Psychology 2e Chapter 1
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Psychology
the scientific study of behavior and mental processes
Scientific Method
steps used by psychologists to acquire knowledge
Hypothesis
tentative explanation about how or why something happens
theory
the best understanding we have of that part of the natural world
observations
information gather by carrying out an experiment to test hypothesis
Steps of the Scientific Method
observation, hypothesis, experiment, conclusion
empirical
based on measurable data
empirical method
based on observation, including experimentation, rather than a method based only on forms of logical argument or previous authorities
late 1800s
when psychology became accepted as its own academic discipline
social
psychology is a ______ science
psychology
one of the most popular majors in the United States
6
____% of all bachelors degrees in the US are awarded to psychology majors
Wilhelm Wundt
first psychologist
1873
Principles of Psychological Psychology published in ______ by Wundt
introspection
examination of one's own thoughts and feelings
structuralism
early school of thought promoted by Wundt and Titchener; used introspection to reveal the structure of the human mind
reaction times
Wundt experimented a lot on
one thousandth
Wundt measured reaction time to ________________ of a second
functionalism
focused on how mental activities helped an organism fit into its environment. by William James
Sigmund Freud
Austrian physician whose work focused on the unconscious causes of behavior and personality formation; founded psychoanalysis.
psychoanalytic theory
focuses on the role of a person's unconscious, as well as early childhood experiences, and this particular perspective dominated clinical psychology for several decades
Psychoanalysis
the patient talking about their experiences and selves, while not invented by Freud, was certainly popularized by him and is still used today.
Gestalt Psychology
the whole is greater than the sum of its parts
Pavlov
Classical conditioning: dogs
Behaviorism
shifting the focus of psychology from the mind to behavior, and this approach of observing and controlling behavior
Humanism
perspective within psychology that emphasizes the potential for good that is innate to all humans.
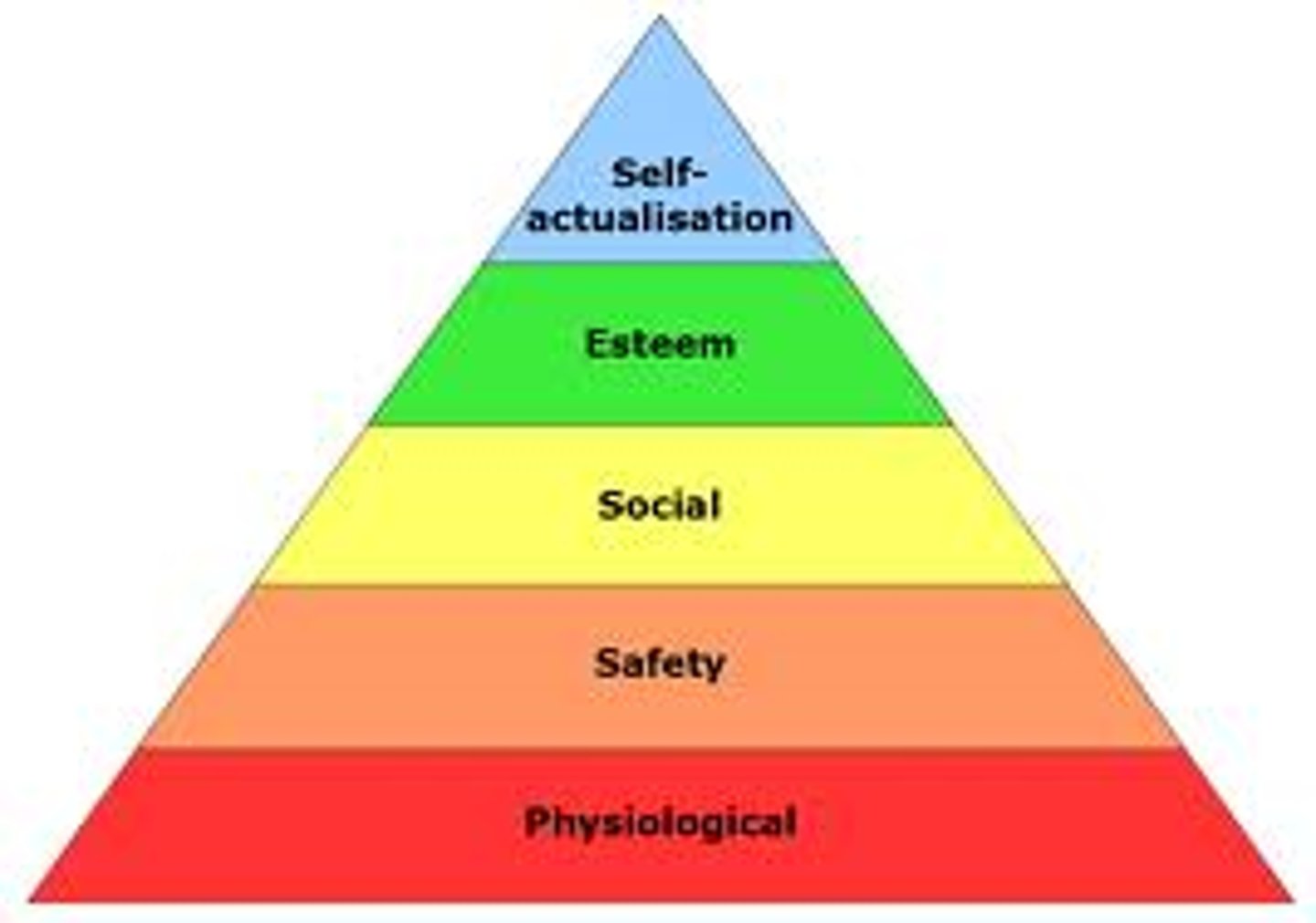
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
physiological, safety, love/belonging, esteem, self-actualization
unconditional positive regard, genuineness, and empathy
Rogers believed that a therapist needed to display three features to maximize the effectiveness of this particular approach:
Cognitive Psychology
1967, Ulric Neisser published the first textbook entitled
American Psychological Association (APA)
the largest organization of psychologists in the world, and its mission is to advance and disseminate psychological knowledge for the betterment of people.
Association for Psychological Science (APS)
professional group of academic and research psychologists founded in 1988
Biopsychology
how our biology influences our behavior
cognitive psychology
area of psychology that focuses on studying cognitions, or thoughts, and their relationship to our experiences and our actions.
Developmental psychology
scientific study of development across a lifespan.
Personality psychology
focuses on patterns of thoughts and behaviors that make each individual unique.
personality traits
identifiable characteristics that define a person
Social psychology
focuses on how we interact with and relate to others.
Industrial-Organizational psychology
subfield of psychology that applies psychological theories, principles, and research findings in industrial and organizational settings.
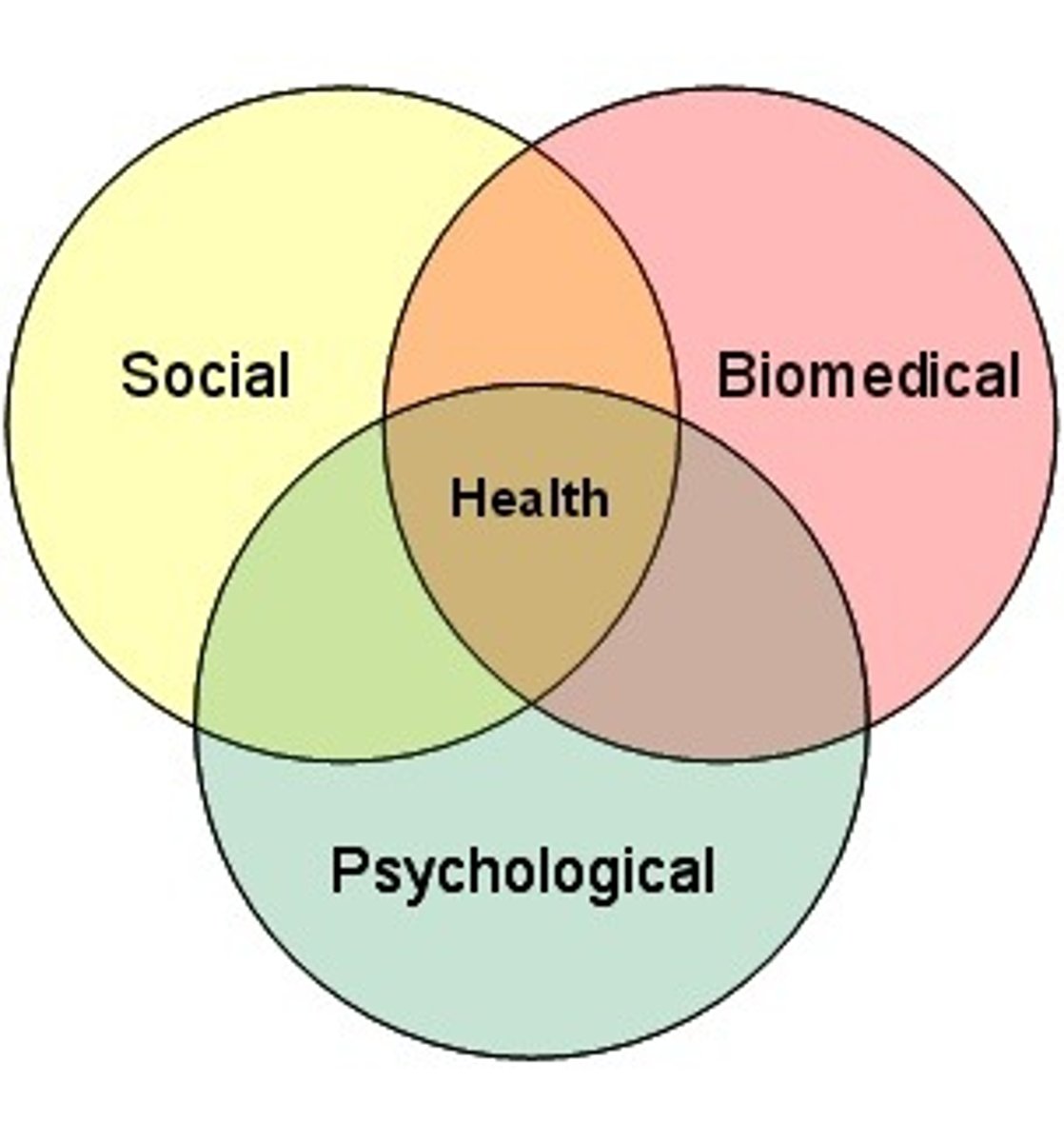
Health psychology
focuses on how health is affected by the interaction of biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors.
biopsychosocial model
sport and exercise psychology
study the psychological aspects of sport performance, including motivation and performance anxiety, and the effects of sport on mental and emotional wellbeing.
Clinical psychology
focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of psychological disorders and other problematic patterns of behavior.
Counseling psychology
focuses on emotional, social, vocational, and health-related outcomes in individuals who are considered psychologically healthy.
Forensic psychology
field that blends psychology, law, and criminal justice
PhD
Doctor of Philosophy
dissertation
a long research paper or bundled published articles describing research that was conducted as a part of the candidate's doctoral training.
postdoctoral training programs
allows young scientists to further develop their research programs and broaden their research skills under the supervision of other professionals in the field
PsyD
Doctor of Psychology