Jensen: Chapter 11 - Hair, Skin, and Nails Assessment
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
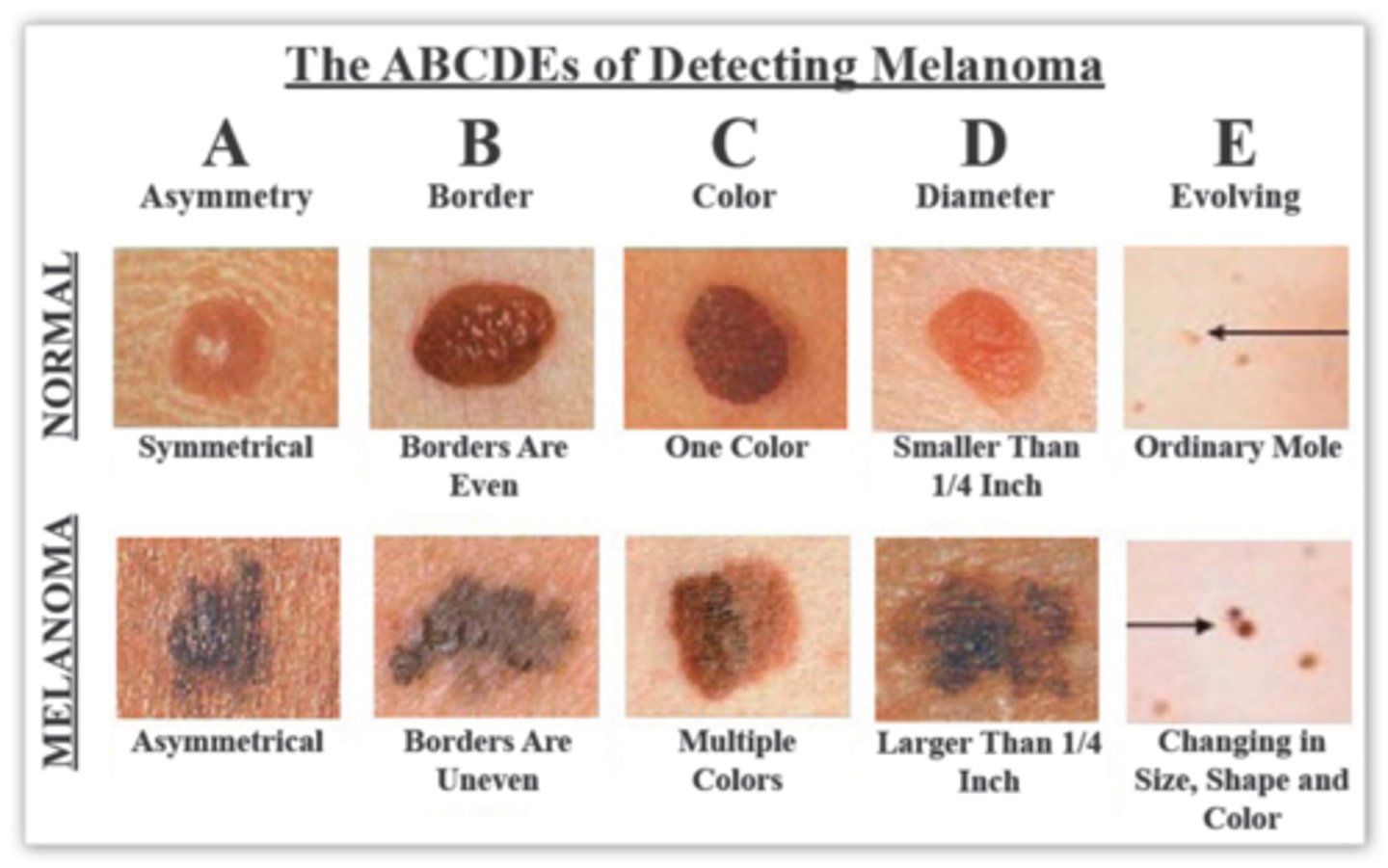
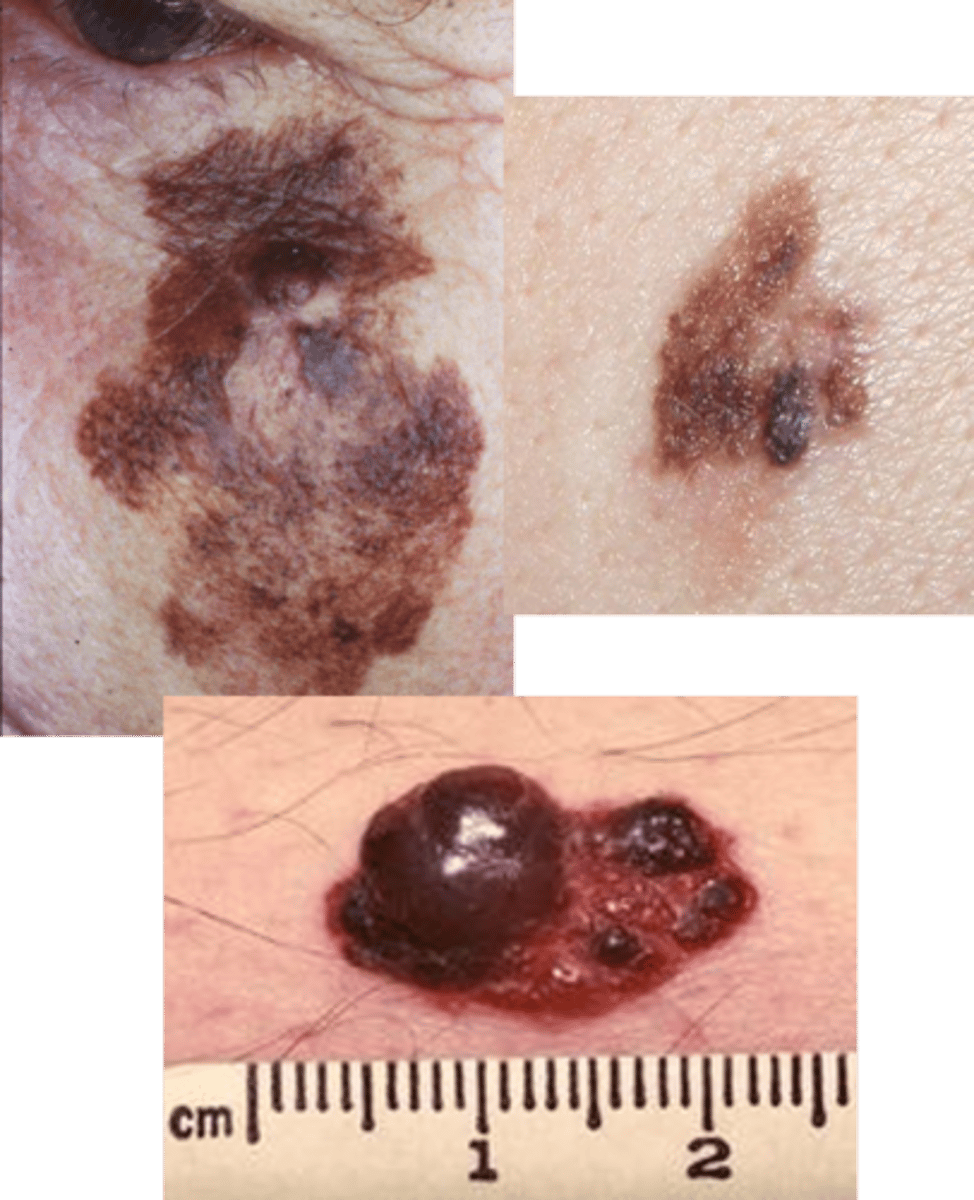
ABCDE of melanoma detection
ABCDE of melanoma detection:
Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color, Diameter of more than 6mm, Evolution of lesion over time
What is the largest organ of the body?
The Skin
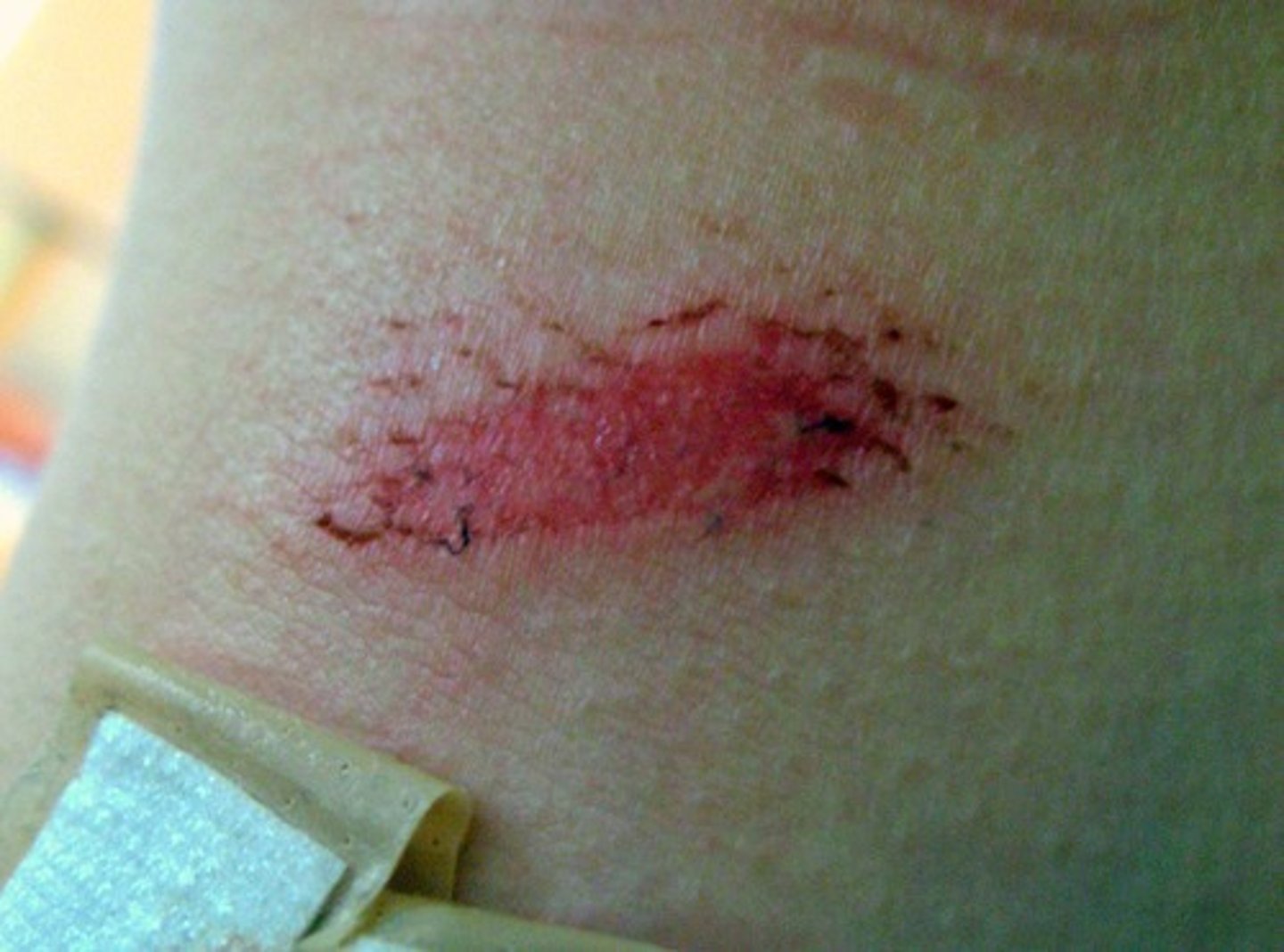
Wound caused by shear force or friction against the skin, removing several layers and exposing the dermis
Abrasion
Can be a window to other body systems
The Skin
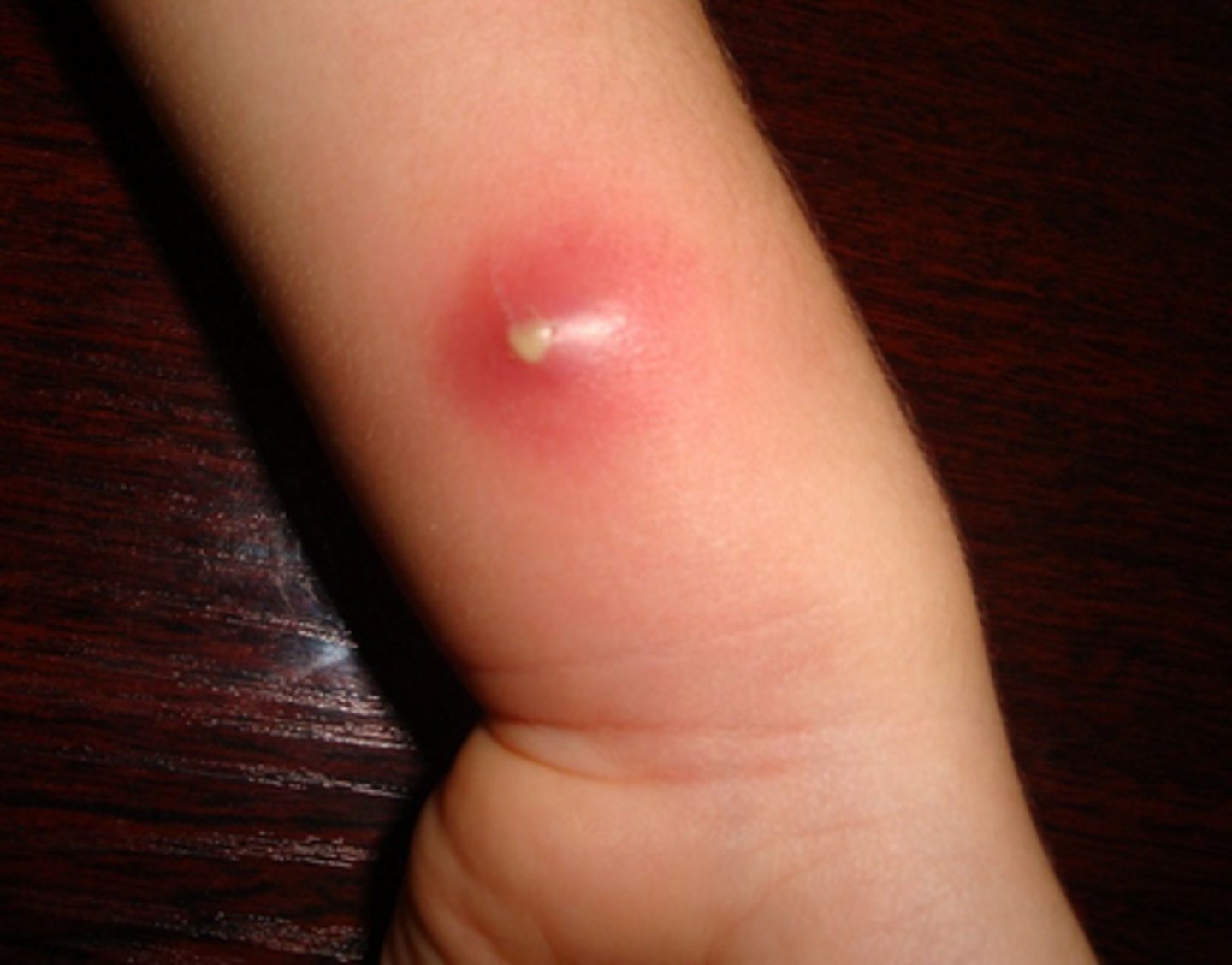
A contained accumulation of pus within a tissue
Abscess
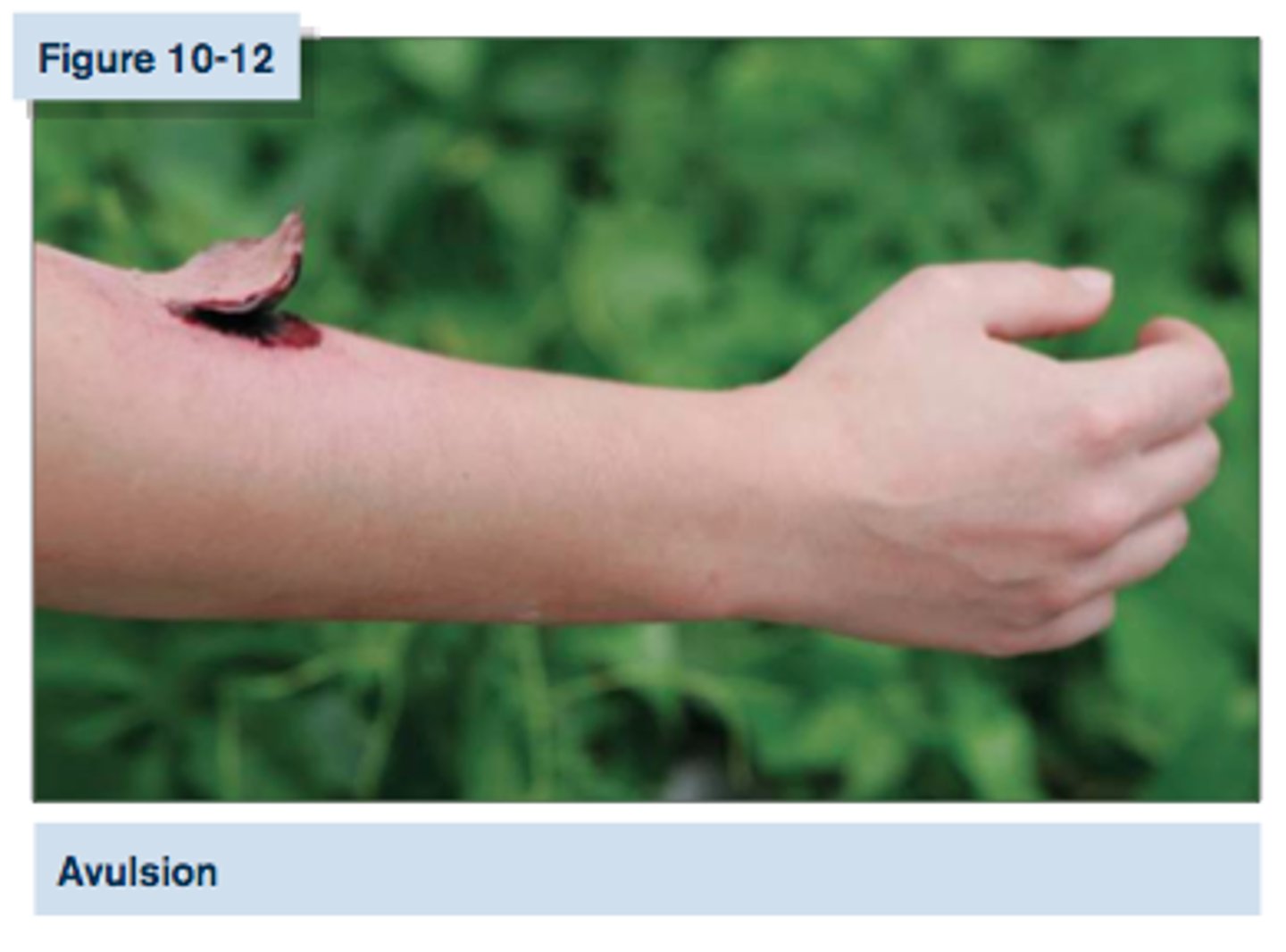
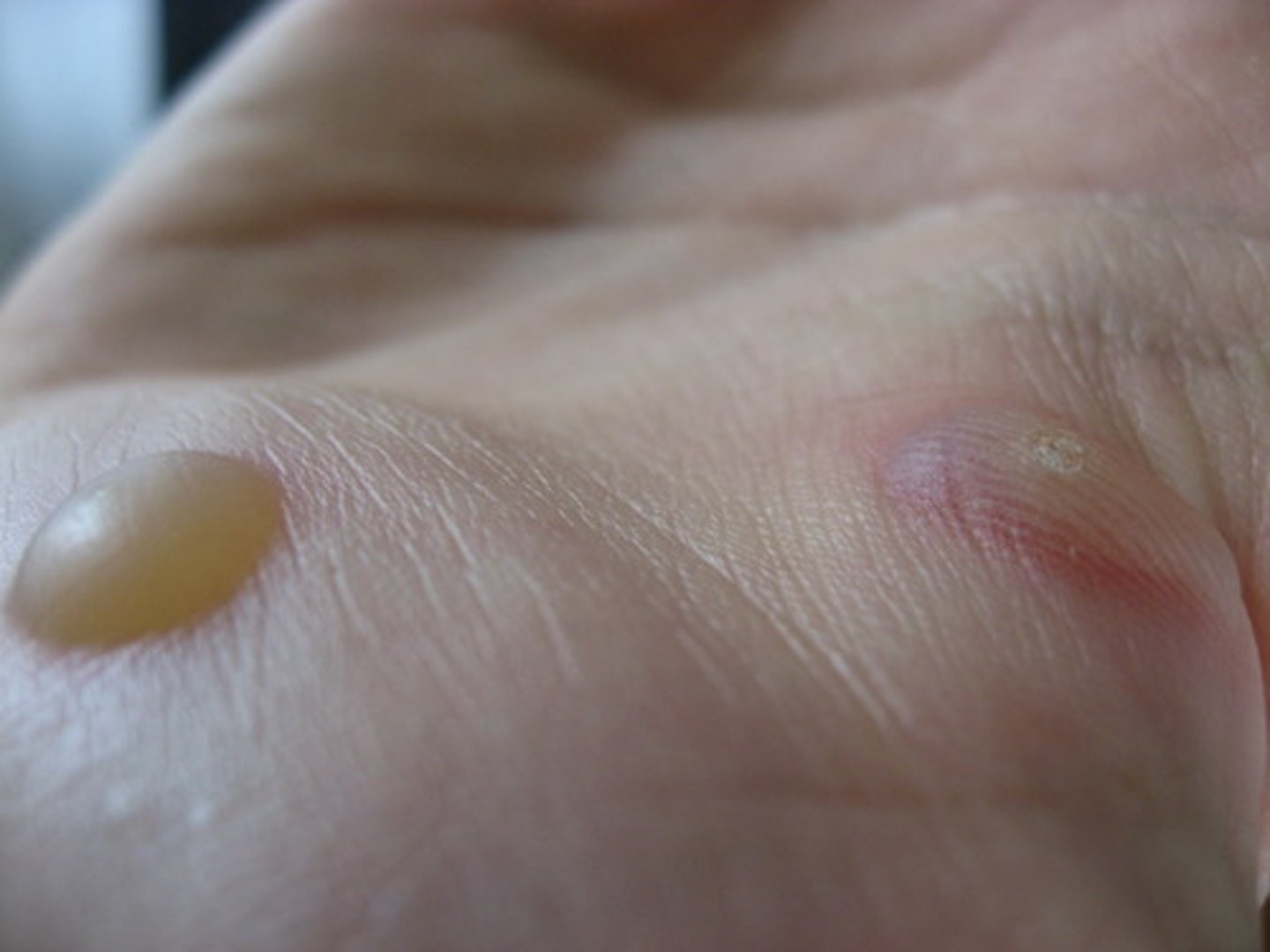
Ragged wound that occurs when trauma forces the skin to separate from underlying structures
Avulsion

A fluid-filled bubble on the skin caused by friction, burning, or hypersensitivity
Blister
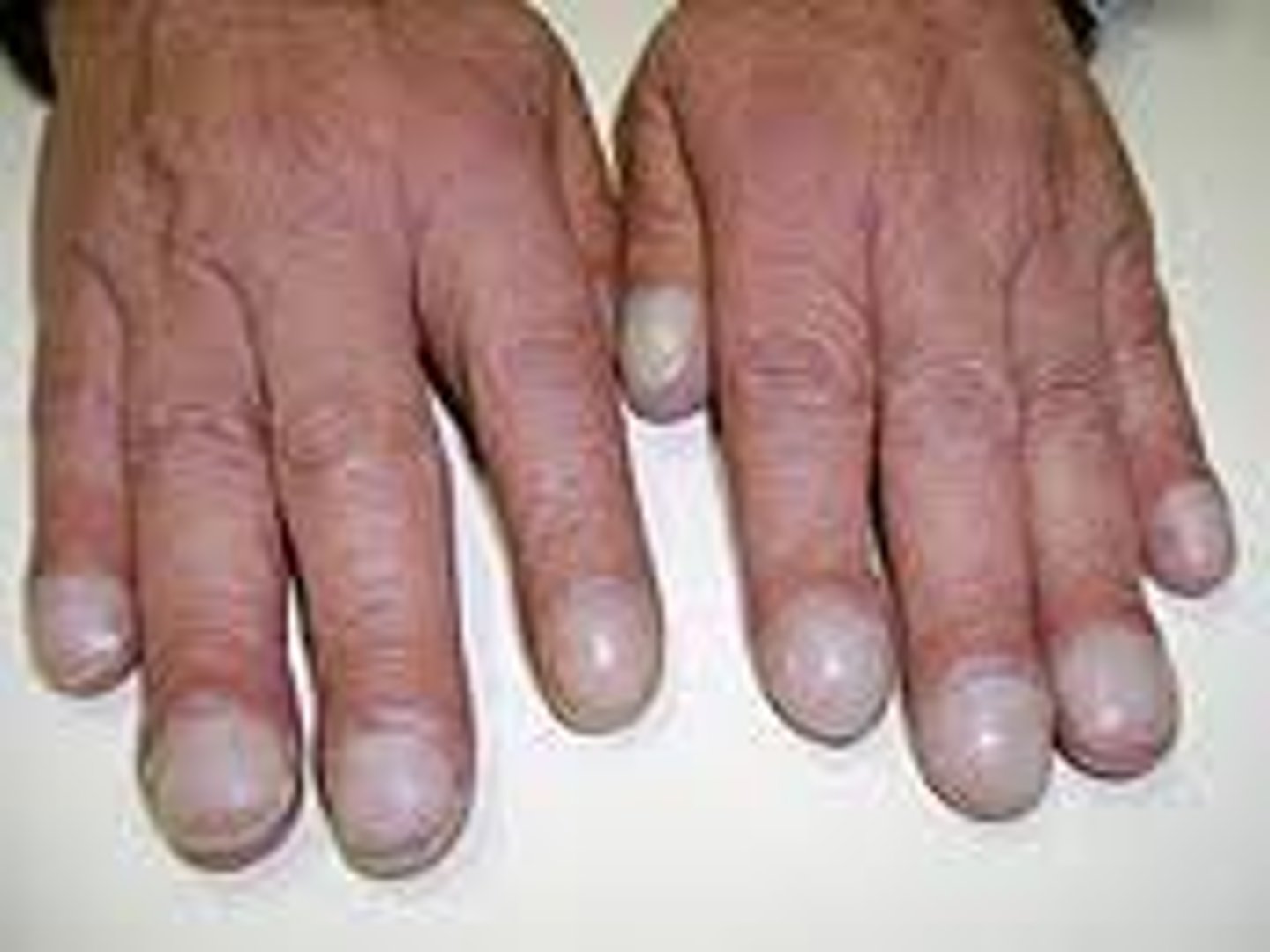
Finding in the nails that indicates chronic hypoxia (LOW O2)
Clubbing of the nails
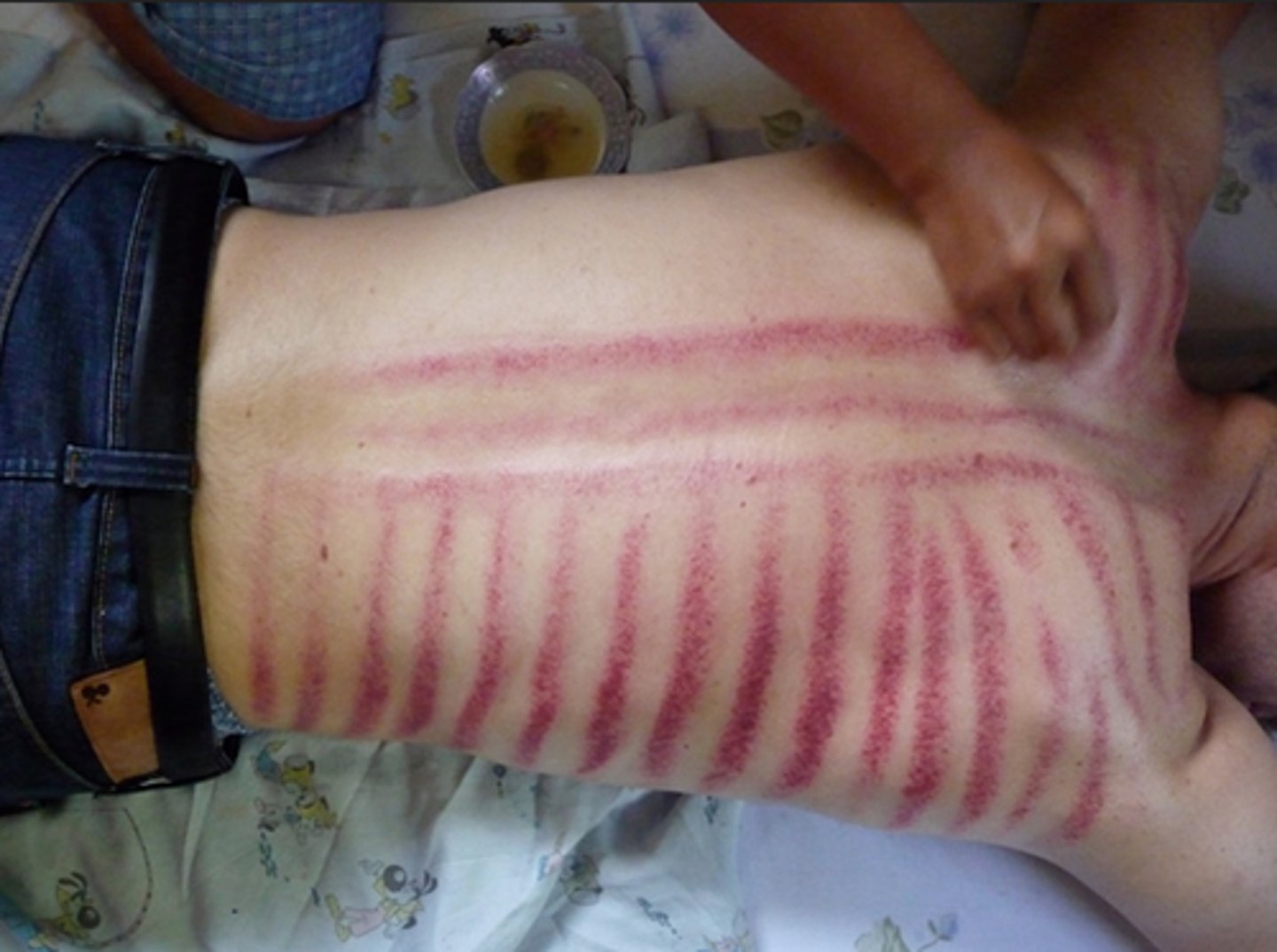
A practice among Southeast Asians in which a coin or other object is rubbed across the skin in a specific manner to treat various health concerns
Coining
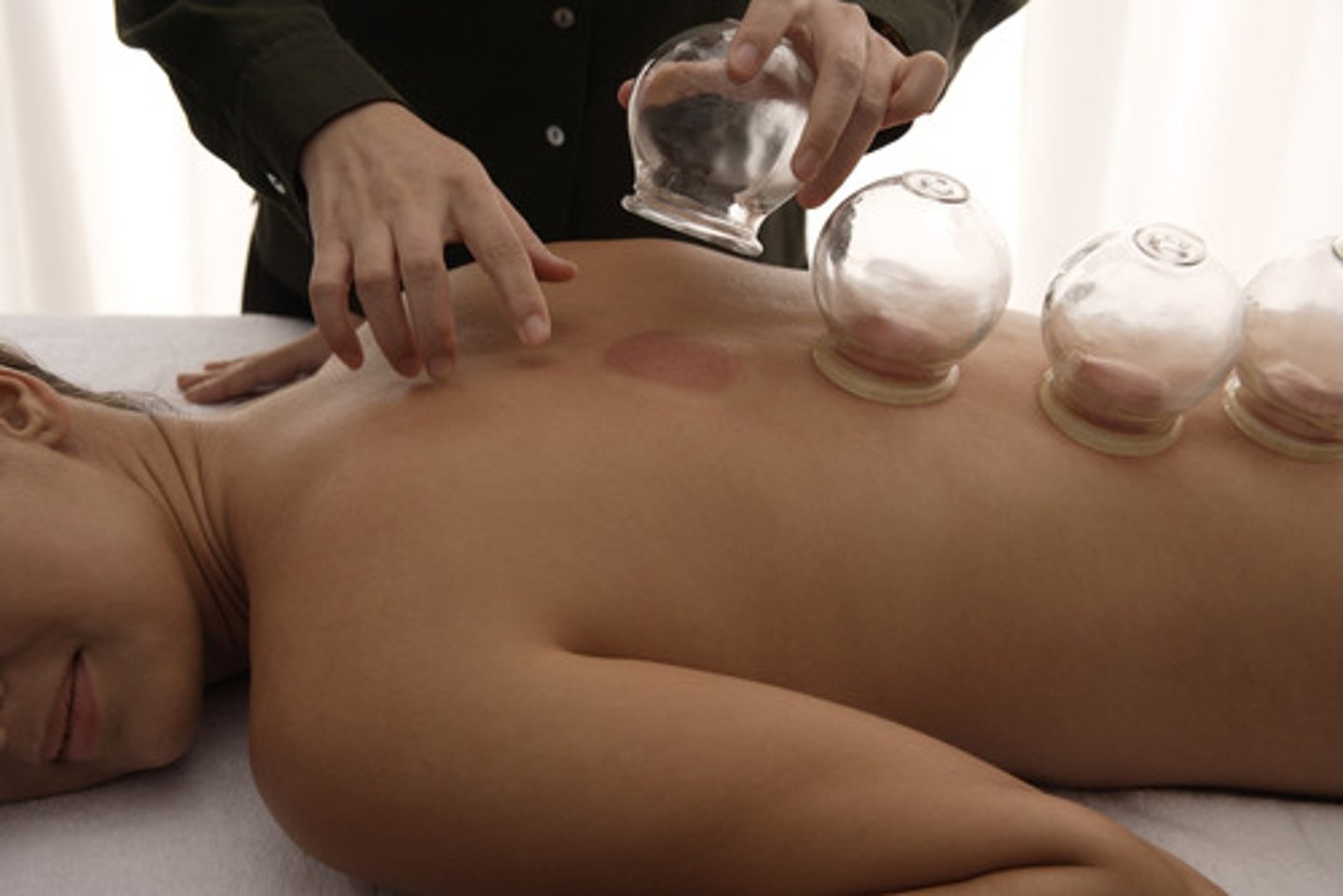
A cultural practice involving the placement of a cup on the skin surface, applying heat to form a vacuum
Cupping

Gray or blue skin color, indicating lack of oxygen
Cyanosis
Skin lesion that is distinct and walled-off and which contains fluid or semisolid material
Cyst
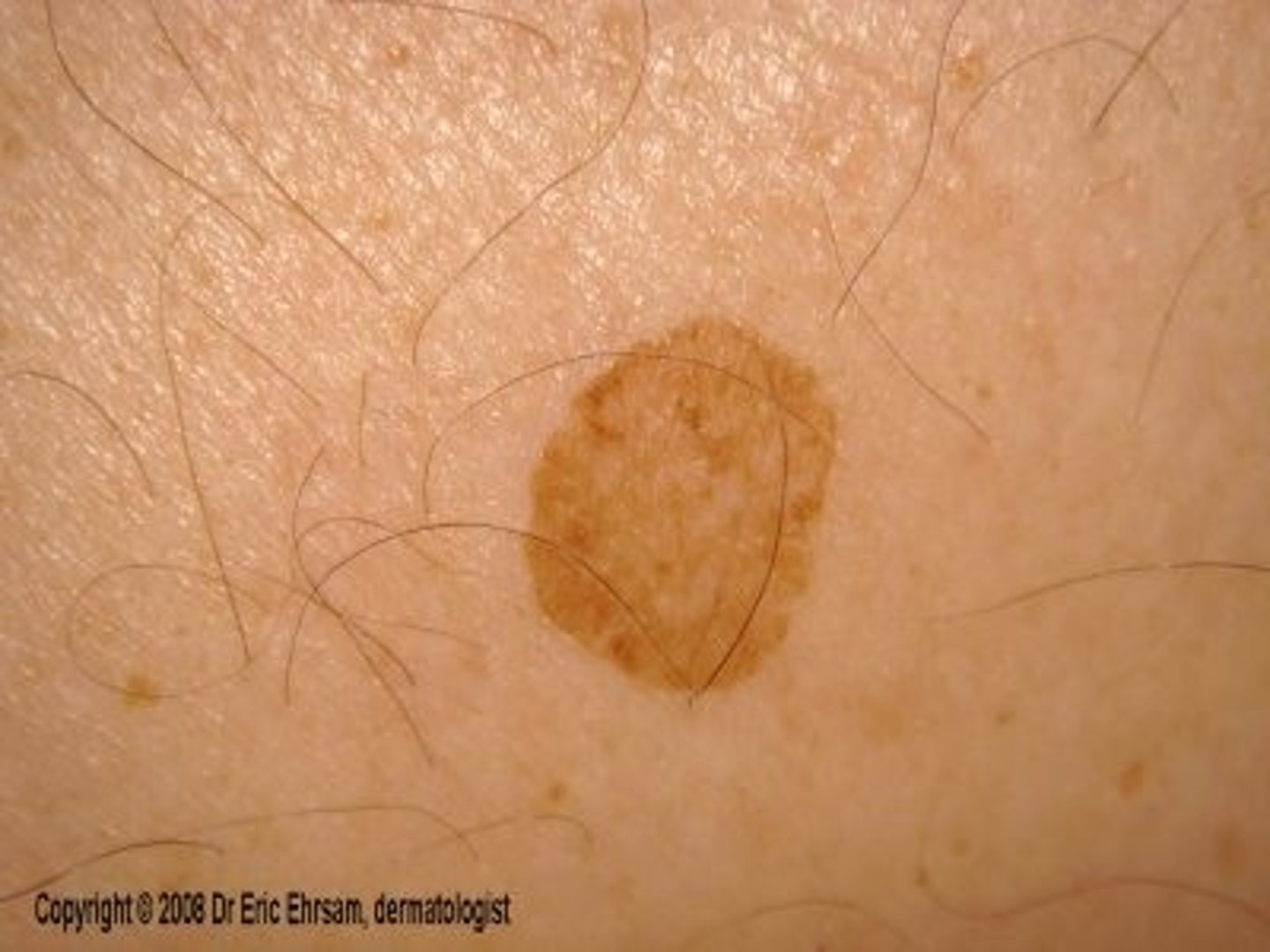
An atypical mole
Dysplastic nevus
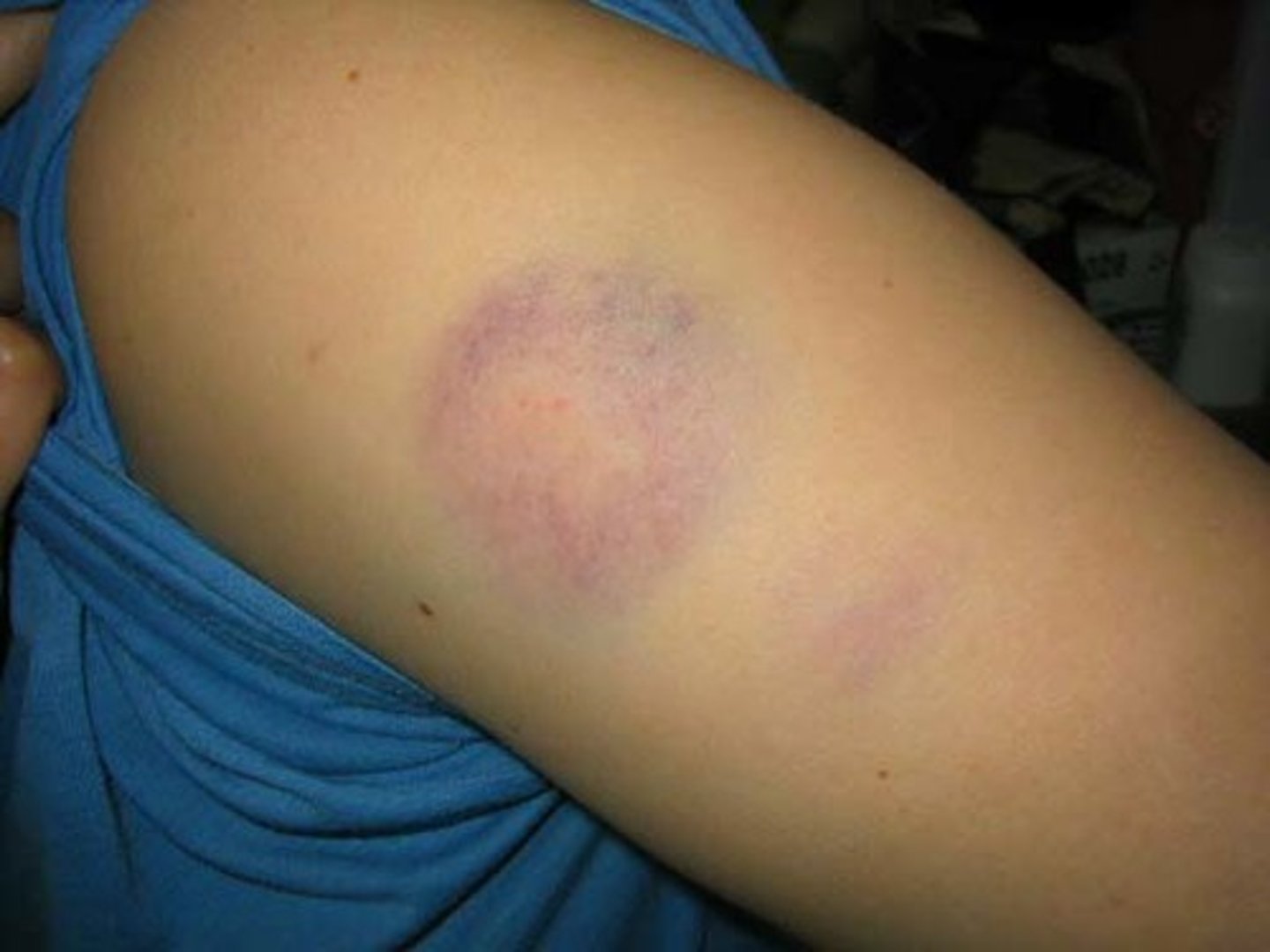
Bruise or bruising
Ecchymosis
Redness
Erythema
Turning red, as with fever
Flushing
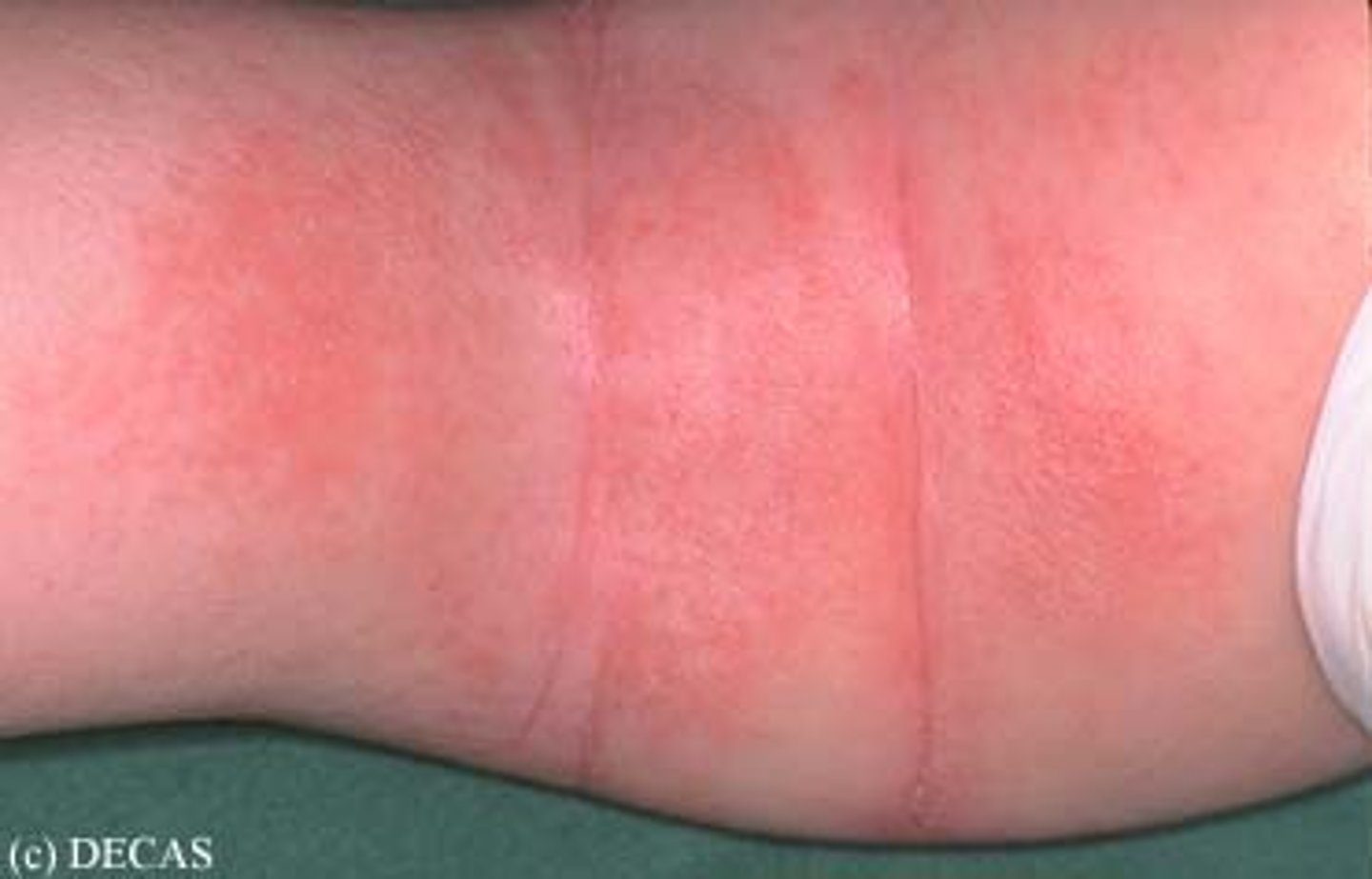
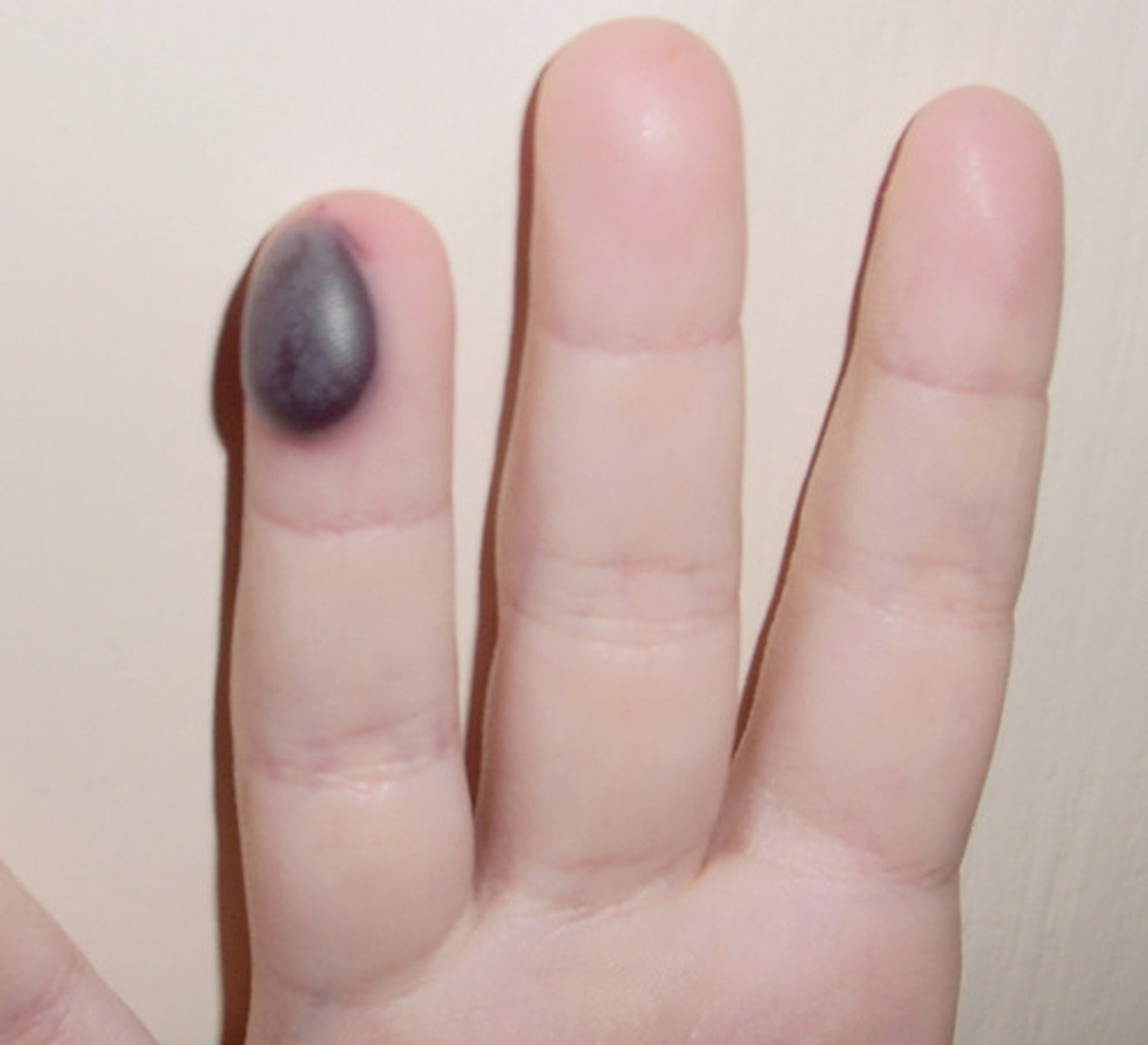
Collection of blood under the skin; usually results from blunt force trauma.
Hematoma
Hematomas are palpable lesions, and their colorations mimics that of ecchymoses (bruises)
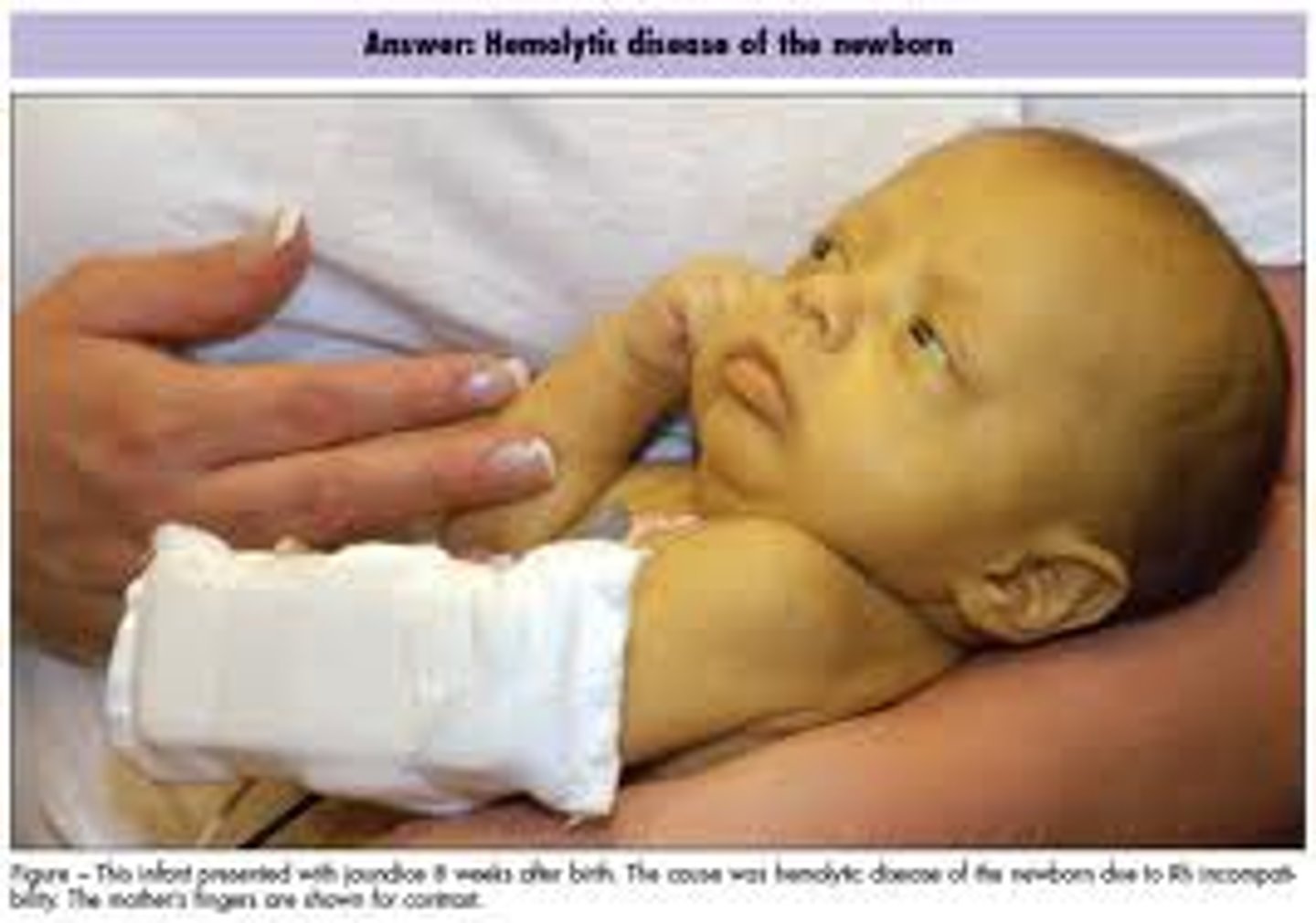
Yellowish discoloration of the skin and conjunctiva caused by a buildup of bilirubin in the body
Jaundice
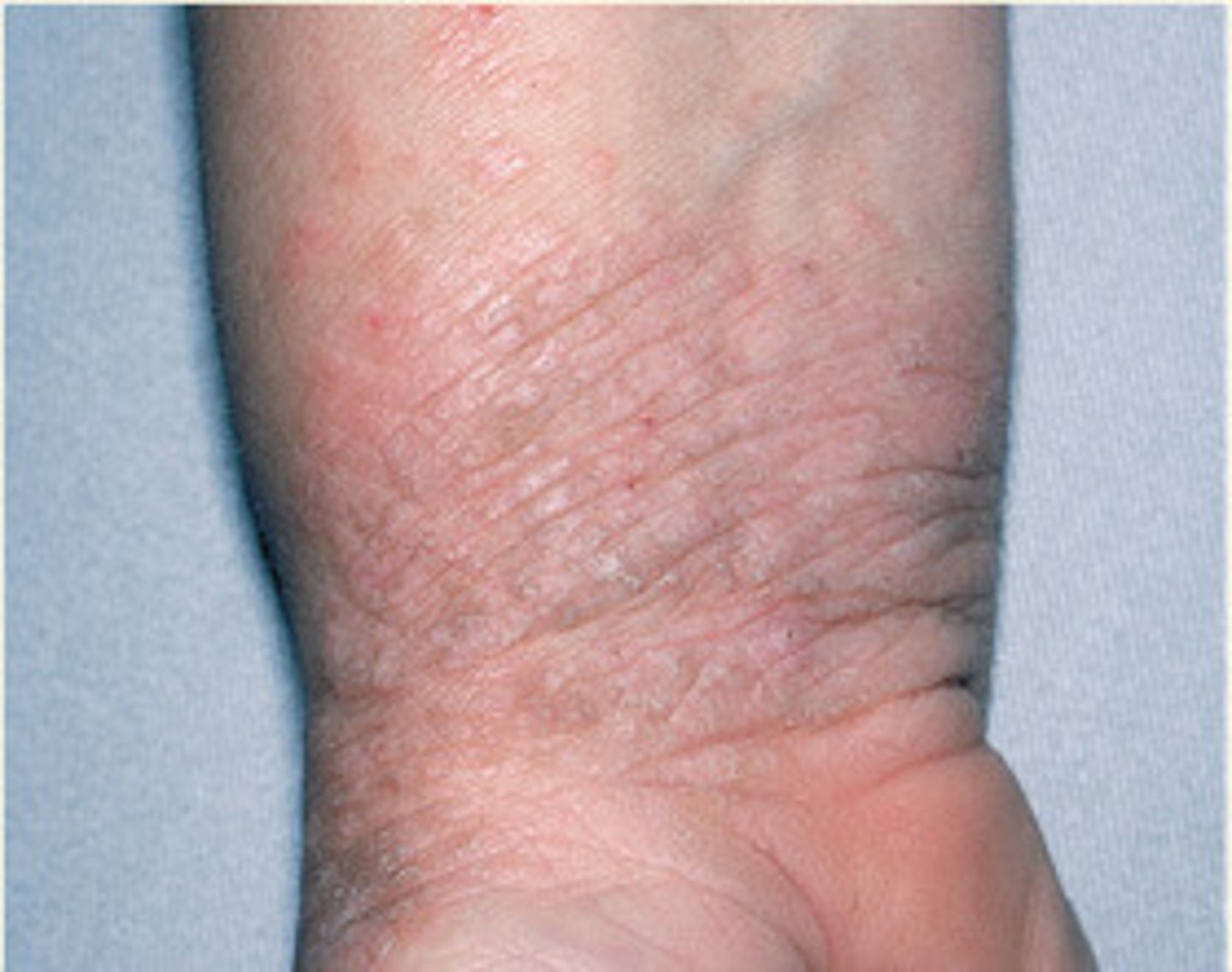
Accentuation of normal skin lines resembling tree bark, commonly caused by excessive scratching
Lichenification
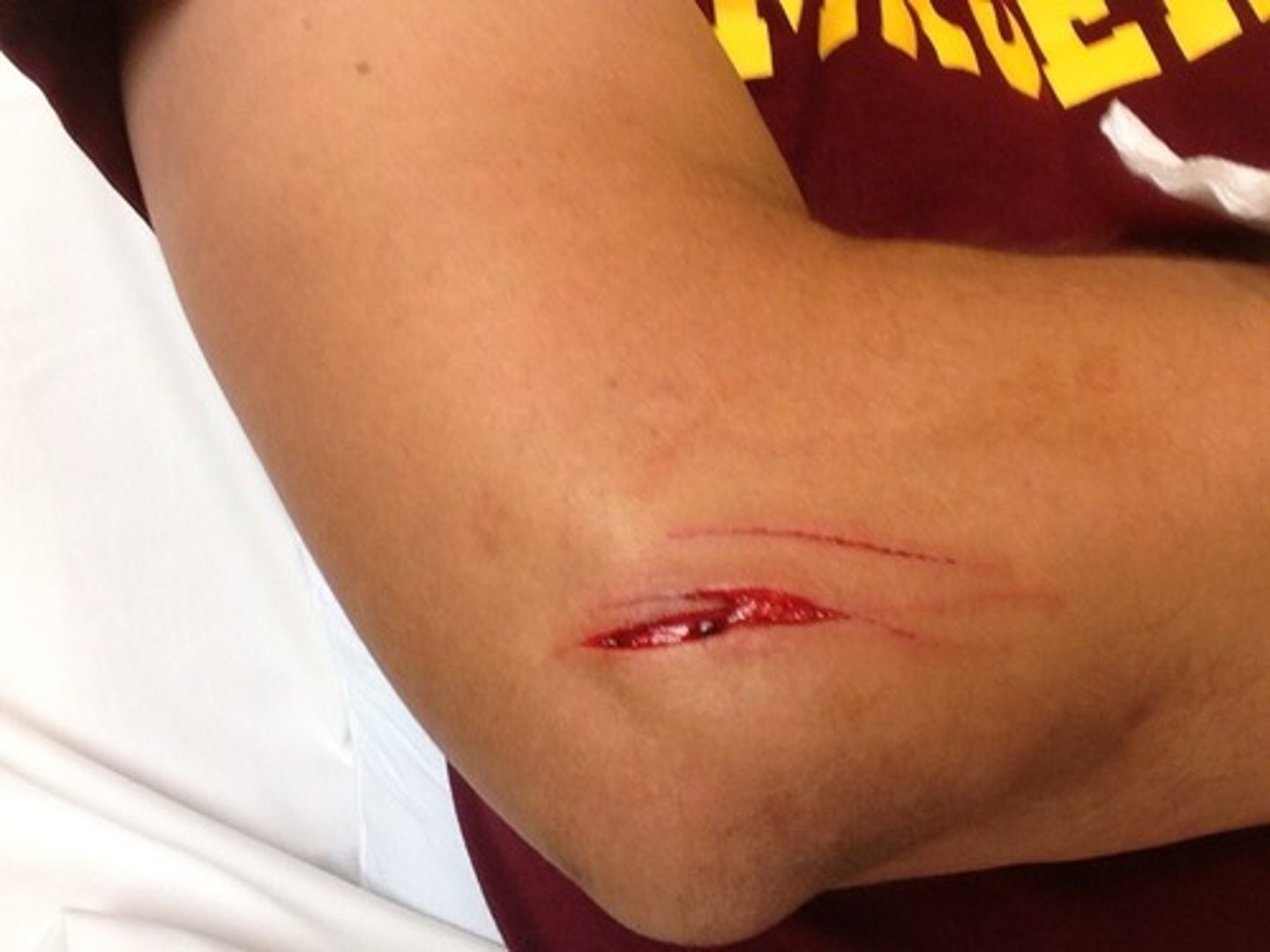
A superficial or deep skin tear, often requiring suturing to heal correctly
Laceration
Flat, distinct, colored area of skin that is less than 10mm(1 cm) in diameter and does not include a change in skin texture or thickness
Macule
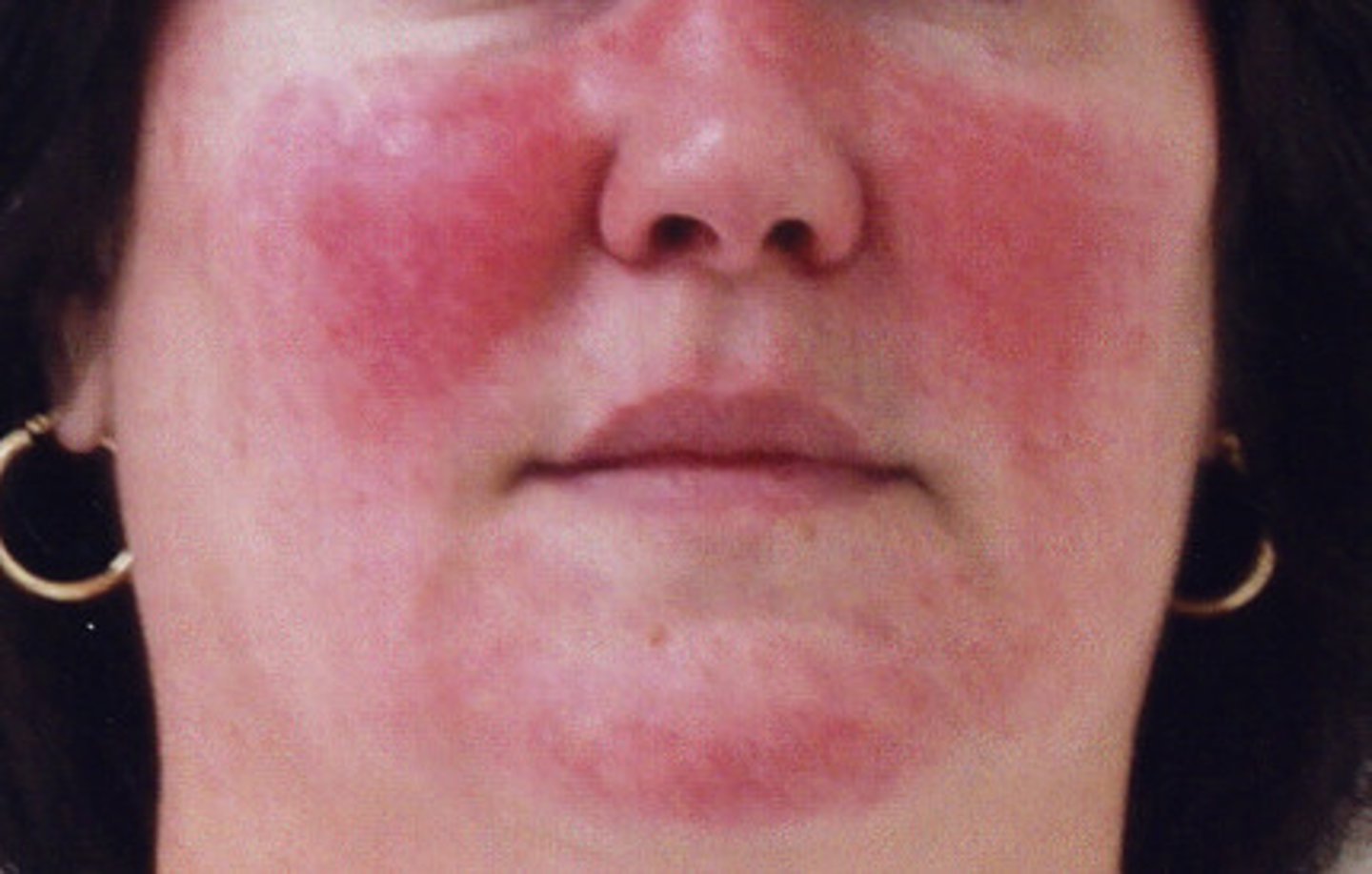
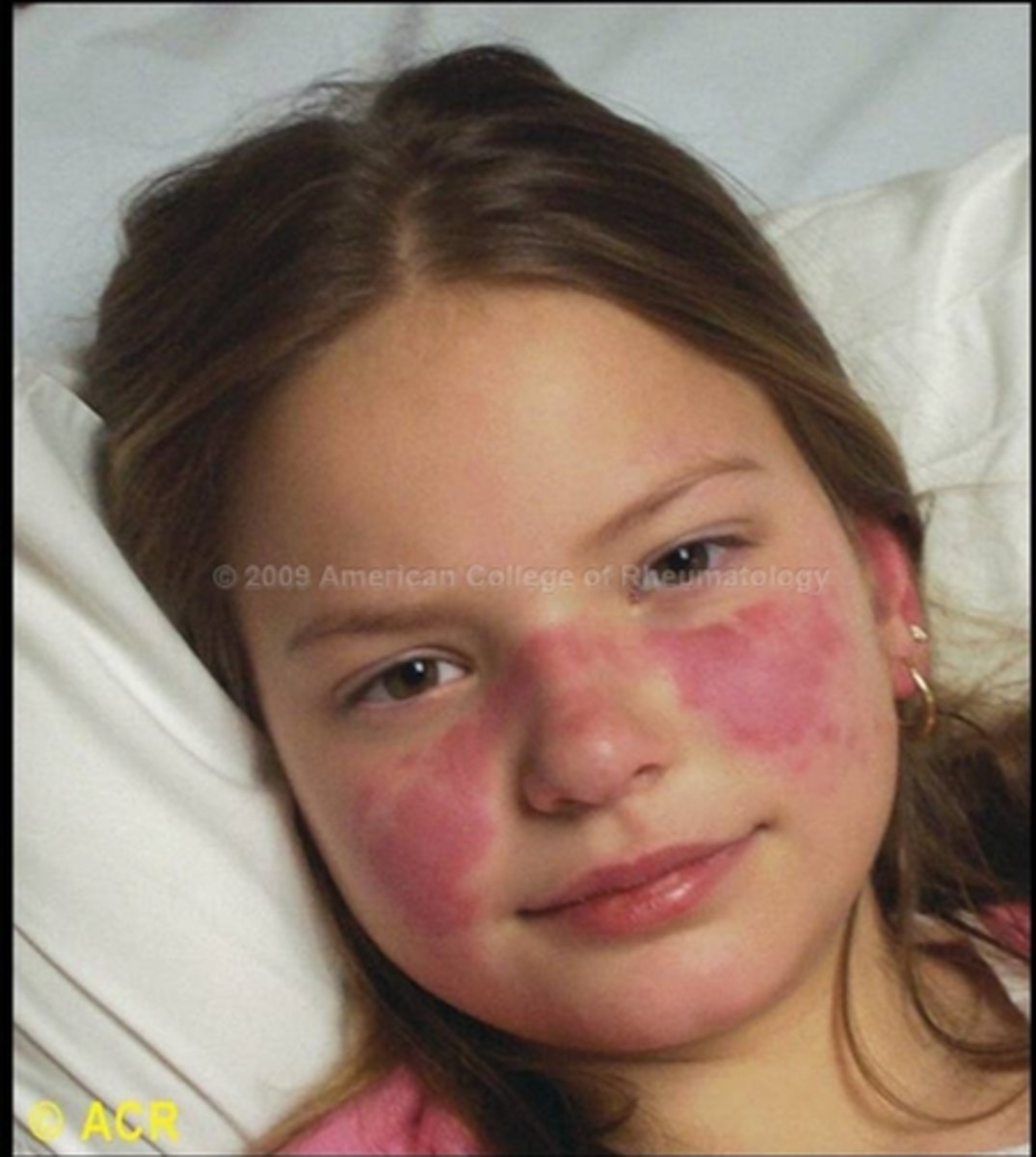
Red macular lesions distributed over the forehead, cheeks, and chin, resembling the pattern of a butterfly
Malar rash
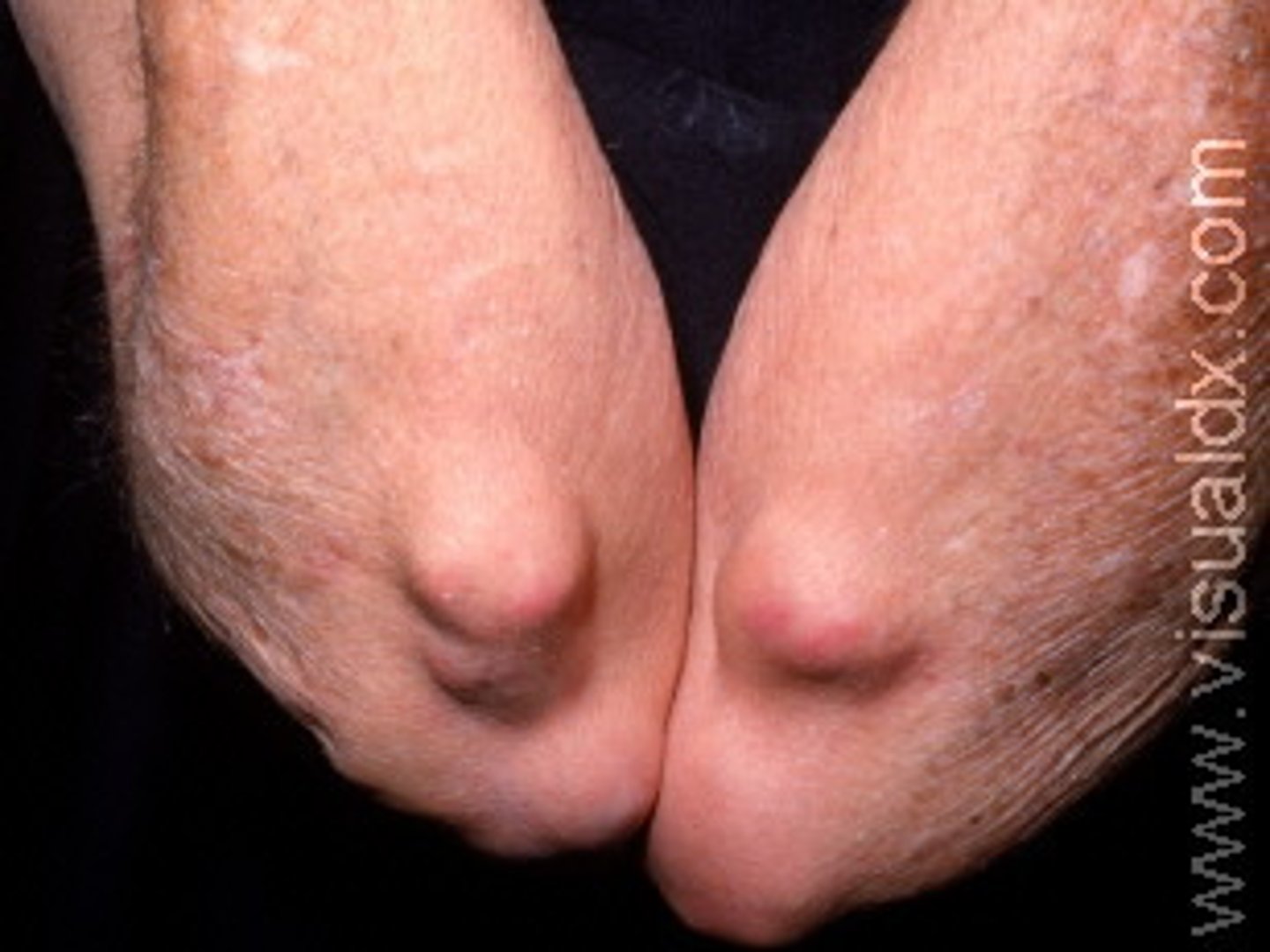
Solid palpable lesion greater than 1 cm in diameter, often with some depth
Nodule
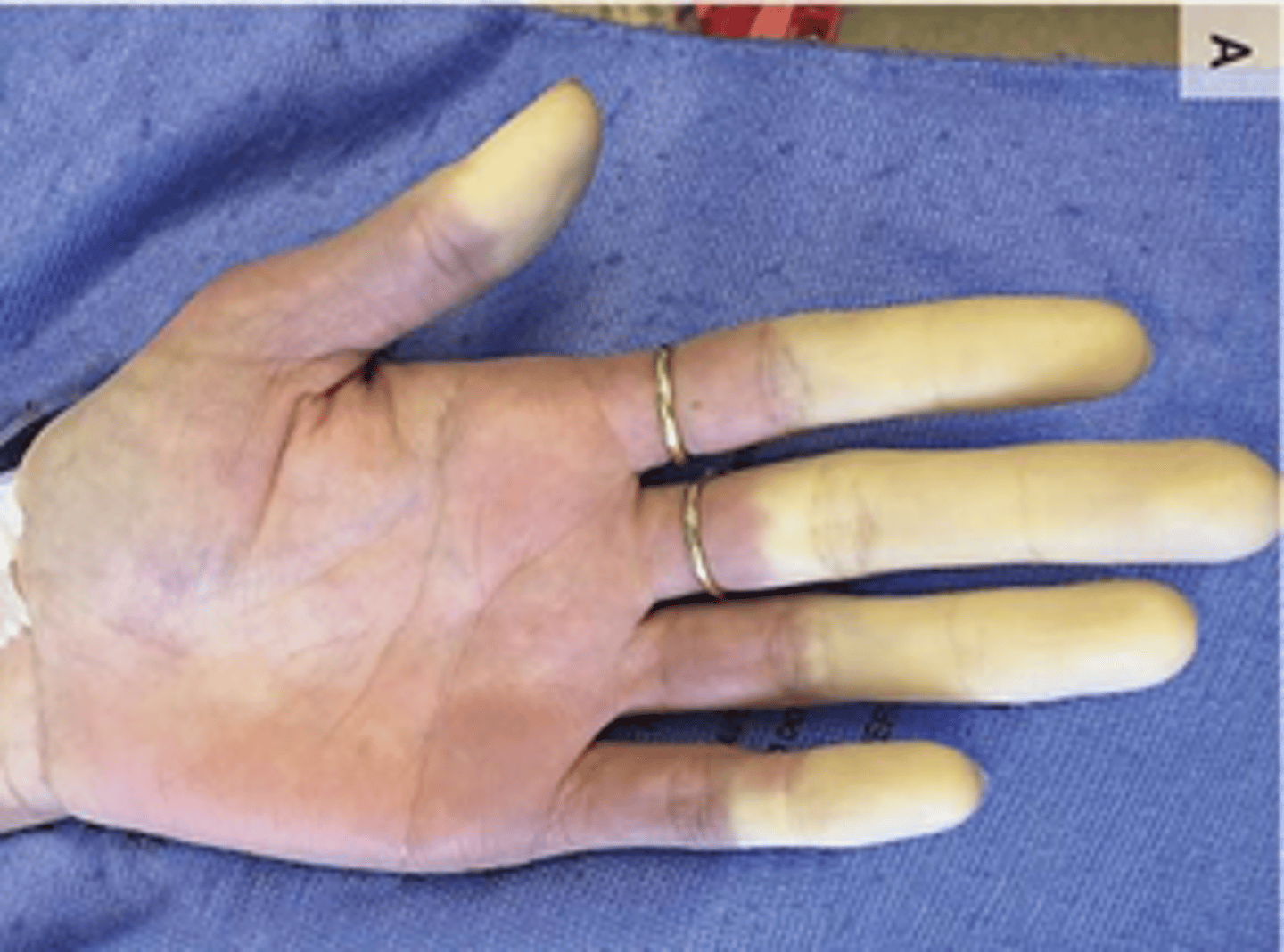
Paleness of the skin (due to anemia)
Pallor
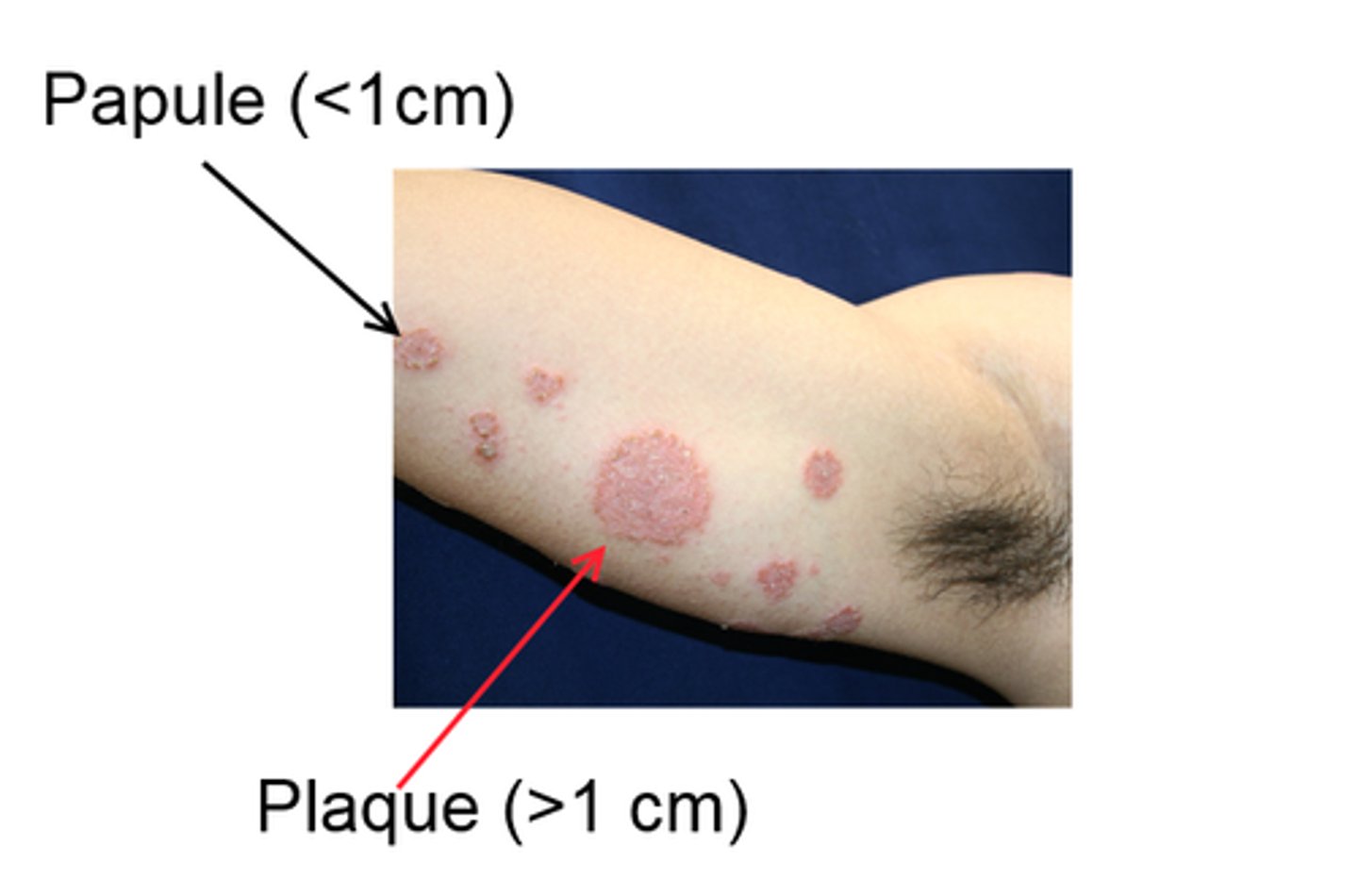
Raised, defined lesion of any color, less than 1 cm in diameter
Papule
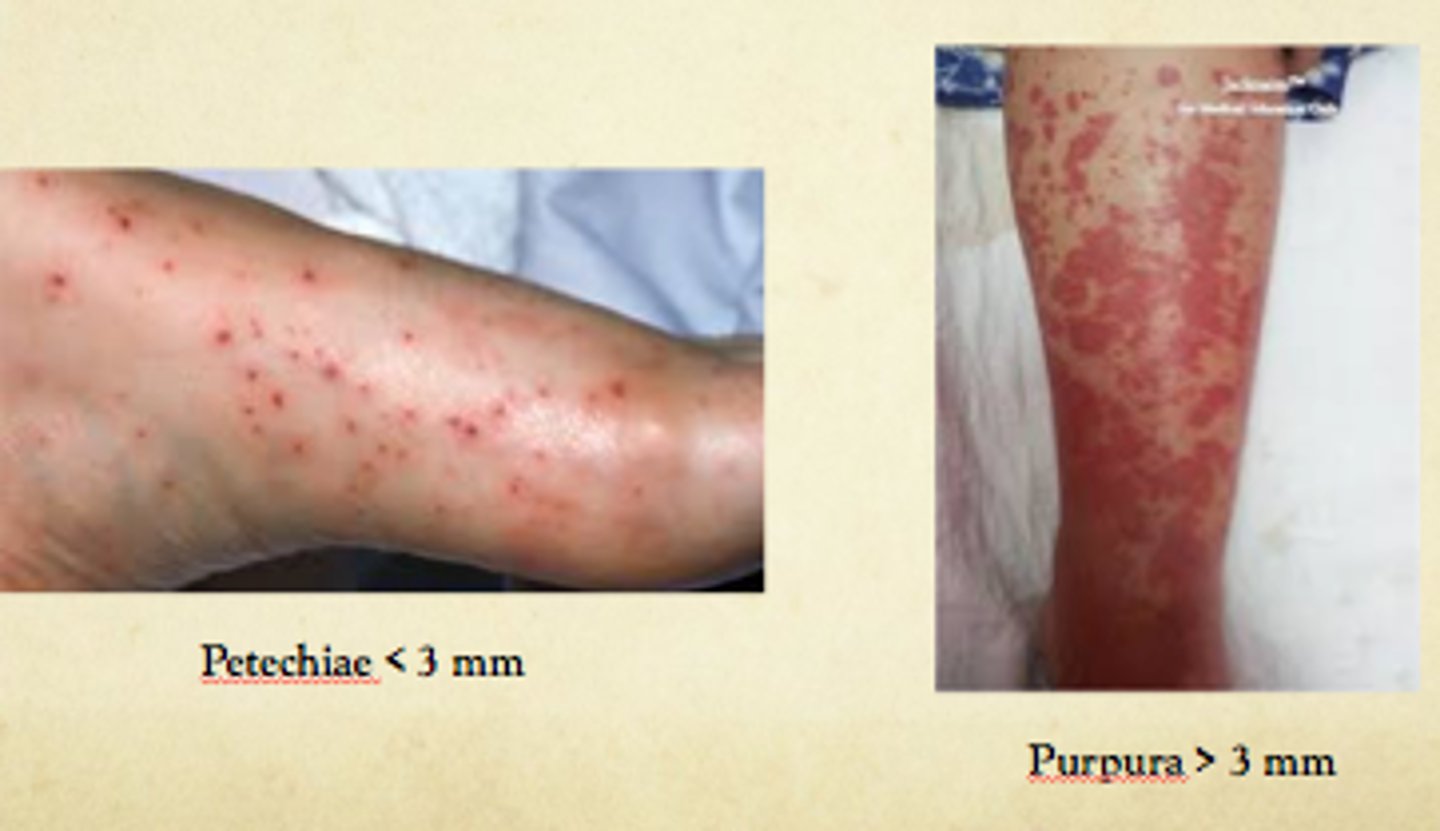
Small reddish to purple macules or papules that can develop anywhere on the body in response to physical trauma
Petechiae
Raised, defined lesion of color, greater than 1 cm in diameter
Plaque
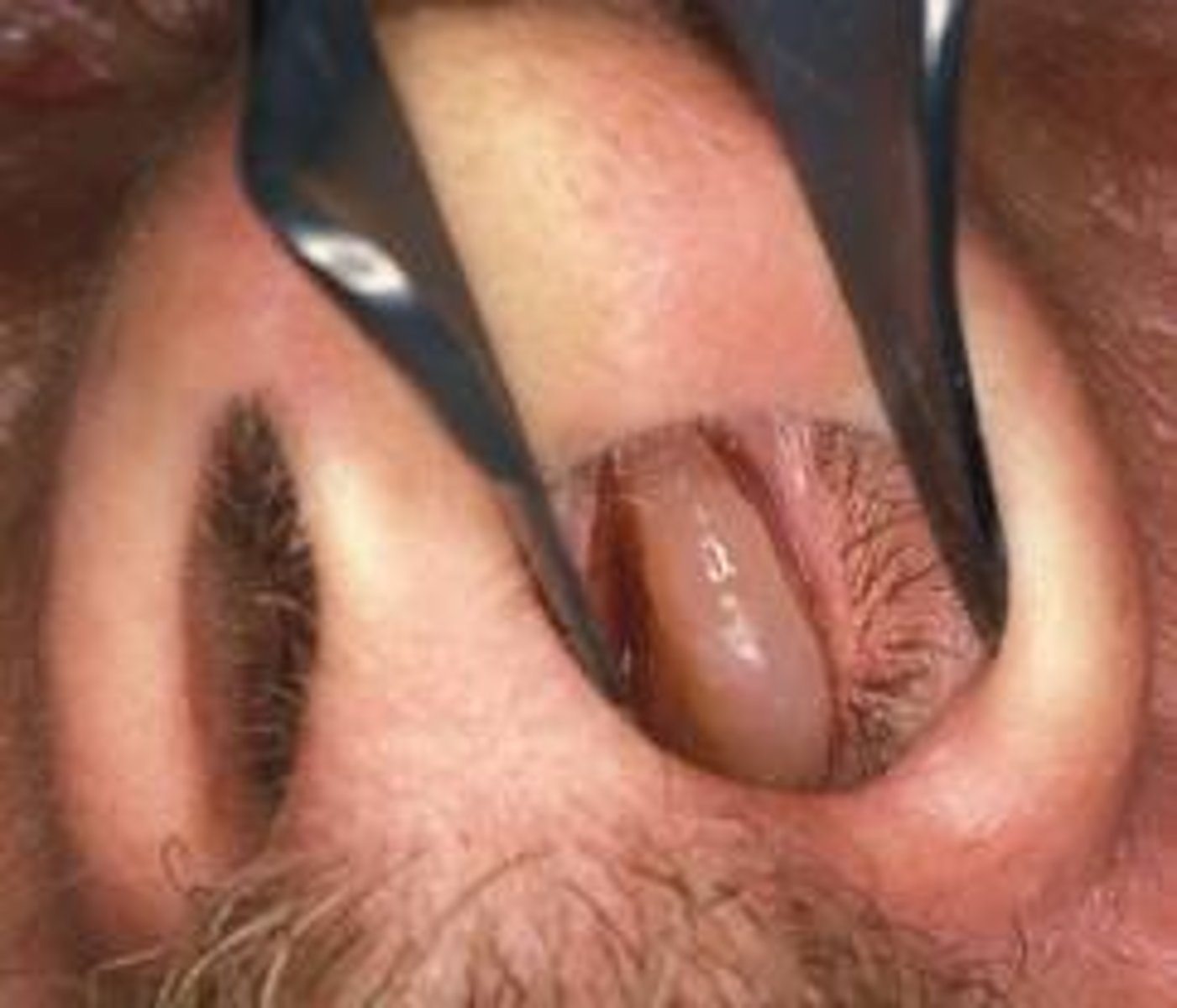
An abnormal growth of tissue originating on a mucous membrane
Polyp
(that photo is a nasal polyp)
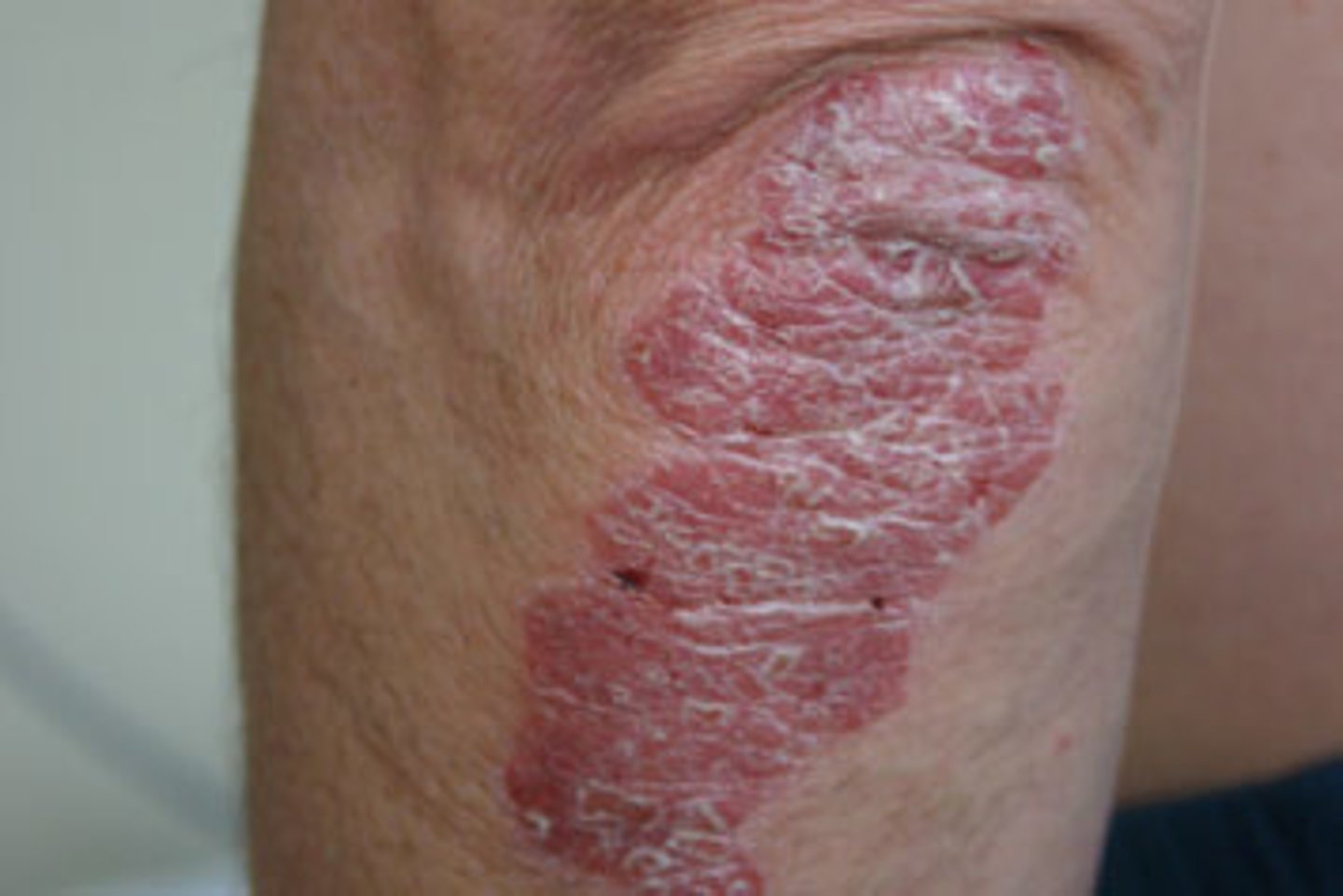
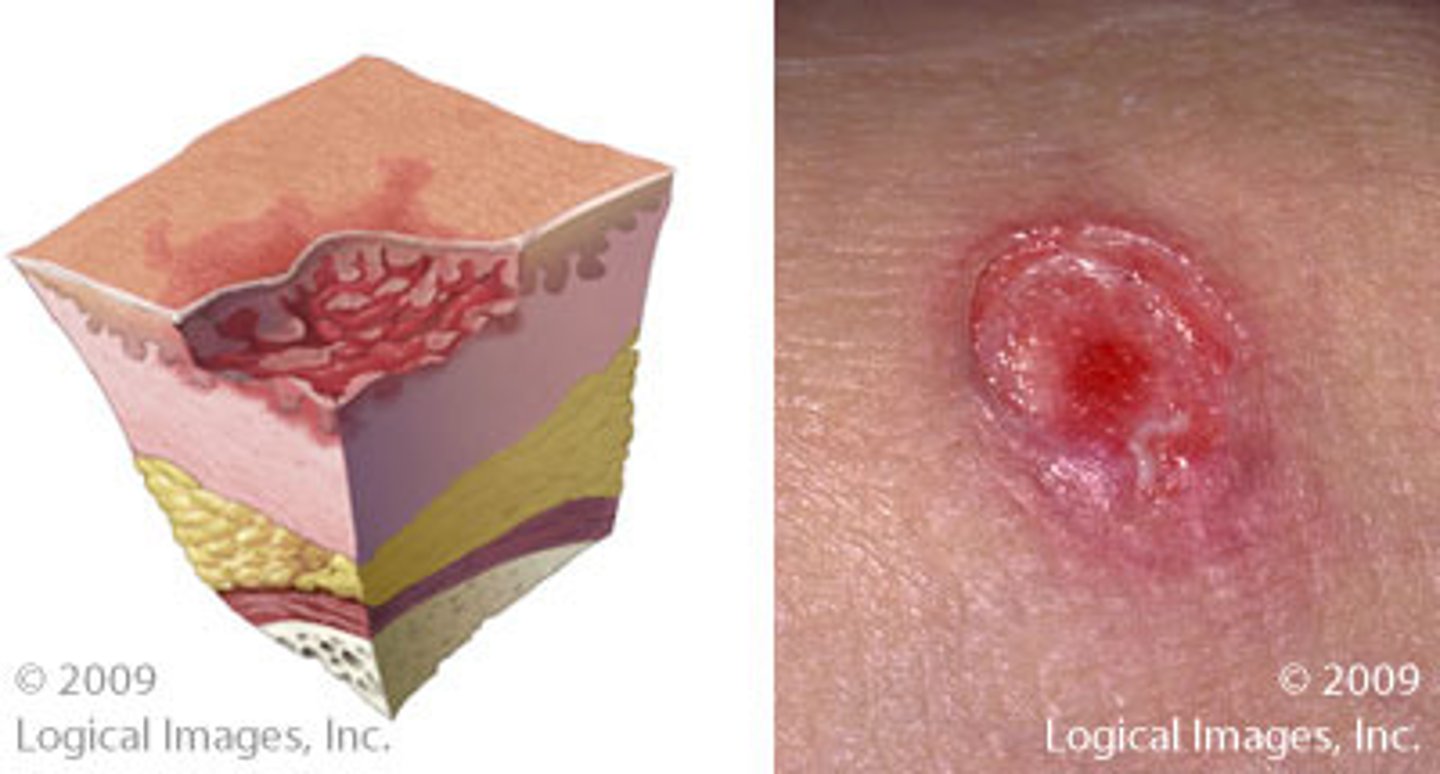
Loss of skin surface, extending into dermis, subcutaneous tissue, fascia, muscle, bone, or all of these
Pressure ulcer
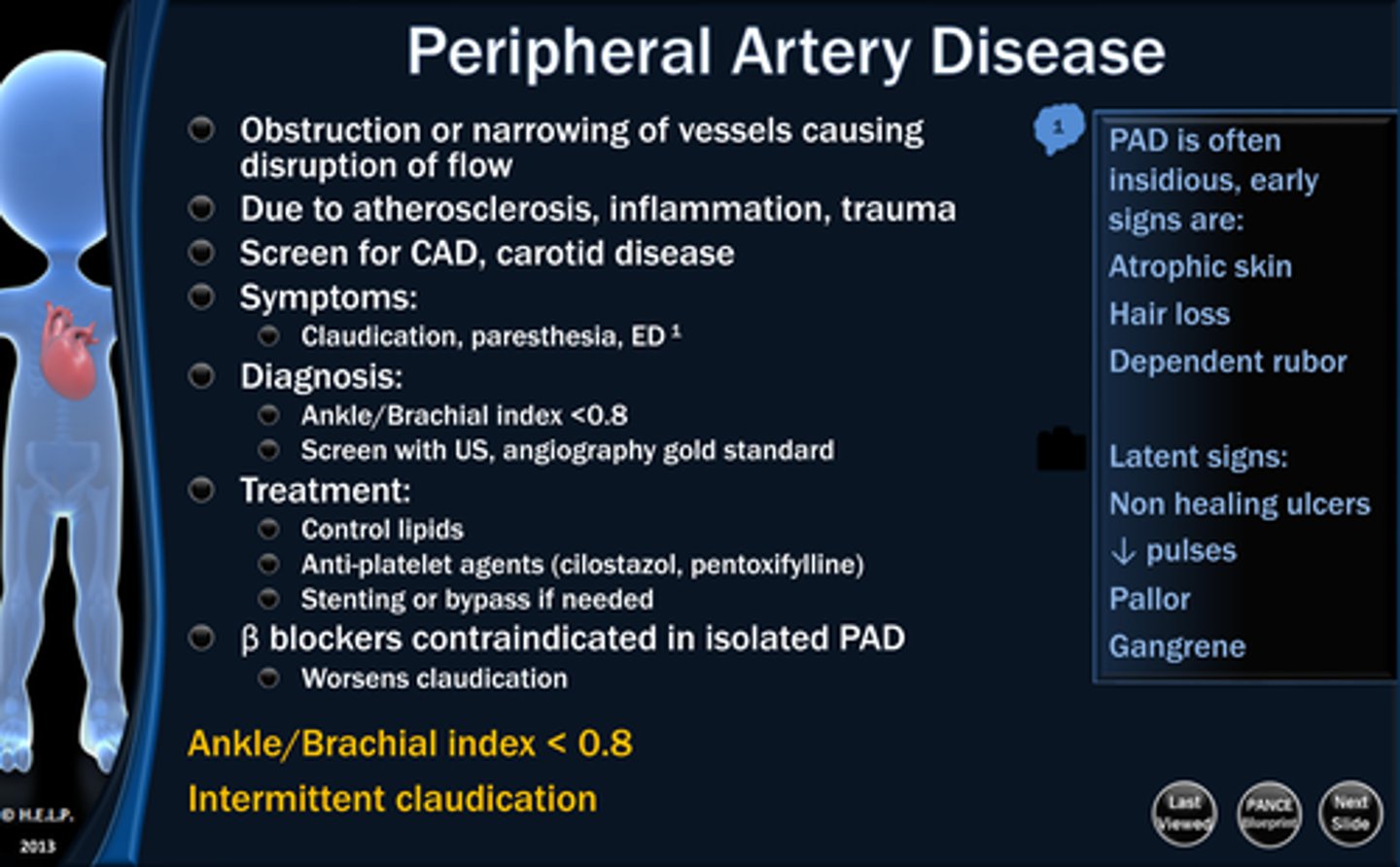
People with no hair on their body often have which disease?
Peripheral Artery Disease
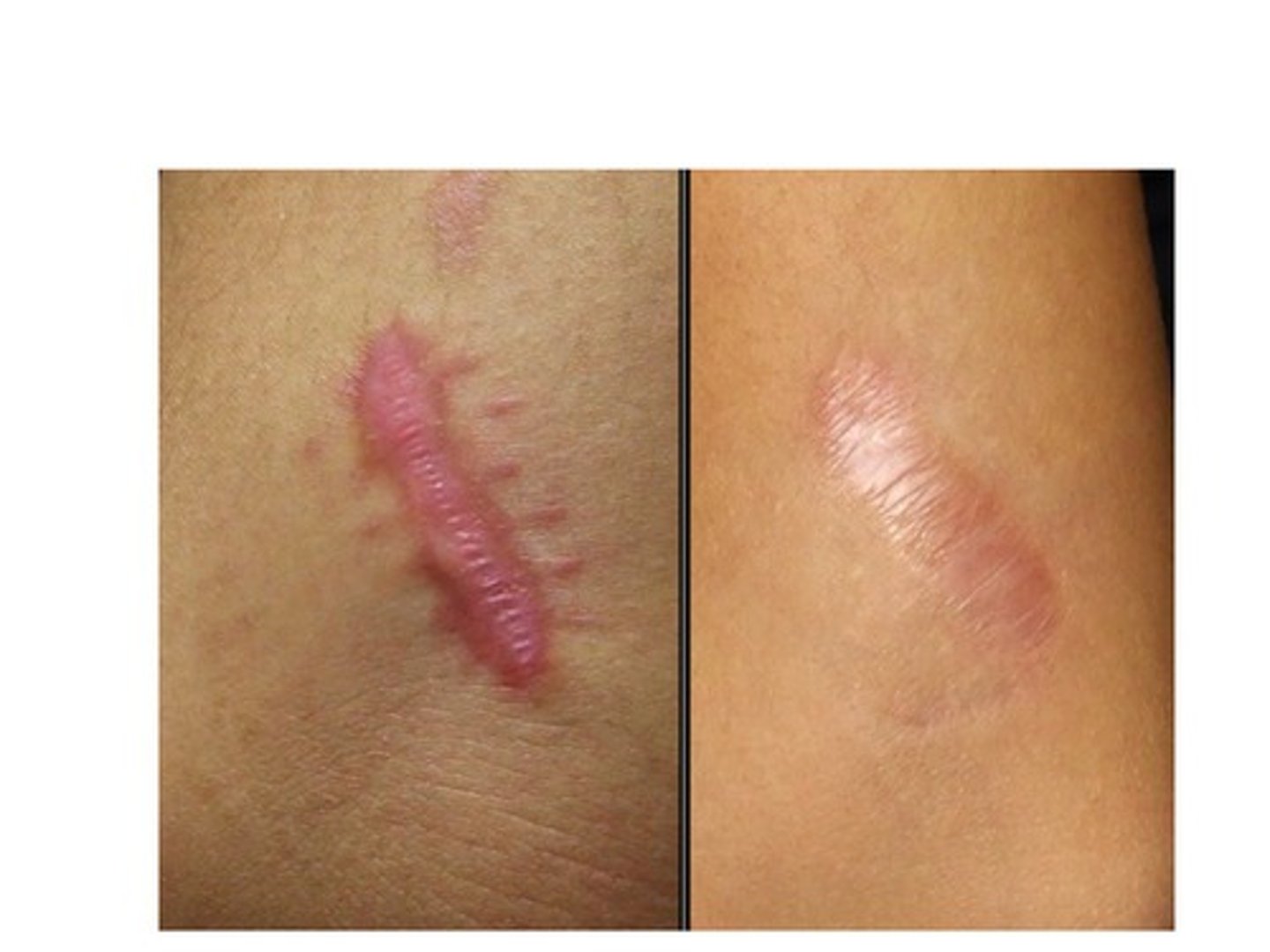
Overgrowth of scar tissue
Keloid
Reddened lesions that arise from previously normal skin and include maculae, papules, nodules, tumors, polyps, wheals, blisters, cysts, pustules, and abscesses. May be further described as nonelevated, elevated solid, or fluid filled.
Primary lesions
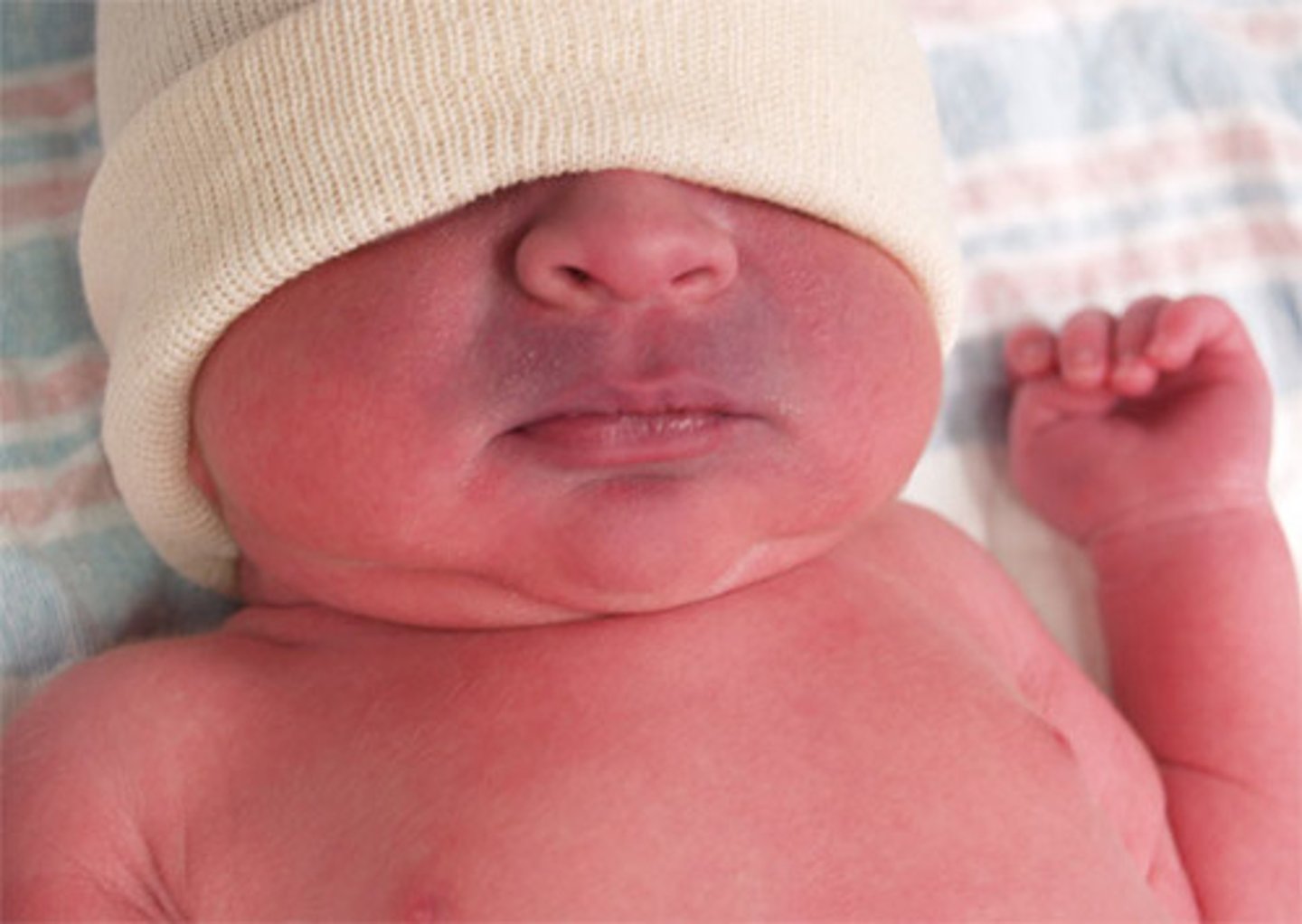
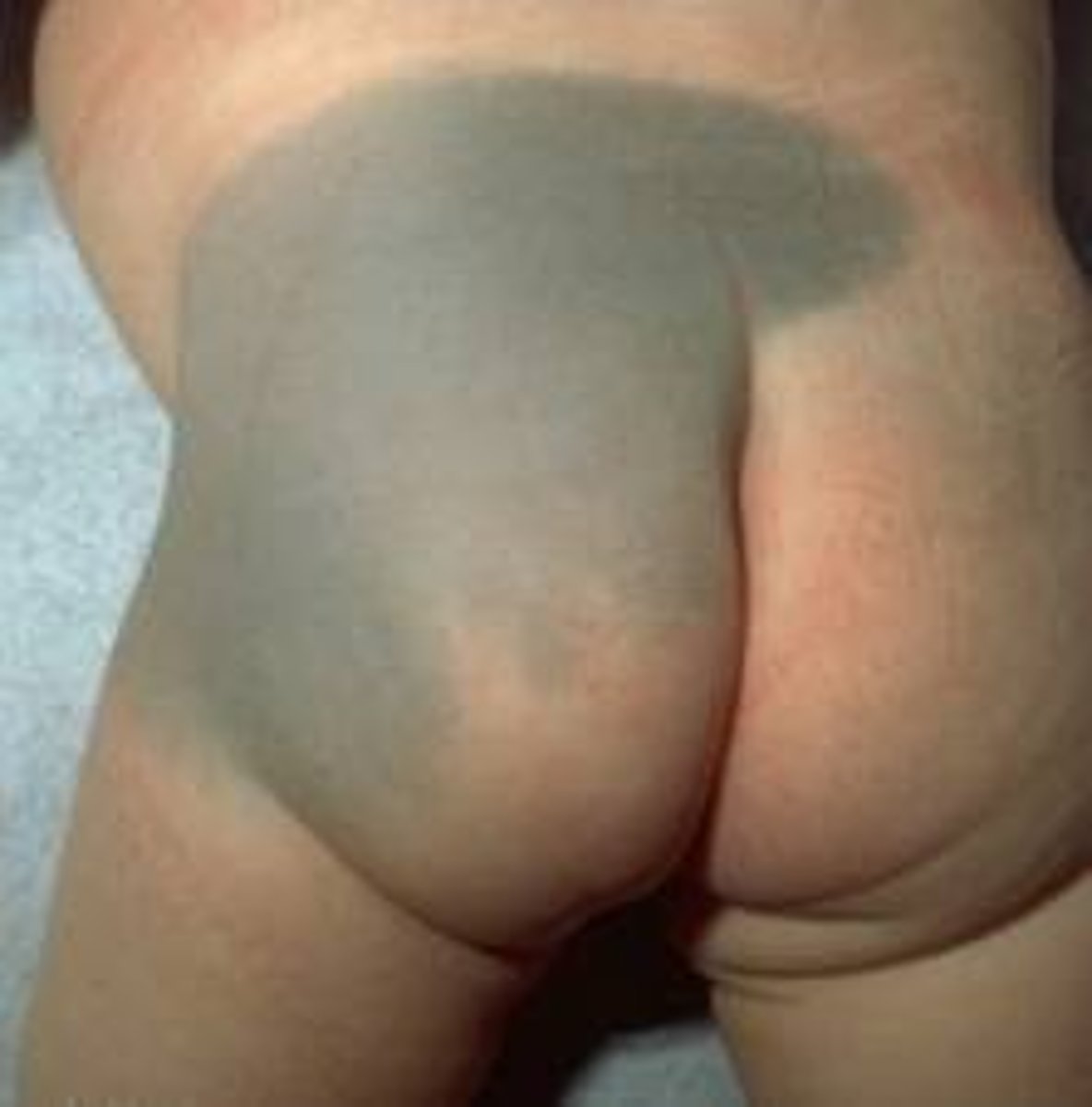
Flat and blue, or blue-gray in color. Hyperpigmentation developed during pregnancy. Common to see on neonates.
dermal melanocytosis
Formerly called "Mongolian spots"
Itching
Pruritus
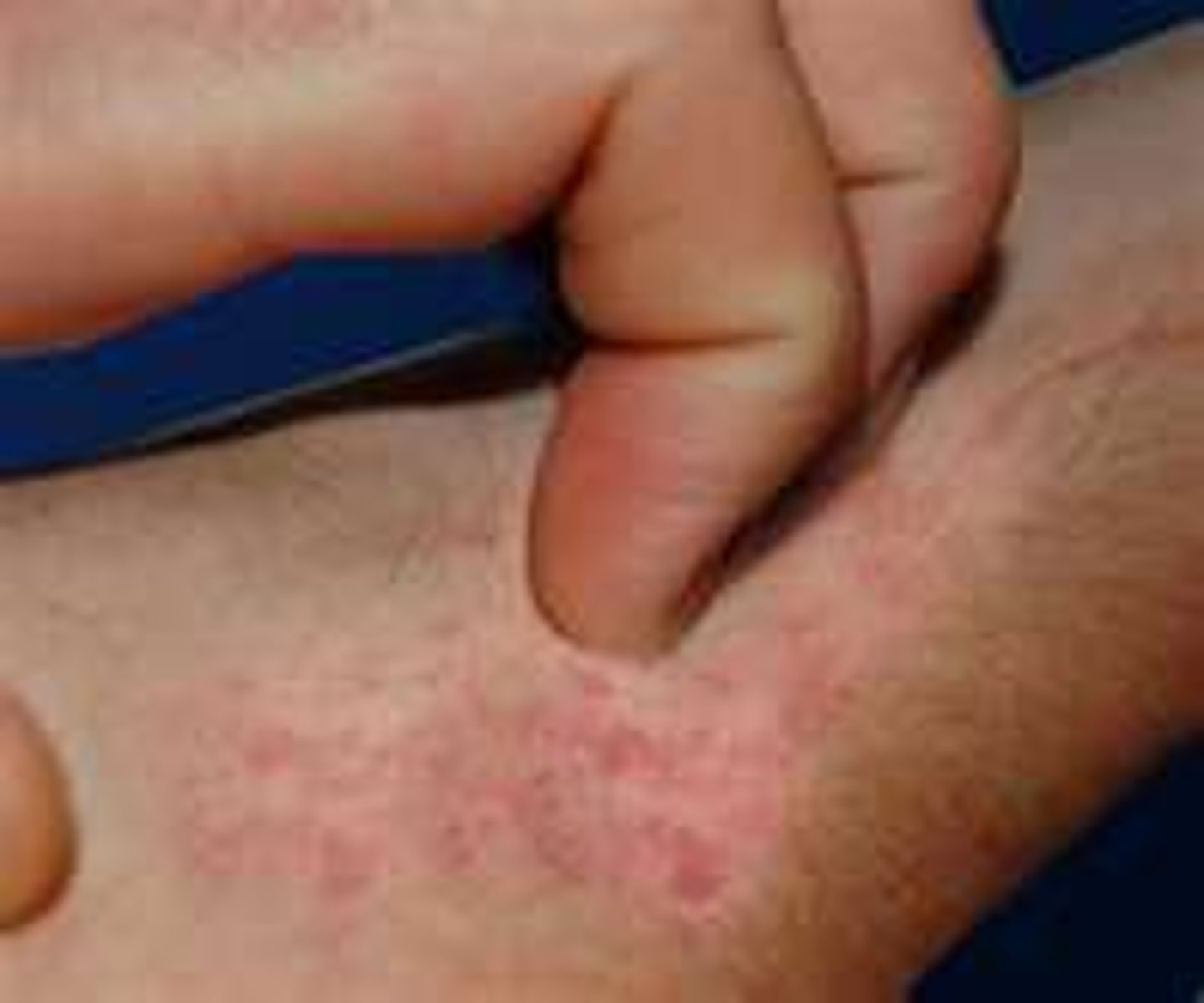
Acute dehydration, cyanosis, or acute lacerations, acute trauma, burns are all requiring what kind of assessment
Urgent Assessment
Suspicious lesions or rash + fever are USUALLY
Not requiring an urgent assessment
Wound with greater depth than width, caused by a sharp object piercing the skin
Puncture wound
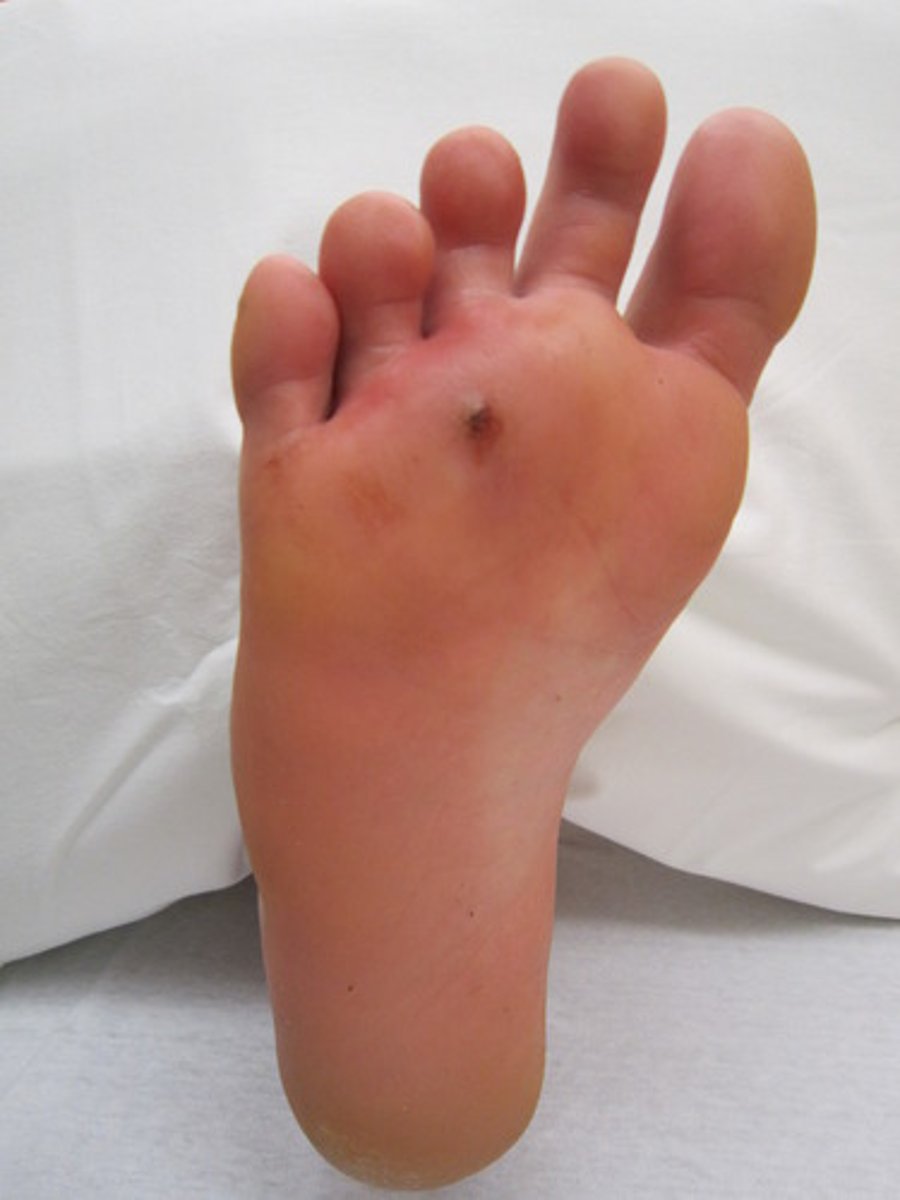
Red or purple skin discolorations that do not blanch when pressure is applied. They are caused by bleeding underneath the skin. Measures 0.3 to 1.0 cm
Purpura
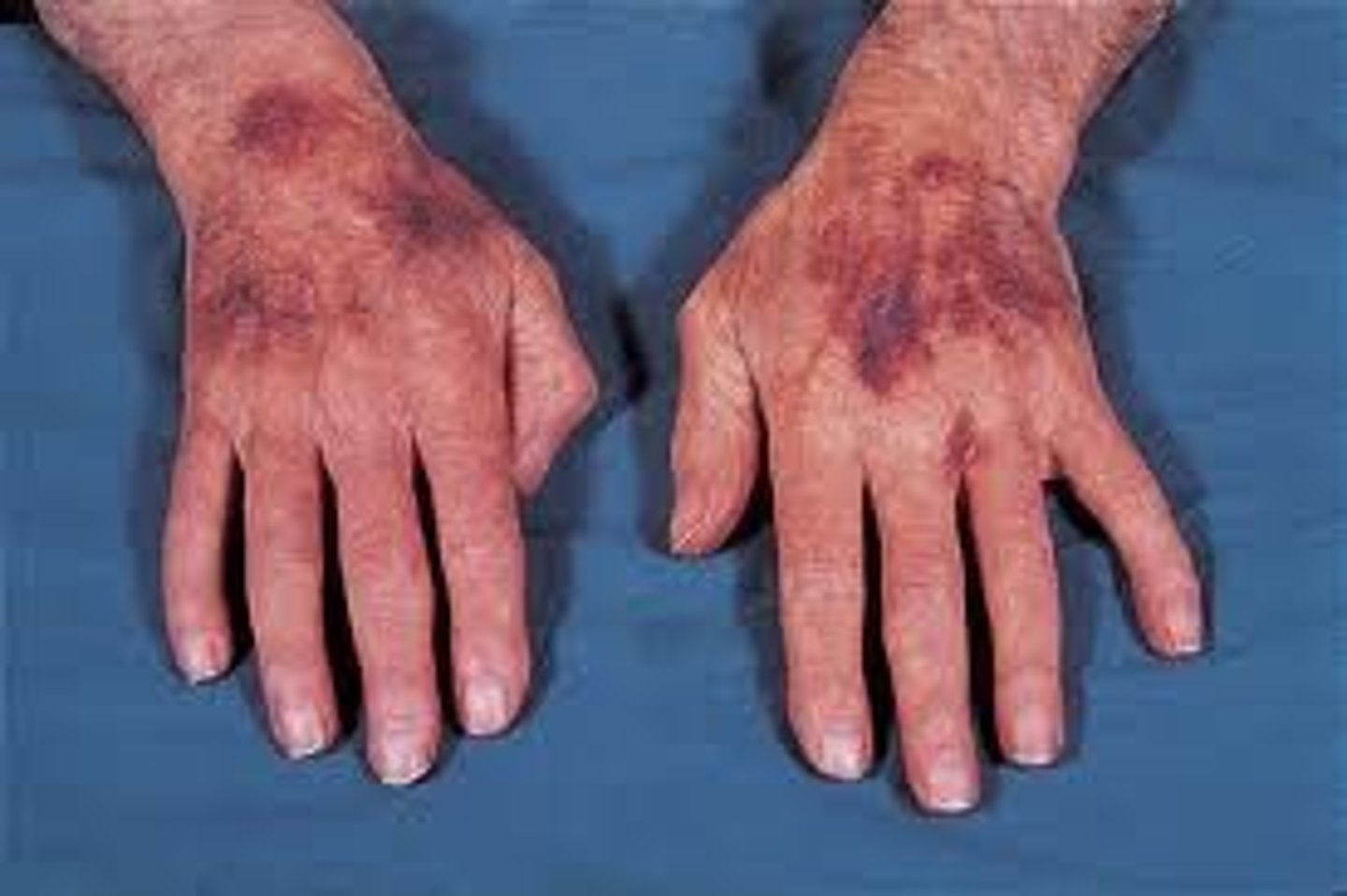
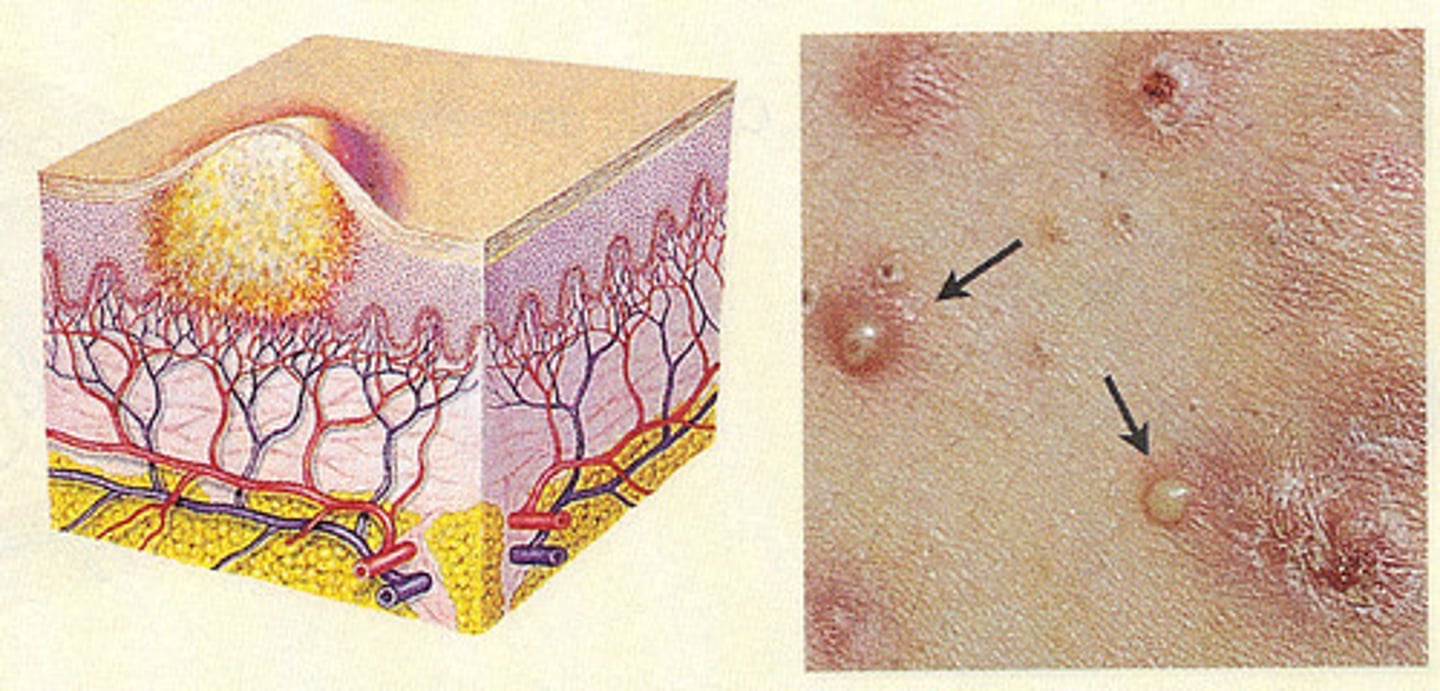
Purulent fluid-filled raised lesion of any size
(purulent = consisting of pus)
Pustule (THINK PUS)
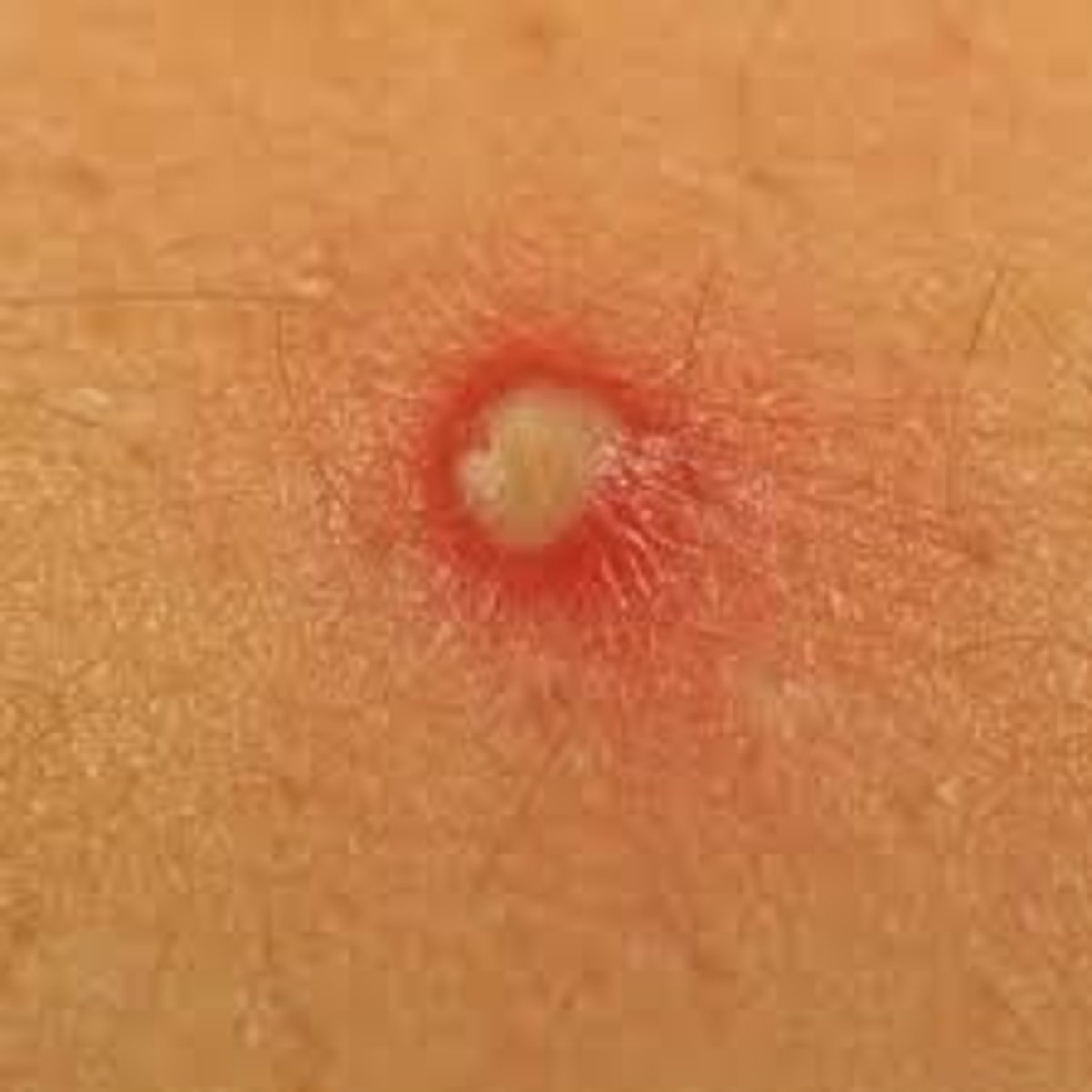
Redness of the skin, commonly as a result of inflammation
Rubor
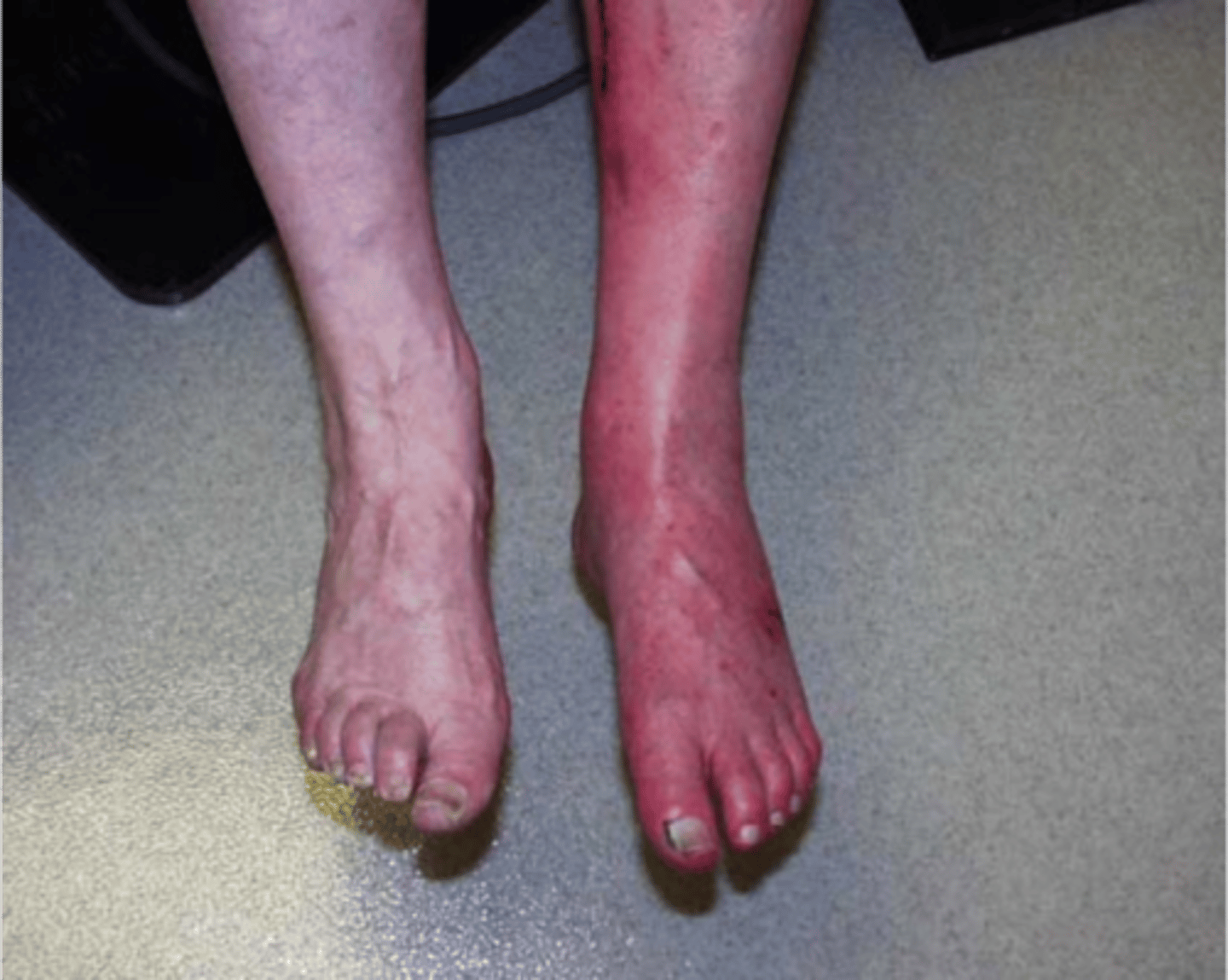
Skin changes that appear following a primary lesion (ex: scar tissue, crusts from dried burn vesicles)
Secondary lesions
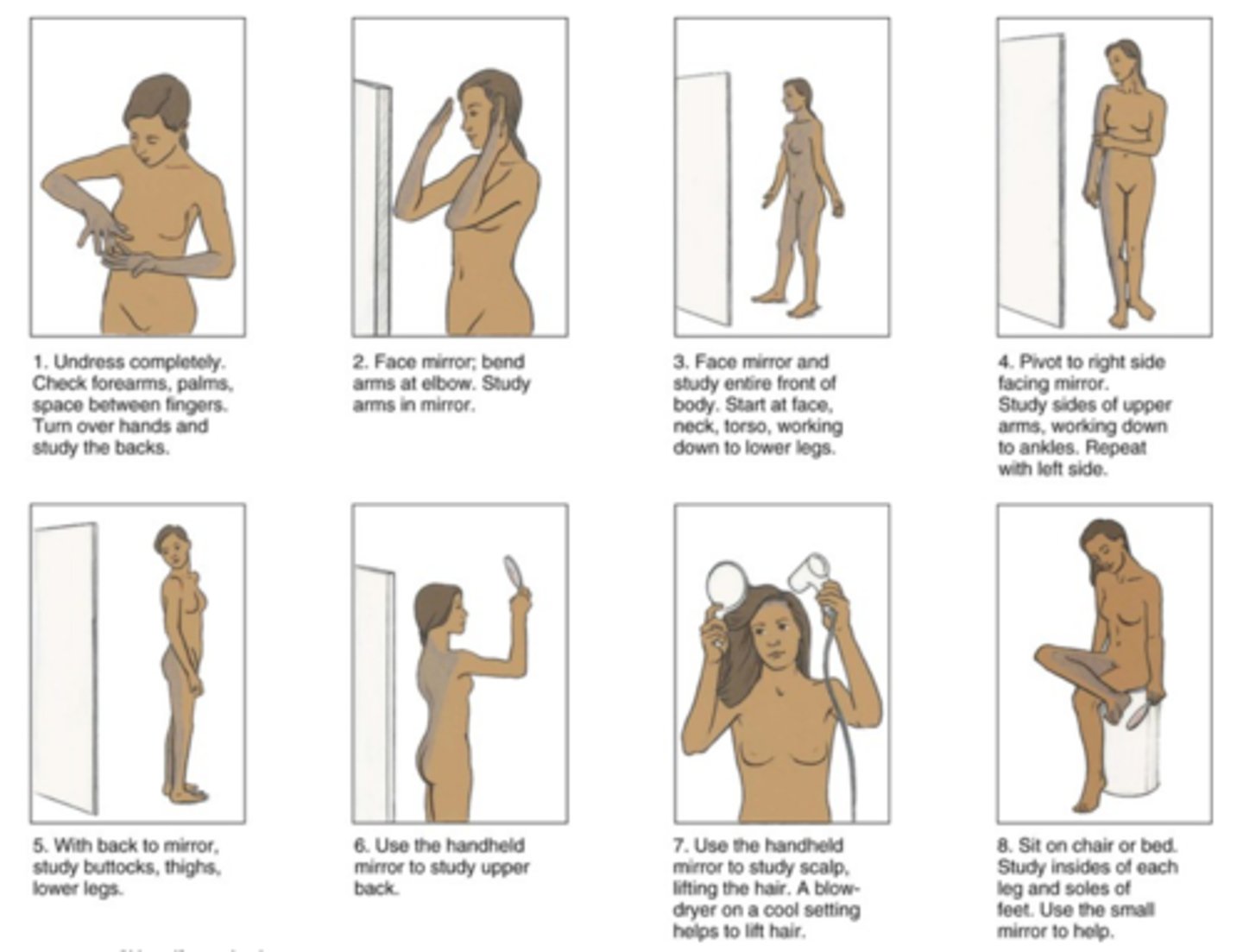
An examination of the skin that the patient himself or herself performs to identify potentially problematic lesions
Self-skin examination
A persistent pinch
Tenting
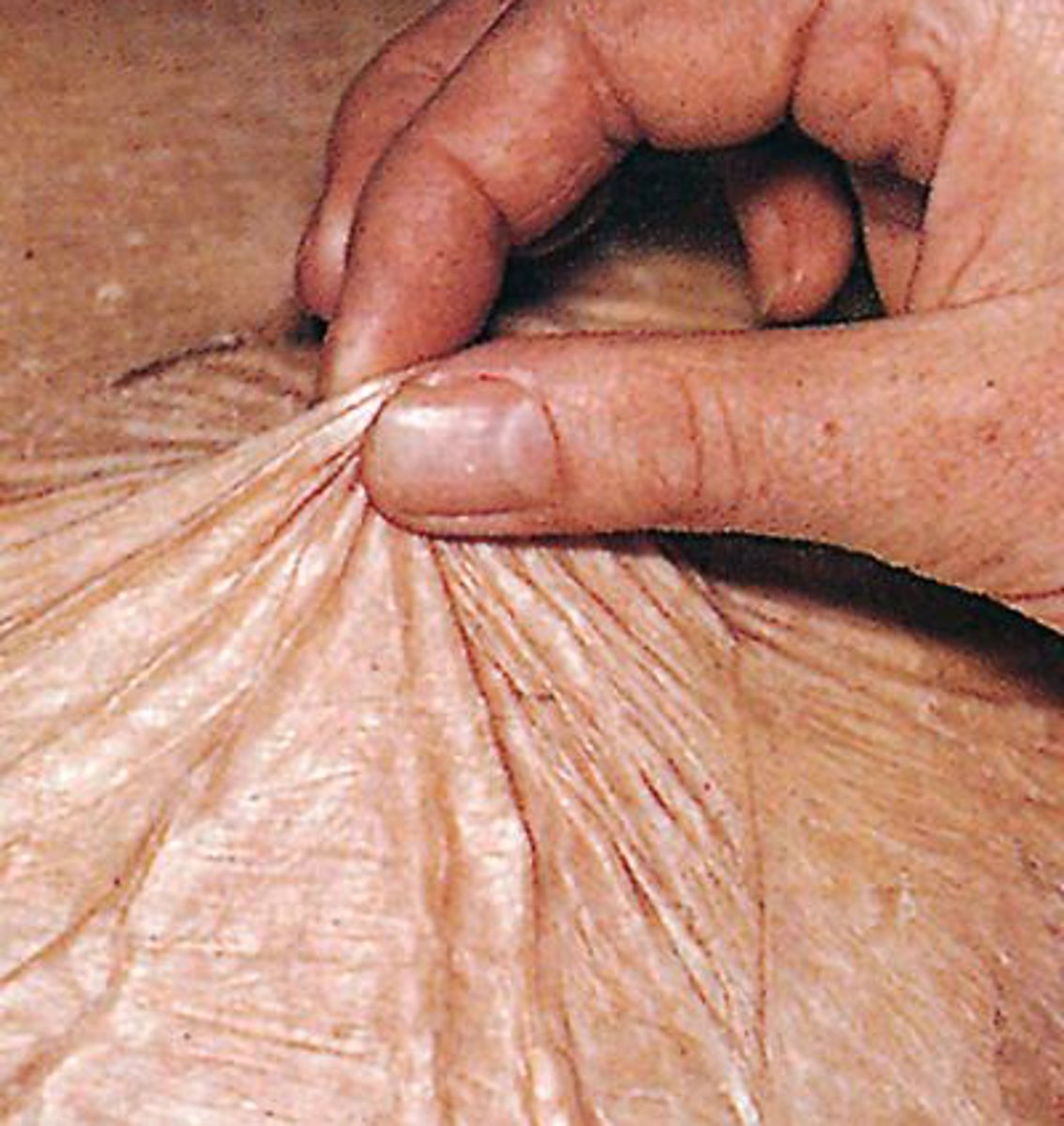
An abnormal growth of tissue, whether malignant or benign
Tumor
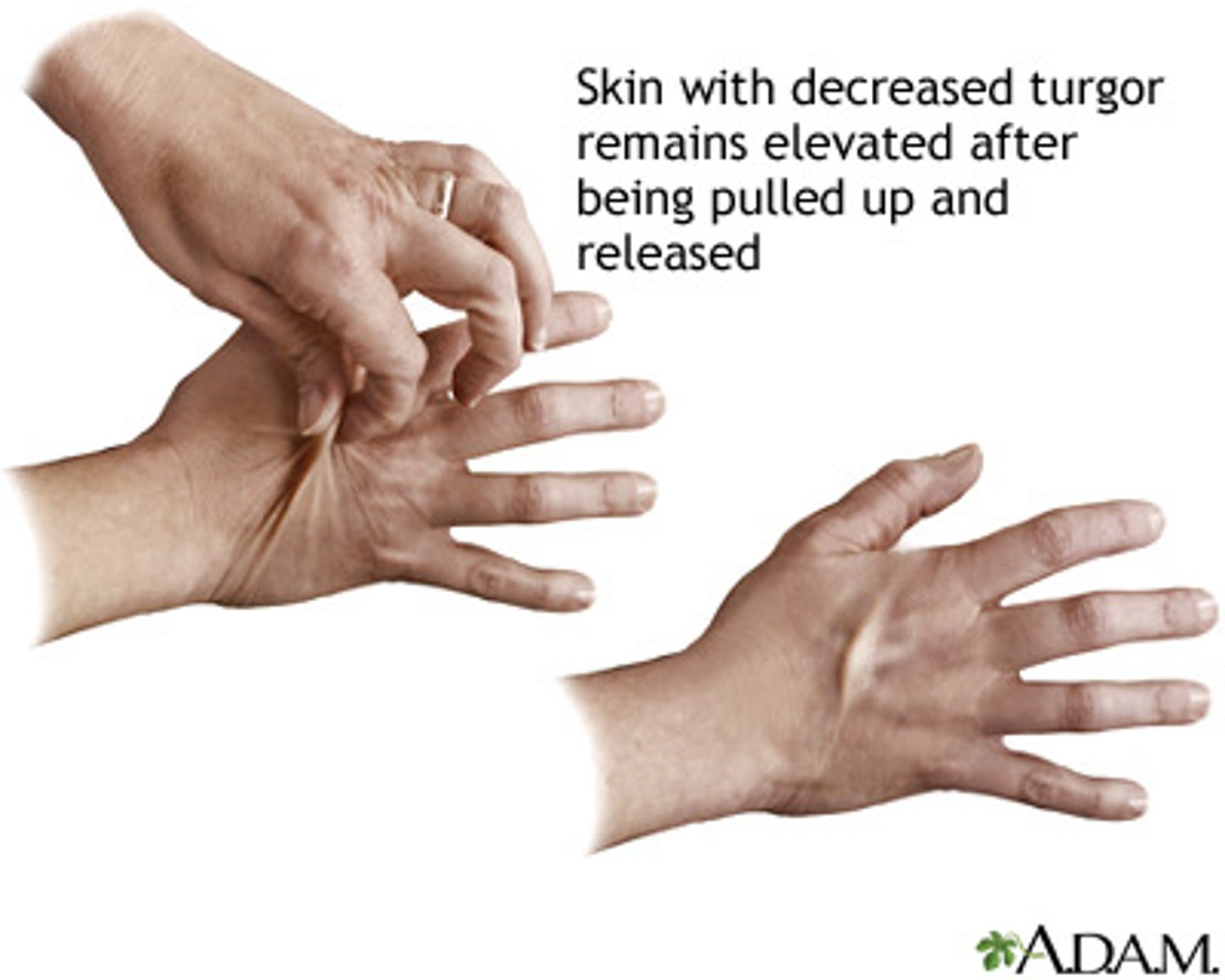
Skin's ability to change shape and return to normal (elasticity). Used to assess the status of fluid loss or dehydration in the body
Turgor
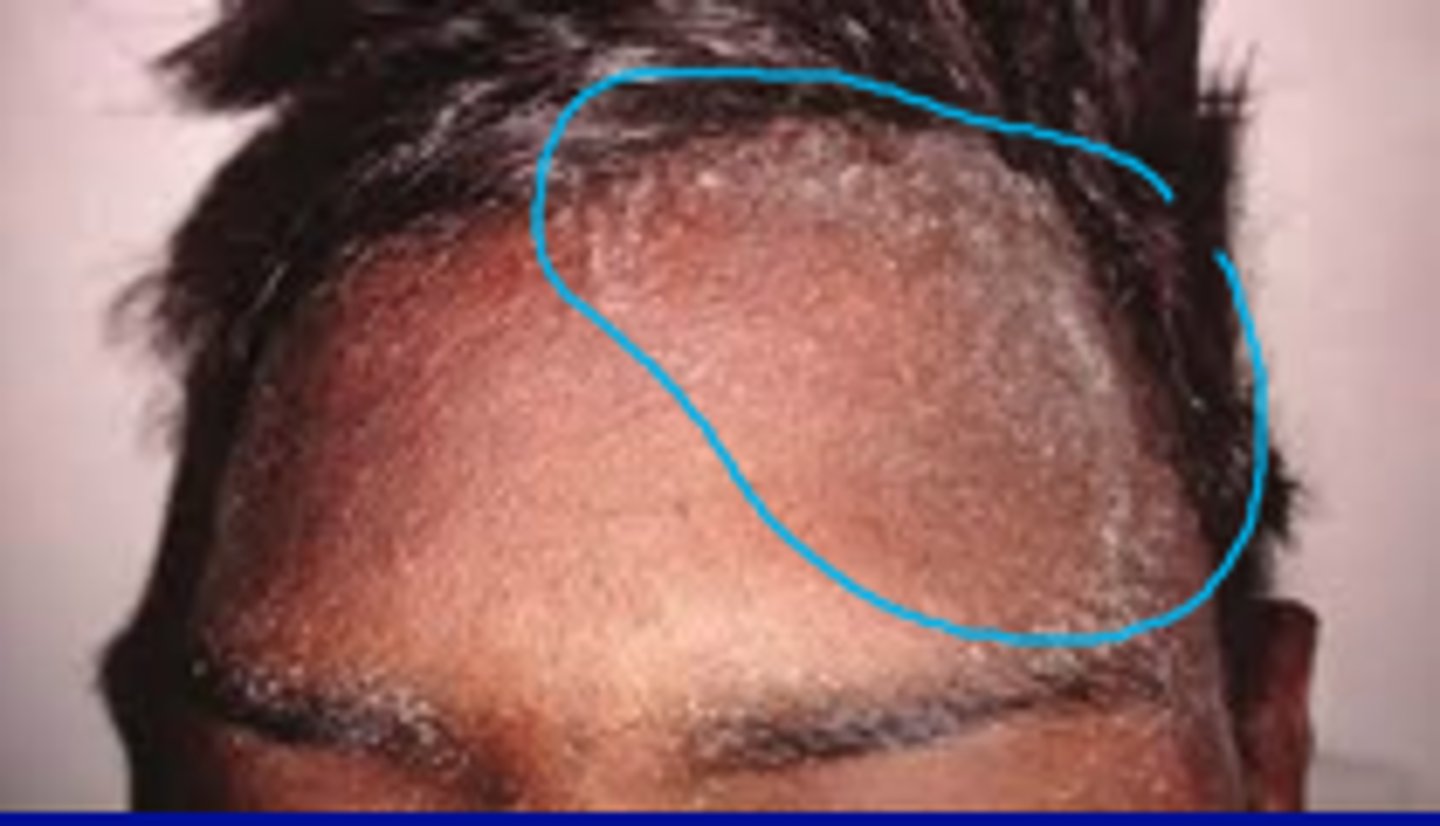
Precipitation of renal urea and nitrogen waste products through swear onto the skin (whitish coating noted with severe kidney failure)
Uremic frost
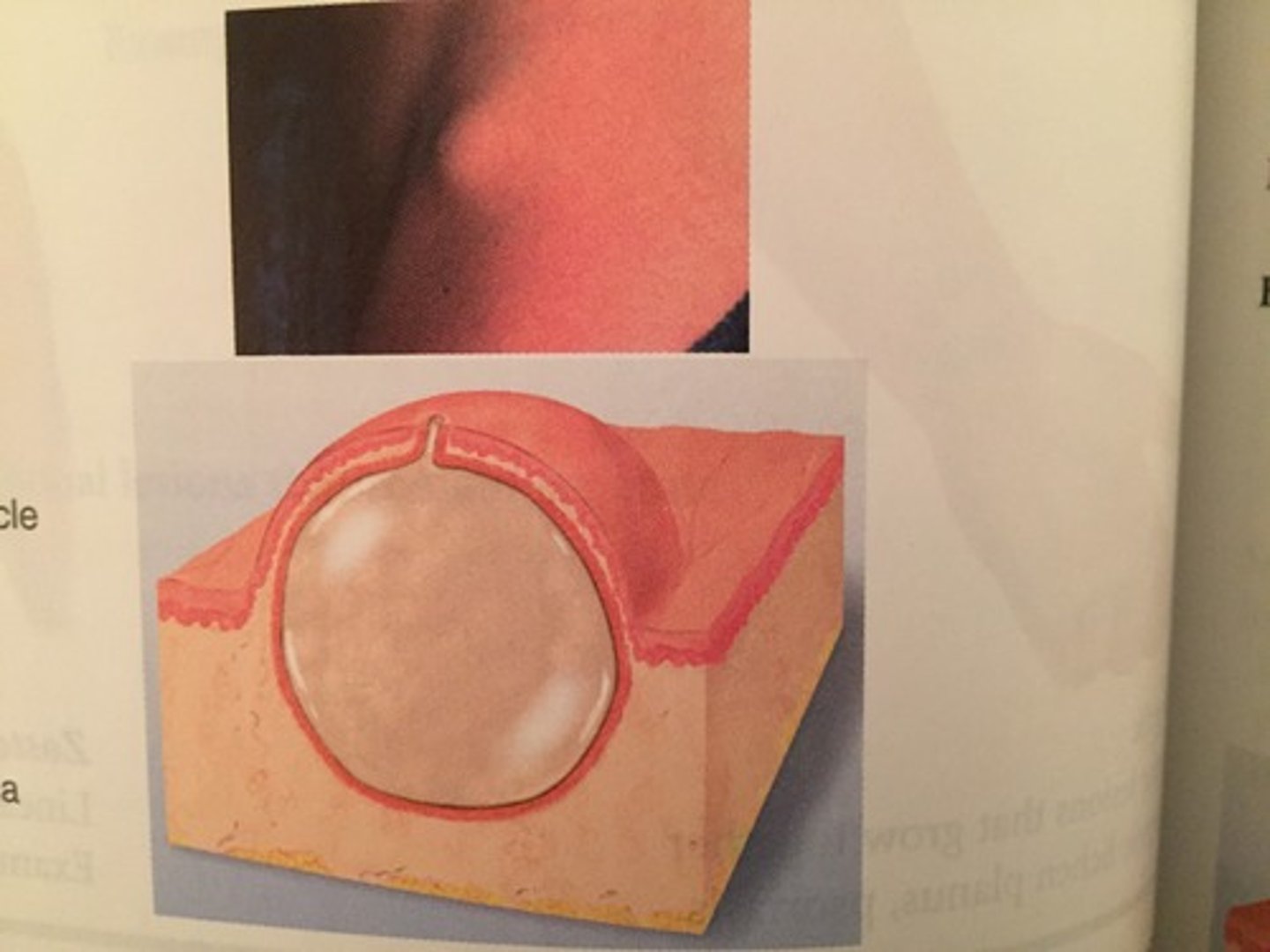
Fluid-filled lesion less than 1 cm in diameter
Vesicle
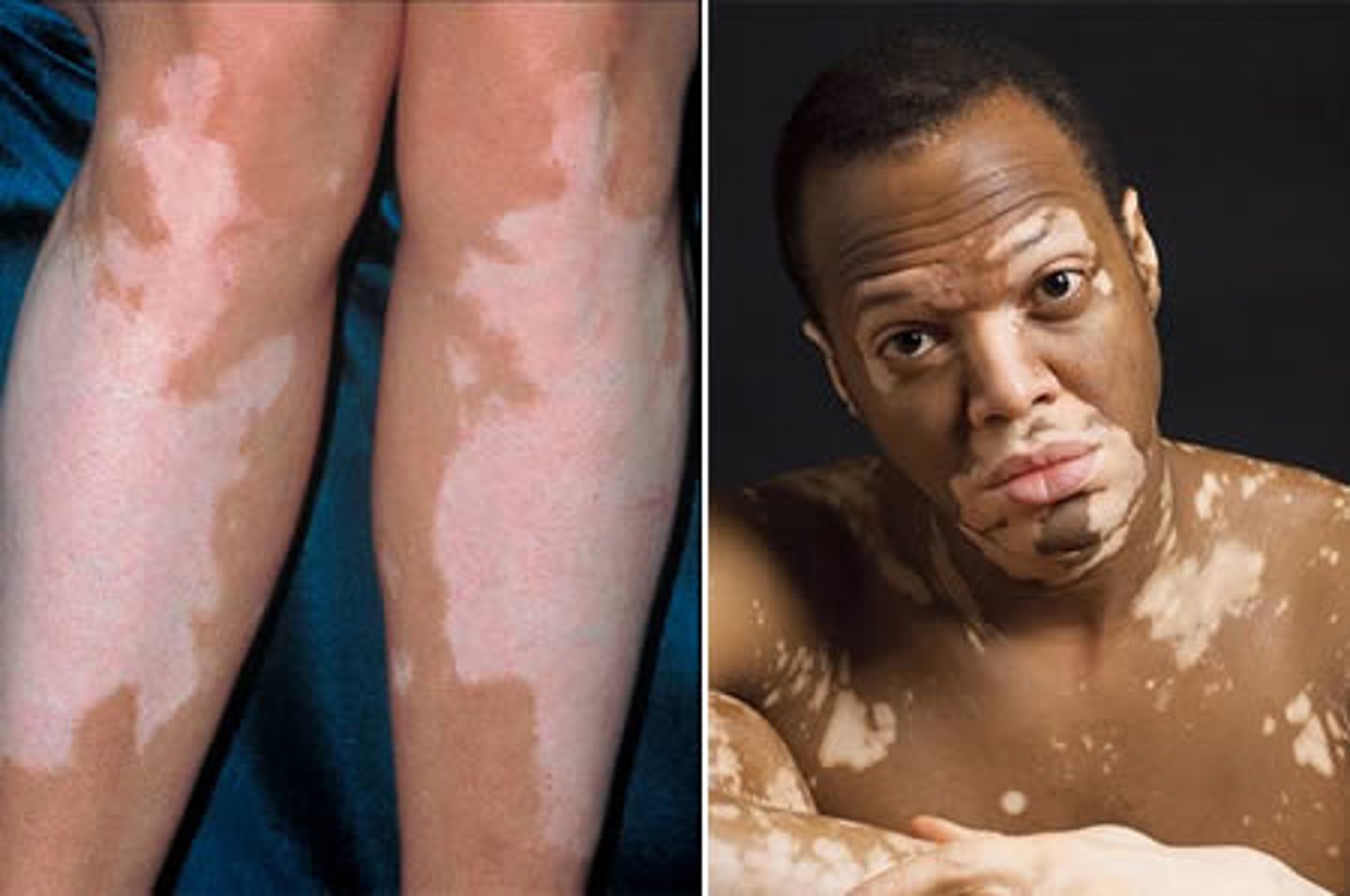
Skin condition characterized by areas of no pigmentation
Vitiligo
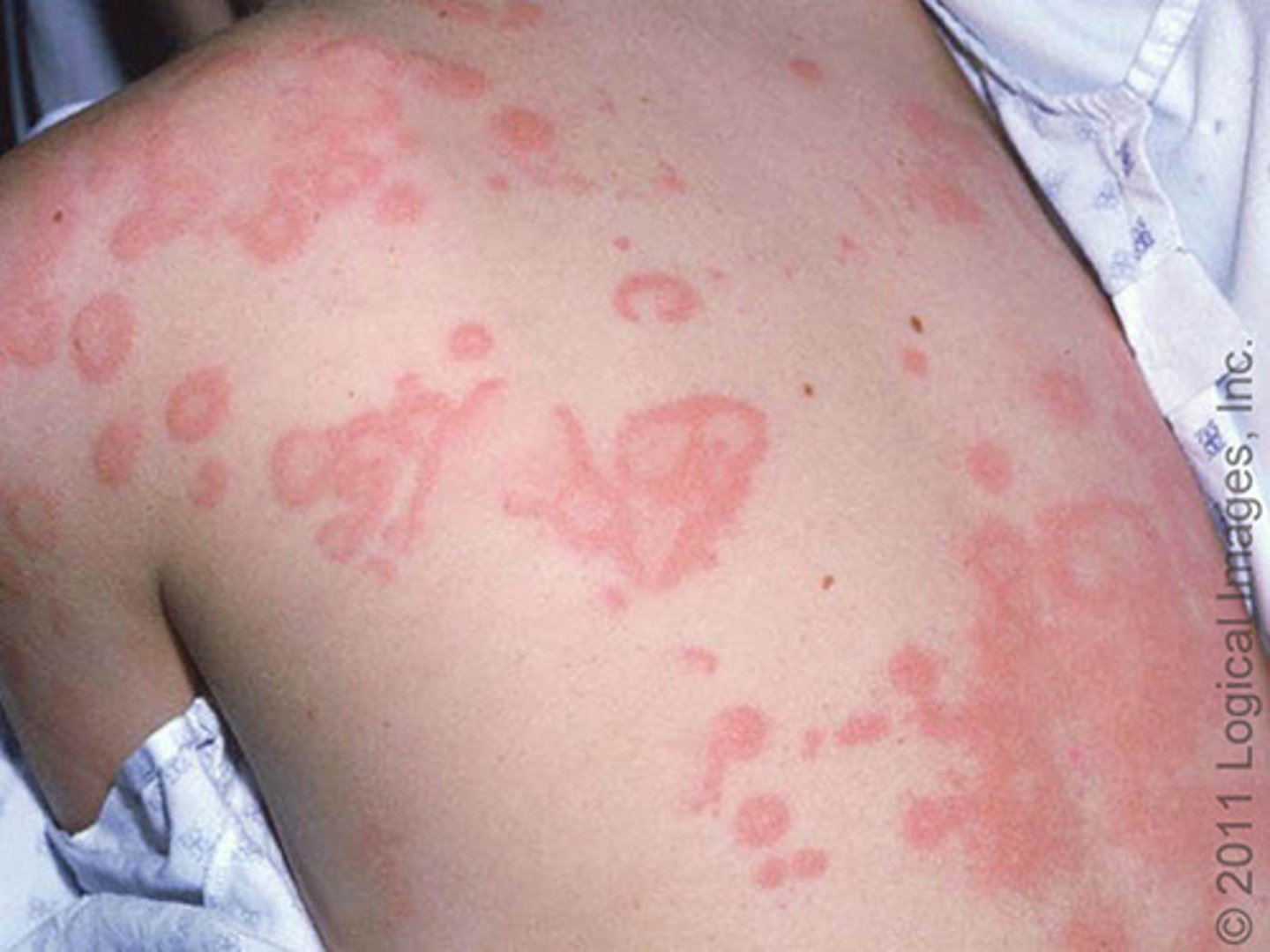
Raised, flesh-colored or reddened edematous papules or plaques, varying in size and shape.
Wheal
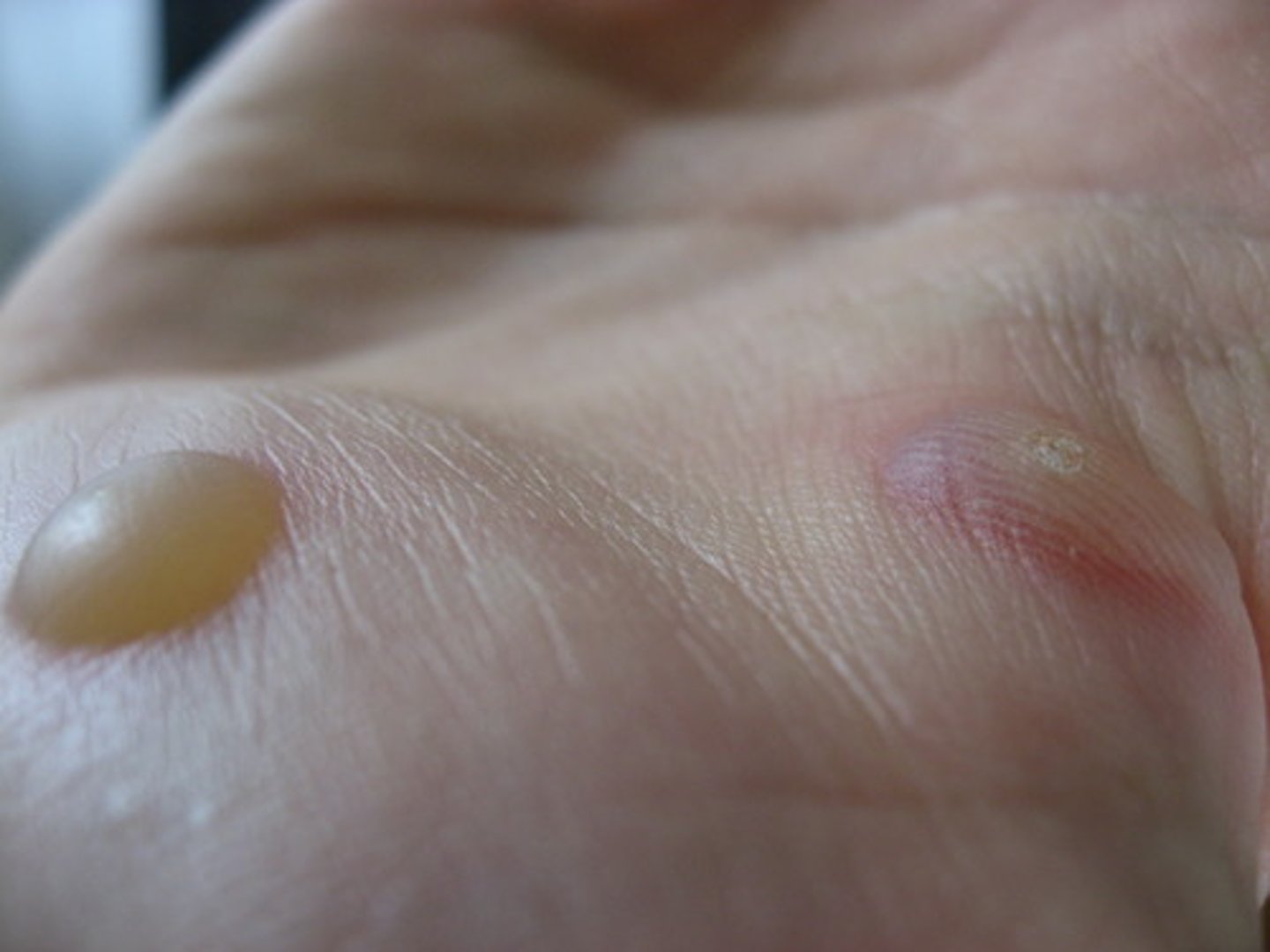
Classified as either serous (clear) or sanguineous (bloody)
Wound drainage
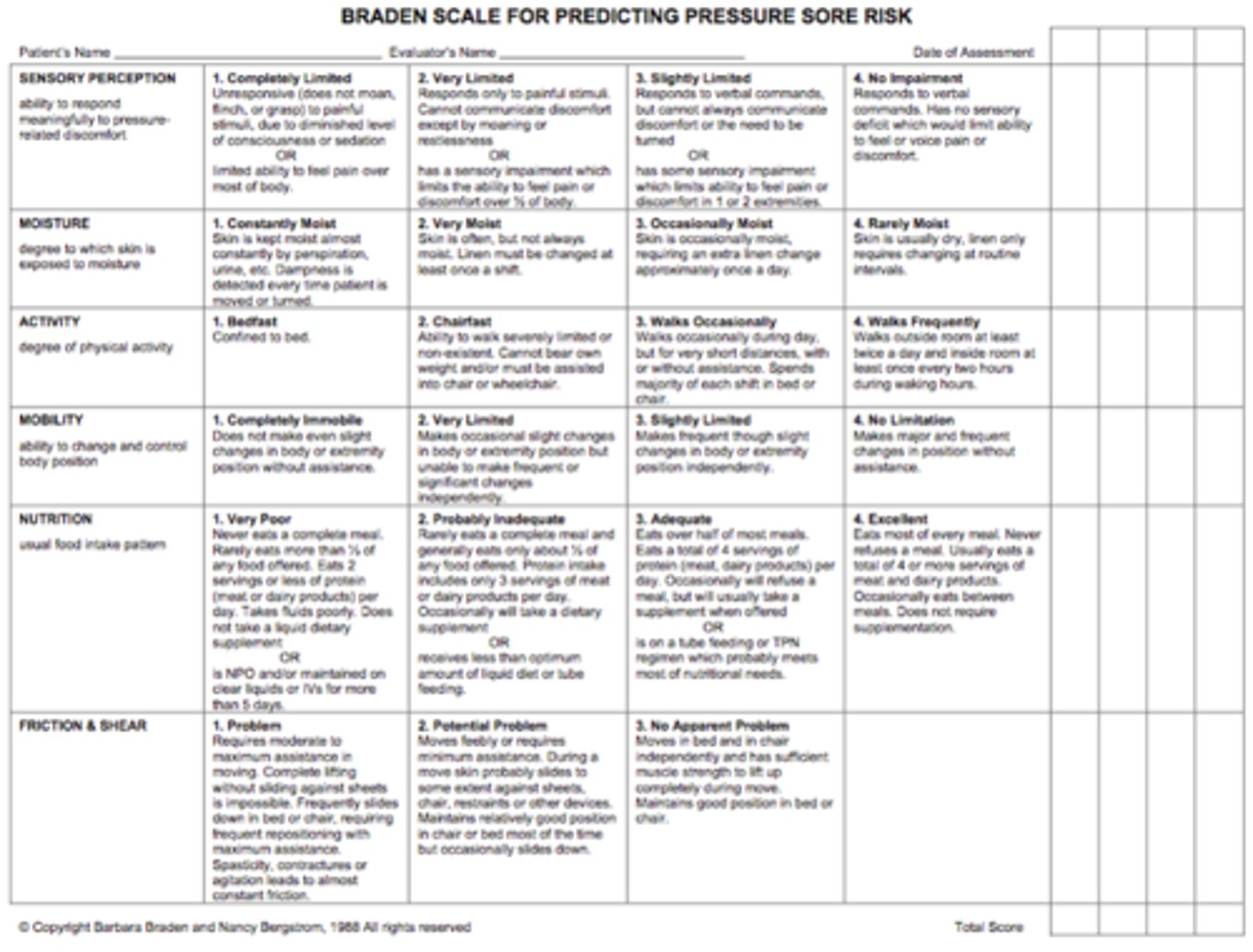
A new nurse on the long-term care unit is learning how to assess a patient's risk for skin breakdown. What would be the most likely instrument this nurse would use?
Braden scale.
The scale consists of six subscales and the total scores range from 6-23. A lower Braden score indicates higher levels of risk for pressure ulcer development.
Total score: 19-23 = no risk; 15-18 = mild risk; 13-14 = moderate risk; 10-12 = high risk; <9 = very high risk
When documenting that a patient has freckles, the appropriate term to use is
Macules
A patient with a zosteriform rash has a rash that
is distributed along a dermatome
(think of herpes zoster)
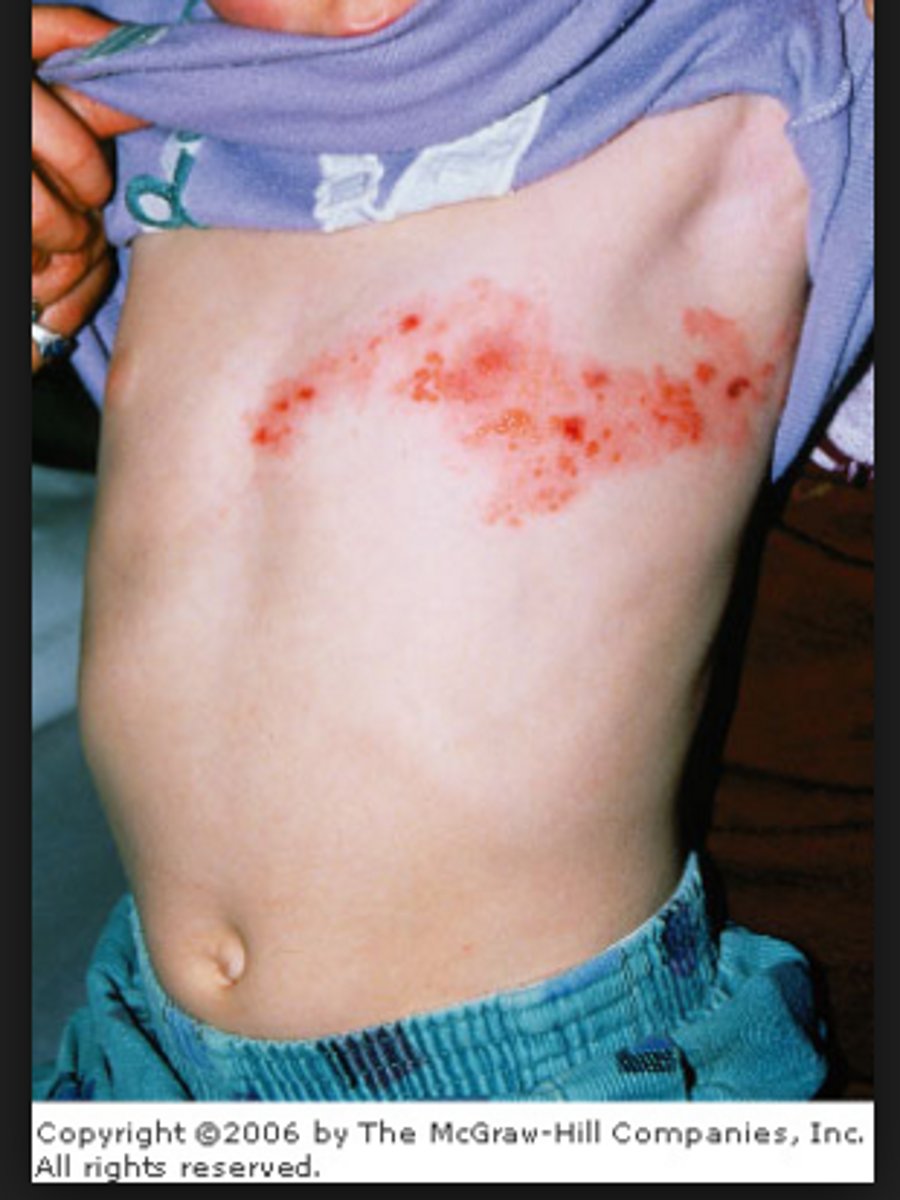
single lesion(s) in close proximity to larger lesion, as if "orbiting" ; cutaneous candidiasis
satellite distribution
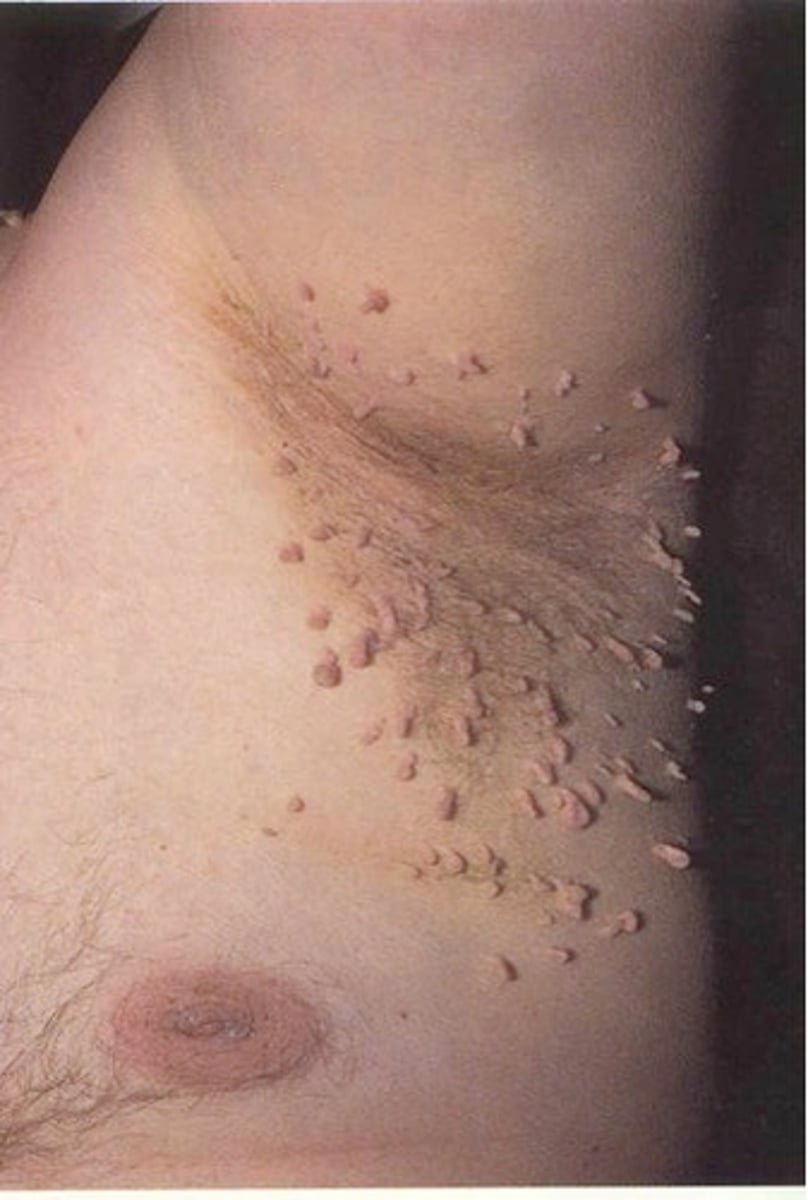
clustered; herpes simplex
grouped distribution
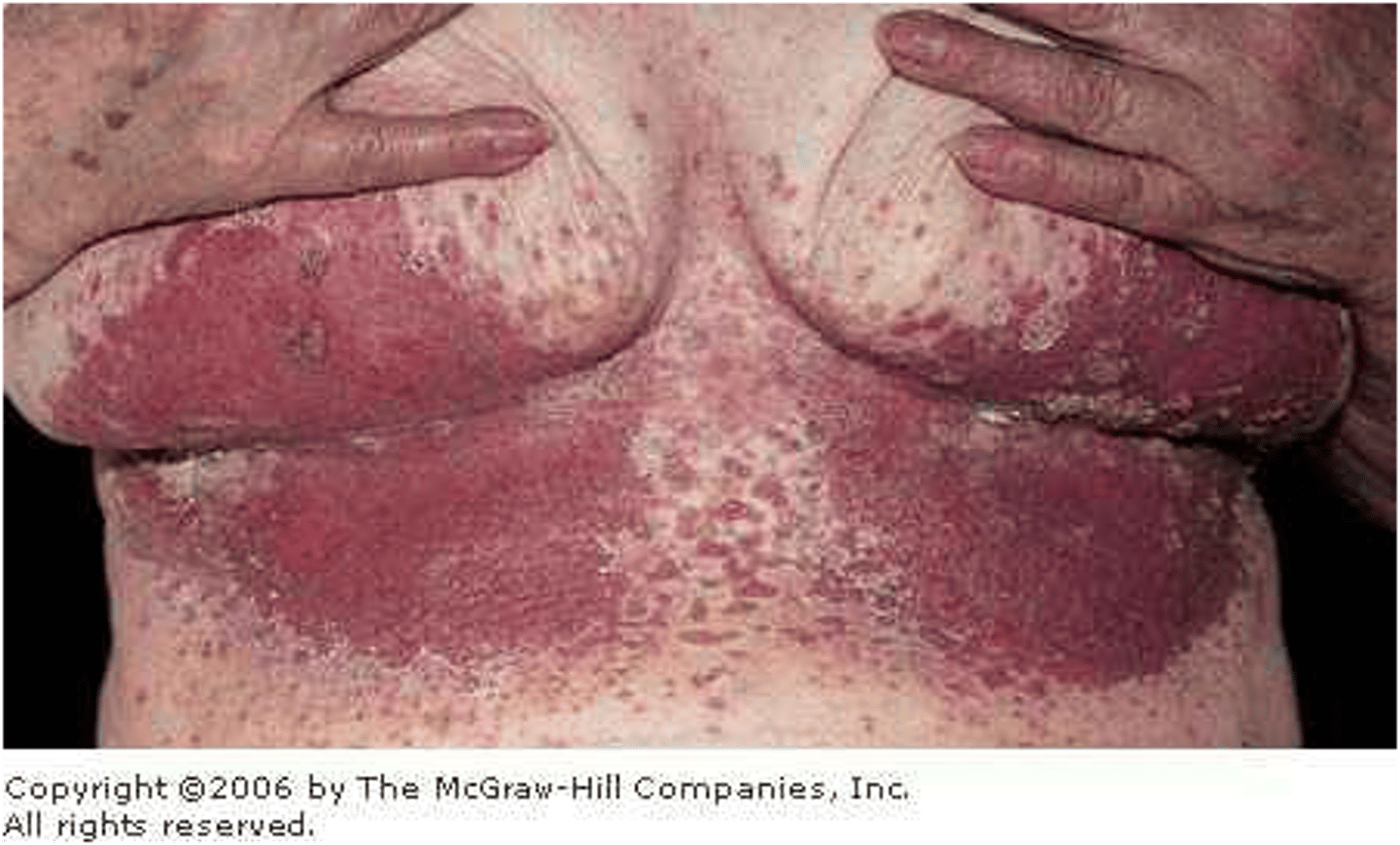
distributed over large body area; psoriasis acbe vulgarisms, exfoliative dermatitis
generalized distribution
with enlargement or multiplication, begins to coalesce to form larger lesion; urticaria, tinea versicolor
confluent distribution
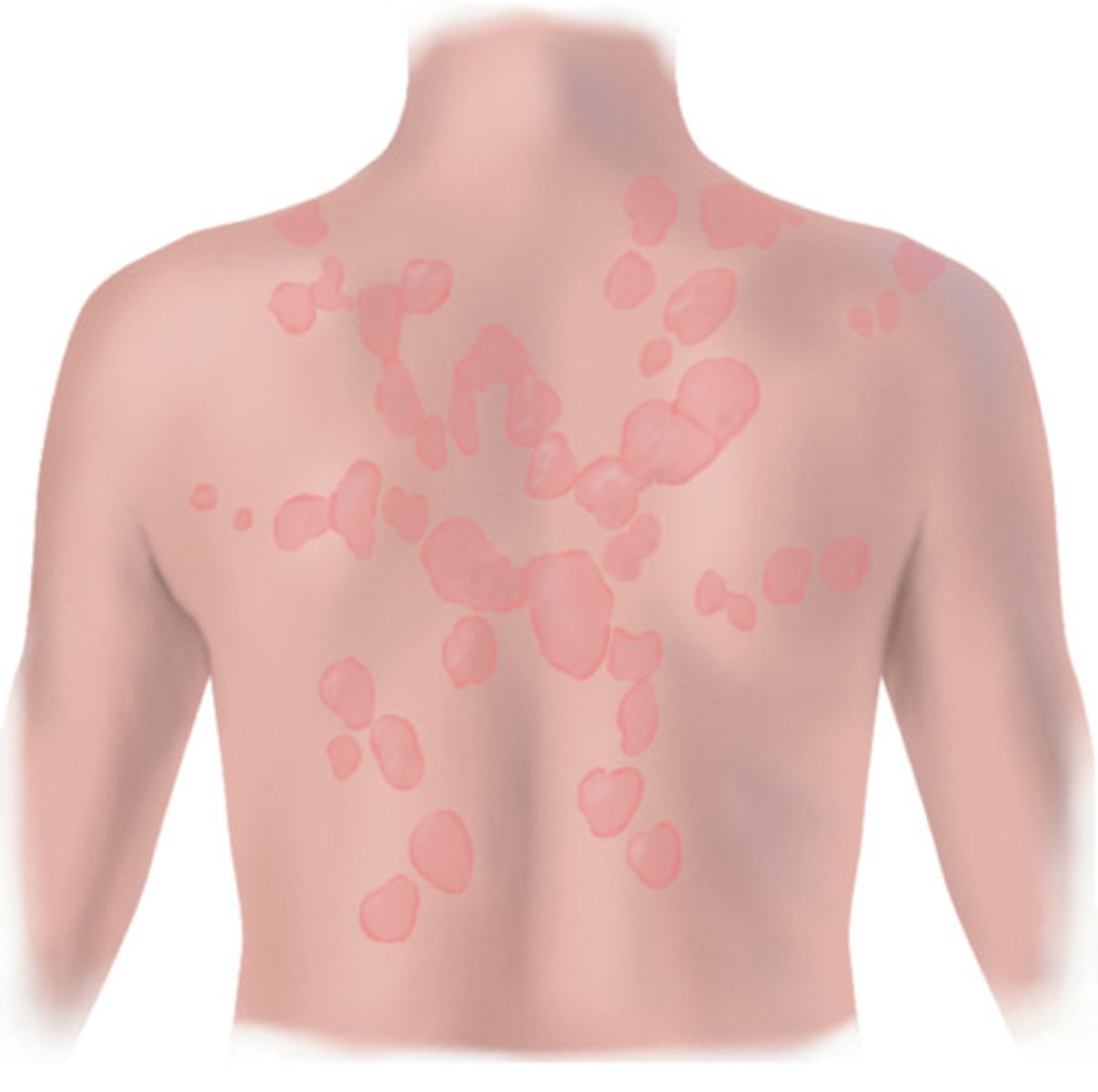
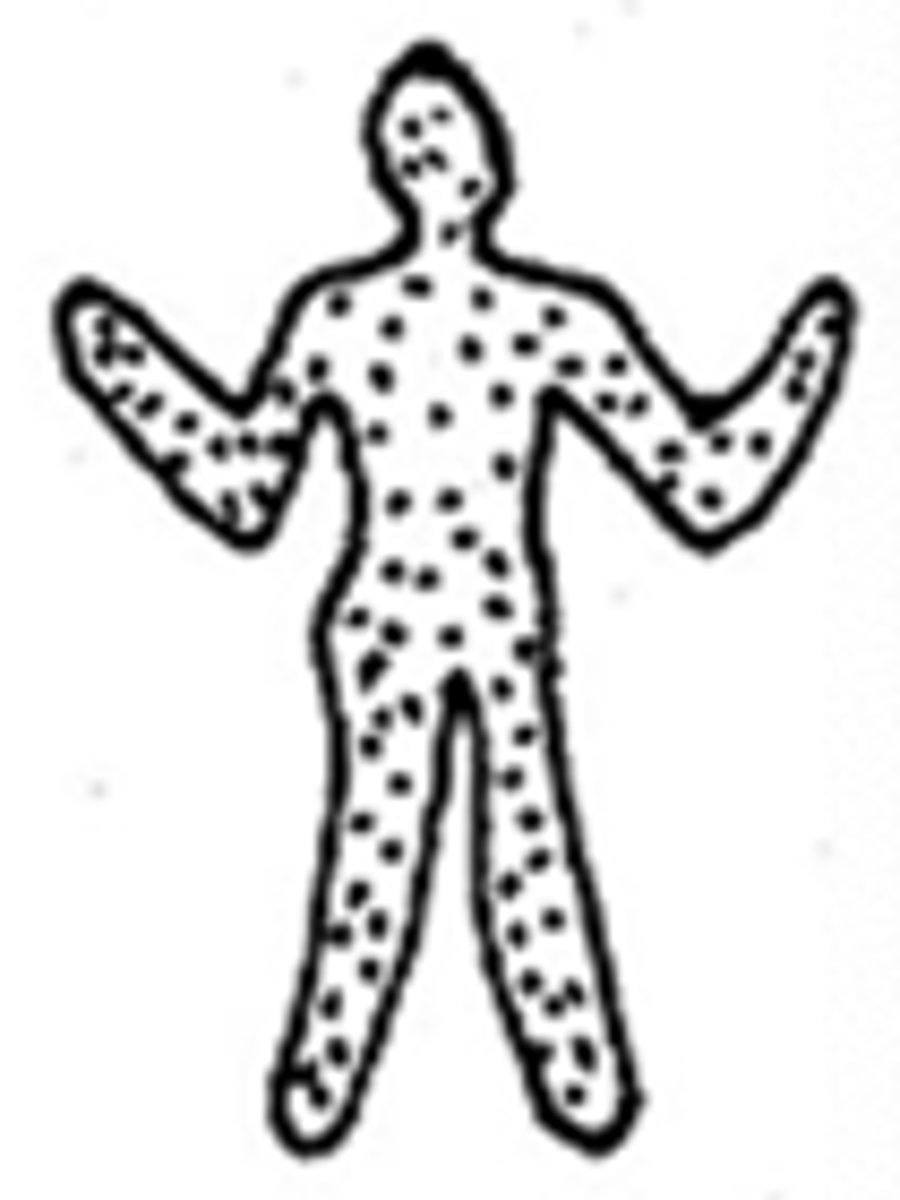
distributed widely across affected area without any pattern; drug reaction, rubella, rubeola
diffuse distribution
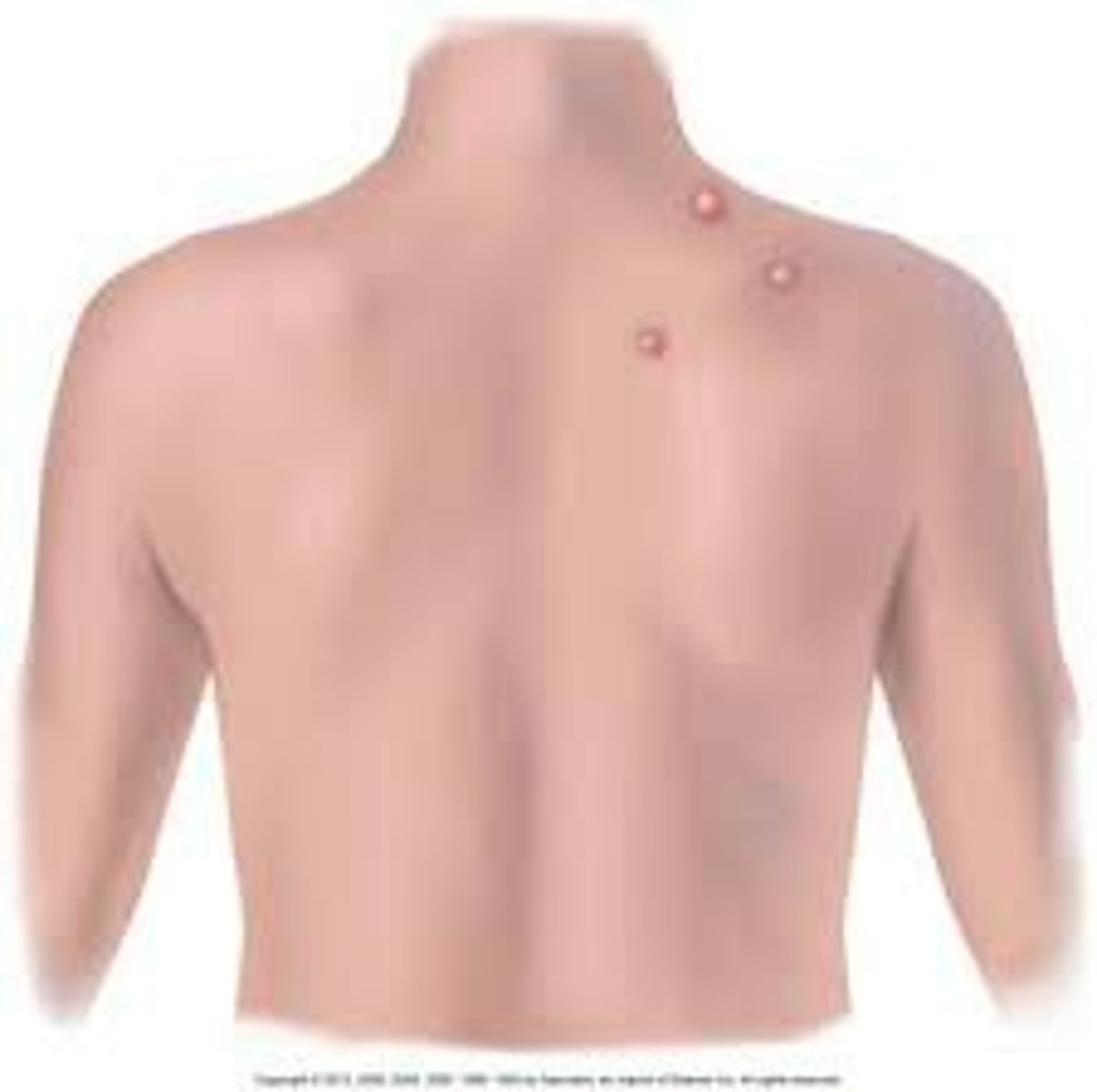
single, separated, well-defined borders; melanoma, wart
discrete distribution
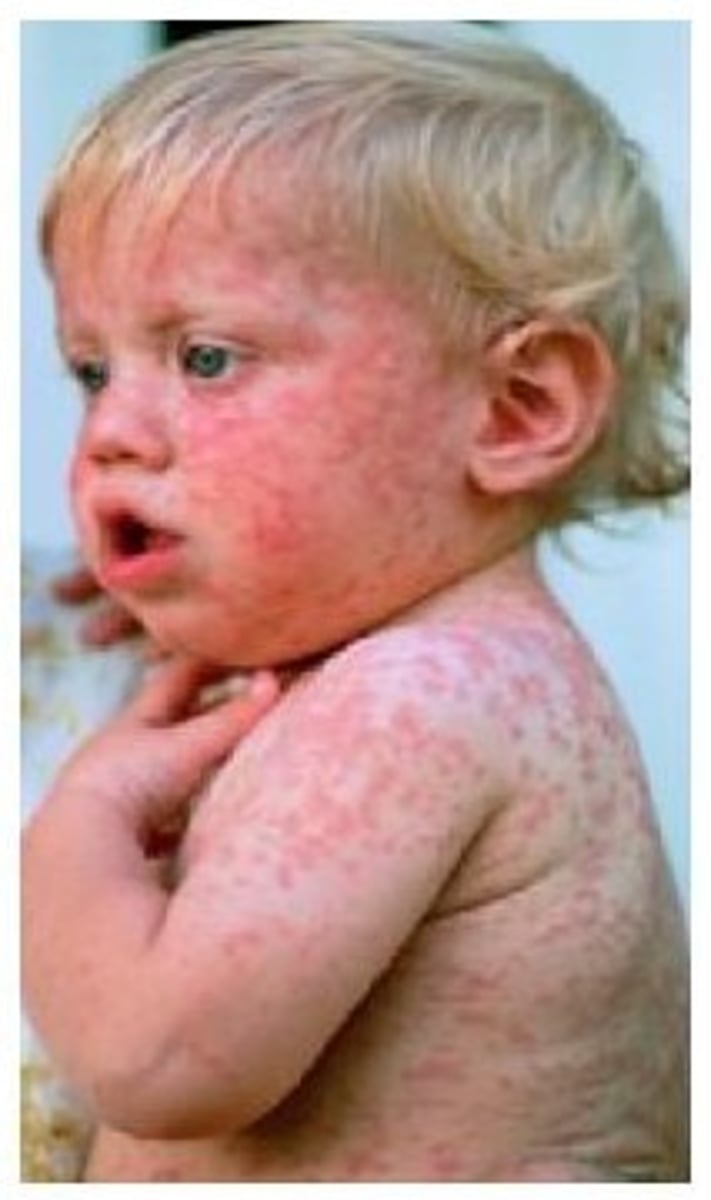
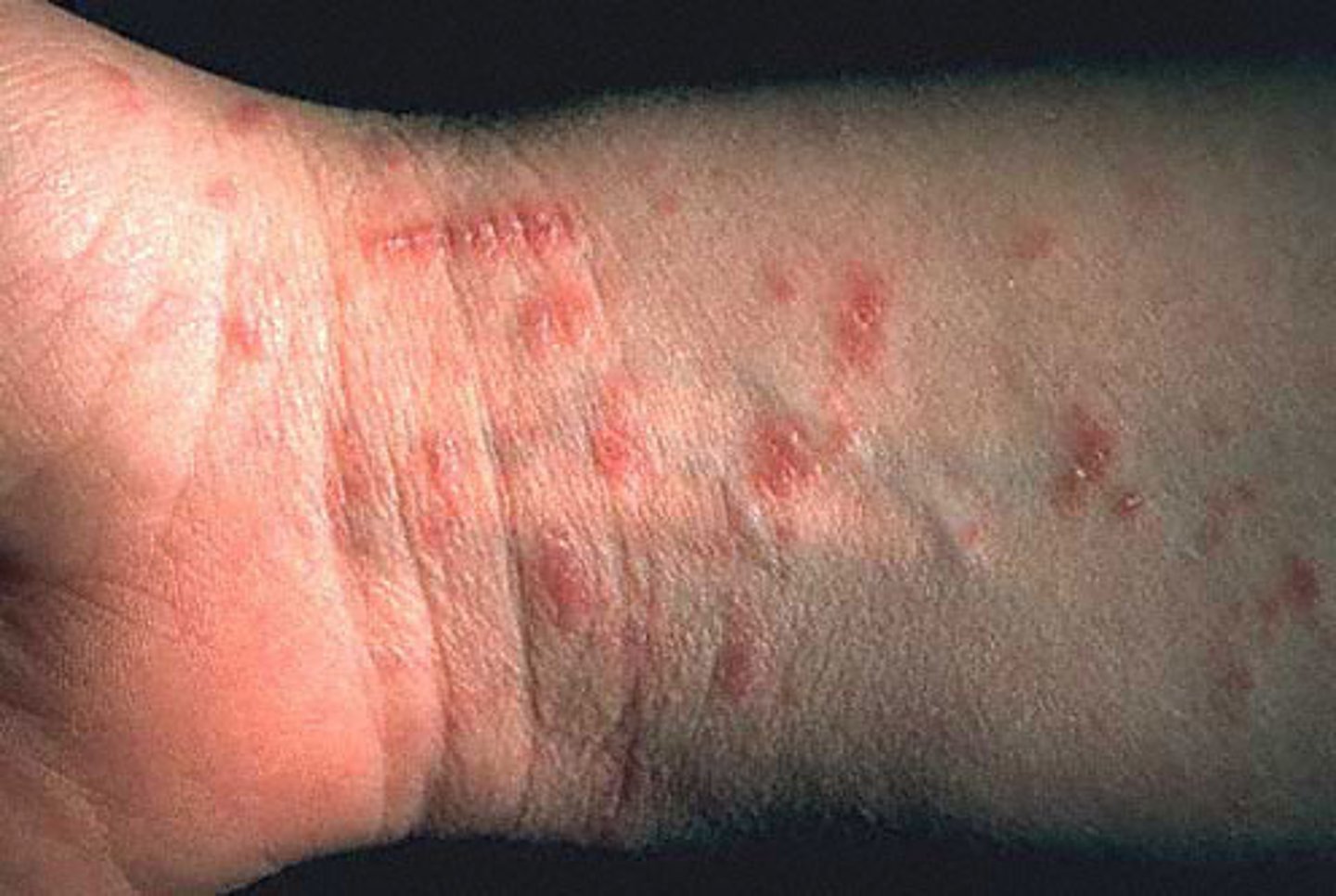
A mother brings her 4 year old daughter to the clinic and reports that the child has developed a rash that she is constantly scratching on her abdomen. One examination the nurse finds that the rash is serpiginous. The nurse would know that the rash is most probably caused by
Scabies
A community health nurse is planning an educational event for the parent-teacher association of the local elementary school. In discussing chickenpox, how would the nurse describe the rash?
Fluid-filled lesions less than 1 cm in diameter.