Blood & body defences
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Haematopoiesis
Formation of the cellular components of blood.
Occurs during embryonic development & throughout adulthood to produce & replenish the blood system
Haematology
Study of blood & associated disorders
Blood
composed of blood cells & plasma
Average volume: males - 5-6L, females - 4-5L
roughly 8% of the body weight
38° (~one degree higher then body temp)
Plasma
55% of whole blood
pH 7.35-7.45
7% proteins (main: albumin,) 91.5% water, other solutes 1.5%
Formed element
Buffy coat - leukocytes (WBCs) & platelets (<1% of whole blood)
Erythrocytes (RBCs) - 45% of whole blood
Functions of blood
transportation - oxygen, hormones & nutrients to cells & tissues; removal of waste products (CO2); transport of ummunoglobulins
regulation - maintains body temp (distribution of what to and away from tissues); control the speed of blood flow; maintain correct pH and water % of cells
protection - carries immune cells, antibodies, etc.; prevents blood loss (platelets & clotting factors); WBC for fighting infection
Abnormal blood parameters reflect organ dysfunction
liver function - ALT & AST levels are indicative of inflamed or injured liver cells
Cardiac markers - troponins released from damaged or dying heart muscle cells after MI
Cardiovascular function - lipid and cholesterol levels. increased levels can increase risk of heart disease
Renal function - creatinine - high levels indicate kidney disease
Haemoglobin
Globin - amino acids
Heme - Iron & Bilirubin (bile)
1/3 weight of RBC
ABO blood groups
Type A - has A antigen, produces Anti-B antibodies
AB - has both antigens, no antibodies
B - has B antigen, anti-a antibodies
O - no antigens, both antibodies
Rhesus (Rh) Blood group
Rhesus antigens are transmembrane proteins at the surface of RBCs
the protein responsible is known as D antigen, or RhD antigen
~ 15% of population has no RhD Antigens and are ‘Rh negative’
Antibodies are only generated after exposure to RhD (I.e. pregnancy)
Rh- can only receive Rh- blood
Rh+ can receive Rh+ or Rh- blood
Haemostatis
3 keys steps to stop blood less when a blood vessel is damaged:
1 - blood vessel damage results in spasm, reduced blood flow, and release of clotting factors
2 - Vasoconstriction limits blood flow, plateletters form a sticky plug & stick to exposed blood vessel
3 - fibrin strands adhere to the plug and form an insoluble clot. RBC are trapped in fibrin threads
3 lines of defence against pathogens
1 - Barriers (anatomical, chemical, biological, mechanical)
2 - Innate immunity
3 - Adaptive ummunity
Barriers
Physical - skin, epithelial cells, mucus
Chemical - lysozyme (tears & saliva) acid (stomach, vagina) and antimicrobial peptides
Biological - commensal microorganisms (produce antimicrobial bacteriocins); lung alveolar macrophages
Mechanical - cilia lining respiratory tract, cough reflex, vomiting & defecation, urinary tract flushing
Innante immune response
proteins (complement, interferon (IFN)
cellular (phagocytes, natural killer (NK) cells)
Inflammation
Components of lymphatic systen
lymph, lymphatic vessels, & lymphatic tissues
Functions of lymphatic system
Drains excess interstitial fluid
Absorbs/transports dietary lipids & fat-soluble vitamins from GIT to blood
Transports antigen to lymph nodes
Transports lymphocytes in and out of lymph nodes
Sequence of flow
Blood capillaries (blood) —> interstitial spaces (interstitial fluid) —> lymphatic capillaries (lymph) —> lymphatic vessels (lymph) —> lymphatic ducts (lymph) —> Junction of the internal jugular & subclavian veins (blood)
Complement system
consists of ~30 plamsa proteins
present in plasma & interstitial tissues
activates pathogens
enhances phagocytosis (via opsonization)
inflammation
lysis of microbe
Cells of Innate Immune response
mast cell - stimulated by complement to secrete histamine
neutrophil - major phagocytic cell
eosinophil
basophil
macrophage - major phagocytic cell
dendritic cell
NK cell (natural killer)
processes of phagocytosis
chemotaxis - movement of phagocytes to the site of damage due to chemical stimulus
adherence - attachment of phagocyte to microbe
ingestion - formation of phagolysosome
digestion - use of lysosome to degrade microbial material
killing - elimination of microbe
opsonisation
opsonins are used to tag foreign pathogens for phagocytosis
opsonins:
antibody (IgG)
complement (e.g. C3b)
antibody + complement (degree of binding is further enhanced, phagocytosis more effective)
antibodies physically block binding sites so pathogens can’t latch onto tissues. they mark the cell for death by phagocyte
Dendritic cells
‘professional antigen presenting cells’
take up foreign material and ride the lymphatic vessels, activating specific lymphocytes in lymph nodes.
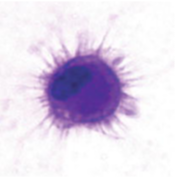
Neutrophils
major phagocytic cell entering infected tissues from the blood.
only last a few hours
most common WBC - ~50-70%
pus is mostly ‘spent’ neutrophils
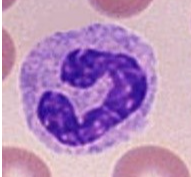
monocytes
comprise 3-10% of wbc
leave the blood, enter tissues & turn into macrophages
Live longer than neutrophils & ingest larger particles
found in sinuses, within spleen, liver, lymph nodes, & bone marrow
remove microorganisms and debris from blood and lymph
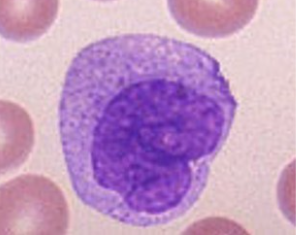
Eosinophils
Rare, 2-4% of WBC.
important in controlling parasitic infections - secrete chemicals that kill/inhibit worms
involved in damage to airways seen in asthma
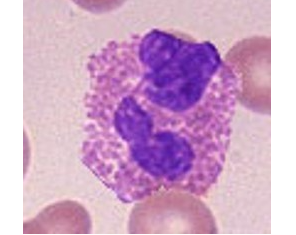
Basophils/Mast cells
Basophils: blood cells which leave circulation and promote inflammation at infection sites.
rare, 0.5-1% of WBC
Mast cells: non-motile cells found in CT.
involved in inflammation & tissue healing, and allergy
release large amounts of histamine when allergen is contacted, causing vasodilation
Natural Killer (NK) cells
special type of lymphocyte - kills cells not expressing as special immune-related molecules called MHC on their surface.
MHC are used to signal the immune system when a cell is infected
can kill distressed, cancerous, or virus-infected cells
they release granules containing toxic substances - perforin which creates perforations in the cell membranes in order to allow granzymes to enter the cell and cause apoptosis
Acute inflammation
Inflammtion is the body’s natural response to harmful stimuli
part of our innant immune response and initial vascular response
localized response to stimulus (infection, damaged cells, trauma, irritation, allergy)
response continues as long as the threat exists
gives no direct protection against future attacks from the same agent
alerts the adaptive immune system & contributes to its activation
acute inflammation characteristics
increased blood flow
leakiness of capillaries (bringing fluid, nutrients, proteins, phagocytes into the tissue to fight infection or trauma)
cardinal signs of inflammation - redness, swelling, heat, pain, sometimes loss of function
allows dendritic cells to take pathogen(-derivied) material to lymph nodes to initiate adaptive immune response
purpose of inflammatory response
contain/isolate offending agents & limit their effects
neutralize & dispose of pathogens & cellular debris
prepare the body to promote healing and repair
stimulate & enhance the adaptive immune response
B lymphocytes
humoral immunity
become plasma (effector) cells after differentiation and activation (by cytokines from T cells) and produce antibodies
T lymphocytes
many different subsets. 2 major subsets:
CD4 T cells - helper cells that help B cells make high affinity antibodies; help & regulate the responses of other cells (B, T, and dendritic cells)
CD8 T cells - cytotoxic lymphocytes or killer T cells. Can kill cells infected with intra cellular pathogens (viruses/bacteria)
produced in marrow, mature in thymus
can only recognize antigen with MHC
Clonal deletion
lymphocytes that recognize self antigens as dangerous are deleted
clonal selection
the receptors on B cells are randomized through somatic recombination (randomizing bits of DNA) so that they can have the best chance to identify every pathogen. Once activated, B cells clone themselves quickly with the same receptors to fight the pathogen.
Adaptive immune response
Lymphocytes - B & T cells
B cells produces antibodies (2000/s for 4-5 days)
has ‘memory’ (B&T cells that are left over become memory cells) so it can fight specific pathogen easily in future
MHC
Major Histocompatibility complex
proteins found on the surface of cells to help immune system distinguish between self & foreign antigens
allows T cells to determine if cells are healthy or infected
can have foreign peptide fragments attached for T cells to recognise and respond
MHC1 is on all nucleated cells
MHC2 is on professional antigen presenting cells (macrophages, dendritic cells, B cells)
antigen
a substance that can evoke an immune response
often proteins (but can be nucleic acids, lipoproteins, etc.)
Epitopes
B cell epitope - the part of a native antigen recognized by an antibody or B cell receptor
T cell epitope - antigenic peptide + MHC
Antibody / immunoglobulin (Ig) structure
Y-shaped with two heavy chains and two light chains
Variable (V) segments are at the antigen binding site
Immunoglobulin classes
IgG - most abundant; effective against virus & bacteria; enhances phagocytosis, neutralizes toxins and tiggeres complement activation; can cross placenta to fetus
IgA - found in sweat, tears, mucus, saliva, breast milk, GI secretions; provides localised protection of mucus membranes
IgM - found in lymph & blood. activates complement, lyses microbes. acts as antigen receptors on B cells.
IgD - found on B cells, involved in activation of b cells
IgE - binds to mast cells & basophils via Fc receptors; protection against worms; allergy and hypersensitivity reactions