food
To make foods available when they are out of season
To prevent waste by making use of foods when they are plentiful and cheap and storing them for later use.
To make available to other territories foods not naturally found in their country
To make a variety of foods available all year round so as to prevent nutritional imbalance
Convenience,frozen and canned foods are quick and easy to prepare
What are the 4 causes of food spoilage?
Microorganisms - growth of microorganisms
Enzymatic Action
Physical damage - bruising
Insect and rodent damage
Three factors contributing to the growth of microorganisms are _____, ______ and _________
moisture, warmth and air
What is meant by the term ‘danger zone’?
The danger zone is the name given to the ideal temperature that facilitates the growth of microorganisms (40 TO 140 DEGREES F) or (4 to 60 DEGREES C)
List 4 symptoms displayed by an individual suffering from a food borne illness
Stomach ache
Nausea
Diarrhoea
Chills
Fever
What is a ‘food borne illness’?
Food-borne illnesses are diseases caused by consuming contaminated food or beverages.
What are examples of perishable foods?
Milk, eggs, raw meat, fish, fresh fruits, vegetables, and yogurt.
What are examples of non-perishable foods?
Rice, flour, canned foods, sugar, pasta, and dry beans.
What is the difference between perishable and non-perishable foods?
Perishable foods spoil quickly, have high water content, and need refrigeration.
Non-perishable foods have a long shelf life, low water content, and can be stored at room temperature.
How should perishable foods be stored?
In the refrigerator (0–5°C) or freezer (-18°C).
Simply outline the steps in sugar production (uding sugarcane)
What is a cereal?
The edible seeds or grains of cultivated grasses
What are the 3 main parts of a cereal grain
Germ
Endosperm
Bran
What is gluten?
The protein that is found in flour
What is meant by the term ‘milling’?
What is cornmeal?
Cornmeal is grounded corn. It is the whole grain grounded to a coarse mixture.
What part of the cereal grain is cornstarch made from?
The endosperm