Parasitology Week 1
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Intro Lab 1 Sporozoea Protozoa
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
Parasitism
Relationship between a host and the organism in which the organism benefits at the expense of the host
Parasitemia
Parasites in the blood
Carrier
Host harboring a parasite but exhibiting no symptoms
Symbiosis
Association of two different species of organisms exhibiting metabolic dependence by their relationship
Commensalism
Association of two different species or organisms where one is benefitted and the other is neither benefited nor injured
Accidental host
Infection of a host other than the normal host species. Parasite may not reach full development
Definitive host
The animal in which the parasite passes its adult existence, sexual reproductive phase, or both
Intermediate host
Animal in which the parasite passes its larval stage or asexual reproduction phase
Reservoir host
Animal that harbors a species of parasite that is also parasitic for humans and can infect
What percentage of the worlds population suffer consequences of parasitic infections ?
24%
environments that lead to parasitic infections
Poverty, poor sanitation, contaminated food and water, poor health education, tropical climates, travel
Helminth classes
Nematoda (nematodes “round worms”)
Cestoda (cestodes “tape worms”)
Digenea ( trematodes “flat worms and flukes”)
Classes in Protozoa
Lobosea (pseudopodia ameba)
Zoomastigophorea (flagella)
Ciliophora (cilia)
Sporozoea (sexual and asexual reproduction)
Sporozoa general characteristics
Lack locomotion
Life cycle alternates between sexual and asexual
Definitive host life cycle stage
Sexual reproduction
Intermediate hosts life cycle stage
Asexual reproduction
Sporogony
Sexual reproduction of spores and sporozoites
Schizogony (human host)
Asexual multiplication
Paroxysm
Toxic materials released from ruptured RBC
Plasmodium epidemiology
Malaria (most common protozoal disease)
Transmitted by Anopheles mosquito
Can cross placenta
Malaria symptoms
Splenomegaly, chills, fever, sweats, anorexia, joint pain, leukopenia, normocytic anemia, hemolytic anemia
Malaria diagnosis
ID of species specific ring forms, gametes, and schizonts (in blood cells) on blood stains
Plasmodium falciparum disease
Malignant malaria
Plasmodium falciparum symptoms
36-48 hour paroxysms, infect RBC, hemolytic anemia (black water fever)
Plasmodium falciparum diagnosis
Trophs (ring forms) and crescent gametocytes in RBCs
Maurer’s clefts or red dots
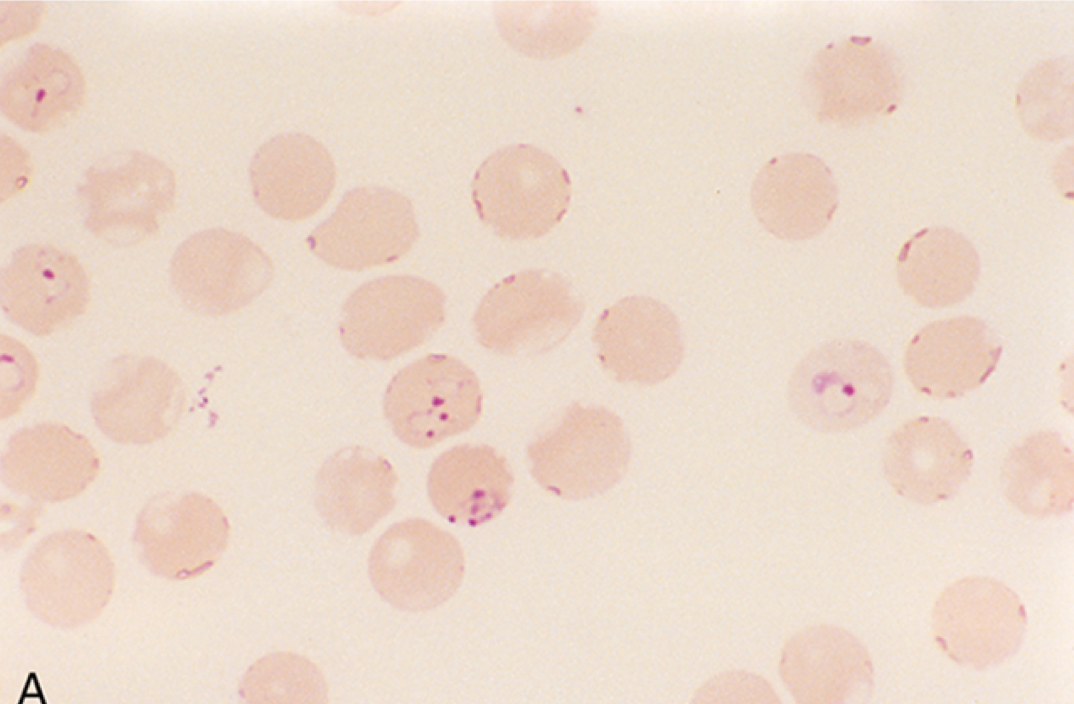
Ring form Plasmodium falciparum
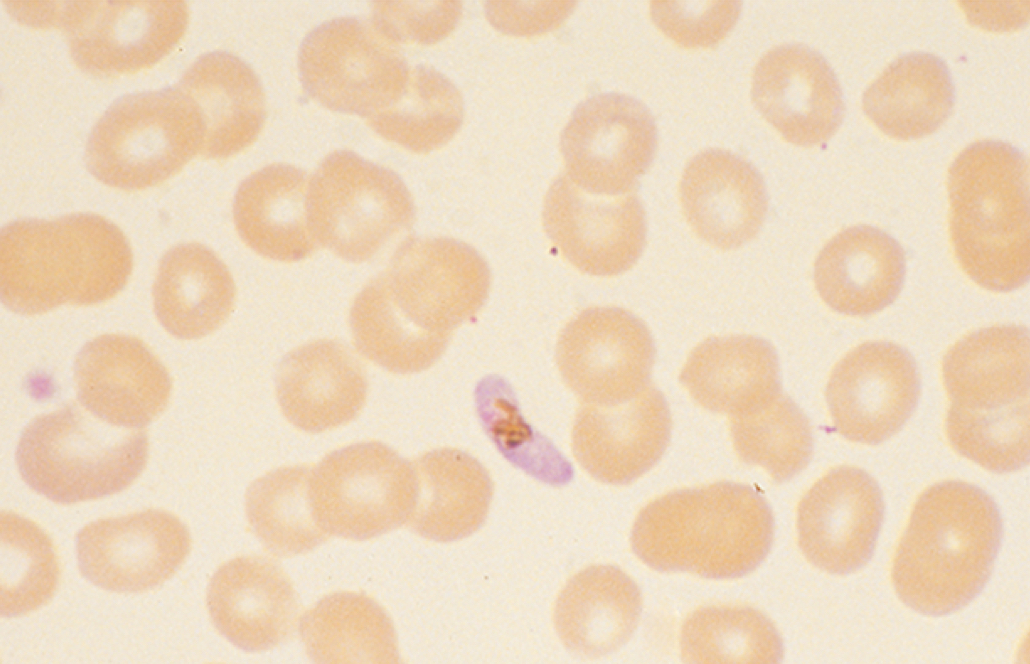
Gametocyte of Plasmodium falciparum
Plasmodium malariae disease
Quartan malaria
Quartan malaria symptoms
Paroxysms every 72 hours
Quartan malaria symptoms
Trophozoite band forms and schizonts (6-12 merozoites in a rosette)
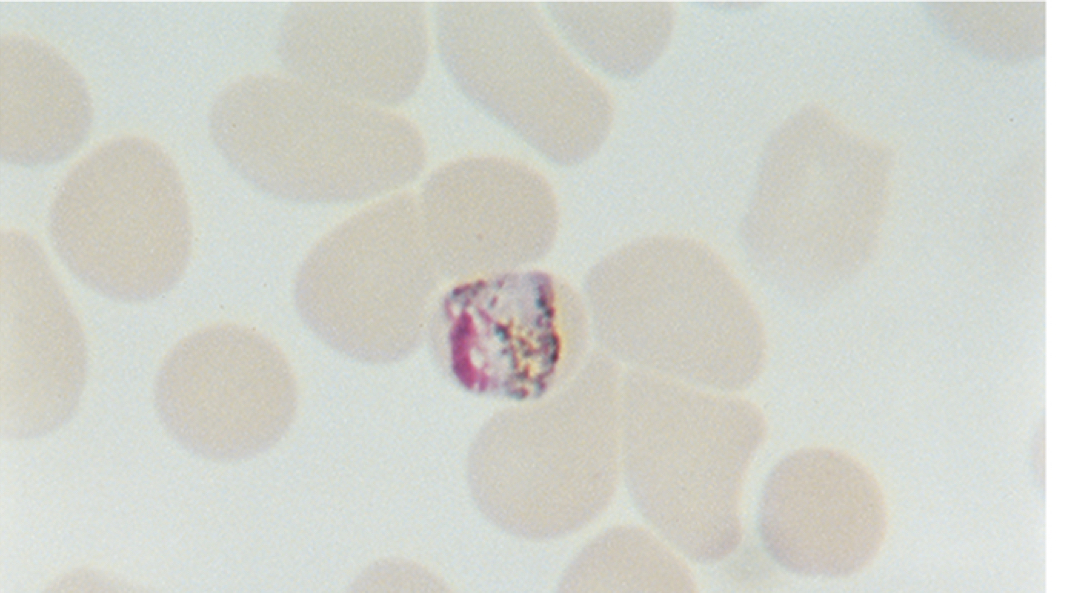
Band form of Plasmodium malariae
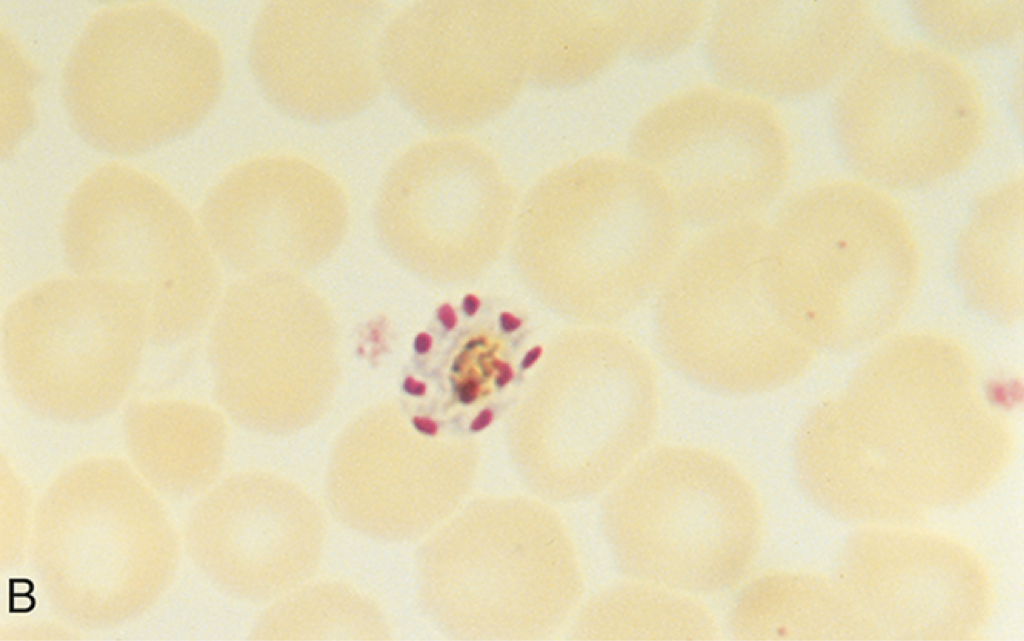
Schizont of Plasmodium malariae
Plasmodium vivax disease
Tertian malaria
Tertian malaria symptoms
Paroxysms every 48 hours
Tertian malaria diagnosis
Ring forms infecting young RBCs, schuffners dots, and schizonts w 12-24 merozoites
Plasmodium ovale disease
Ovale malaria
Ovale malaria diagnosis
Ring forms, oval RBCs, schuffners dots, schizonts 8-12 merozoites
Babesia characteristic ring form
Maltese cross formation
Toxoplasma gondii transmission
Oocytes shed in cat feces and aerosolized
Toxoplasmosis symptoms in adults
Asymptomatic or mimic mononucleosis (headache, fever, malaise, myalgia, lymphadenopathy)
Toxoplasmosis symptoms in children
Rash myocarditis, encephalomyelitis, hepatitis, retinochoroiditis (blindness)
Toxoplasma gondii diagnosis
Encrusted tachyziotes in biopsy materials
Serology
PCR
Cryptosporidium parvum and hominis transmission
Common infection for cattle, rodents, and fowl
Fecal-oral
Not killed by chlorine
Cryptosporidium parvum and hominis symptoms
Abdominal pain and diarrhea
Cryptosporidium diagnosis
Acid fast oocytes in feces, ID in biopsies, PCR, serology
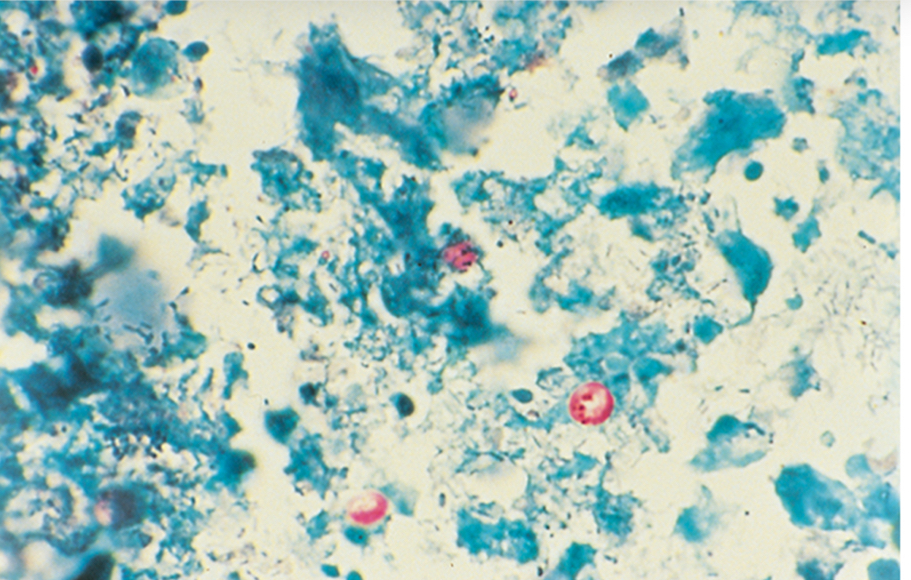
Cryptosporidium parvum oocytes
Cystoisospora belli infection/symptoms
Indistinguishable from C. parvum
Low fever, headache, diarrhea, colicky and abdominal pain
Cystoisospora belli diagnosis
Elliptical/oval oocyst 20-33um long and 10-19um wide
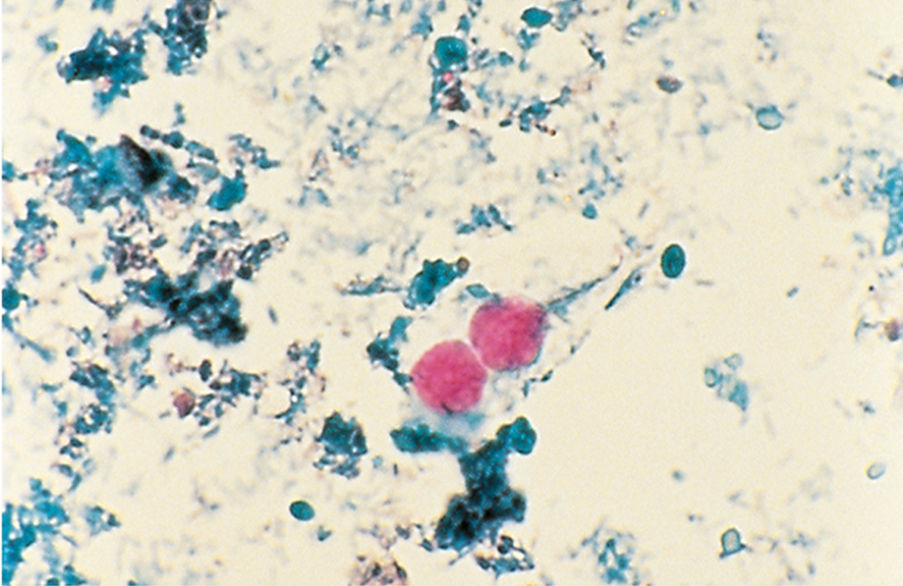
Cystoisospora belli oocysts
Cyclospora cayetanensis transmission
Contaminated food or water (humans are the only hosts)
Cyclospora cayetanensis symptoms
Diarrhea alternating w constipation, anorexia/weightloss, cramping, vomiting, nausea, low fever
Enterocytozoon bieneusi infections
Intestinal and hepatobiliary
Encephalitozoon hellem infections
Ocular
Encephalitozoon intestinalis infections
Intestinal and disseminated
Microsporidia (encephalo/entero) diagnosis
Small intestinal biopsy
1-3um spores (deep red dot)
PCR
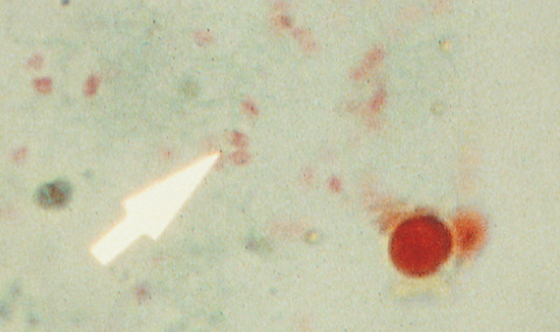
Microsporidia spore
Amoebae
Single celled eukaryotes that feed by engulfing and move by pseudopodia
Trophozoite form
Motile reproductive and feeding stage
Cyst form
Non motile resting stage that is resistant to the environment
Chromatoidal bodies
Dark staining cytoplasmic inclusion of chromatin
Endosome or karyosone
Mass of organelles or chromatin in the nucleus
Amoebae diagnosis
Motile throphozoites in fresh warm liquid stools via wet mount and iodine preps
Trophozoites / cysts in fixed smears w trichrome stain
Trophozoites/ cysts in other body tissues or fluids w serology
Differentiation of amoebas
Shape of nucleus, number of nuclei, size, shape, inclusions
Entamoeba histolytica disease
Amebiasis, transmission by ingestion, intestinal disease, dissemination
Trophozoite microscopic characteristics of E. histolytica
10-20um, irregular shape (teardrop), single nucleus w karyosome , ingested RBCs (only one)
Cyst microscopic characteristics of E.histolytica
10-20um, 1,2, or 4 nuclei w central karyosome, rounded chromatoidal bars
Entamoeba coli characteristics
Commensal, smaller than 10um, up to 8 nuclei w eccentric karyosome, pointed sharp chromatin bars
Blastocystis hominis disease symptoms
Recurrent diarrhea, abdominal cramping, anorexia, flatulence
B. hominis microscopic description
5-15 um
Empty central body with nuclear material on the outer layer
Naegleria fowleri disease
Entry through nasal mucosa, causes primary amebic meningoencephalitis, found in csf and tissues
Flagella
Provides locomotion
Axoneme
Intracellular portion of a flagellum
Axostyle
Rod that provides support in flagellates
Pathogenic intestinal flagellates
Giardia lamblia
Dientamoeba fragilis
Pathogenic vaginal flagellate
Trichomonas vaginalis
Blood and tissue flagellates
Trypanosoma sp
Leishmania
Giardia lamblia
Most common diarrheal disease transmitted by contaminated water
Only Protozoa that resides in the duodenum
Giardiasis
“Traveler diarrhea”, “beaver fever”, “backpackers diarrhea”
Mild-severe diarrhea
Trophozoites/cysts in stool and biopsies
Microscopic characteristics of Giardia lamblia
Trophozoite: bilateral symmetry, 2 nuclei, 8 flagella
Cyst: oval w 2-4 nuclei
Dientamoeba fragilis
Associated w diarrhea
No cysts, Trophozoite has 2 nuclei
Trichomonas vaginalis
Trophs live in vagina, urethra, epididymis and prostate
Trichomonas vaginalis diagnosis
Wet mount from urethral discharge, vaginal smear, or urine
“Jerky” motility
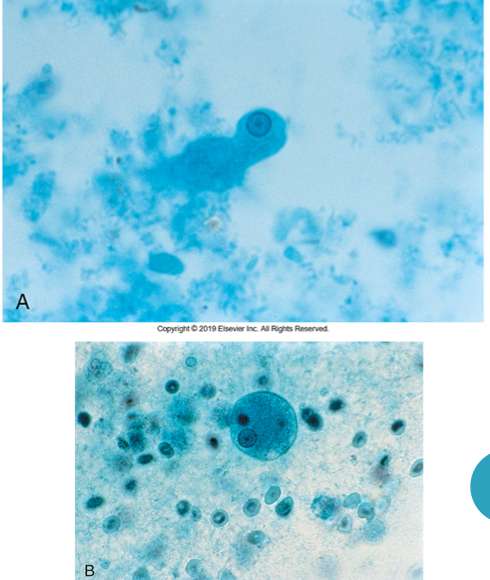
Trophozoite of E. histolytica
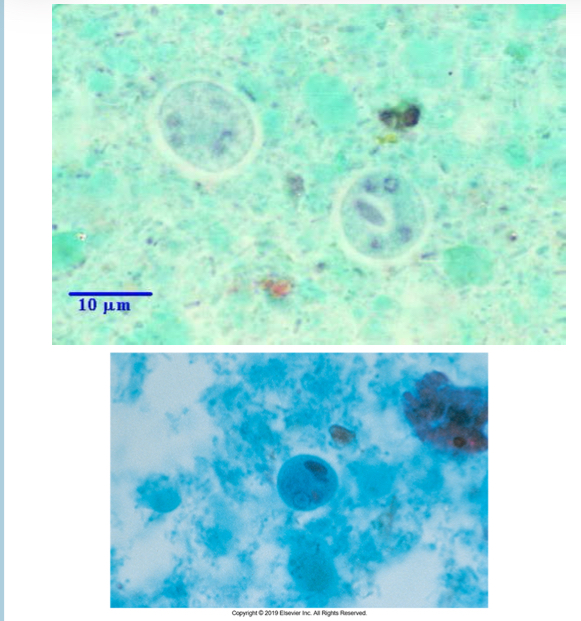
Cyst of E. histolytica
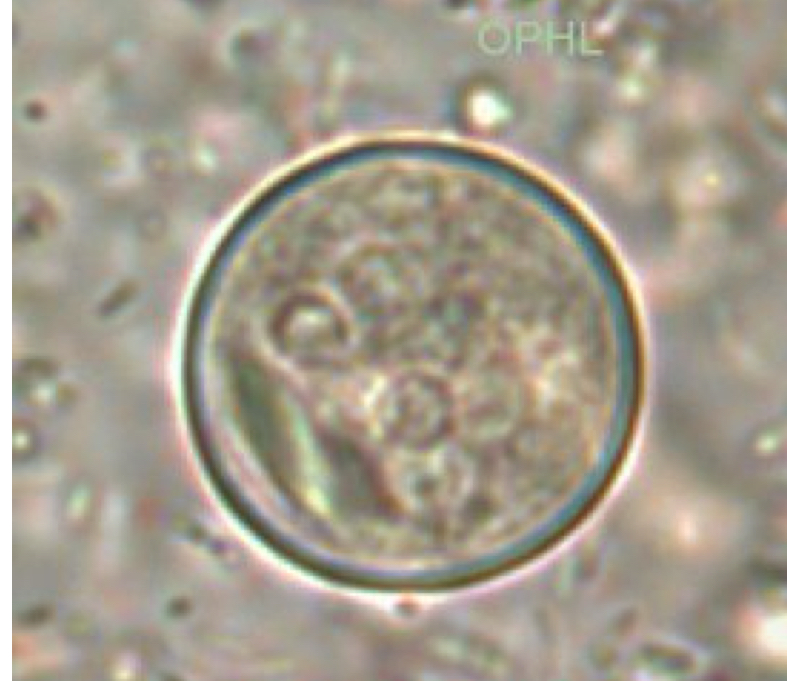
Entamoeba coli cyst
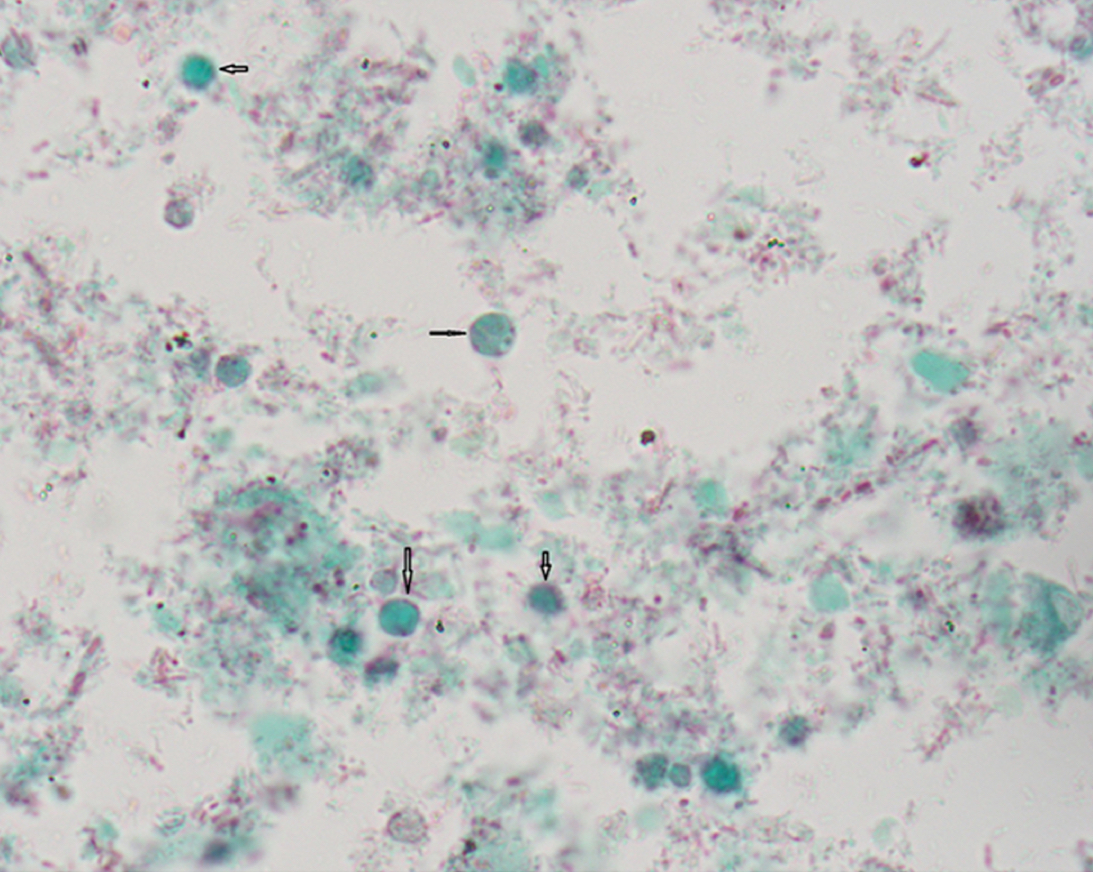
Blastocystis hominis
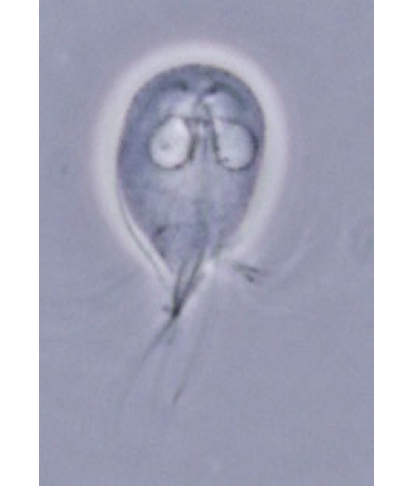
Trophozoite of Giardia lamblia
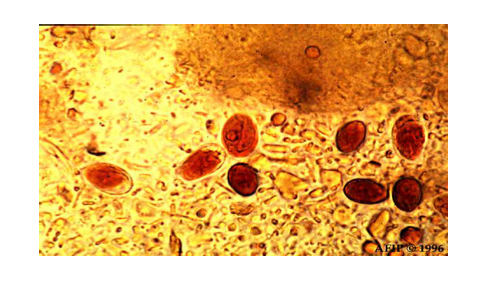
Giardia lamblia cysts
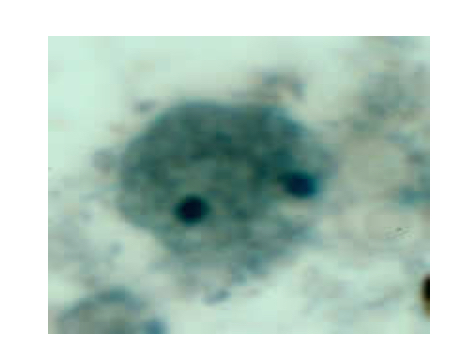
Dientamoeba fragilis Trophozoite
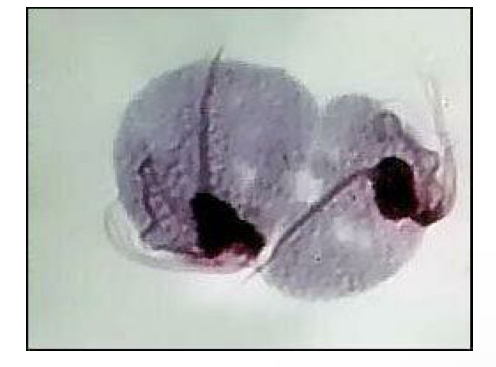
Trichomonas vaginalis trophozoite
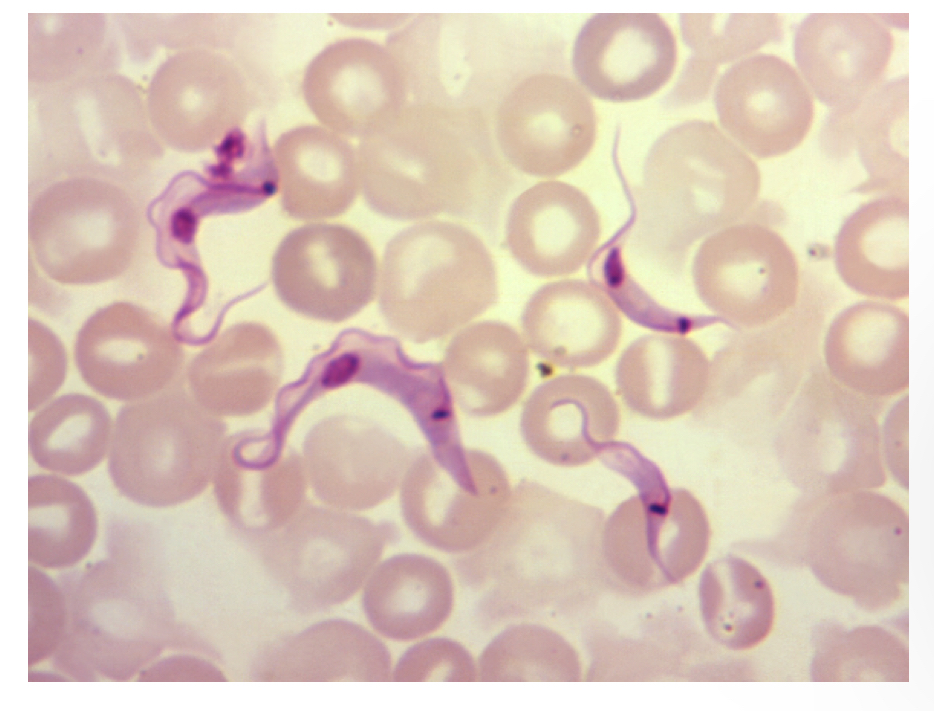
Trichomonas cruzi trypomastigote
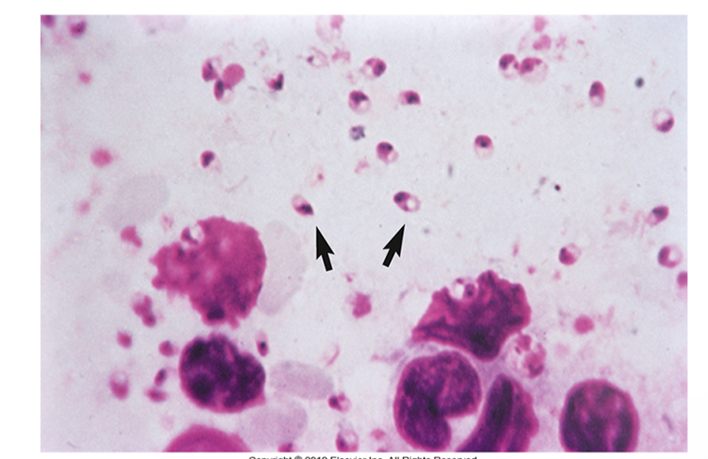
Leishmania donovani amastigote forms
Trypanosoma cruzi disease
Chagas: mild swelling (infected site) and fever
Leishmania donovani disease/symptoms
Spread from cutaneous lesion to internal organs
Ciliophora pathogenic species
Balantidum coli
Largest human intestinal protozoa
Balantidium coli
Symptoms of balantadium coli
Asymptomatic or diarrhea w alternating constipation
Blastintidium coli diagnosis
Trophozoites or cysts in feces
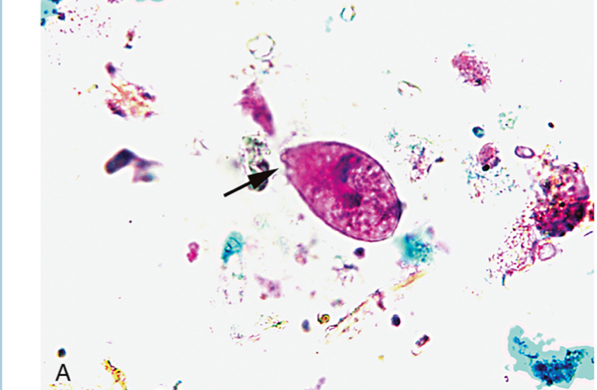
B.coli trophozoite