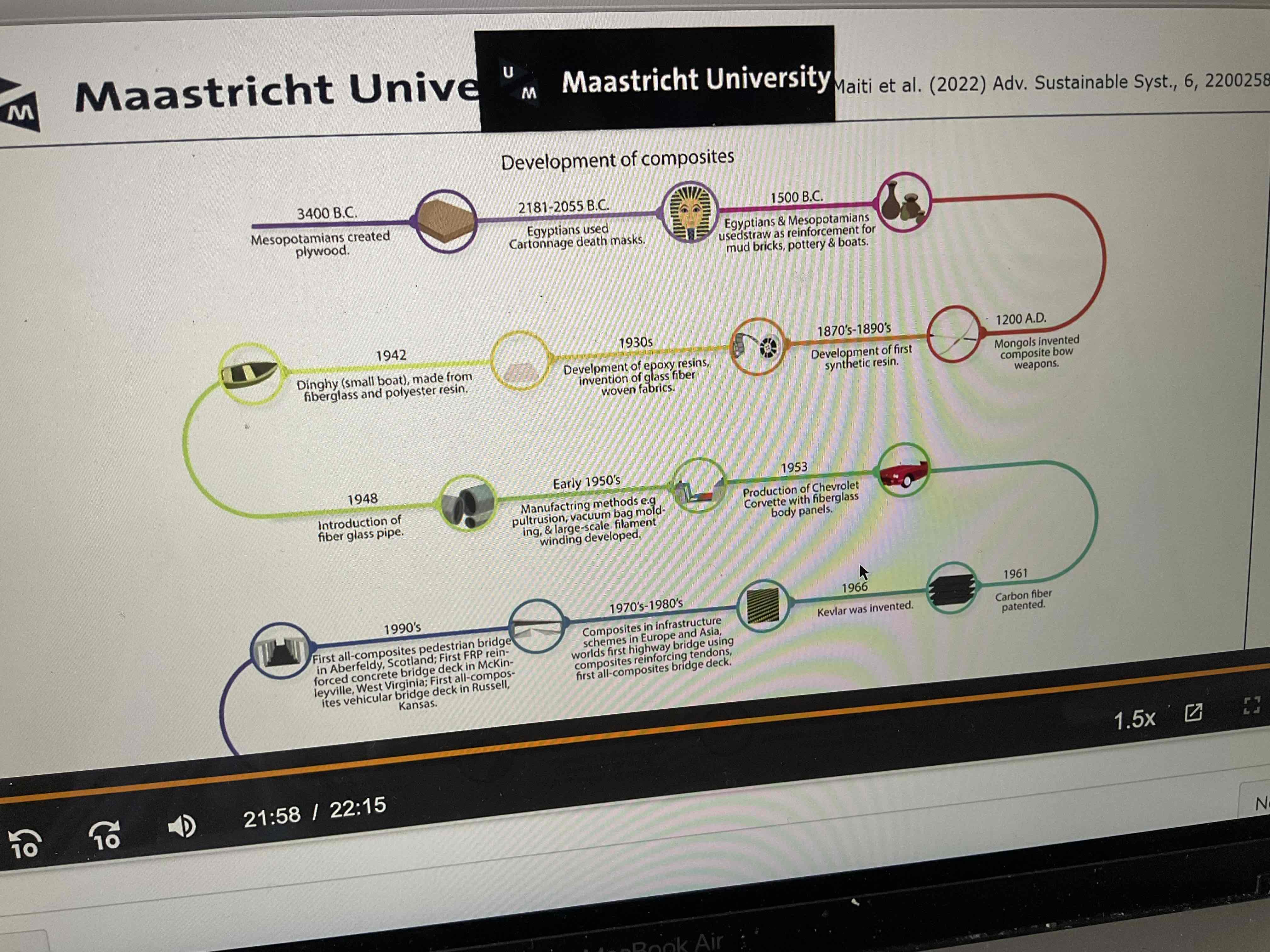
Materials engineering lecture 5 composites
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
What are composites
A combination of two or more materials with mostly different properties when out together give a unique set of properties. The materials to not blend or dissolve and can still be clearly distinguished from one another.
What are three types of composites and give examples
Natural: wood, bone, oyster
Synthetic: aerospace, automobile parts, appliances and parts, skis, nylon, fiberglass, reinforced concrete
Industrial: concrete, reinforced concrete, glass inforced aluminium, fiberglass
Draw the composite schema
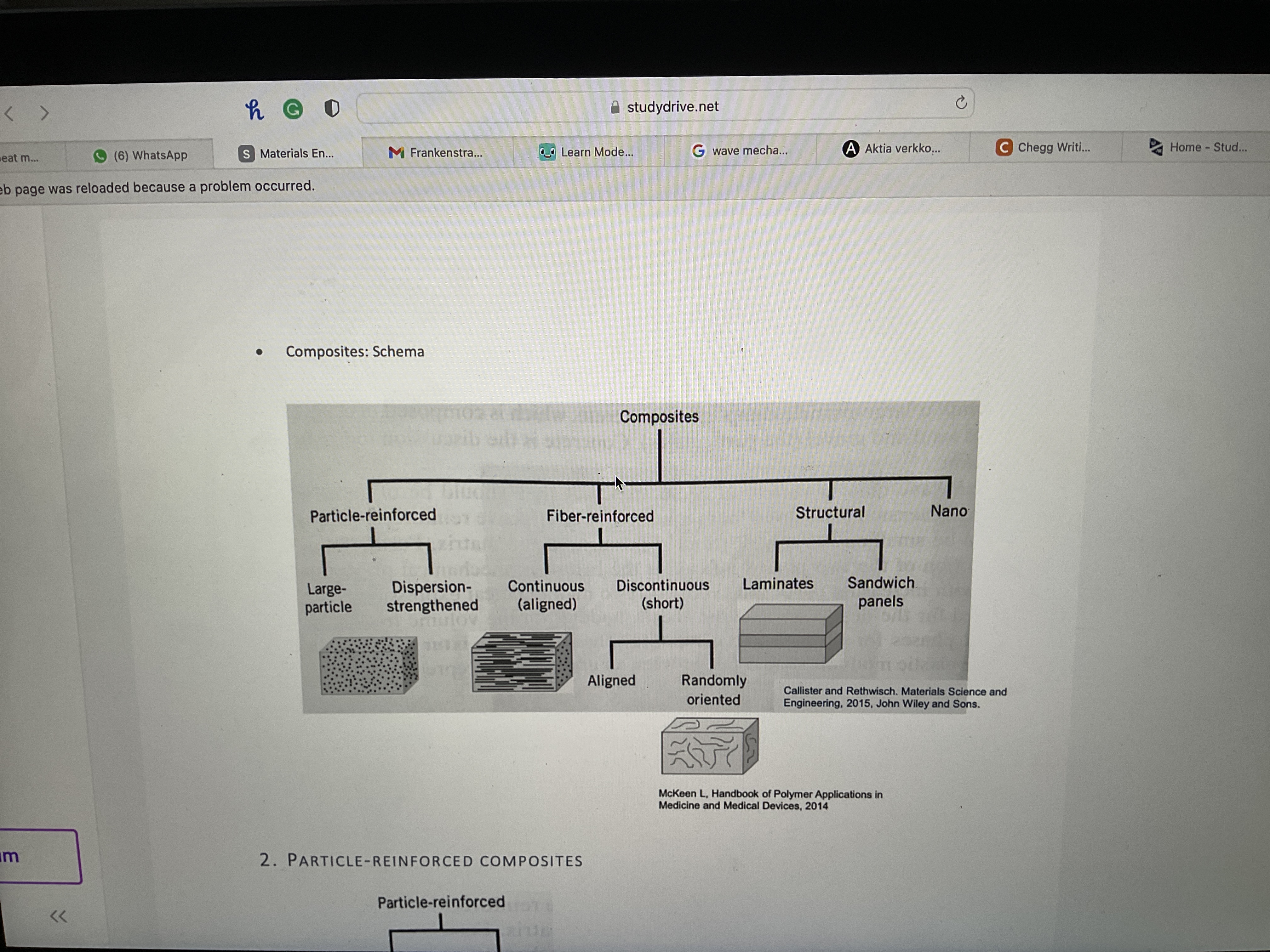
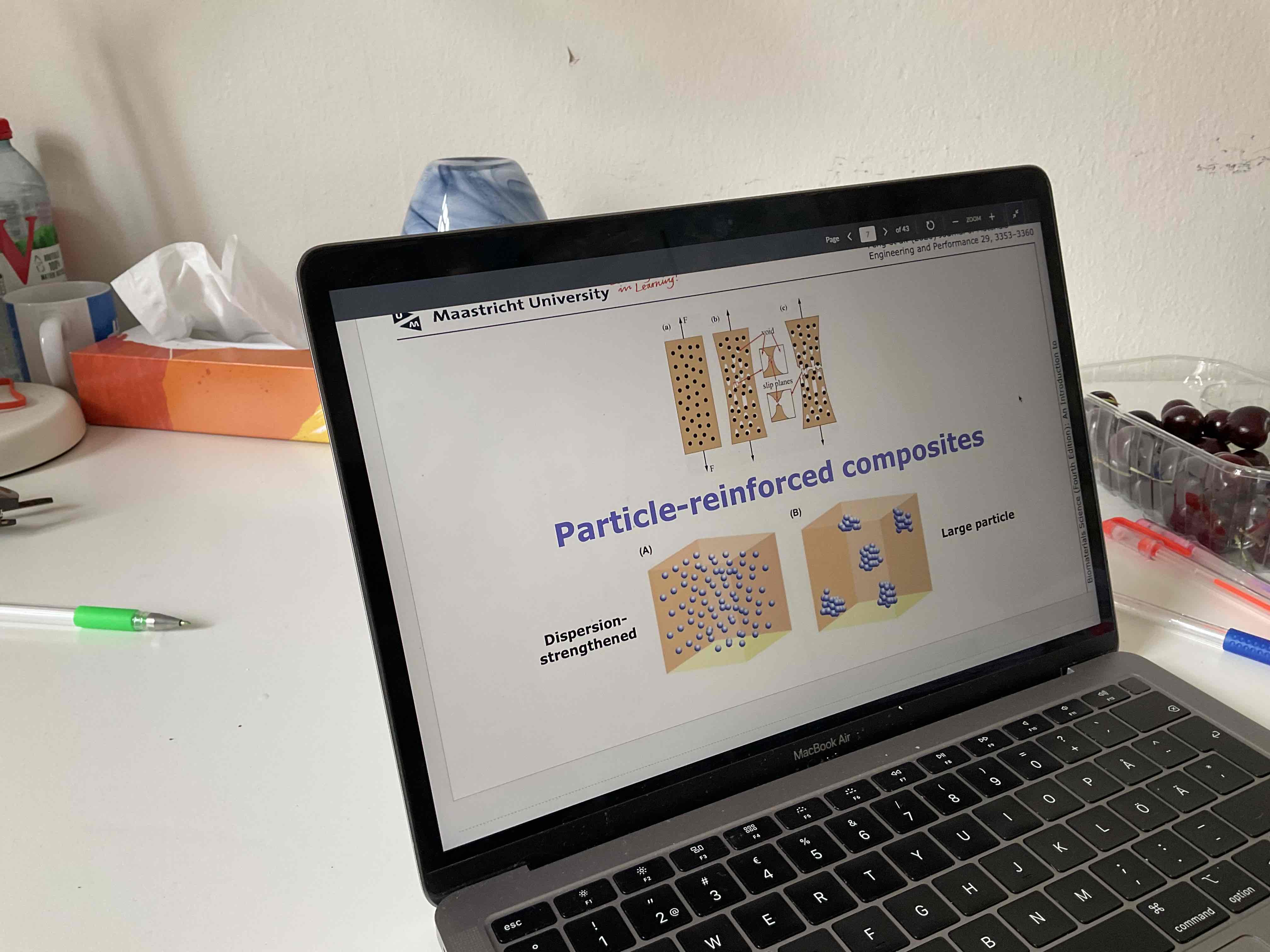
What main groups are particle reinforced composites in?
Large particle and dispersion streangthened
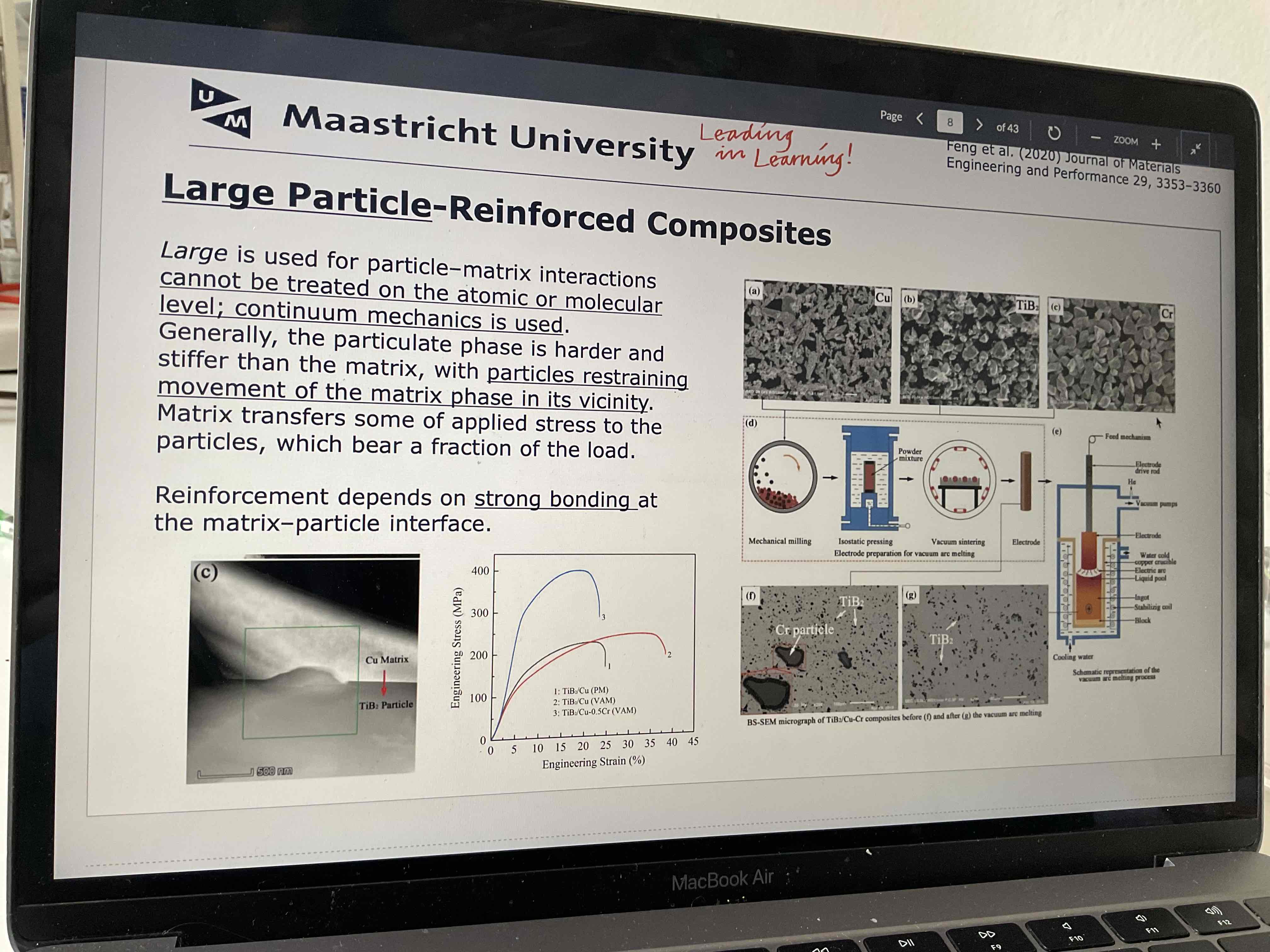
Tell about large particles: what? What do they do? Ex? Dimension?
Large particles, no atomic/molecular interaction between particles and the matrix
Large particles restrain movement of the matrix
Matrix transfer applied stress to particles that then bear a part of the load
Mechanical behaviour depends on bonding at the matrix particle interface
Example: concrete
Important: the particles have the same dimensions in all directions
Even distribution throughout the matrix—> good mechanical performance
Tell about dispersion-strengthened. What? How strengthened? Ex + 3 prop? 3 props?
Smaller particles (10-100nm), interaction at the atomic/molecular level
fine, very hard particles uniformly dispersed
Dispersed particles unreactive with the matrix—> streanghtening retained at elevated temperature and for extended periods of time
Ex: sintered aluminium powder; high strength, high creep resistance, high insensitivity to high-temp exposure
High thermal conductivity
High melting point
Excellent thermal stability

What are properties of fiber reinforced composites?3
High strength, stiffness, sensitive to gravity in terms of elasticity and specific strenght

What does critical fiber length mean? And what is the formula?
Necessary length for effective strengthening and stiffening of the material (Lc)

What are the three types of fibers?
Continuous+aligned, discontinuous+aligned, discontinuous+randomly oriented
What are the anisotropic, longitudal direction and transversal properties of continuous+ aligned fibers? + draw pic
Anistropic: properties of the composite depend on the direction in which they are measured
longitudinal direction: loading applied along the direction of the fiber alignment—> strongest
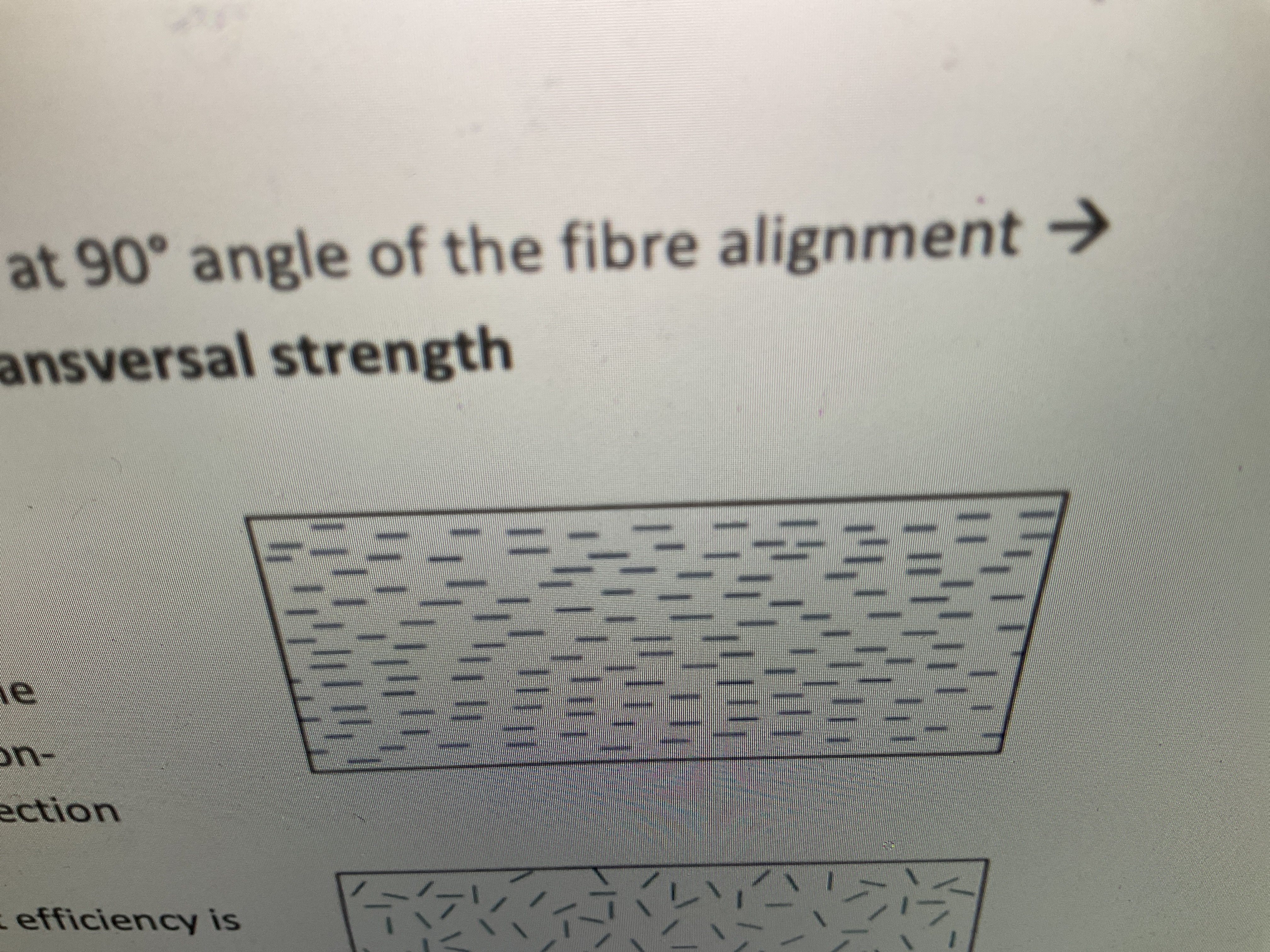
Transversal direction: loading applied at 90 degrees angle of fiber alignment—> premature failure: extremely low transversal strength (due to presence of voids)
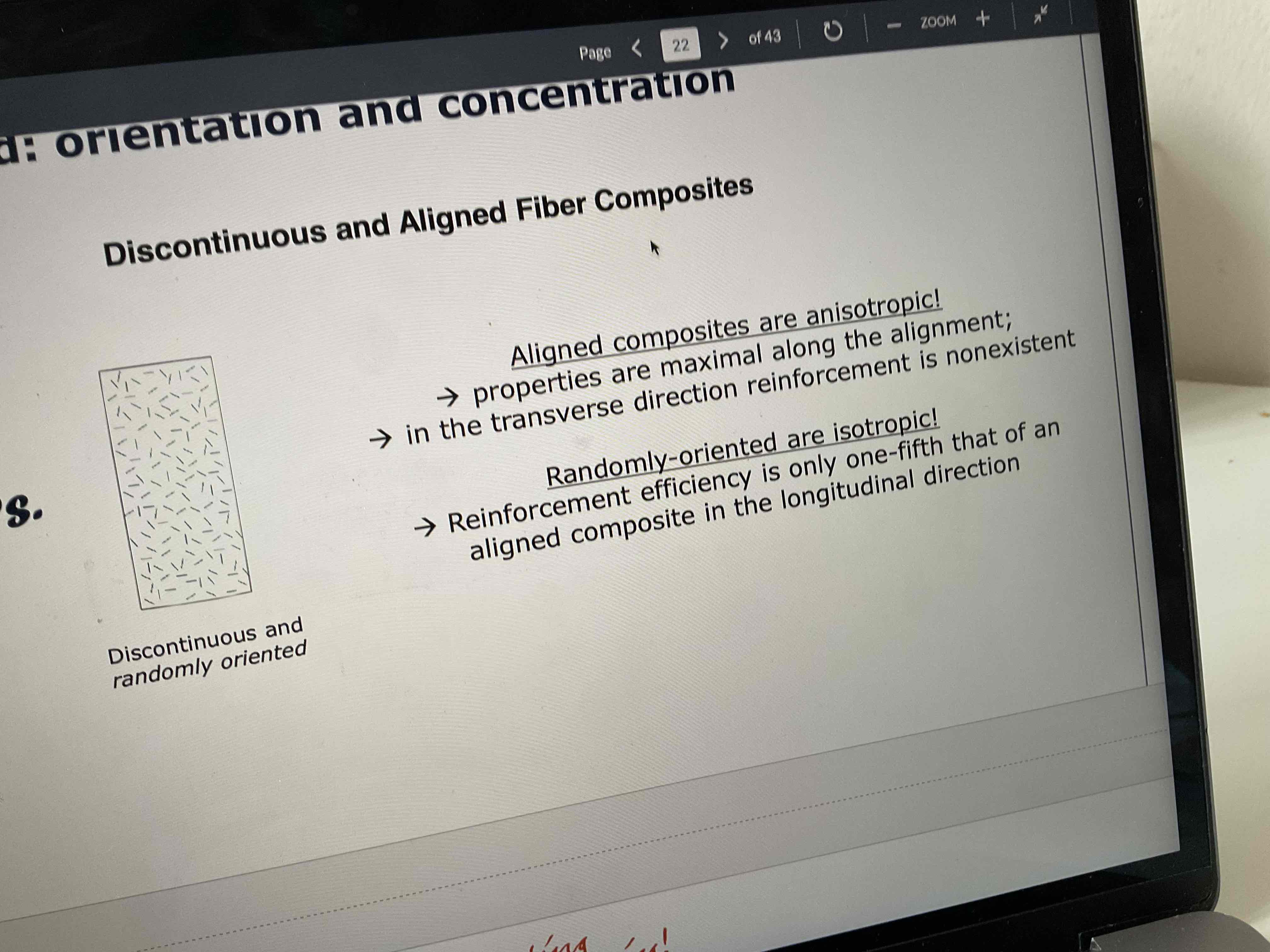
Is discontinuous+aligned anisotropic or isotopic? What properties does it have? Draw it
anisotropic!!!
Properties are maximal along the alignment, reinforcement is non-existent in the transverse direction
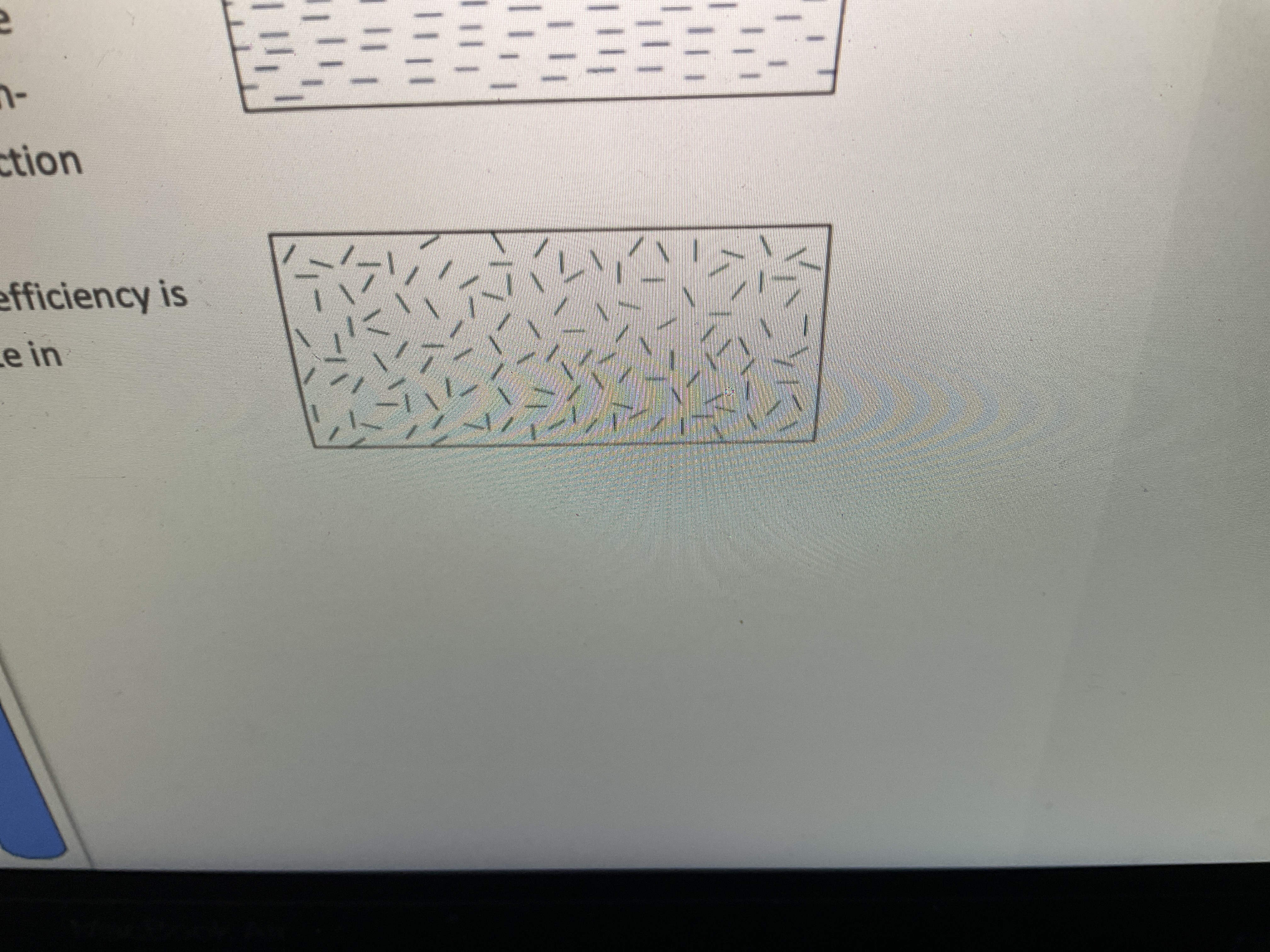
Is discontinuous+ randomly oriented anisotropic or isotropic? What is its reinforcement efficiency? Draw it
Isotropic!!! Reinforcement efficiency is 1/5 of an aligned composite in longitudinal direction
What are properties of whiskers (5)?
very thin crystal
Large length to diameter ratio
Flaw free (high crystalline perfection)
High strengths —> strongest known materials
Very expensive —> limited applications
what are properties of fibers? 2 and what materials usually 2
Polycristalline or amorphous
Small diameters
Either polymers or ceramics
What is the property of wires? What made of + 2 ex
metals (ex. Steel inforced concrete, molybdenum)
Large diameter
Read carefully (DONT CHEAT) polymer
easy fabrication low cost most common reinforcement (fibres) Glass → high-strength (composite), available, low cost, chemically inert Carbon → high specific modulus & strength, retained at elevated temp, not affected by moisture or solvents at room temp, specific engineering properties and cost effective Aramid → high strength, high modulus, relatively weak in compression, toughness, impact resistance, and resistance to creep and fatigue failure |
Read carefully (DONT CHEAT) ceramic
Resilient to oxidation at elevated temp
Improved fracture properties: advantageous when compared to only ceramic materials
Increase in fiber content improves strength and fracture toughness
What are 3 processing techniques of reinforced fibers
Pultrusion
Prepreg
Filament winding
What are properties of structural composites 6? What do they depend on?
multi layered
Low density
Structural integrity
high tensile
Compressive
Torsional strength
Properties also depend on geometrical design of the structural elements
What are the two main categories of structural composites?
Laminates and sandwich panels
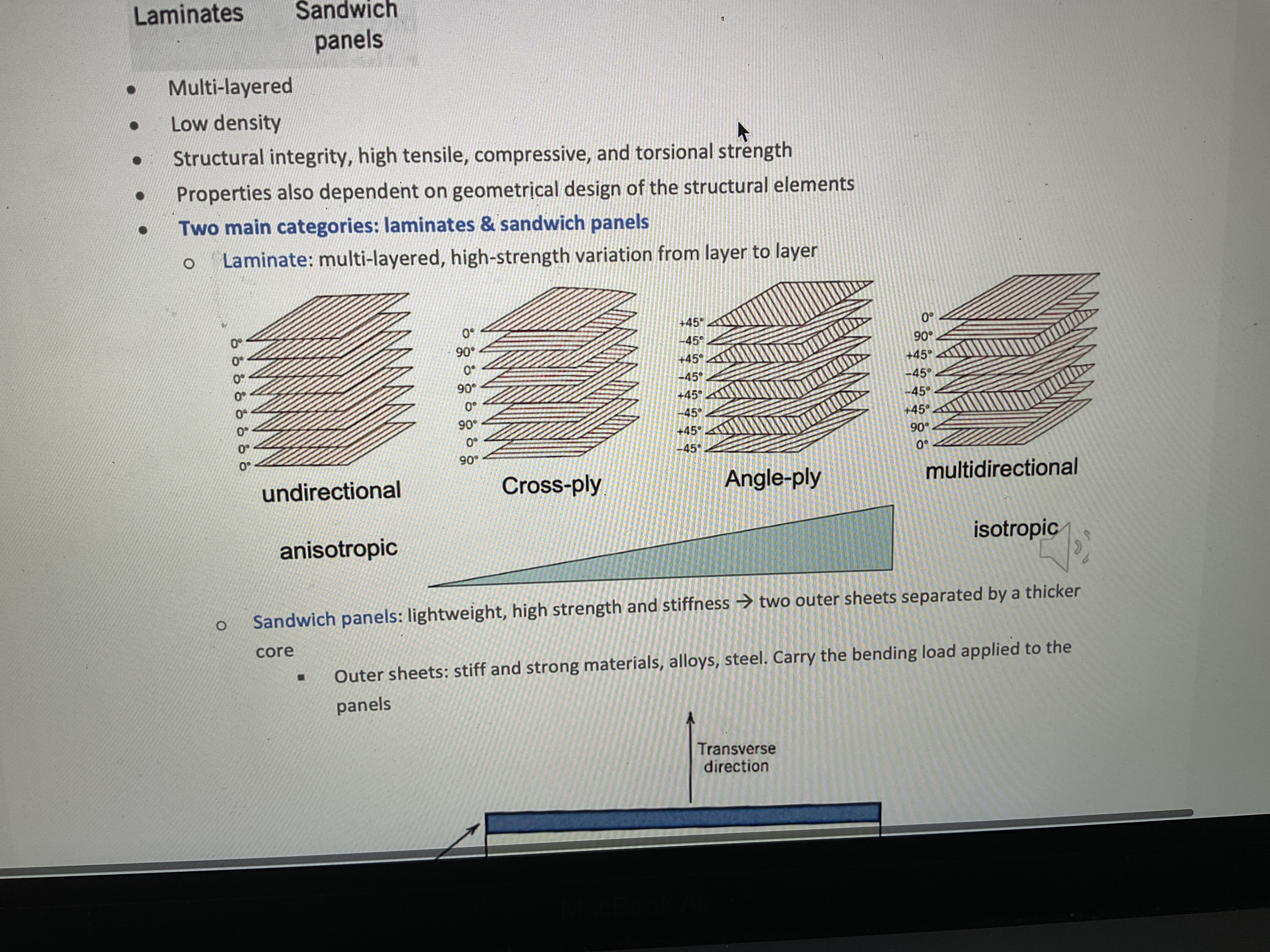
what are laminates? What do they look like? And what are the 4 options from anisotropic to isotropic?
Multi layered, high strength variation from layer to layer
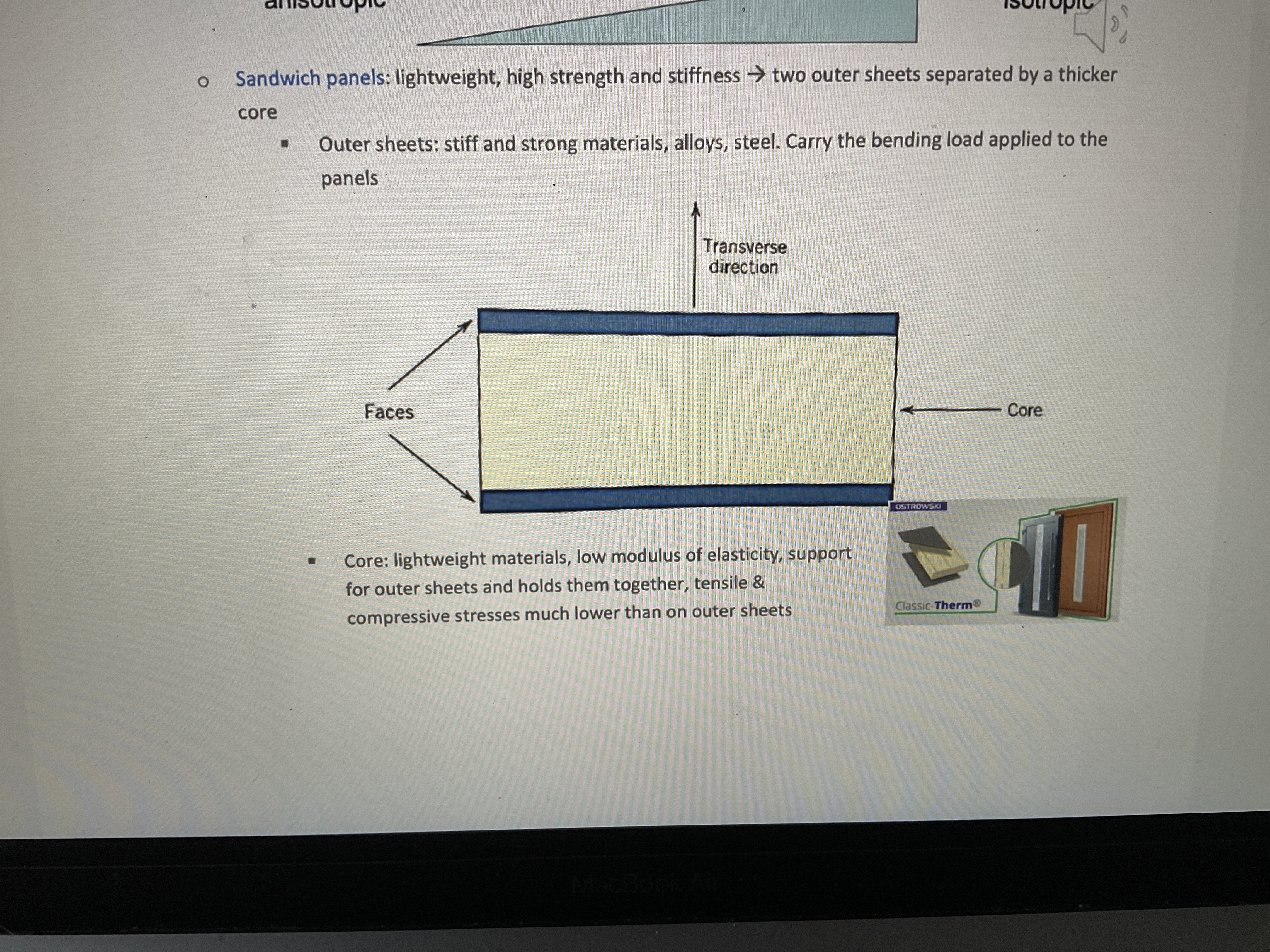
What are sandwich panels? Draw their build and explain about core
What are nanocomposites?
Nanoparticles embedded in a matrix
what size induced properties do nanocomposites have? 2
Increase in ratio of particle surface area to volume
Particle size
What material is the matrix usually? 3
Matrix may be metals and ceramic, the most common are polymers
Explain about nanoparticle properties 3
properties depend on shape of nanoparticles (Nanocarbons, nanoclays, nanocystals)
Properties can be taylored to meet requirements of specific applications
Size induced properties
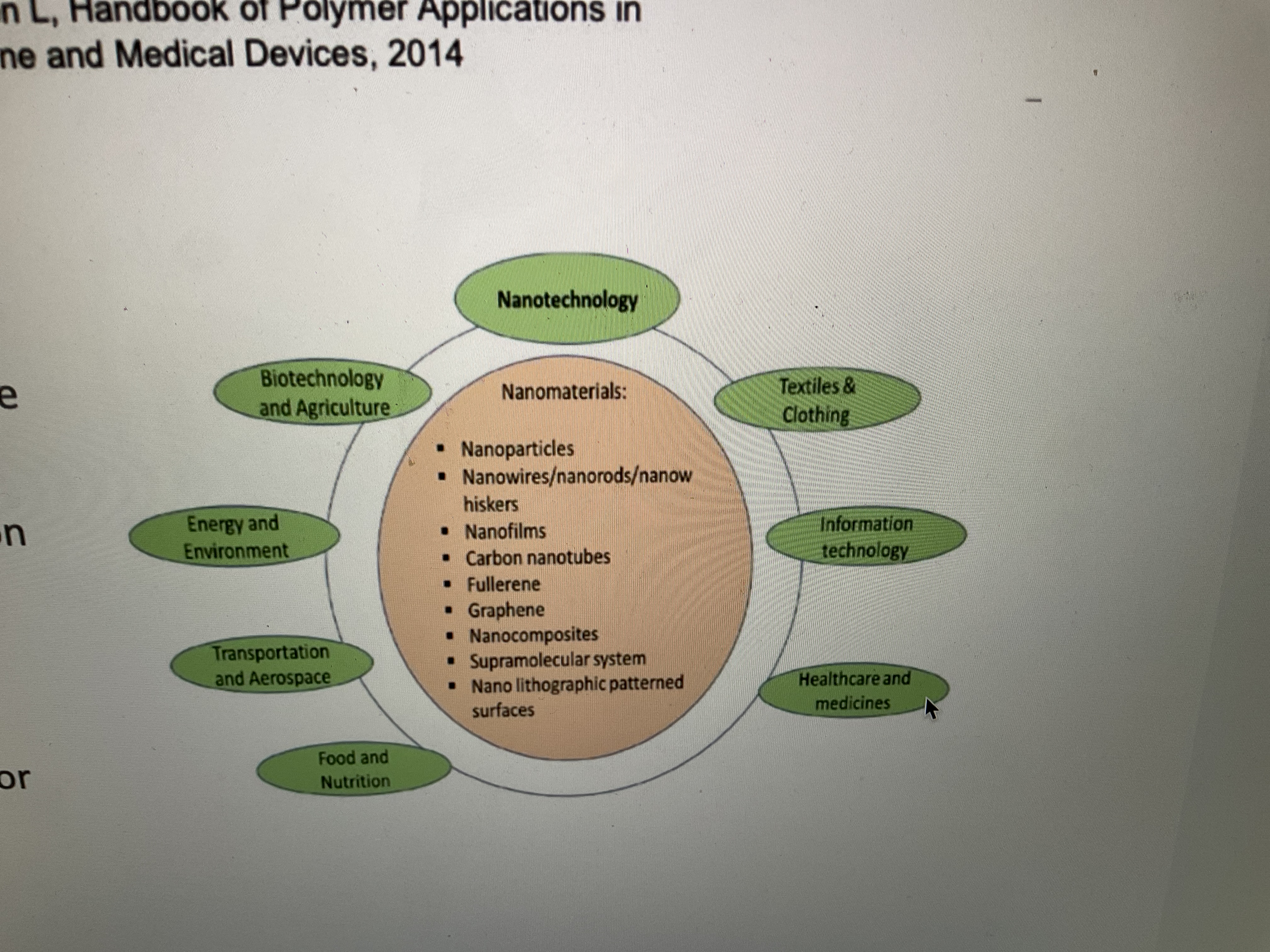
Study this pic. What is nanotechnology used for? Ex of materials
Give examples of three natural fibers and three synthetic fibers
Natural: palm, chicken fether and banana
Synthetic: carbon, Kevlar and glass
To effect a significant improvement in strength of the composite the fibers must be ___!
Continuous
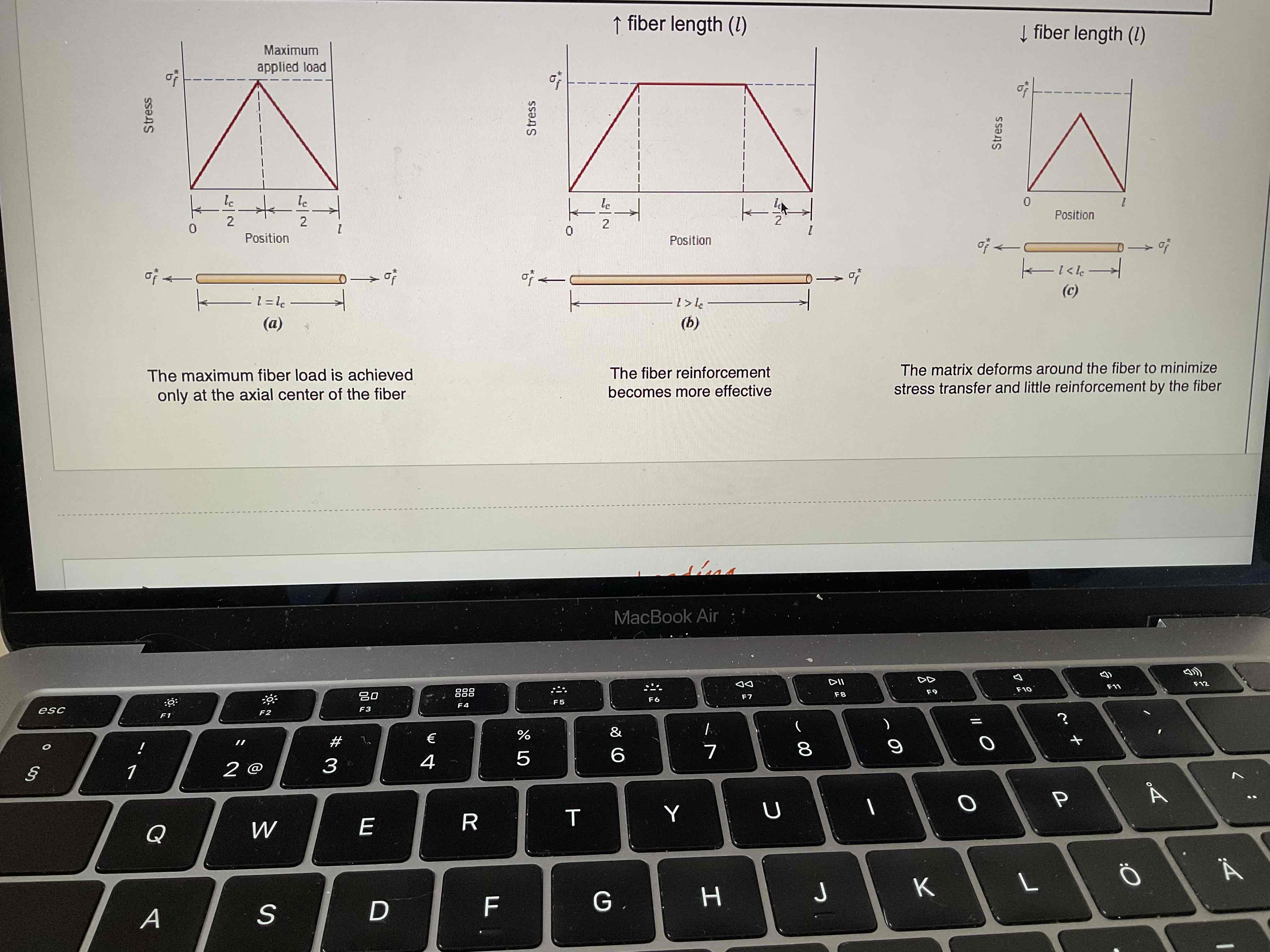
=<> of the scenarios
Critical fiber length= lc
Fiber length= l
A) l=lc
B) l>lc
C) l<lc
What do the mechanics of continuous and aligned fibers depend on?
stress strain behaviours
Phase volume fractions - fibers and matrix
Direction of the applied stress
Direction of the applied load
What does anisotropic mean?
Properties of the composite depends on the direction in which they are measured
What’s a fiber fracture?
Onset of composite failure. Once the fibers have fractured, the load borne by the fibers will be transferred to the matrix.
What is transverse strength influenced by?
properties of the fiber and matrix
Fiber matrix bond strength
Presence of voids
Is reinforcement efficiency lower or higher for discontinuous fibers?
Lower

Which is anisotropic and which is isotropic?
Tell about why would you want to process glass as fiber reinforced
high strength composite
Highly available
Low cost
Easy fabrication
Chemically inert
Tell about the reinforced matrix phase for metals
Ductile
Can be used at higher
temperatures → advantageous
Reinforcement improves stiffness, strength, abrasion resistance, creep resistance, thermal conductivity, stability
Noninflammable
Resistant to degradation
EXPENSIVE → limitation
Tell me why would you want to process carbon as fiber reinforced? 5
high specific modulus and strength, retained at elevated temp
High t oxidation
Moisture/solvents resistant at RT
Specific engineering (composite)
Cost effective
What are the 10 processing methods for reinforced fibers (ex glass and carbon)
Dry hand lay-up process
Resin transfer molding
Spray lay-up process
Vacuum-Assisted resin transfer molding process
Injection molding
Silicon rubber molding process
Compression molding
Filament winding process
Pultrusion (extrusion “pull”)
Autoclave molding process
Give three examples of when to use fiber reinforcements.

What is a structural composite?
Multilayered/hierarical and normally low density composite used in applications requiring structural integrity, ordinarily high tensile, compressive and torsional strengths and stiffnesses.
What do the properties od structural composites depend on?
properties of the consistent materials
Geometrical design of the structural elements
What are laminar composites composed of+
two dimensional sheets or panels (piles or laminae) bonded to one another
What are the different kinds of stacked piles of laminate panels (from most anisotropic to isotropic)

What are sandwich panels designed to be? And what are they made of (+structure)?
lightweight beams or panels having a relatively high stiffness and strength
Consists of 2 outer sheets separated by an adhesively bonded thicker (cheaper) core
The outer sheets are made of relatively stiff and strong material, typically aluminium alloys, steel and stainless steel, fiber reinforced plastic and plywood

What happens when a sandwich panel is bent? What does the panel stiffness depend on?
One face experiences compressive stresses, the other tensile.
Panel stiffness depends primarily on the properties of the core material (density, design) and it’s thickness (usually lightweight with low modulus of elasticity)
Give example of three core materials for sandwich panels
rigid polymeric foams
wood
Thin film honeycombs
What are examples of where sandwich panels are used?
What are nanocmoposites?
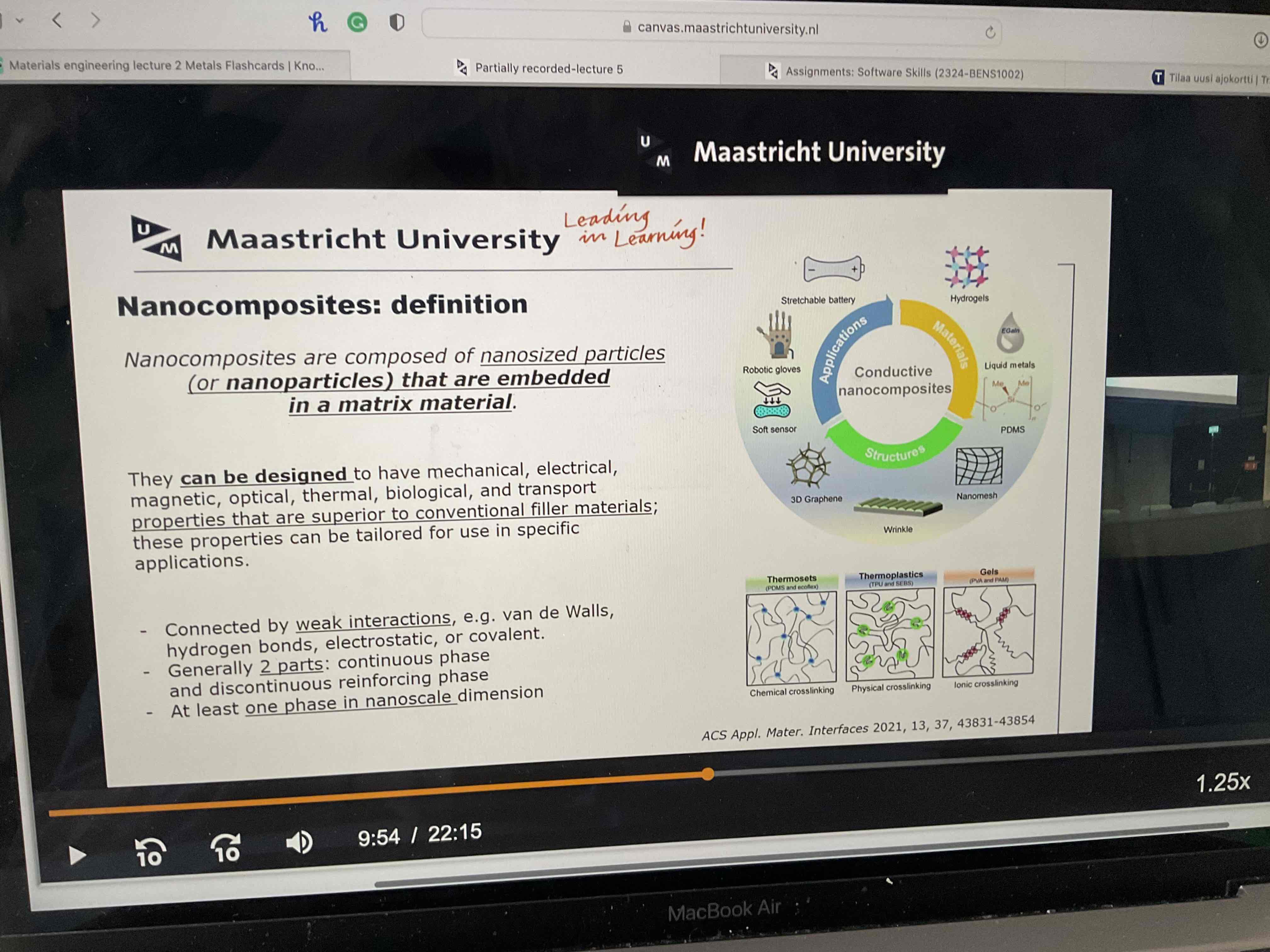
What two factors account for size induced properties in nanoparticles?
Ratio of particle surface to area volume
Particle size
Give an example of as the size of the particle decreases, the relative ratio of surface atoms to bulk atoms increases; this means that surface phenomena begin to dominate
ex. The permanent magnetic behaviour of some materials (for example iron cobalt and iron oxide) disappears for particles having diameter smaller than about 15 nm
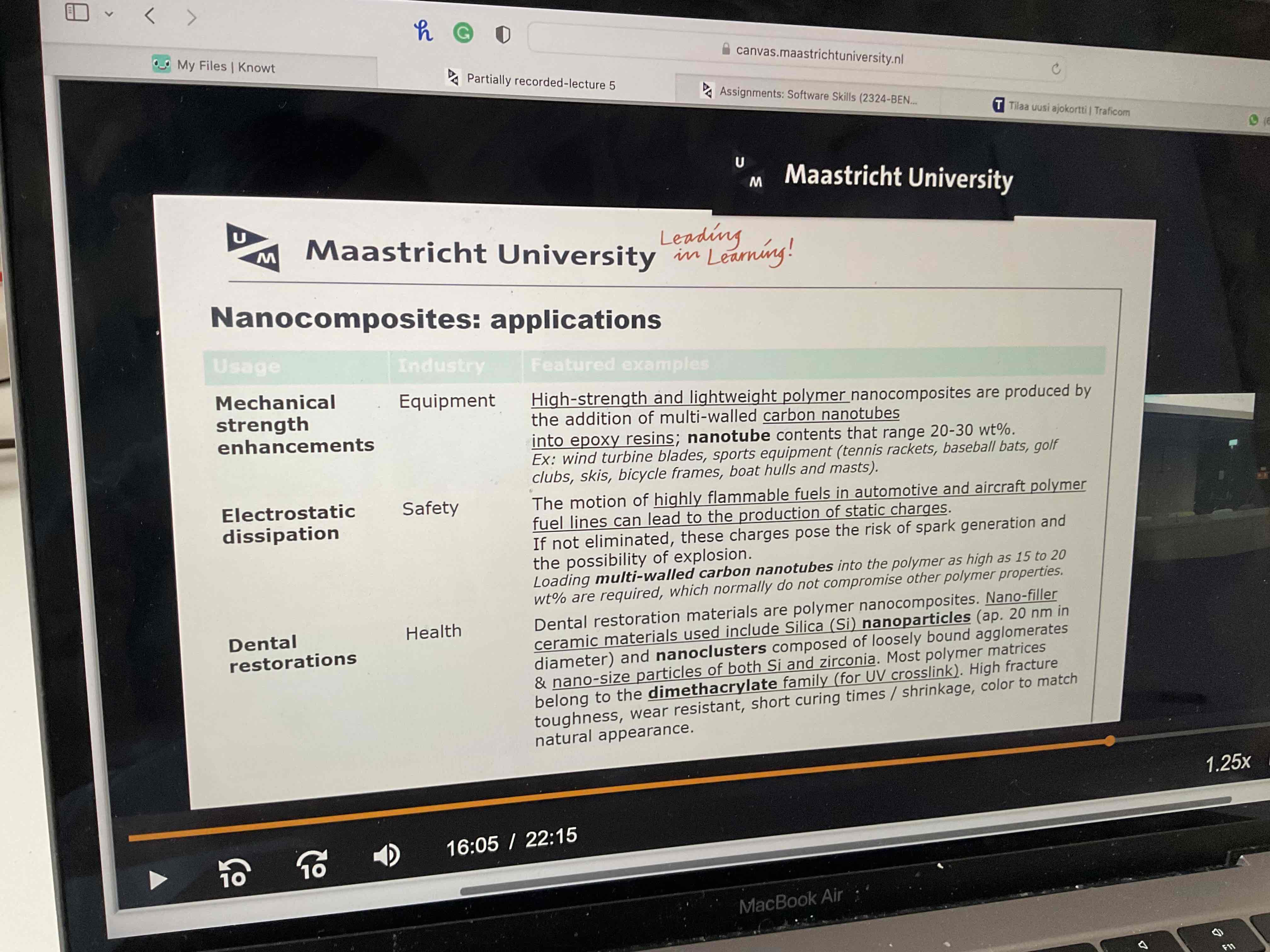
What can napcomposites be used for? 6 (dont look at pic before answering)
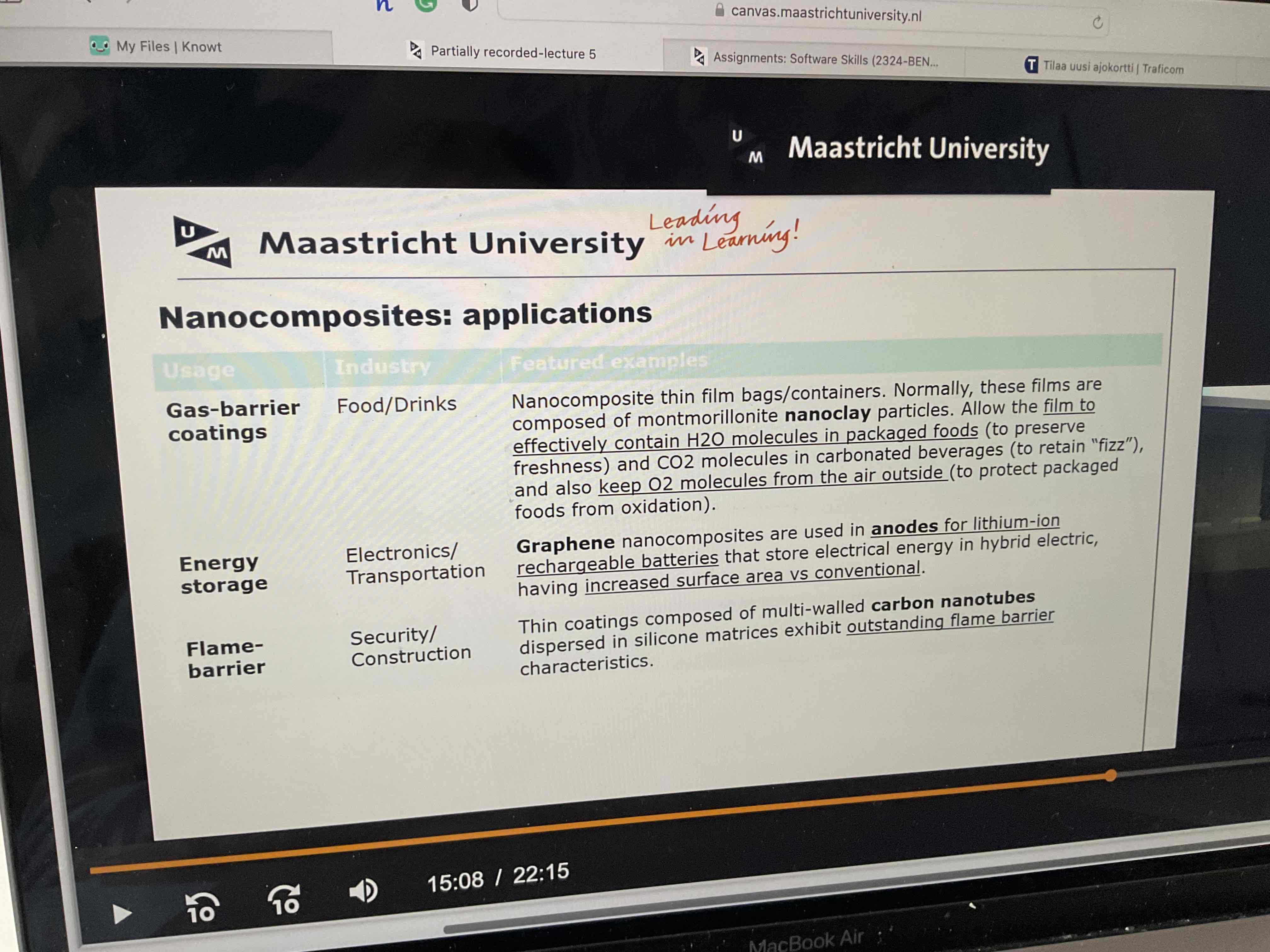
Look at pic
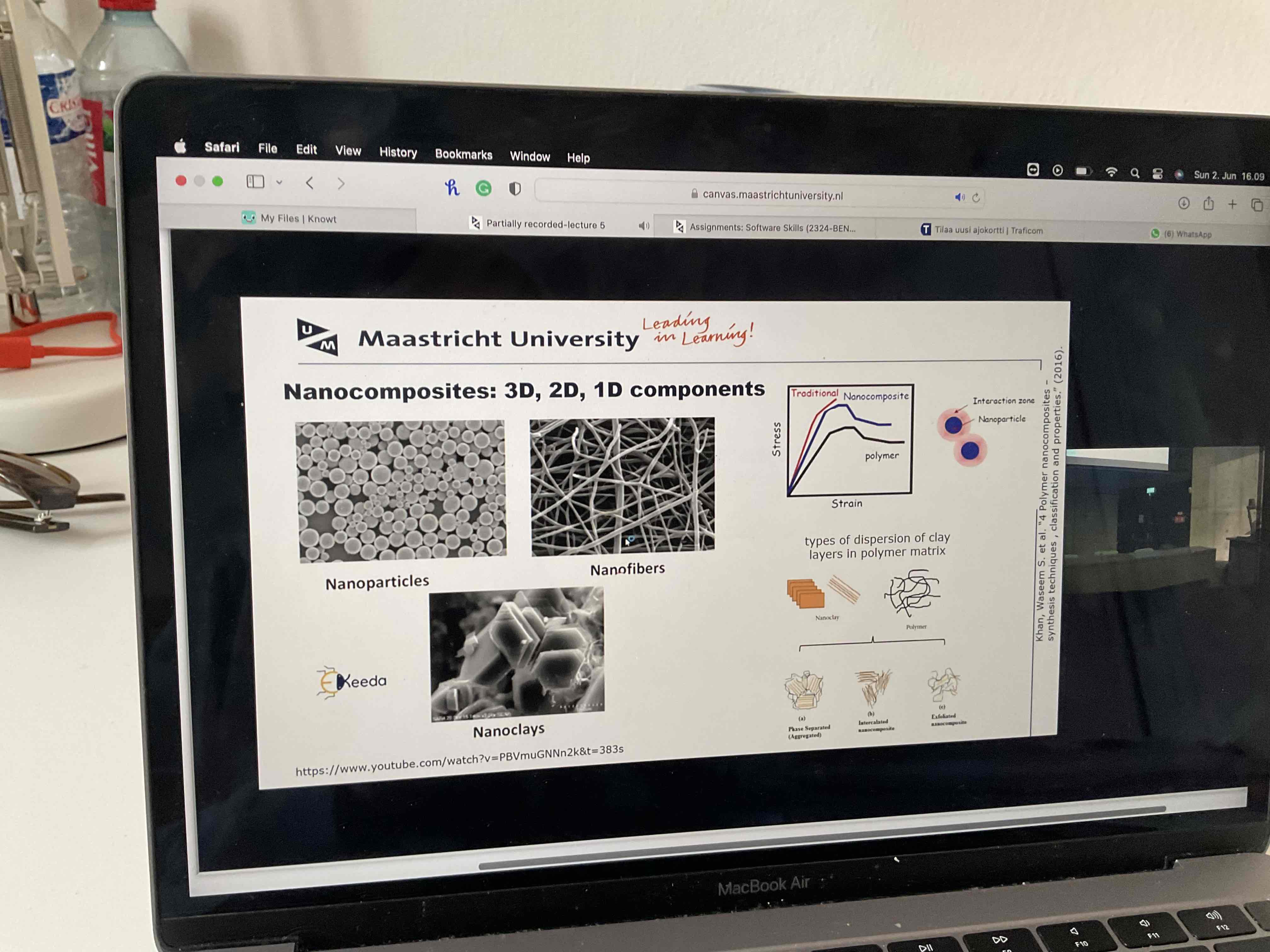
Read
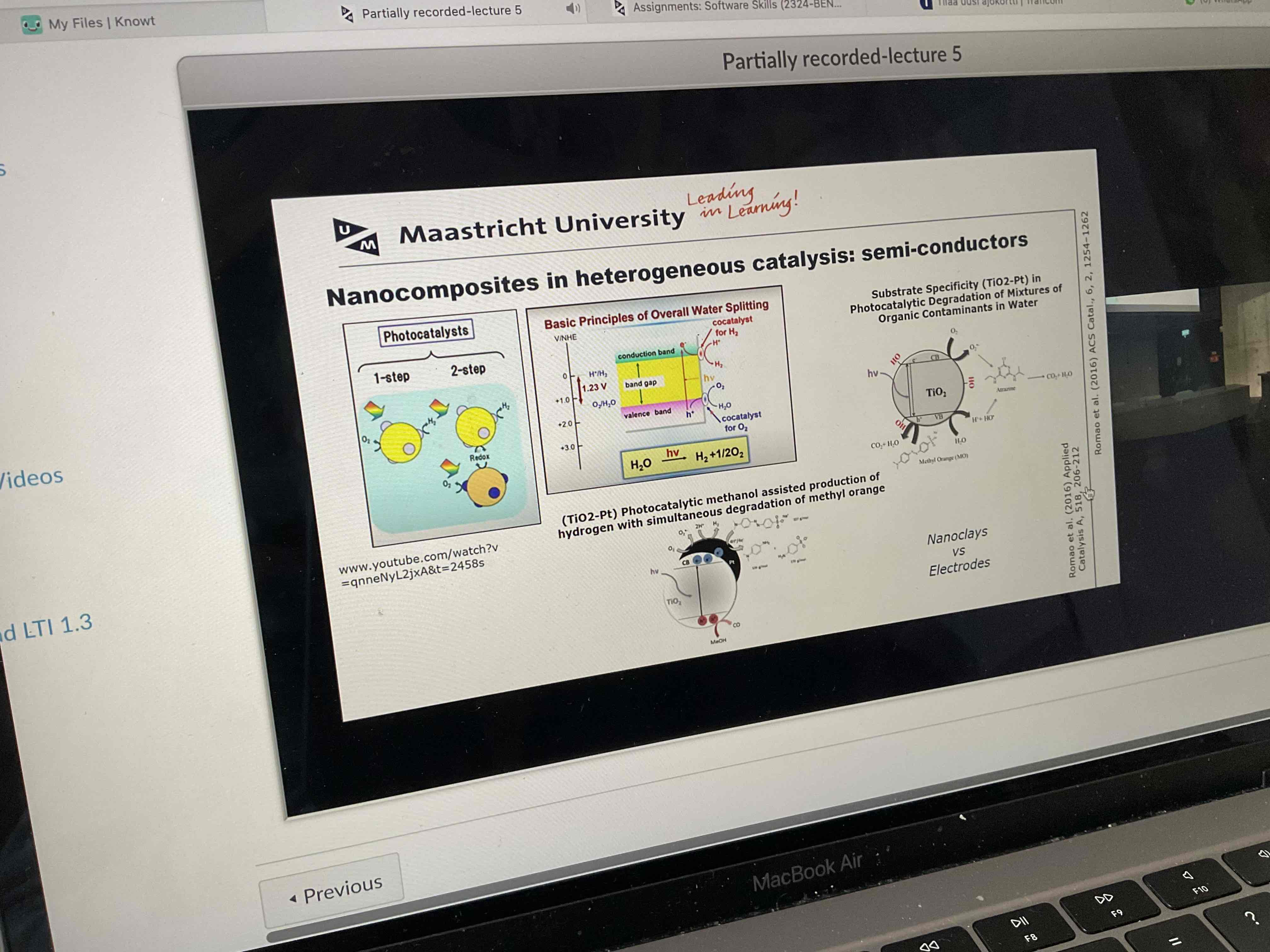
Skim through