Chapter 16: The Autonomic Nervous System
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
Visceral (Organ) motor system that controls involuntary effectors: glands, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle.
Visceral Reflexes
Unconscious, automatic, stereotyped responses of visceral effectors to stimuli.
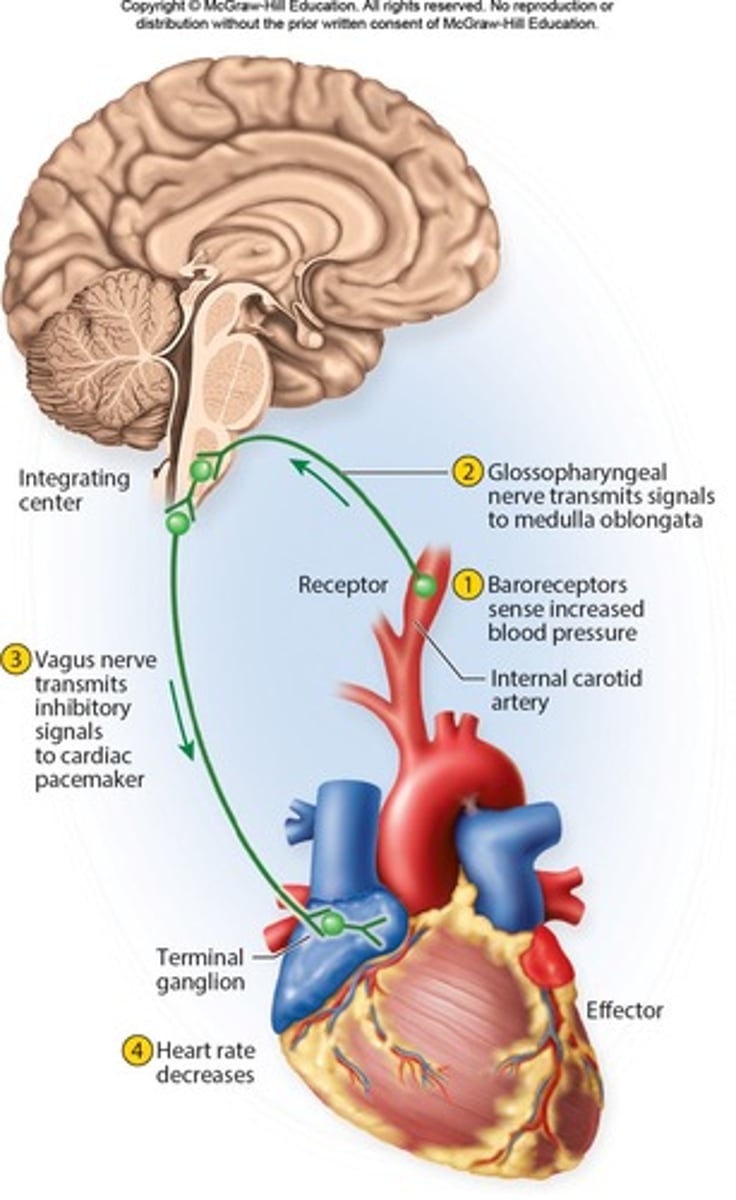
Example of Visceral Reflex
A rise in blood pressure triggers a reflexive decrease in heart rate.
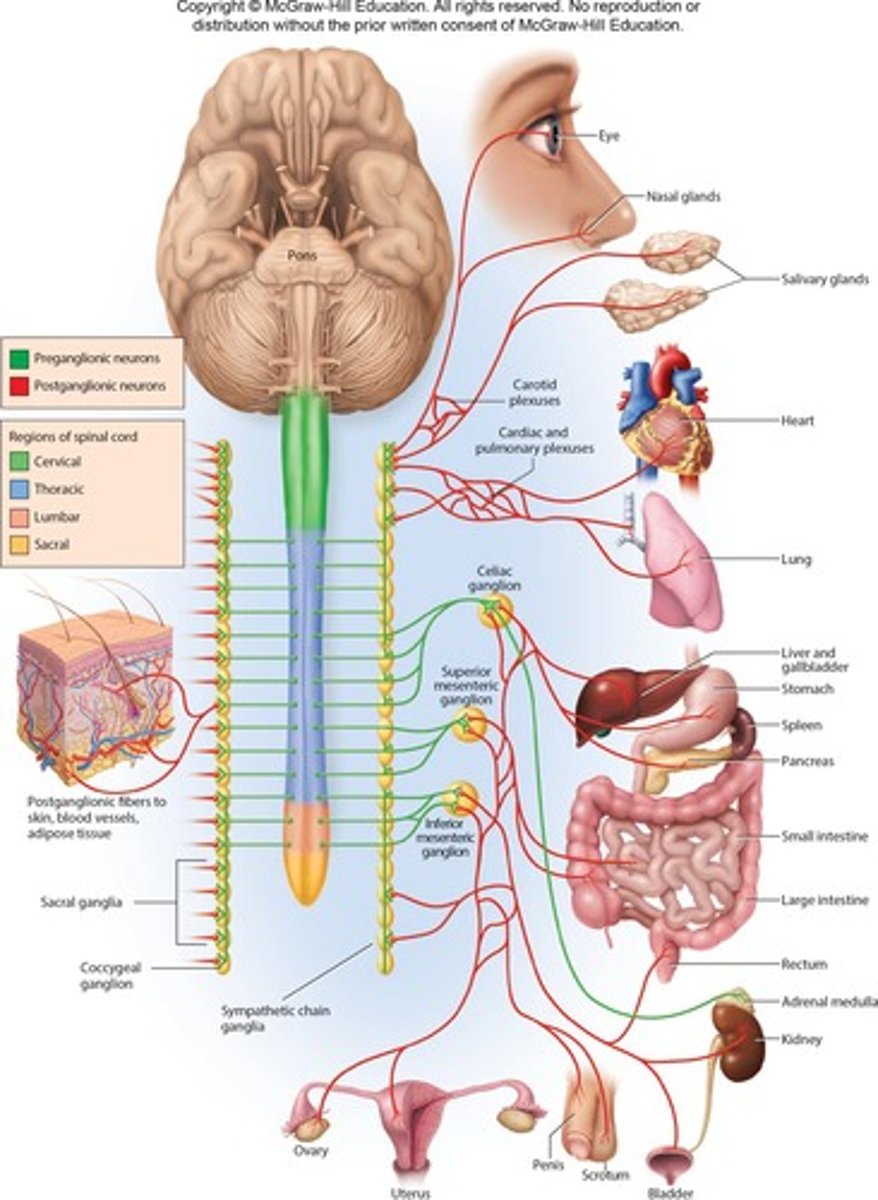
Sympathetic Division
Part of the ANS responsible for 'fight-or-flight' responses for increased physical activity.
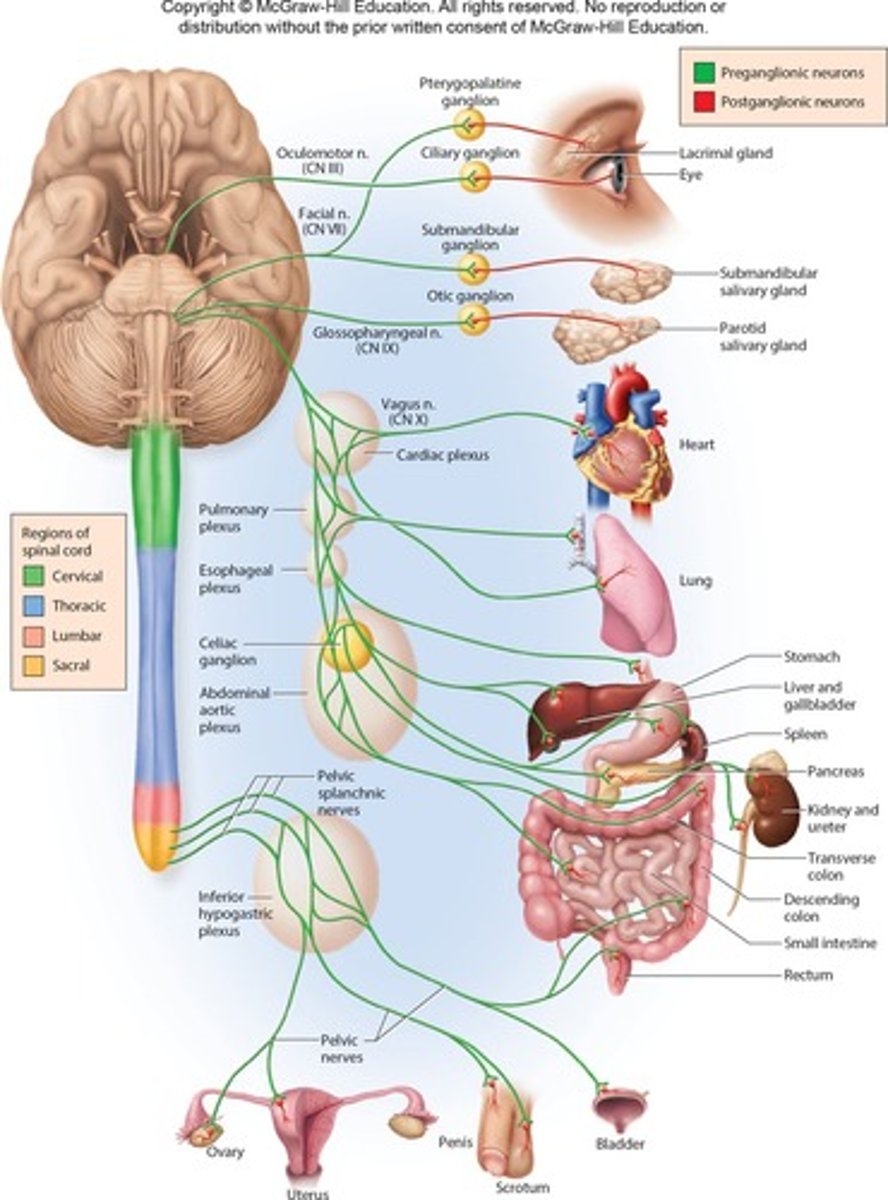
Parasympathetic Division
Part of the ANS responsible for 'rest and digest' responses with calming effects.
Autonomic Tone
Balance between activity of sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
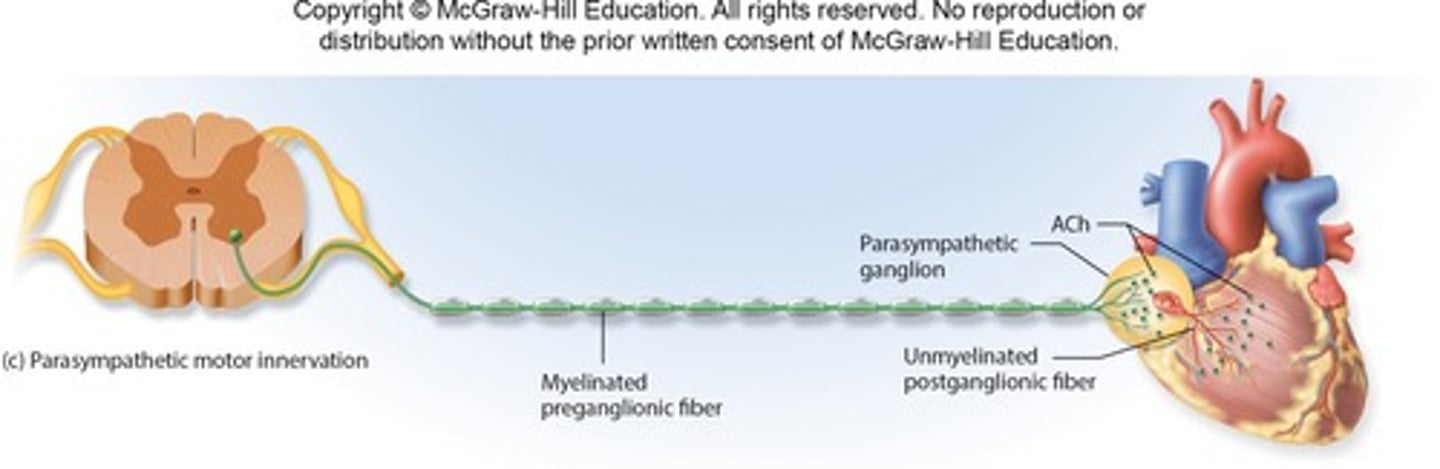
Preganglionic Fiber
Neurosoma in brainstem or spinal cord, axon terminals in ganglion
Postganglionic Fiber
Neurosoma in ganglion, axon extends to target
Somatic Nervous System
Nervous system that controls skeletal muscle and is usually voluntary.
Effectors of the Autonomic Nervous System
Glands, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle.
Control of the Somatic Nervous System
Usually voluntary.
Control of the Autonomic Nervous System
Usually involuntary.
Efferent Pathways of Somatic Nervous System
One nerve fiber from CNS to effector; no ganglia.
Efferent Pathways of Autonomic Nervous System
Two nerve fibers from CNS to effector; synapse at a ganglion.
Effect on Target Cells in Somatic Nervous System
Always excitatory.
Effect on Target Cells in Autonomic Nervous System
Excitatory or inhibitory.
Thoracolumbar Division
Includes Sympathetic division where preganglionic neurosomas are in lateral horns of spinal cord.
Craniosacral Division
includes Parasympathetic division with long preganglionic fibers and short postganglionic fibers.
Enteric Nervous System
Nervous system of the digestive tract that innervates smooth muscle and glands.
Regulation by Enteric Nervous System
Regulates motility of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and secretion of digestive enzymes and acid.
Origin in CNS of Sympathetic Division
Thoracolumbar.
Origin in CNS of Parasympathetic Division
Craniosacral.
Location of Ganglia in Sympathetic Division
Paravertebral ganglia adjacent to spinal column and prevertebral ganglia anterior to it.
Location of Ganglia in Parasympathetic Division
Terminal ganglia near or within target organs.
Effects of Sympathetic Division
Often widespread and general.
Effects of Parasympathetic Division
More local and specific.
Horner Syndrome
Unilateral pupillary constriction, sagging of eyelid, and flushing of skin due to lesions in sympathetic division.
Raynaud Disease
Paleness, cyanosis, and pain in digits when cold or stressed due to excessive vasoconstriction.
In sympathetic, is pre ganglion longer or shorter than pre-ganglion
pre-ganglion is is shorter than post-ganglion
In parasympthatetic, is pre-ganglia shorter or longer than post-ganglion
Pre-ganglia is longer than post-ganglion, closer to target organ