Biology 189A - Chapter 2 Pre-Lecture
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Match the arrow from the figure with its correct label of the atom.
1. Electron - Negative Charge
2. Nucleus - the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons
3. Proton - Positive Charge
4. Neutron - No Charge
Paper, water, computers, and you are all forms of ______ because each of these items takes up space.
Multiple choice question.
organisms
matter
energy
electromagnetic radiation
matter
What is an element?
Multiple choice question.
A negative particle of an atom
The central portion of an atom that contains protons and neutrons
The smallest type of organism
A pure chemical substance that cannot be further broken down
a pure chemical substance that cannot be further broken down
A peptide bond is a type of ______ bond between amino acids.
Multiple choice question.
ionic
covalent
ester
hydrogen
covalent
The sum of the number of protons and the number of _______ equals the mass number of an atom.
neutrons
The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide chain forms the ______ structure of a protein.
Multiple choice question.
primary
quaternary
tertiary
secondary
primary
When two or more atoms are chemically joined they form a(n)
Multiple choice question.
molecule.
element.
orbital.
shell.
molecule
An electron ______ is an area around the nucleus of an atom where an electron is likely to be found.
Multiple choice question.
trace
biosphere
orbital
isotope
orbital
Match each atom or molecule with its correct description
Sodium atom (Na) <----->
chlorine atom (Cl) <----->
salt (NaCl) <----->
donates an electron when an ionic bond is formed
gains an electron when an ionic bond is formed
crystal that results from the attraction of oppositely charged ions
What type of bond involves two atoms sharing electrons that travel around both nuclei?
Multiple choice question.
Covalent
Hydrogen
van der Waals
Ionic
Covalent
What type of bond forms between opposite partial charges on adjacent molecules or within a large molecule?
Multiple choice question.
Covalent
Hydrogen
Ionic
Atomic
Hydrogen
Which of the following substances regulates temperature, dissolves many chemicals, and has cohesive and adhesive properties?
Multiple choice question.
Carbon dioxide
Water
Oxygen
Hydrogen
Water
The property of water that produces water's surface tension is called ______, which is the tendency of water molecules to stick together.
Multiple choice question.
solvency
thermoregulation
cohesion
adhesion
cohesion
What is a pure chemical substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means into other substances?
Multiple choice question.
Work
Energy
Matter
Element
Element
What type of bond is formed from the attraction of two ions with opposite charges?
Multiple choice question.
Hydrogen
Ionic
Atomic
Covalent
Ionic
A(n) ________ bond forms between a hydrogen atom with a partial positive charge on one molecule and another atom, such as oxygen, with a partial negative charge on an adjacent molecule.
Hydrogen bond
What property of water causes water droplets and surface tension to form due to the tendency of water molecules to stick together?
Multiple choice question.
Electronegativity
Adhesion
Cohesion
Density
Cohesion
Water is the ______ in aqueous solutions because it can dissolve polar molecules.
Multiple choice question.
hydrophobic component
solvent
solute
nonpolar component
solvent
Living organisms require a large temperature stimulus before the body temperature changes because the ______ bonds of water counteract molecular movement.
Multiple choice question.
phosphodiester
hydrogen
peptide
ionic
hydrogen
Water expands as it freezes because the hydrogen bonds in ice
Multiple choice question.
are doubled between adjacent oxygen atoms.
constantly form and re-form.
are broken.
are stable and "lock" molecules into a more widely-space array.
are stable and "lock" molecules into a more widely-space array.
True or false: Atoms are created and destroyed in chemical reactions.
False
A special type of covalent bond called a(n) ________ bond joins two amino acids to each other through dehydration synthesis.
Peptide bond
A hydrogen ion (H+) has only one subatomic particle, a(n) ______.
Multiple choice question.
neutron
electron
proton
orbital
protons
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4) are acids because they release positively charged ______ ions into the solution.
Multiple choice question.
hydroxide
hydrogen
sodium
chloride
hydrogen
Organic molecules are defined as chemical compounds that contain both ______ and hydrogen.
Multiple choice question.
carbon
helium
sodium
calcium
carbon
A single unit (subunit) of an organic molecule is called a ______.
Multiple choice question.
monomer
solution
solute
solvent
monomers
What is an organic molecule with carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 proportion?
Multiple choice question.
lipid
nucleic acid
carbohydrate
protein
carbohydrate
The smallest carbohydrates are called ______ and consist of a single monomer.
Multiple choice question.
oligosaccharides
complex carbohydrates
monosaccharides
polysaccharides
monosaccharides
In ______, two or more molecules swap their atoms to form different molecules, and some bonds break while other new bonds form.
Multiple choice question.
radioactive decay
electronegativity
hydrogen bonding
a chemical reaction
a chemical reaction
Select all of the following that are true about proteins.
Multiple select question.
may contain one or more polypeptide chains
made up of monomers called amino acids
consist of monomers called nucleotides
perform a vast variety of functions for the cell
several linked together form a polysaccharide
may contain one or more polypeptide chains
made up of monomers called amino acids
perform a vast variety of functions for the cell
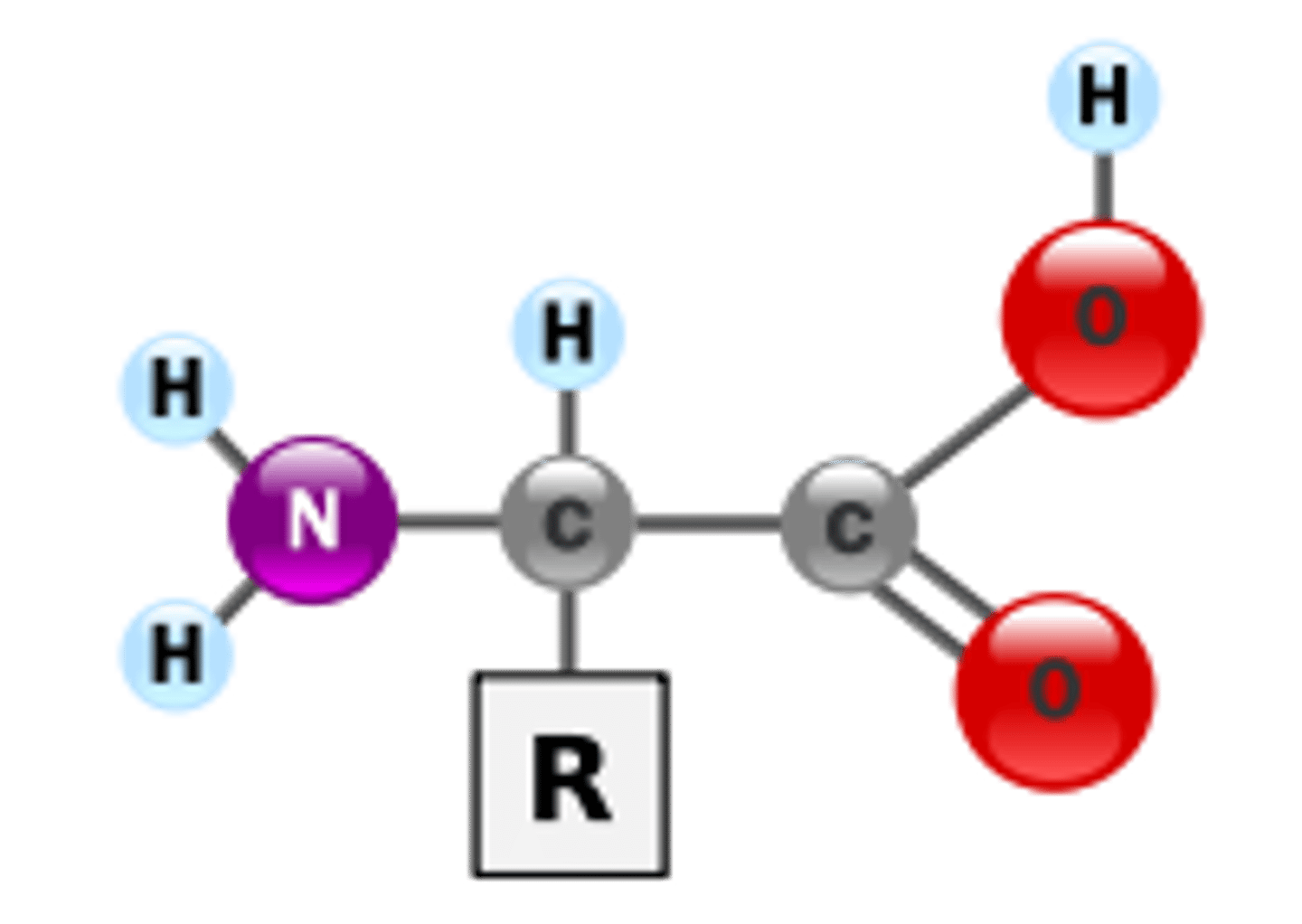
What type of monomer is shown in the picture?
Multiple choice question.
Amino acid
Nucleotide
Glycerol
Monosaccharide
Amino Acid
Once a polypeptide or multiple polypeptides are folded into a functional shape, they are referred to as a(n)
Multiple choice question.
dipeptide.
protein.
carbohydrate.
amino acid.
Protein
______ are one of the four most abundant types of organic molecules in organisms and consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen often in a proportion of 1:2:1. These organic molecules include monosaccharides and polysaccharides.
Multiple choice question.
Steroids
Fats
Triglycerides
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates
What type of organic molecule is made up of monomers called amino acids?
Multiple choice question.
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Lipids
Nucleic acids
proteins
One hundred or more amino acids linked through dehydration synthesis produce a molecule called a ______.
Multiple choice question.
lipid
nucleic acid
carbohydrate
polypeptide
polypeptide
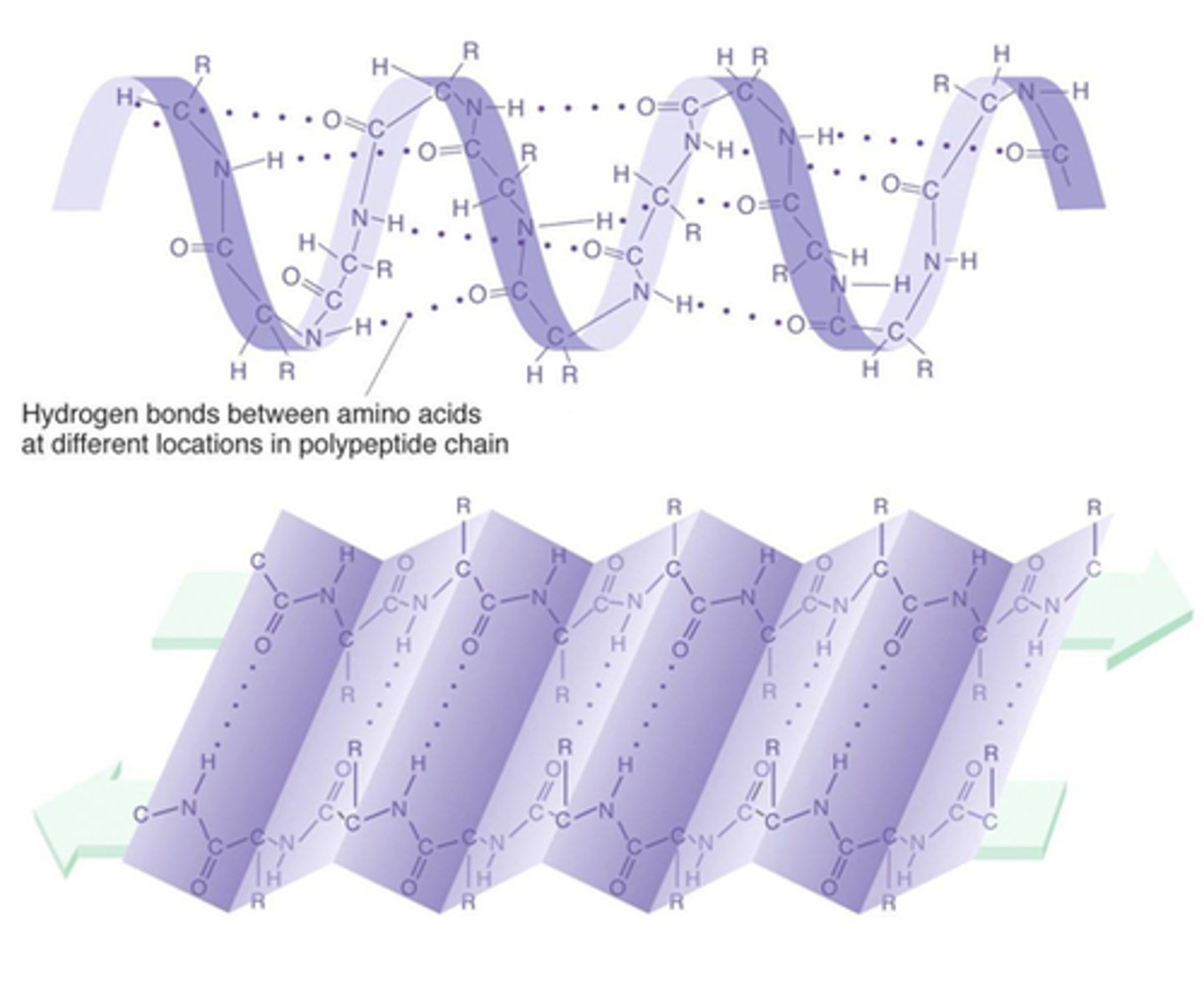
What structure of protein folding is shown in the picture?
Multiple choice question.
Quaternary
Primary
Tertiary
Secondary
secondary
In ______, two or more molecules swap their atoms to form different molecules, and some bonds break while other new bonds form.
Multiple choice question.
electronegativity
hydrogen bonding
a chemical reaction
radioactive decay
chemical bonding
The ______ structure of a polypeptide is its overall shape and is formed through the interaction between R groups and water.
Multiple choice question.
secondary
primary
tertiary
denatured
Tertiary
What type of polymer is made up of many nucleotide monomers?
Multiple choice question.
Carbohydrate
Lipid
Protein
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid
______ are organic molecules characterized by large areas that contain many nonpolar carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen bonds, making them hydrophobic.
Multiple choice question.
Lipids
Alcohols
Amino acids
Proteins
lipids
Phospholipids that form cell membranes, steroids that act as hormones, waxes that prevent water loss or water saturation, and triglycerides (fats) that act as energy reserves are all types of organic molecules called ____________ .
lipids
What molecule is formed by dehydration synthesis reactions that link three fatty acids to a glycerol molecule?
Multiple choice question.
triglyceride
steroid
carbohydrate
deoxyribonucleic acid
triglyceride
The ______ structure of proteins involves the folding of the polypeptide chain into beta-sheets and alpha-helix coils due to hydrogen bonding.
Multiple choice question.
primary
tertiary
secondary
quaternary
secondary
What level of protein structure makes up the overall shape of a polypeptide, arises primarily through interactions between R groups and water, and consists of one polypeptide chain?
Multiple choice question.
Primary
Tertiary
Subsidiary
Secondary
Tertiary
Nucleotides are the monomers of polymers called ______ acids, including DNA and RNA.
Multiple choice question.
carboxylic
hydrochloric
nucleic
amino
nucleic
Select all of the following that are components of lipids called triglycerides.
Multiple select question.
phosphate group
fatty acids
amine group
glycerol
fatty acids
glycerol
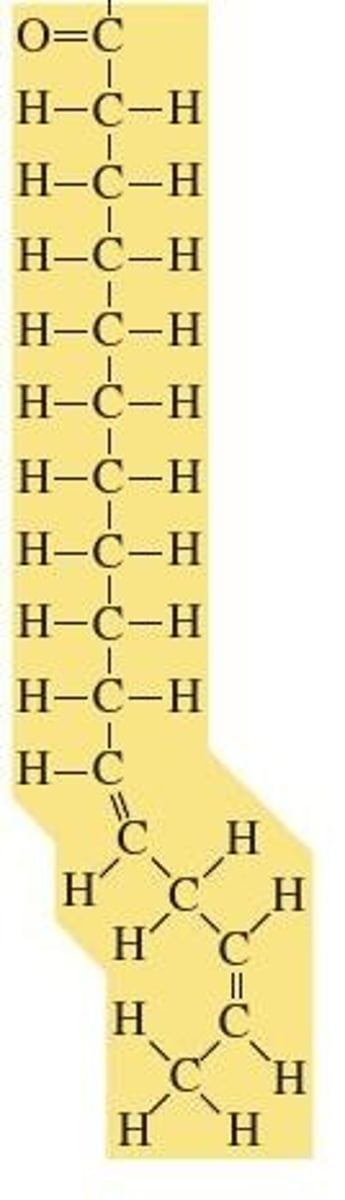
Triglycerides such as bacon fat and butter contain ______ fatty acids, in which single bonds connect all the carbons; however, triglycerides such as olive oil and vegetable oil contain ______ fatty acids, in which there is at least one double bond between carbon atoms.
Multiple choice question.
unsaturated; saturated
hydrophobic; hydrophilic
saturated; unsaturated
hydrophilic; hydrophobic
saturated; unsaturated
Why is the fatty acid in the image called unsaturated?
Multiple choice question.
All of the carbon atoms are bonded to at least two hydrogens.
It contains the maximum number of hydrogens.
It is part of a solid fat.
It contains at least one double bond between carbon atoms.
It contains at least one double bond between carbon atoms.
The ______ structure of a polypeptide is its overall shape and is formed through the interaction between R groups and water.
Multiple choice question.
tertiary
primary
secondary
denatured
tertiary
Rank the following in order from smallest mass (at the top) to largest mass (at the bottom).
1. electron
2. proton
3. atom
What level of protein structure is shown in the picture?
Amino acid sequence of polypeptide connected with 6 R groups
Multiple choice question.
Secondary
Primary
Quaternary
Tertiary
Primary
______, a group of lipids, are more commonly known as fats and are composed of fatty acids bonded to a glycerol.
Multiple choice question.
Triglycerides
Waxes
Carbohydrates
Steroids
Triglycerides
What type of triglyceride, or fat, contains fatty acids with at least one double bond between the carbons, causing kinks in the fatty acids?
Multiple choice question.
Secondary
Saturated
Unsaturated
Primary
unsaturated
The ______ structure of proteins involves the folding of the polypeptide chain into beta-sheets and alpha-helix coils due to hydrogen bonding.
Multiple choice question.
primary
quaternary
tertiary
secondary
secondary
The total number of protons and neutrons for an atom equals the ______.
Multiple choice question.
valence weight
half-life
atomic number
mass number
mass number
Molecules consist of two or more chemically linked ________ , which are the smallest "pieces" or units of elements.
atoms
In an atom, each individual electron orbital (not energy level) may contain up to ________ electrons.
2
Select all of the reasons why water is essential to life.
Multiple select question.
It plays a role in many chemical reactions.
Its solid form is more dense than its liquid form.
It dissolves a wide variety of substances.
It regulates temperature.
It plays a role in many chemical reactions.
It dissolves a wide variety of substances.
It regulates temperature.
Ice cubes float in a glass of water because ice is less ______ than liquid water.
dense
In liquid water, some water molecules break down into one hydroxide ion (OH-) and one hydrogen ion, which is represented as
Multiple choice question.
H2+.
H+.
OH+.
H-.
H+.
What type of chemical adds H+ to a solution?
Multiple choice question.
acid
alkaline
base
neutral
acid
What type of molecules are found in living things and contain both carbon and hydrogen?
Multiple choice question.
organic
neutral
inorganic
alkaline
organic
Polymers, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids, consist of small subunits called ________ linked together to form long chains.
monomers
The monomers of polypeptides and proteins are called ______ acids and have a central carbon bonded to a hydrogen, an amino group, a carboxyl group, and an R group.
amino acids
What group of organic molecules does not dissolve in water and does not consist of long chains of monomers?
Multiple choice question.
carbohydrates
proteins
nucleic acids
lipids
lipids
Select all of the following that are types of lipids.
Multiple select question.
phospholipids
starches
triglycerides
steroids
amino acids
phospholipids
triglycerides
steroids
Animal fats are ______ at room temperature and are called ______, while plant-derived lipids are ______ at room temperature and are called unsaturated fats.
Multiple choice question.
solid; saturated fats; liquid
solid; oils; liquid
liquid; oils; solid
liquid; saturated fats; solid
solid; saturated fats; liquid