Consumer and Producer Surplus
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Consumer Surplus definition
The difference between the price consumers are willing and able to pay for a good/services and the price they actually pay
Producer surplus definition
The difference between the price producers are willing and able to supply a good/service for and the price they actually receive
How do you find consumer surplus
Below the supply curve and above the price line

How do you find producer surplus
Above the supply curve and below the price line

Consumer surplus explained
A consumer pays less for a good than the amount that they’re prepared to pay for it
E.g: someone was prepared to pay £10 for a good and bought for £8 then there would be a consumer surplus of £2
Producer surplus explained
If a producer receives more for a product/service than the price they’re willing to accept, the extra earnings are known as the producer surplus.
e.g: the equilibrium price of a good is £15 but a supplier would be happy to sell for £10 then the producer surplus would £5.
Anything that causes a shift in the supply or demand curve can lead to a change in the
price of a good
A change in price will
bring a good closer to or further away from the amount the buyer was willing to pay or the supplier was willing to sell for - and this will change the consumer/producer surplus
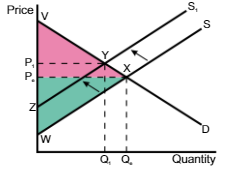
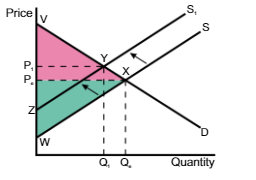
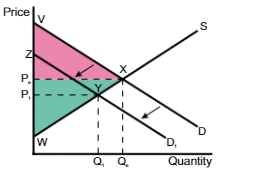
A shift of the supply curve from S to S1 means the price and quantity will
increase from Pe → P1 and quantity will decrease from Qe → Q1
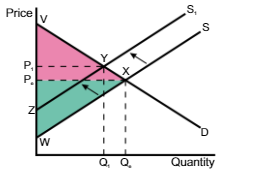
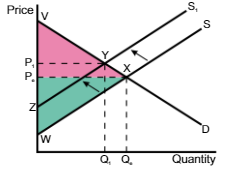
A shift in the supply curve from S → S1, the consumer surplus changes from
VPeX to VP1Y
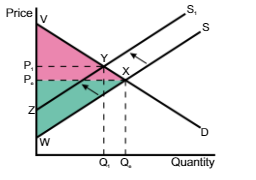
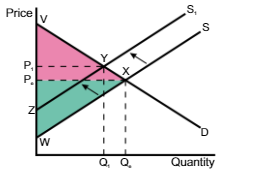
A shift in the supply curve from S → S1, the producer surplus changes
from PeWX to P1ZY
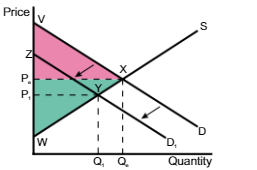
A shift in the demand curve from D → D1 means
the price and quantity will decrease from Pe → P1 and Qe → Q1
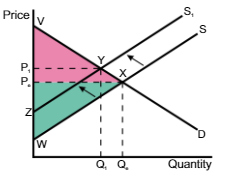
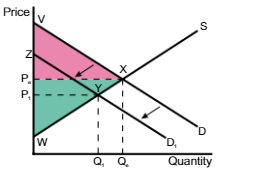
A shift in the demand curve from D → D1, the consumer surplus changes
from VPeX to ZP1Y
A shift in the demand curve from D → D1, the producer surplus changes
from PeWX → P1WY