OCR A GCSE Chemistry: C1 and C2.2 set
1/167
Earn XP
Description and Tags
From Quizlet official GCSE resource centre
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
168 Terms
Ancient greek model of the atom
Atoms are tiny solid spheres which cannot be divided.

JJ Thompson
Discovered the electron and developed the "plum-pudding" model of the atom
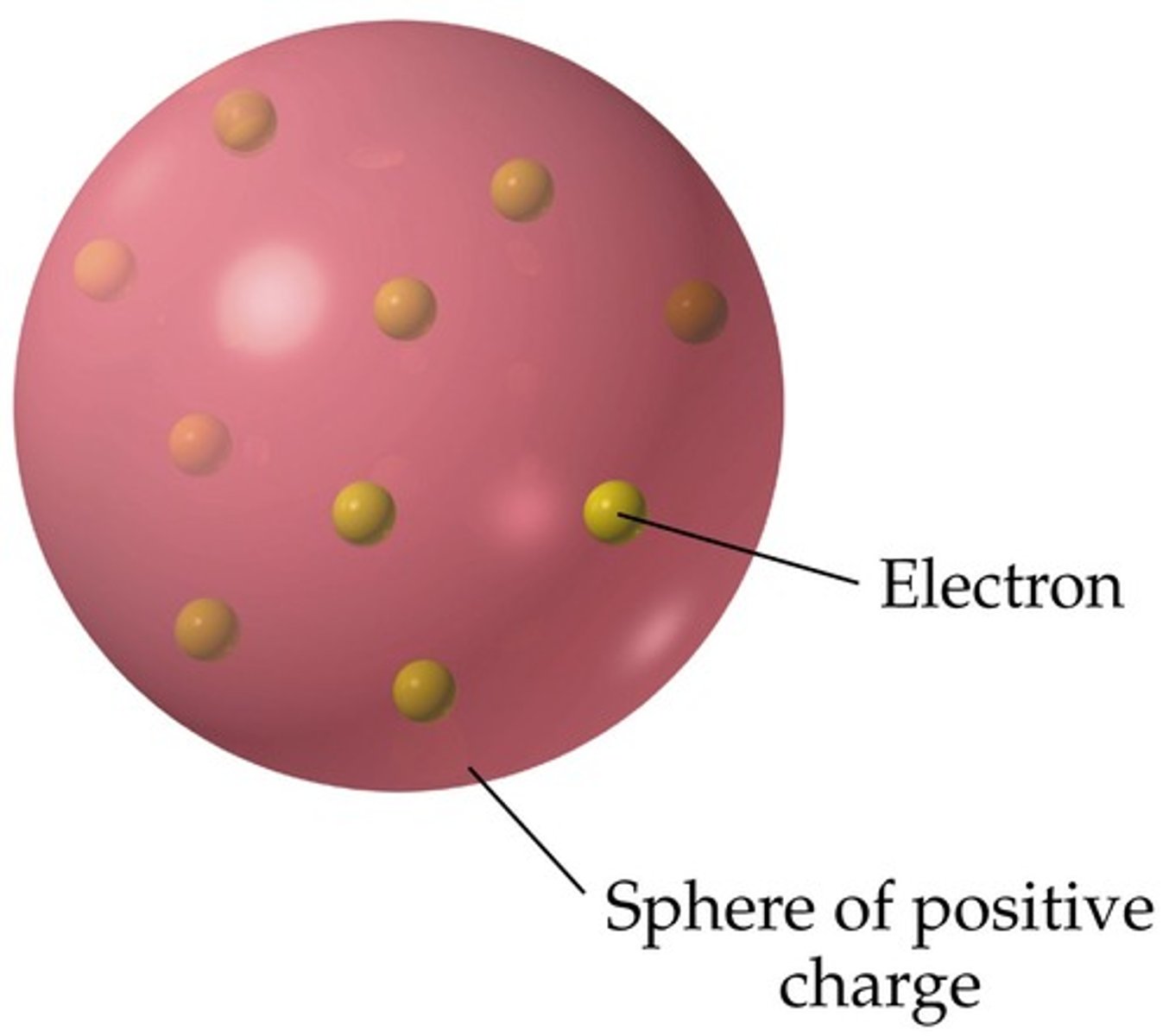
plum pudding model of the atom
atoms are balls of positively charge with negative electrons embedded in it
Rutherford, Geiger, and Marsden
carried out the alpha particle scattering experiment and developed the nuclear model of the atom
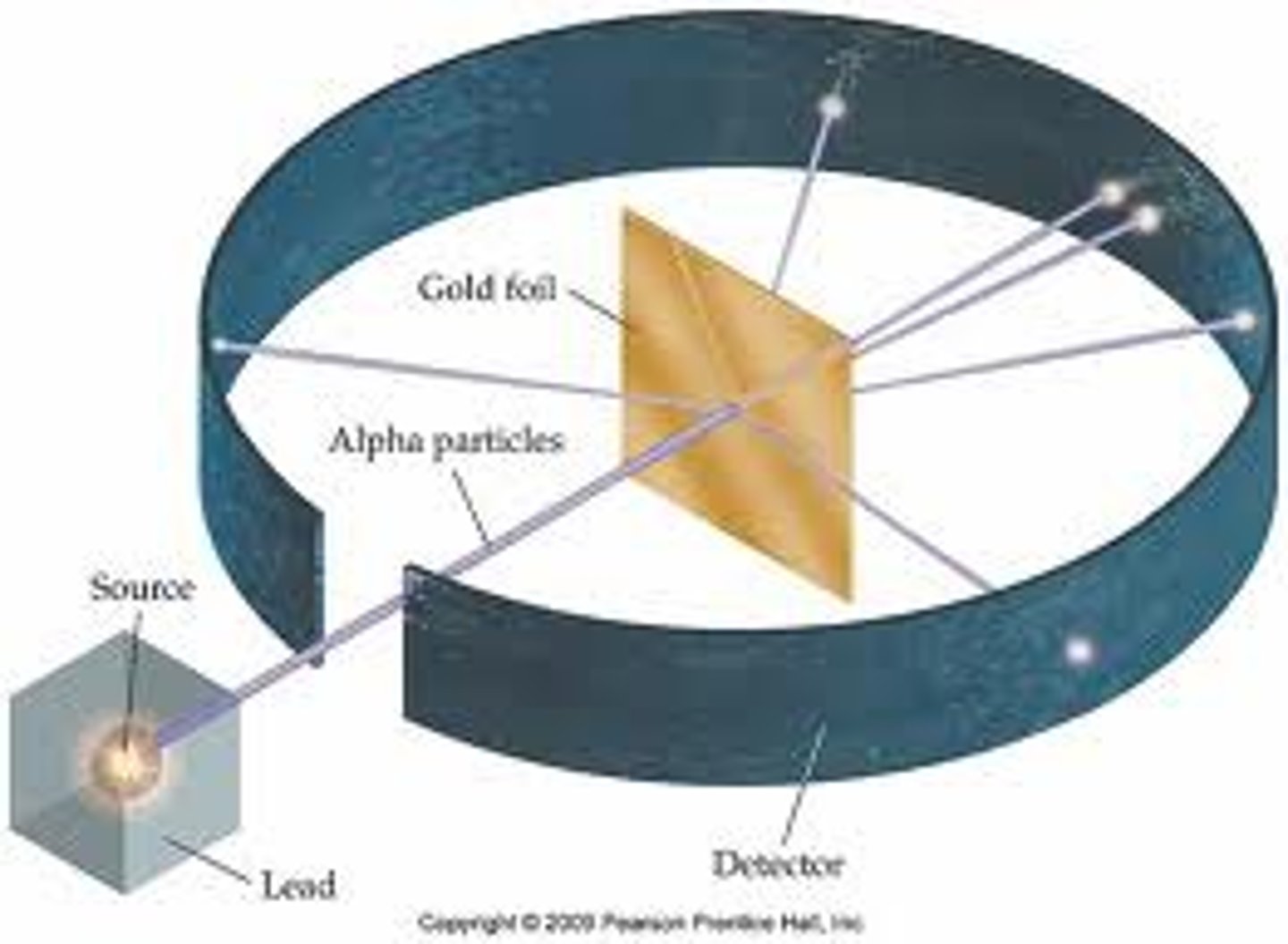
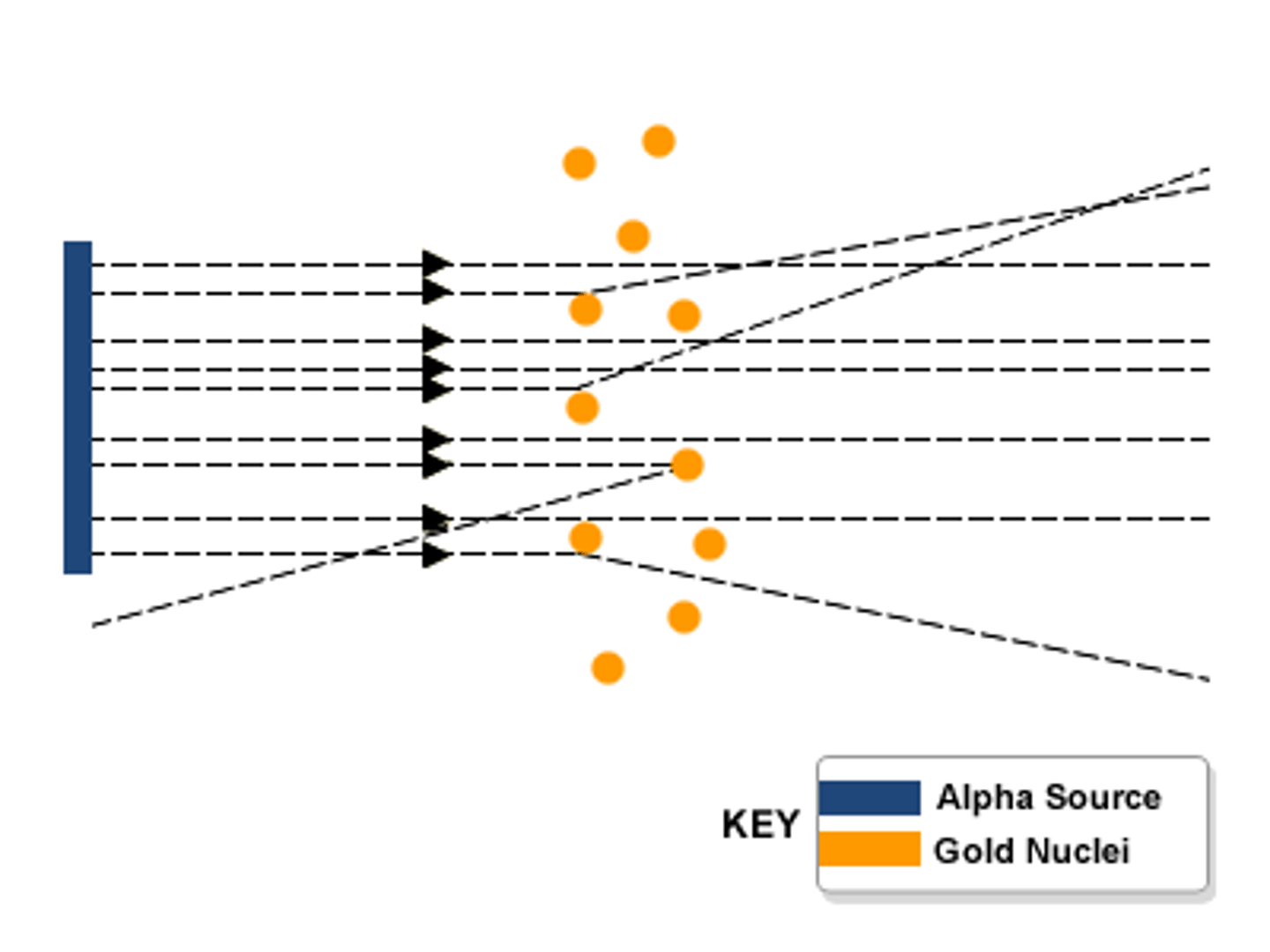
Alpha particle scattering experiment
Fired alpha particles at a thin sheet of gold foil.
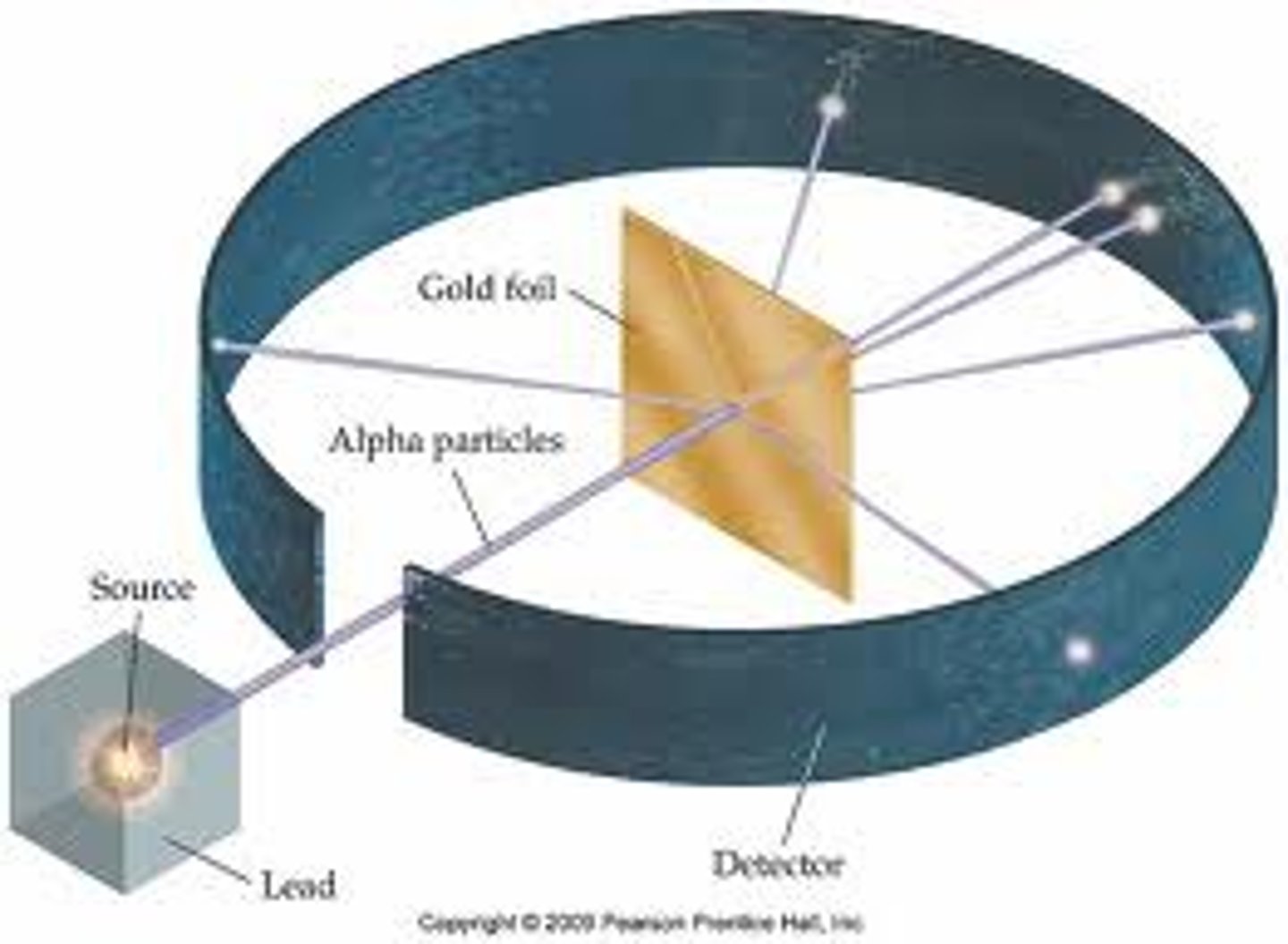
Conclusions of the alpha particle scattering experiment
Most of the atom is empty space except for a tiny positive nucleus.
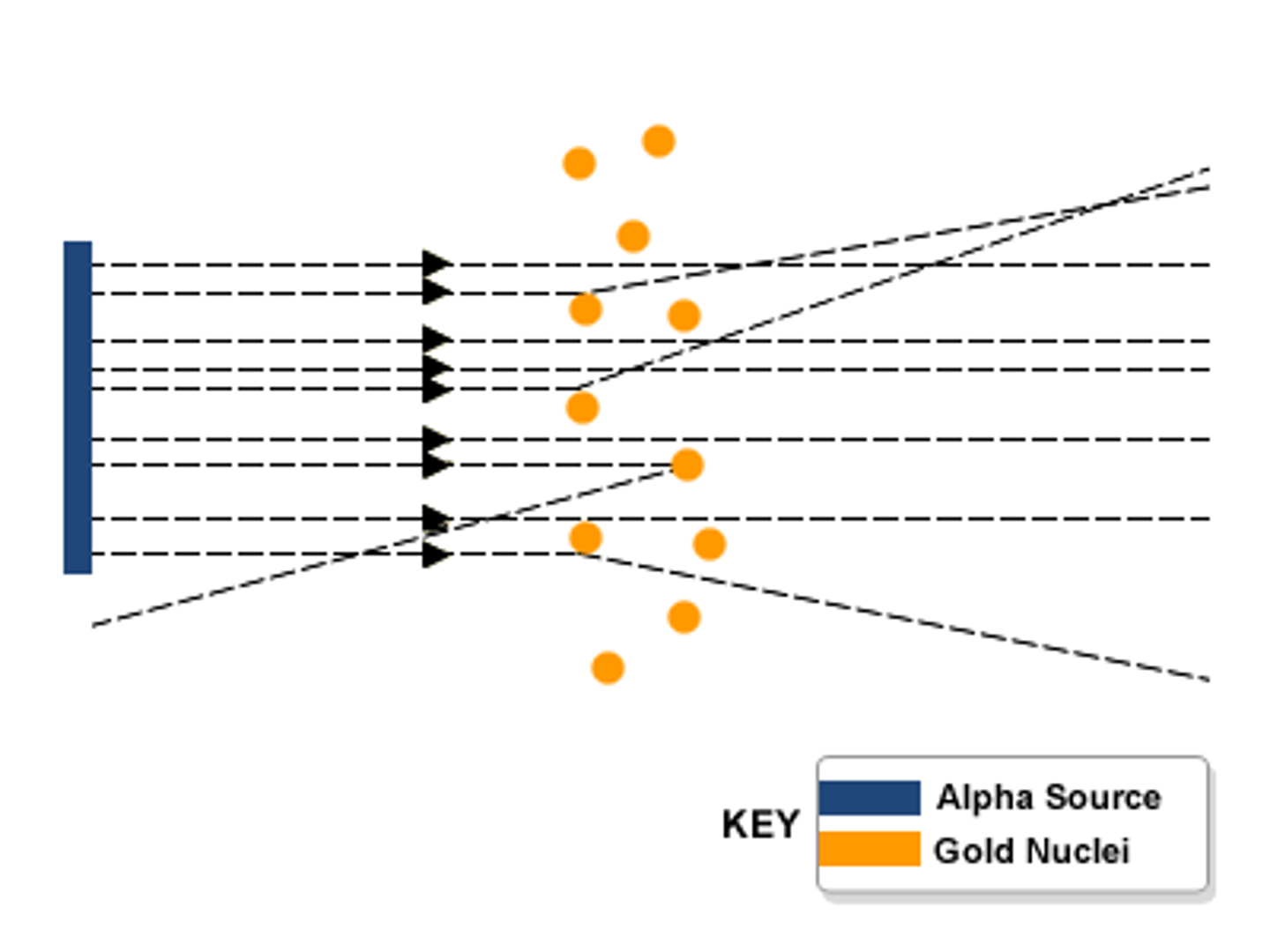
Observations of the alpha particle scattering experiment
Most of the alpha particles went straight through the atom, a few alpha particles bounced back.
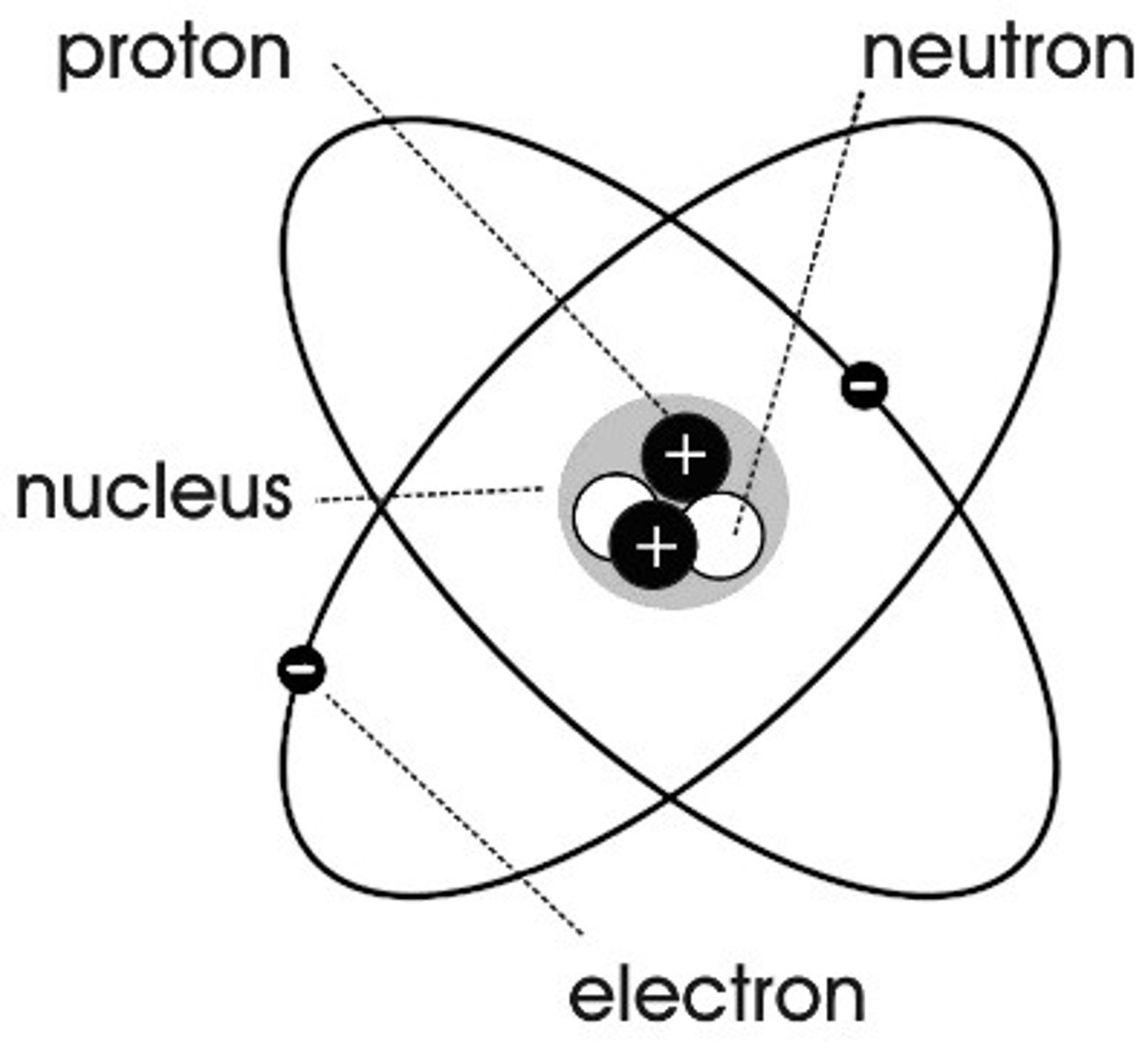
Nuclear model of the Atom
Atoms are made of a small positive nucleus orbited by negative electrons.
Niels Bohr
Adapted the nuclear model, by suggesting that electrons orbit the nucleus at specific distances.
James Chadwick
Carried out experiments which provided evidence of neutrons.
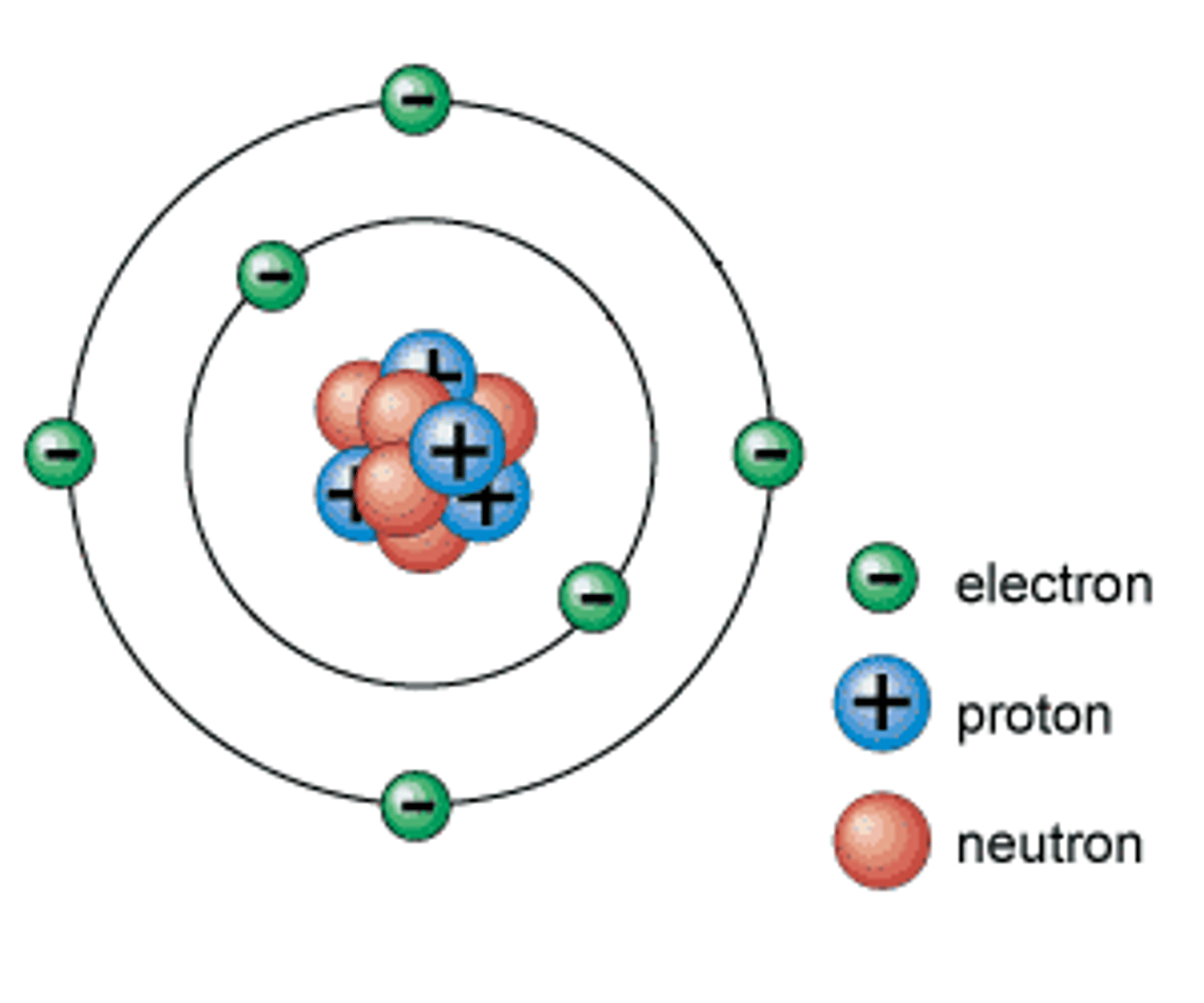
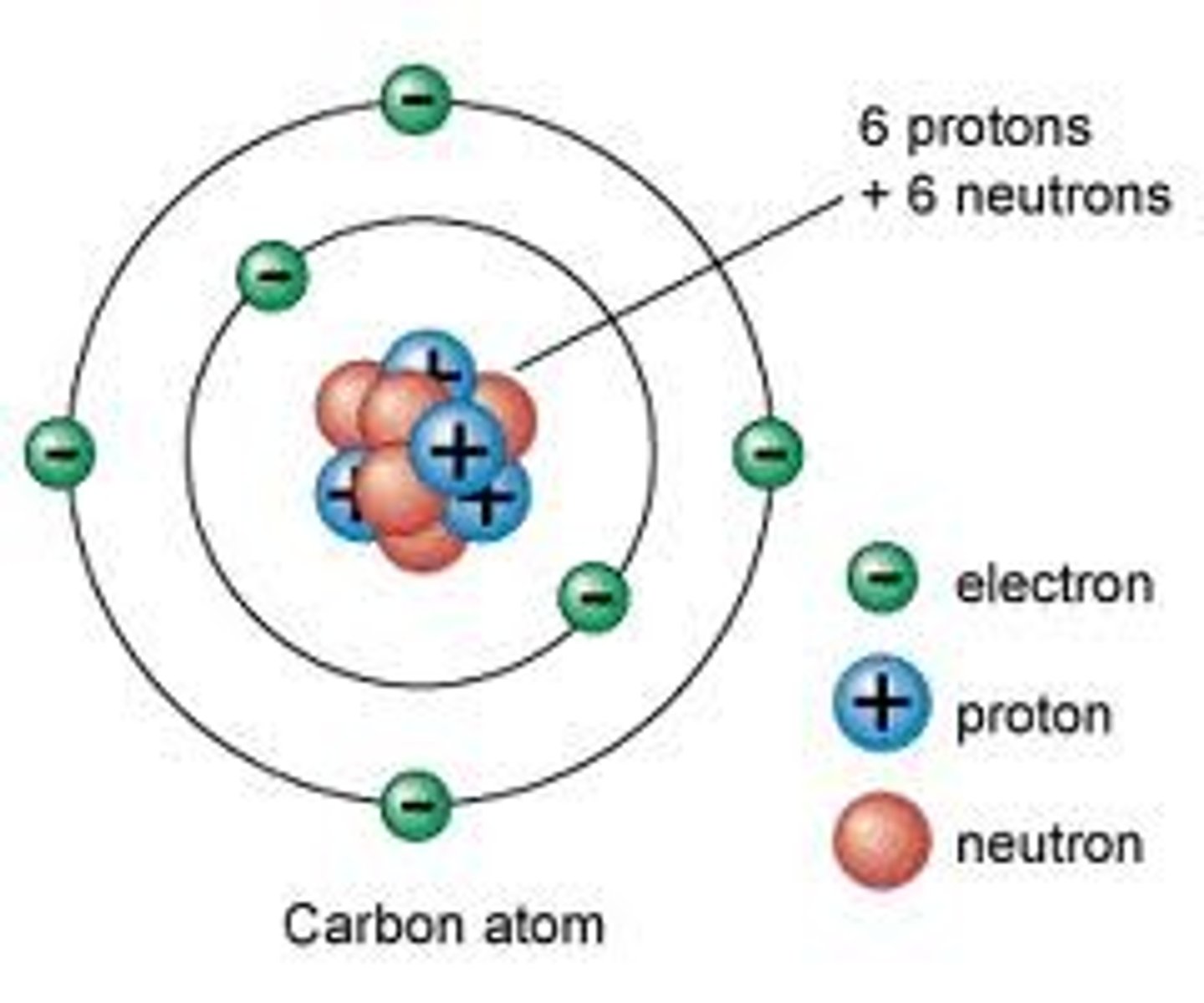
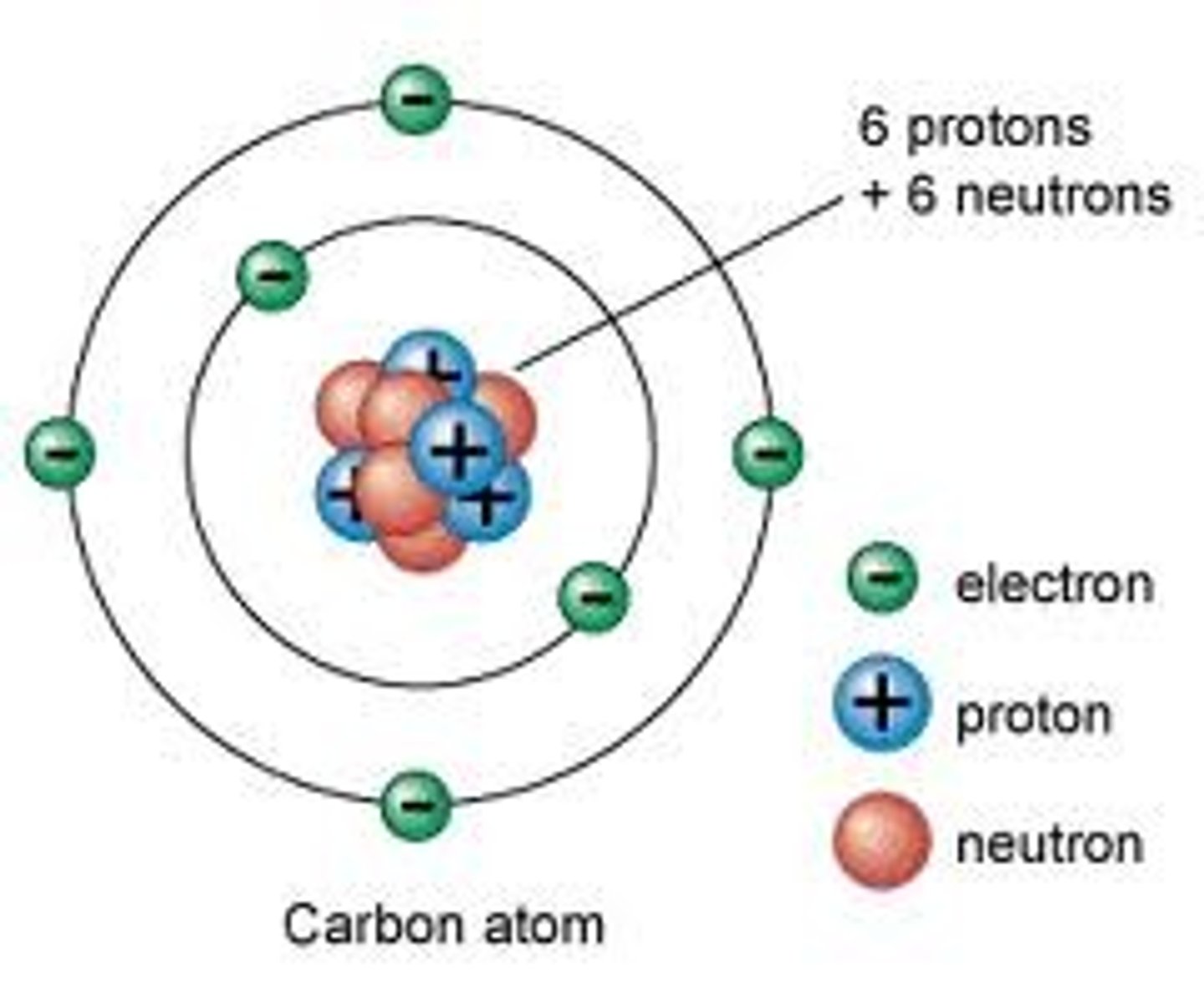
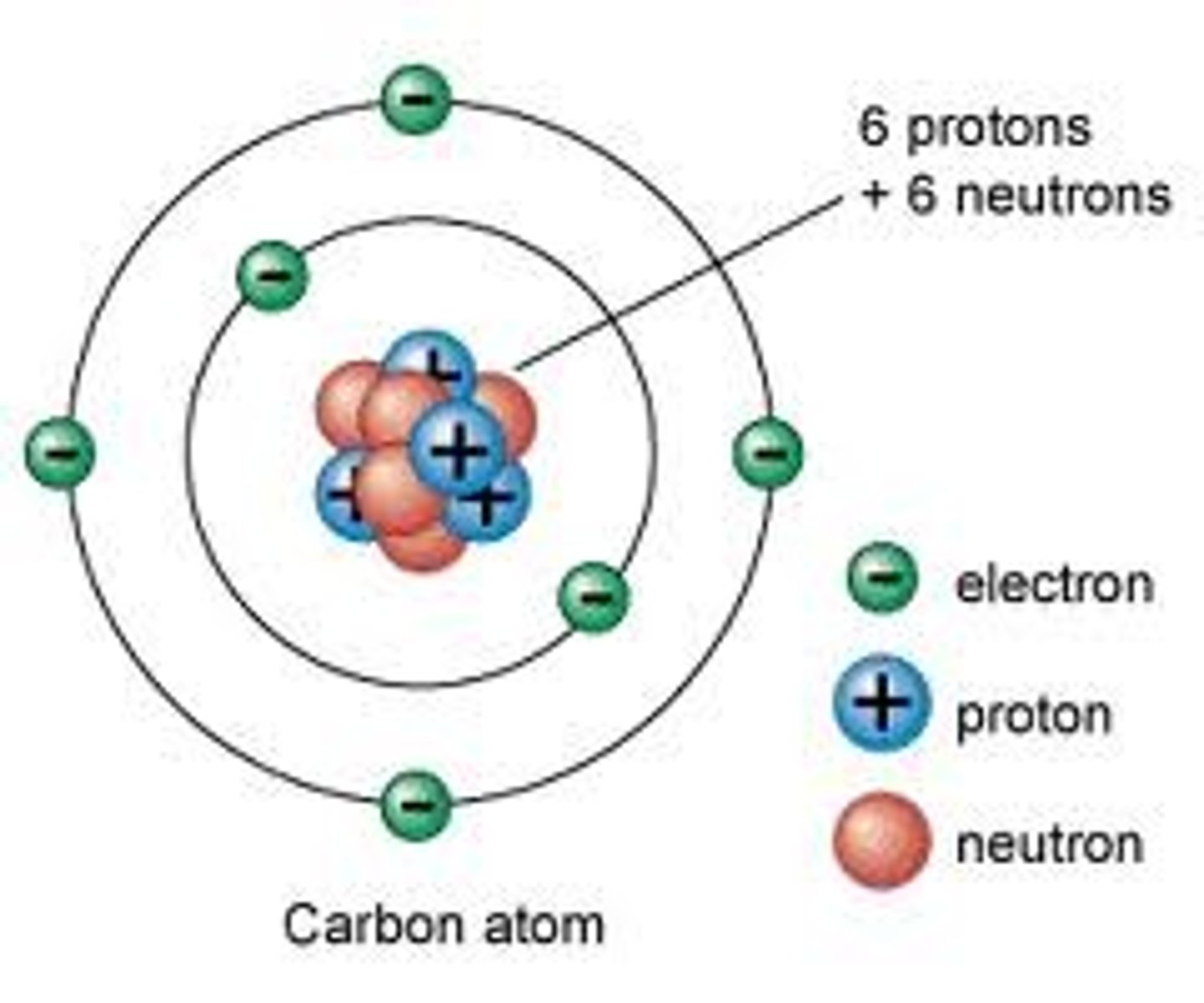
Proton
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom.
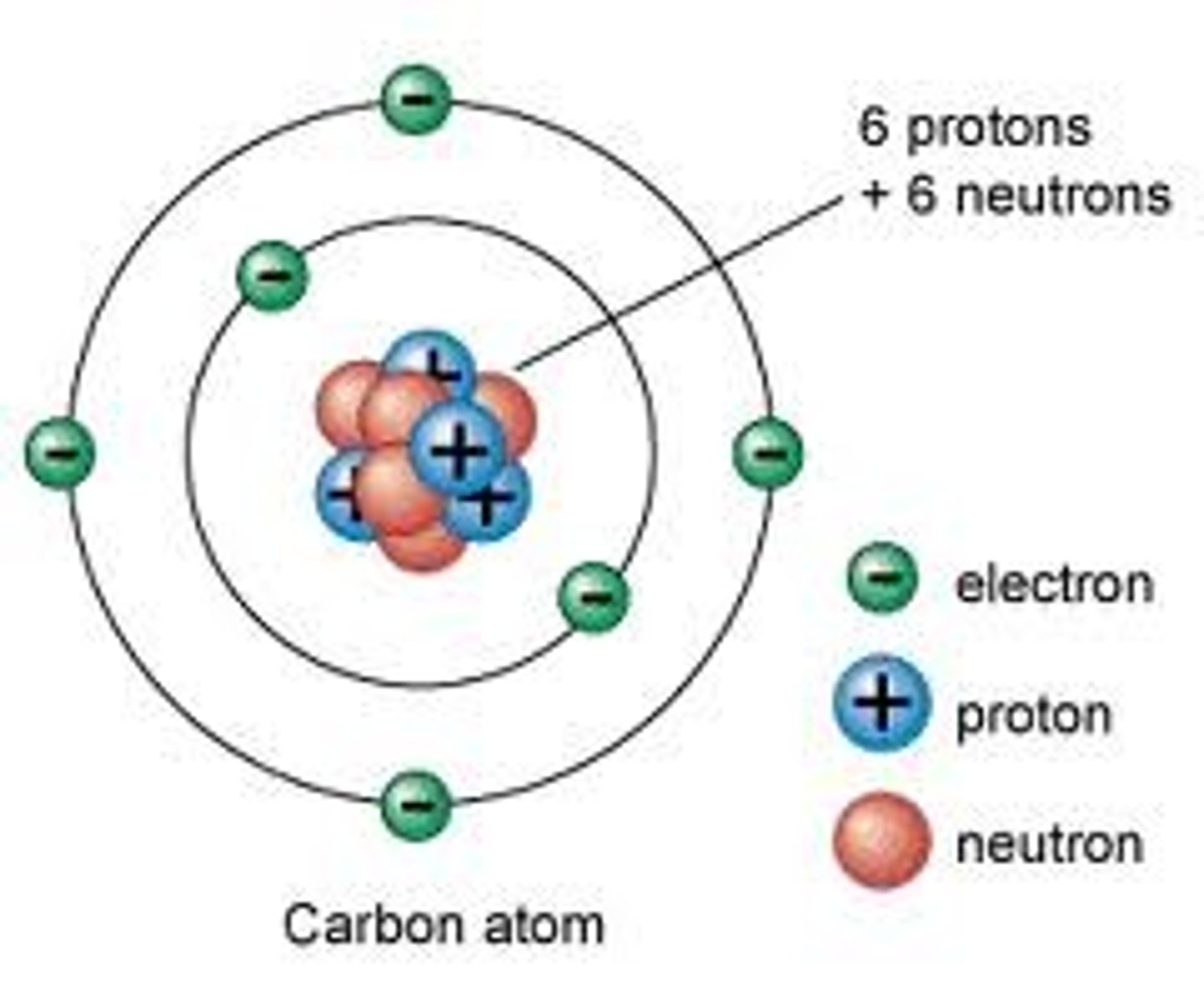
Neutron
A subatomic particle that has no charge and is found in the nucleus of an atom.
Electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge and orbits the nucleus in shells.
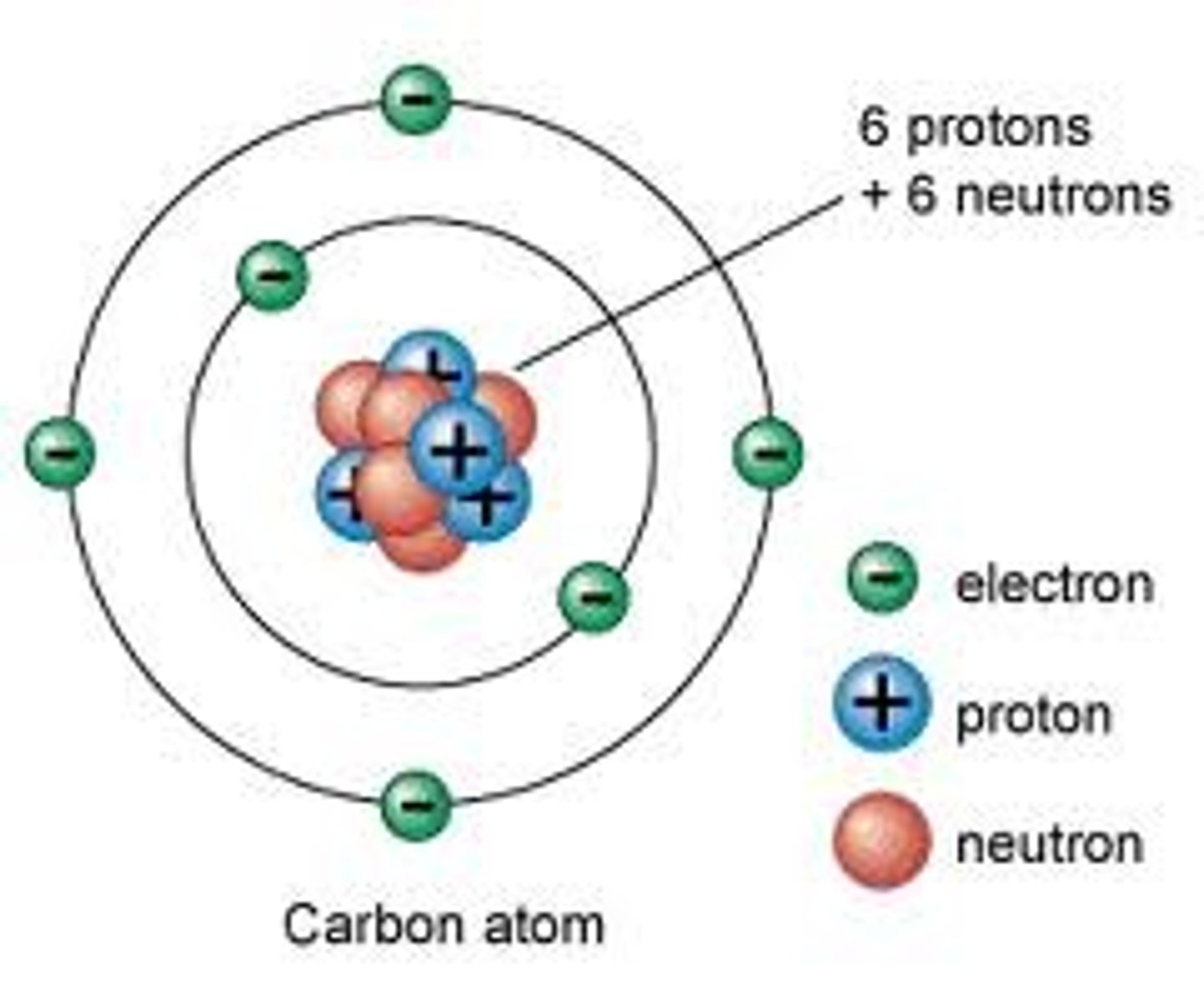
Relative mass of a proton
1
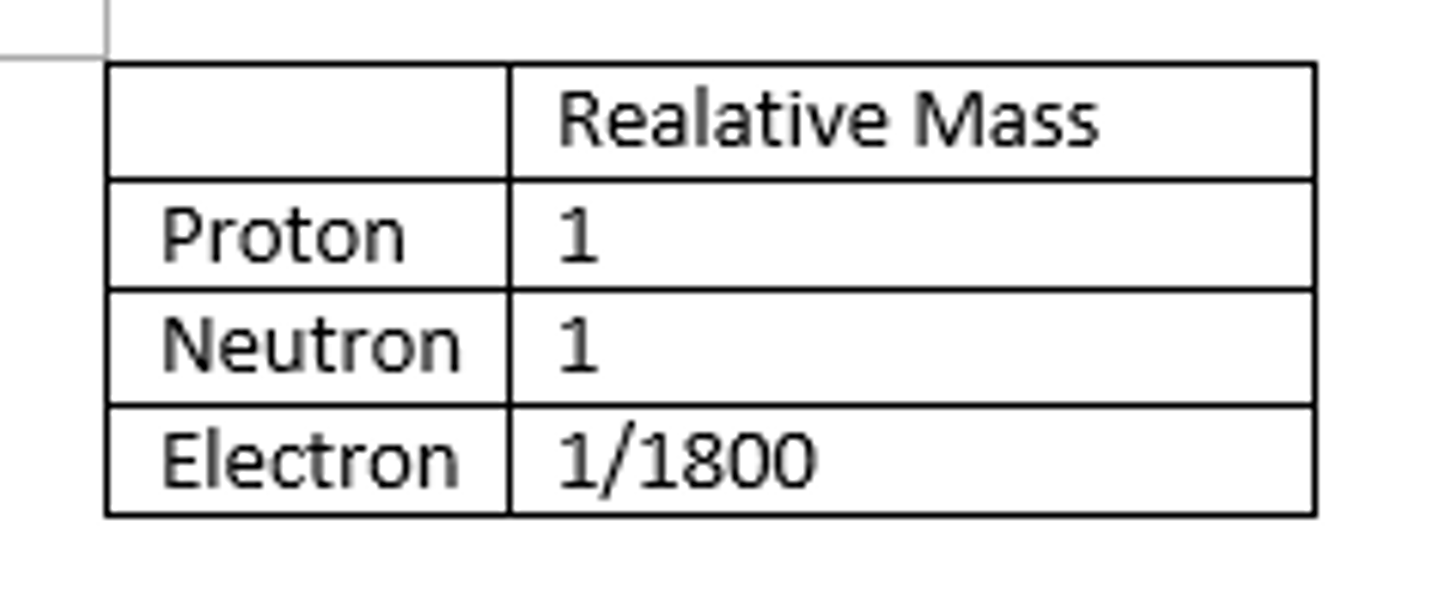
Relative mass of a neutron
about the same as that of a proton
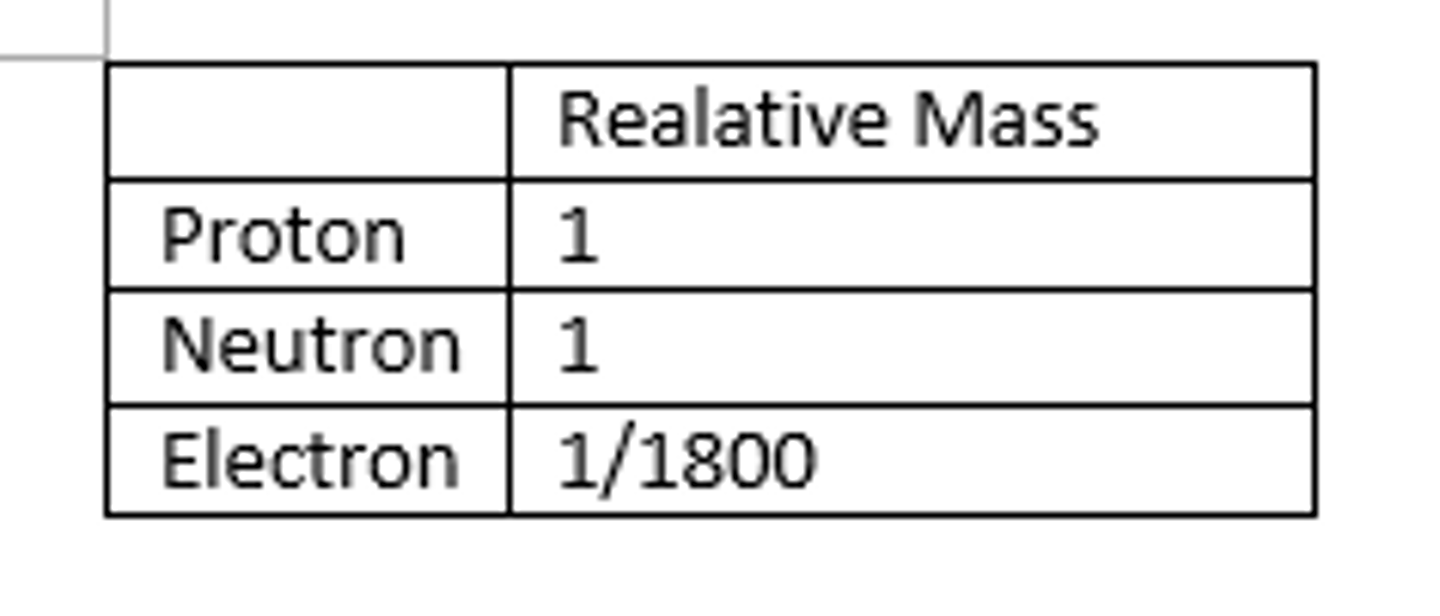
Relative mass of an electron
1/1840
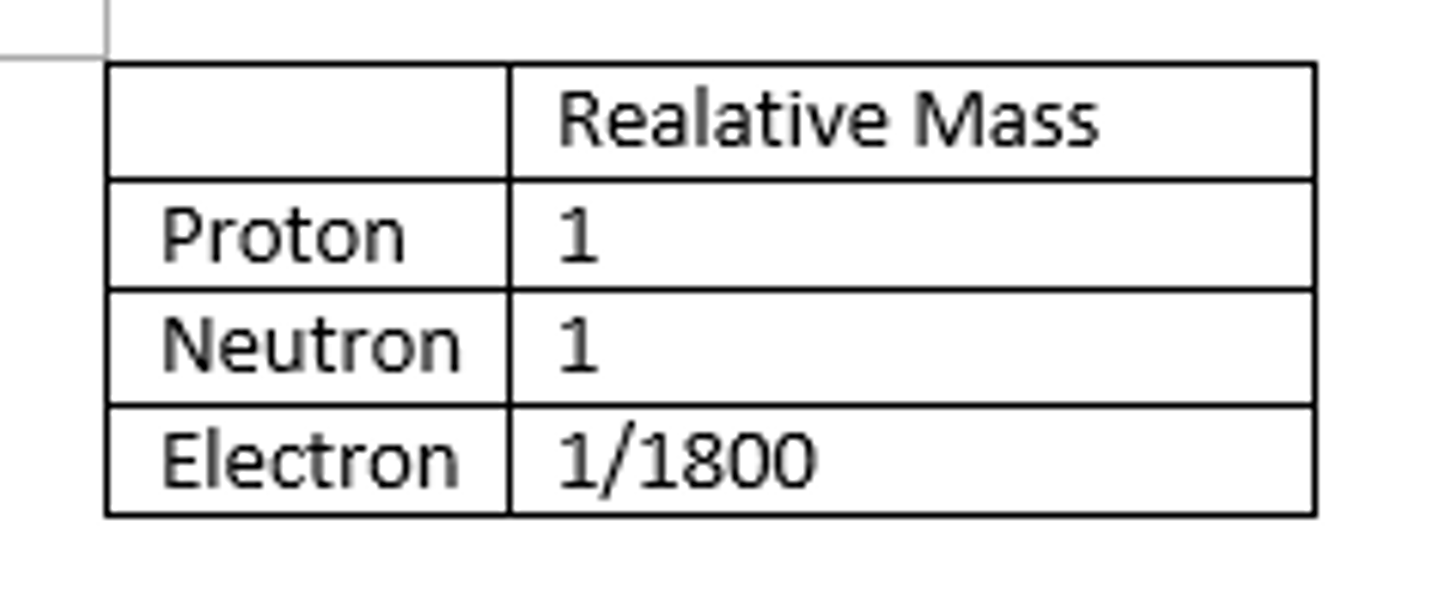
Relative charge of a proton
+1
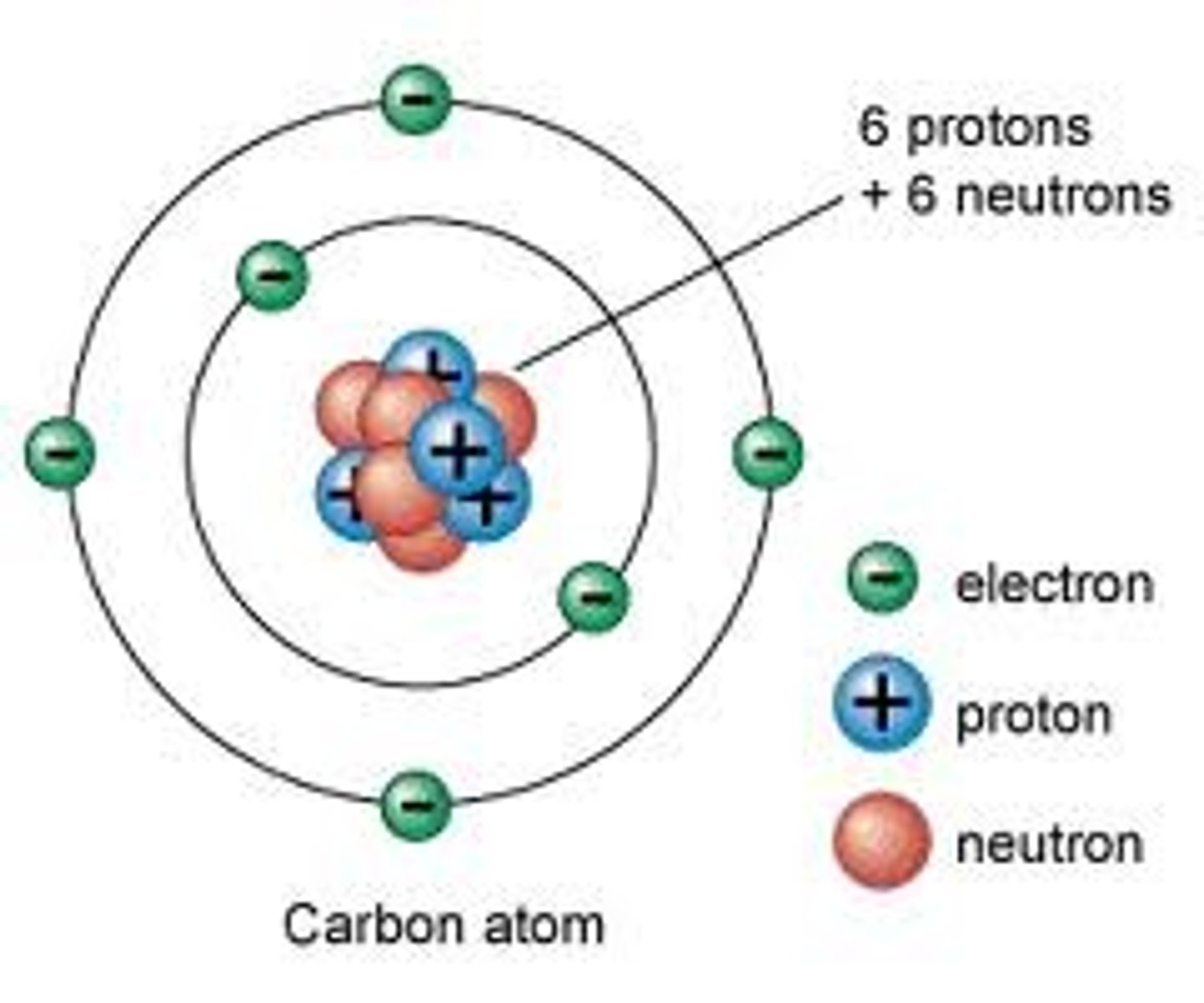
Relative charge of a neutron
0
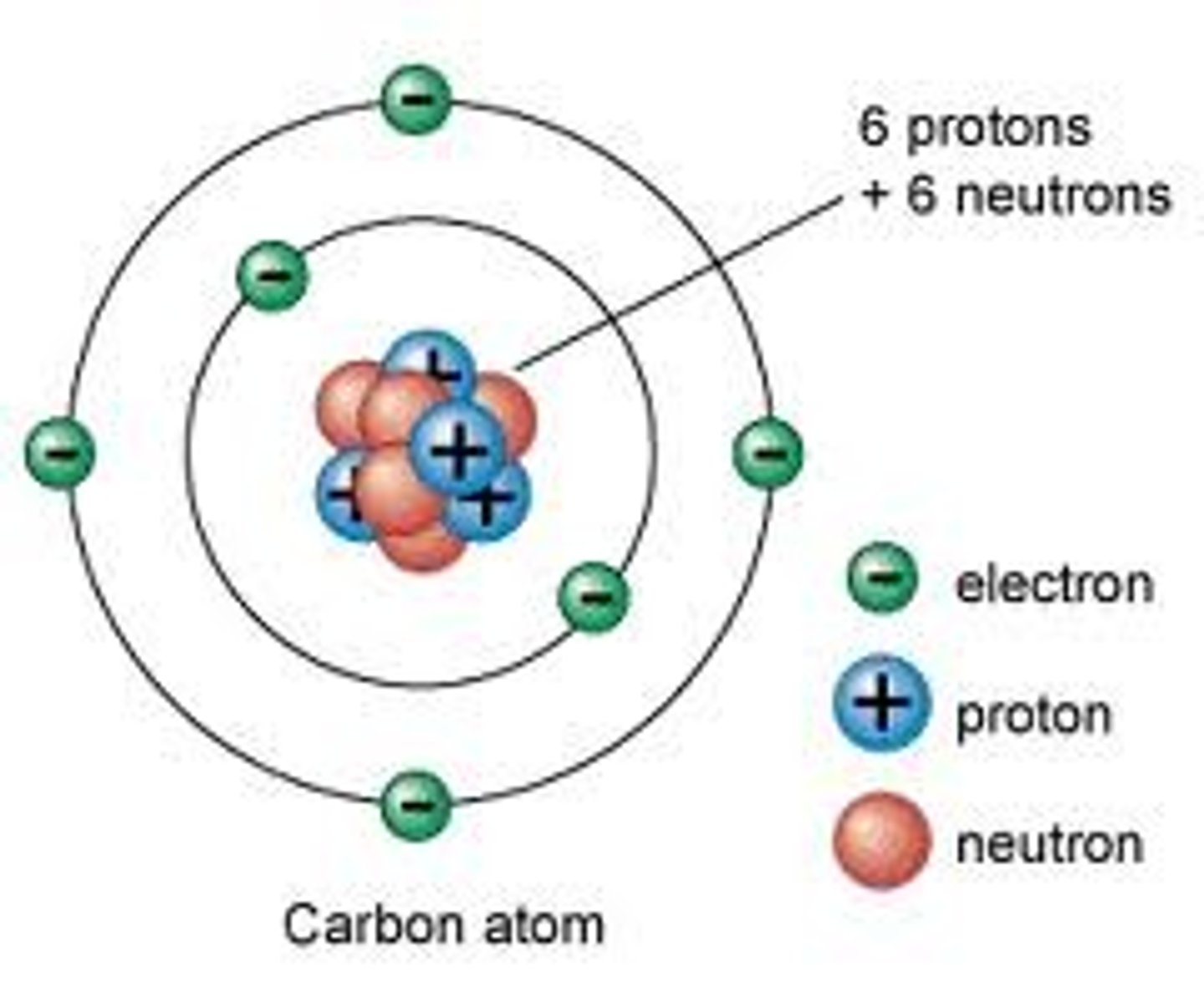
Relative charge of an electron
-1
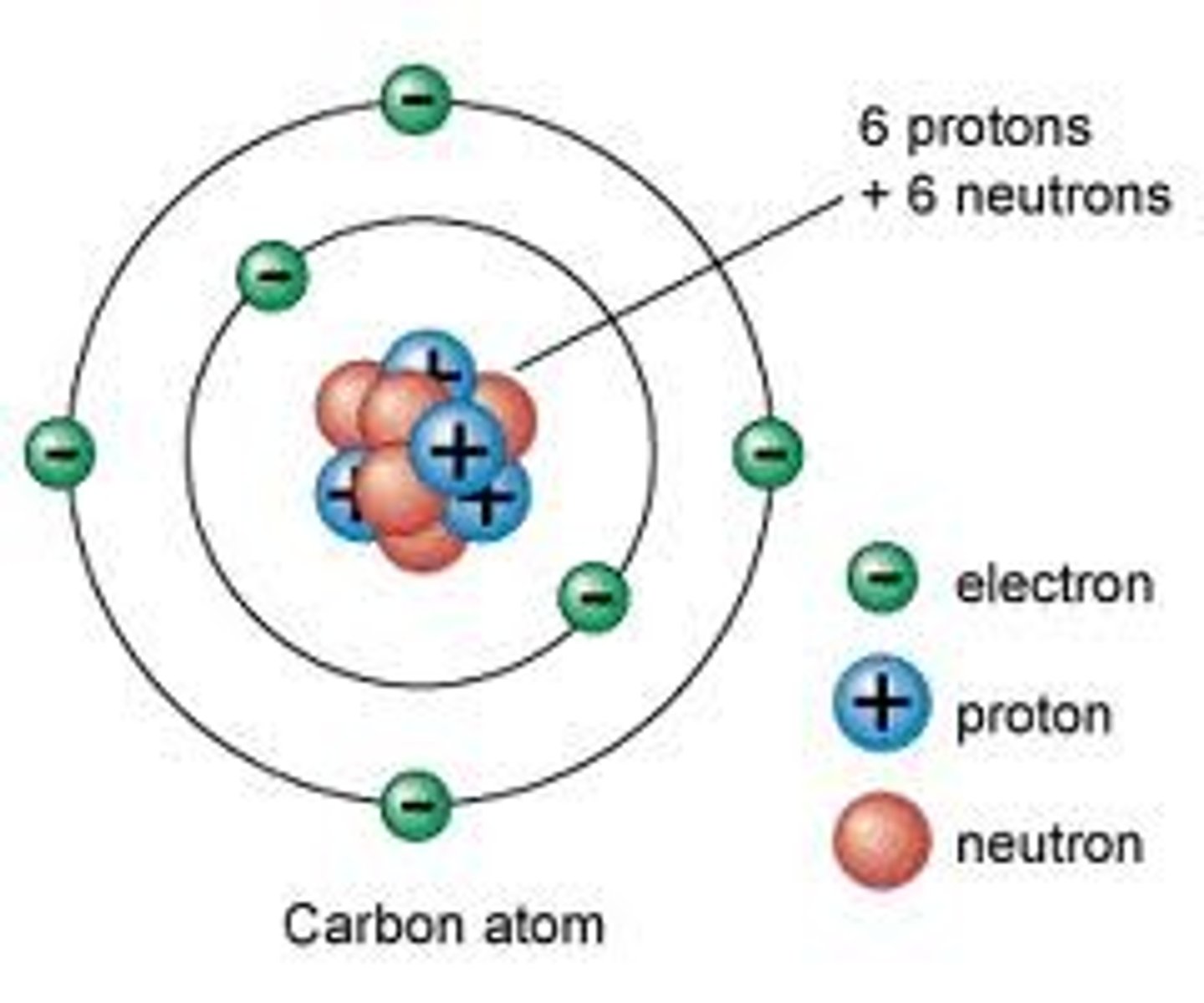
Neutral atoms
same number of positive protons as negative electrons
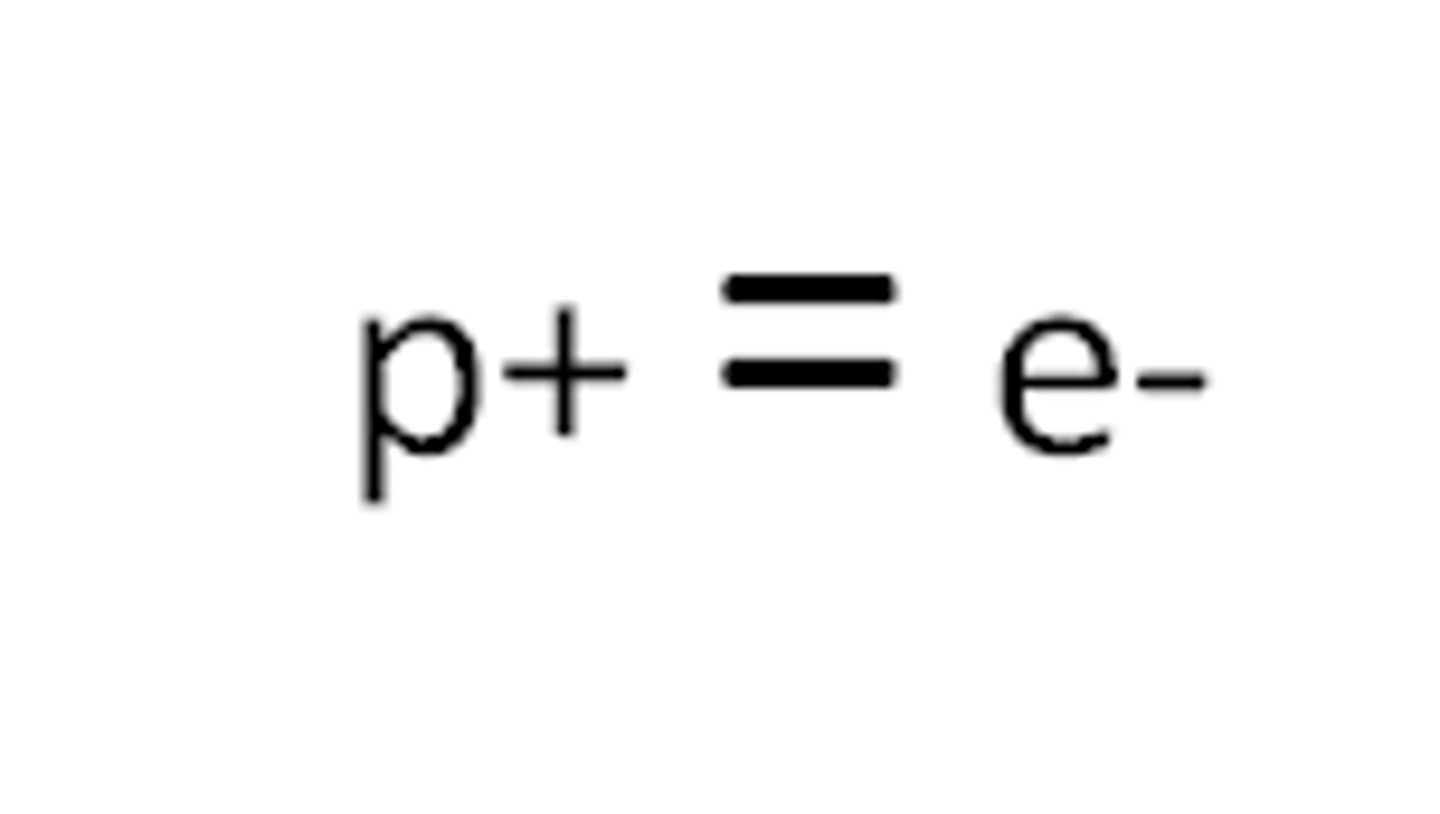
Atomic (proton) number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
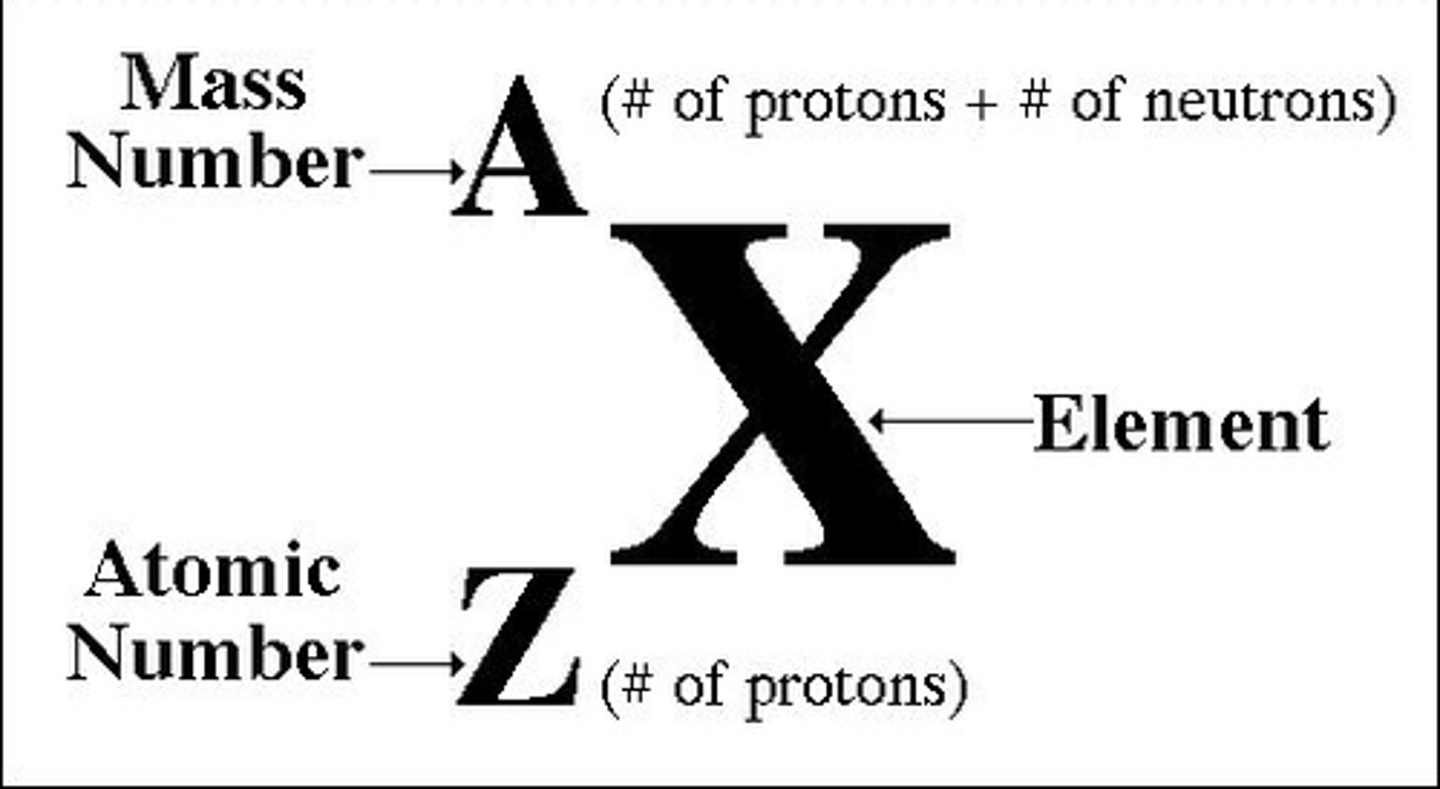
Subatomic particles in the nucleus
protons and neutrons
Energy Levels/Electron Shells
The region surrounding the nucleus where electrons orbit the nucleus.
Proton
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge, defines the type of atom and that is found in the nucleus
Neutron
A subatomic particle that has no charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
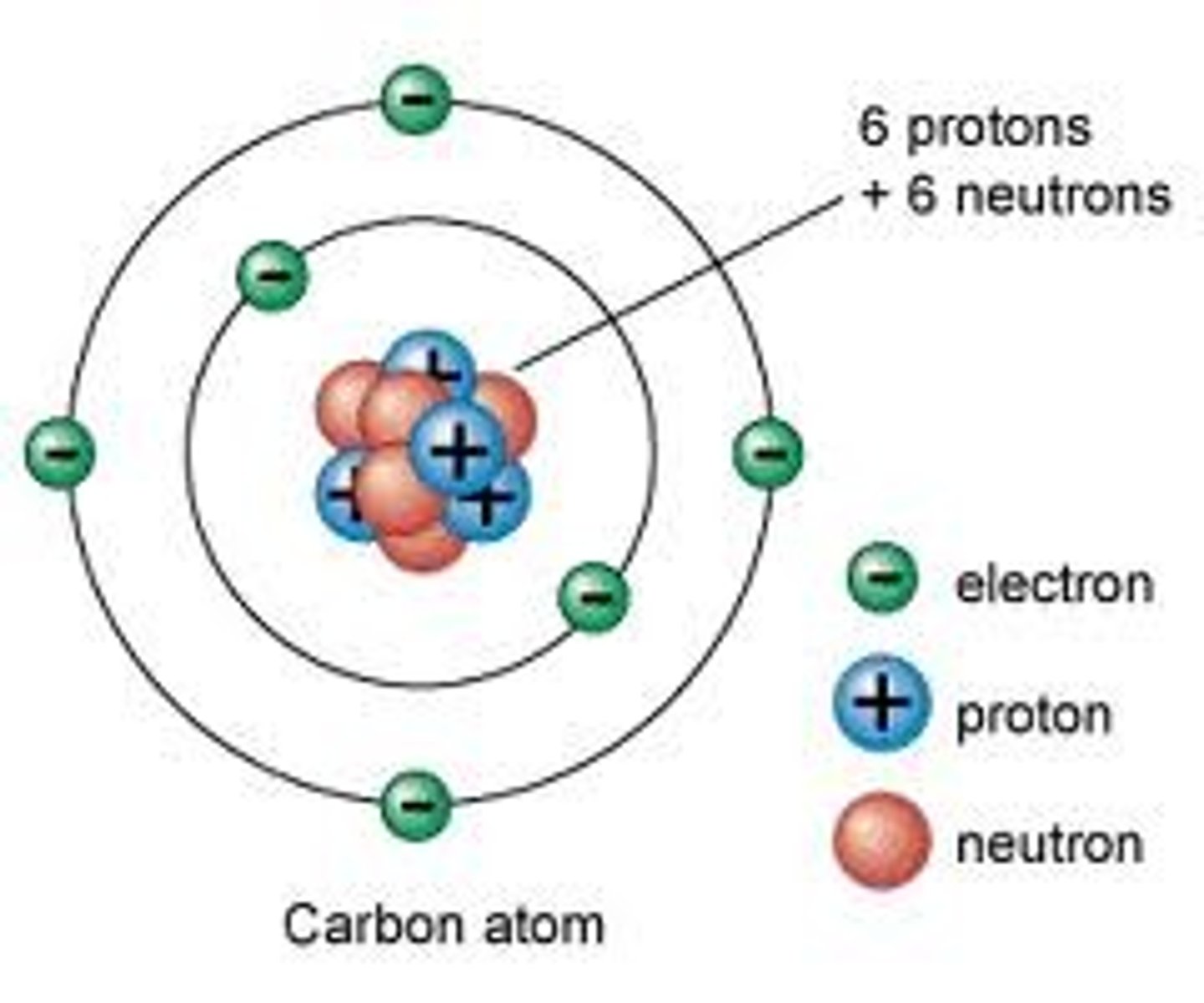
Electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge and is found in electron shells, orbiting the nucleus
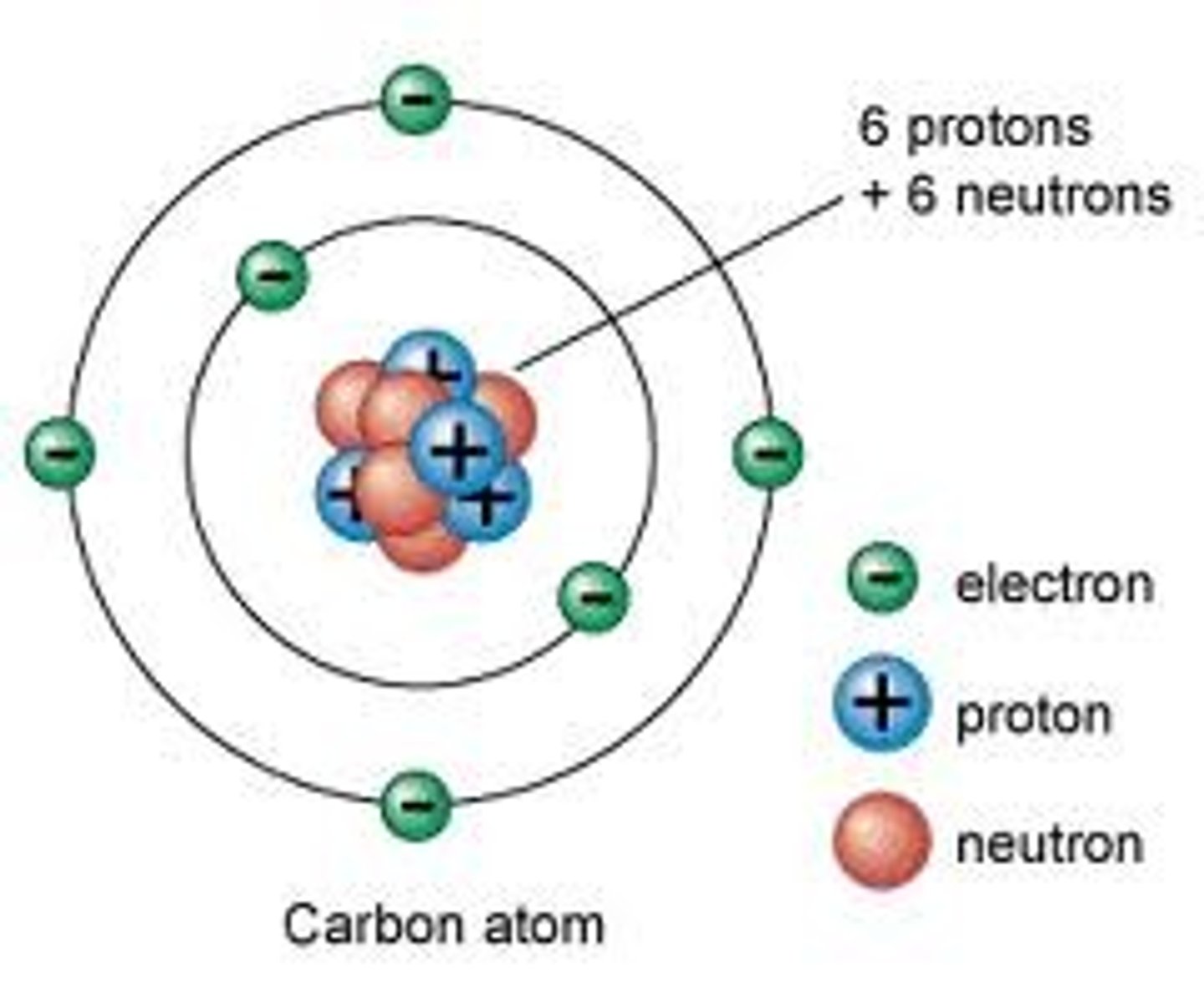
Mass number (atomic mass)
number of protons plus the number of neutrons in an atom of an element
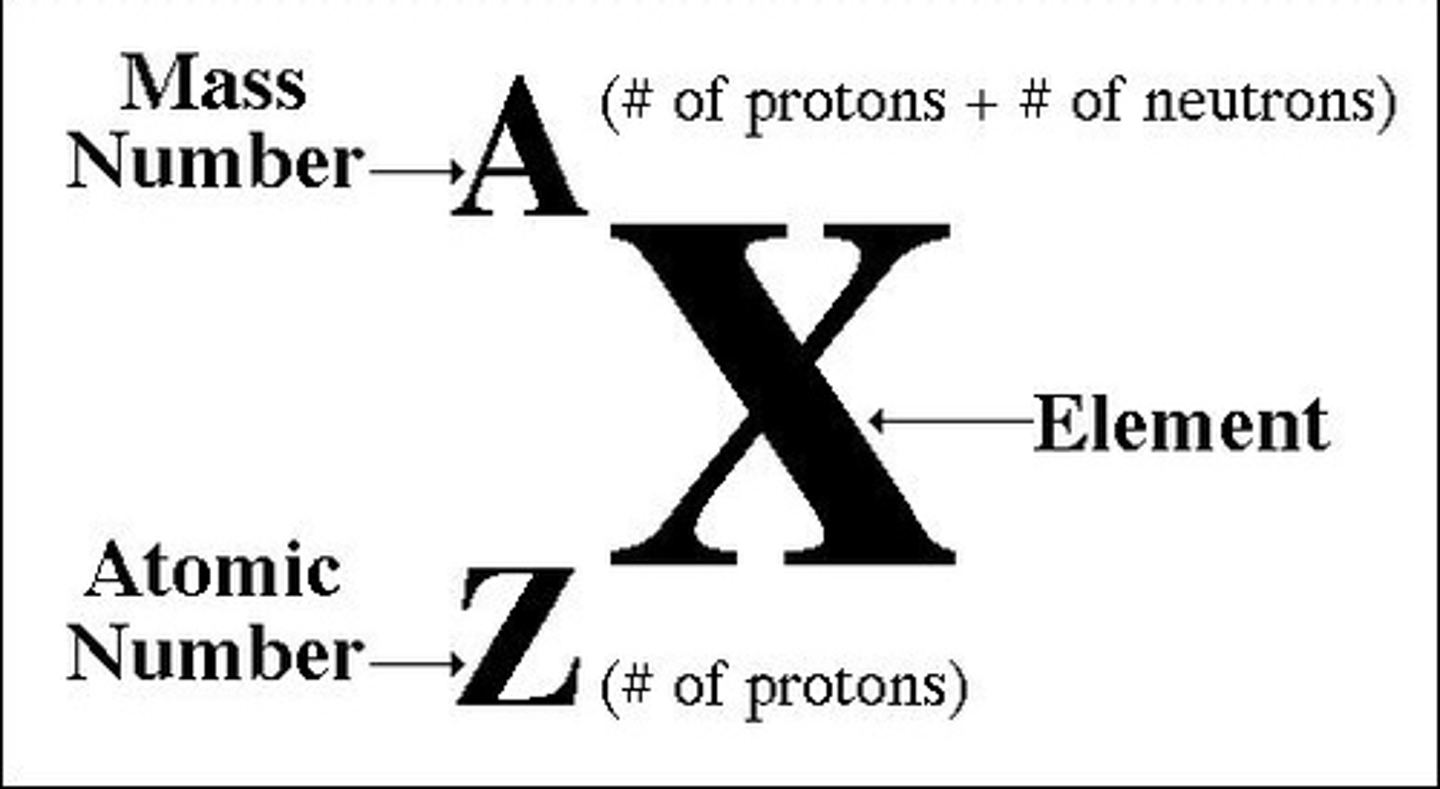
Average atomic radius
0.1 nm (1 x 10^-10 m)

Average radius of an atomic nucleus
10,000 times smaller than an atom (1 x 10^-14 m)
Number of protons in an atom
atomic number
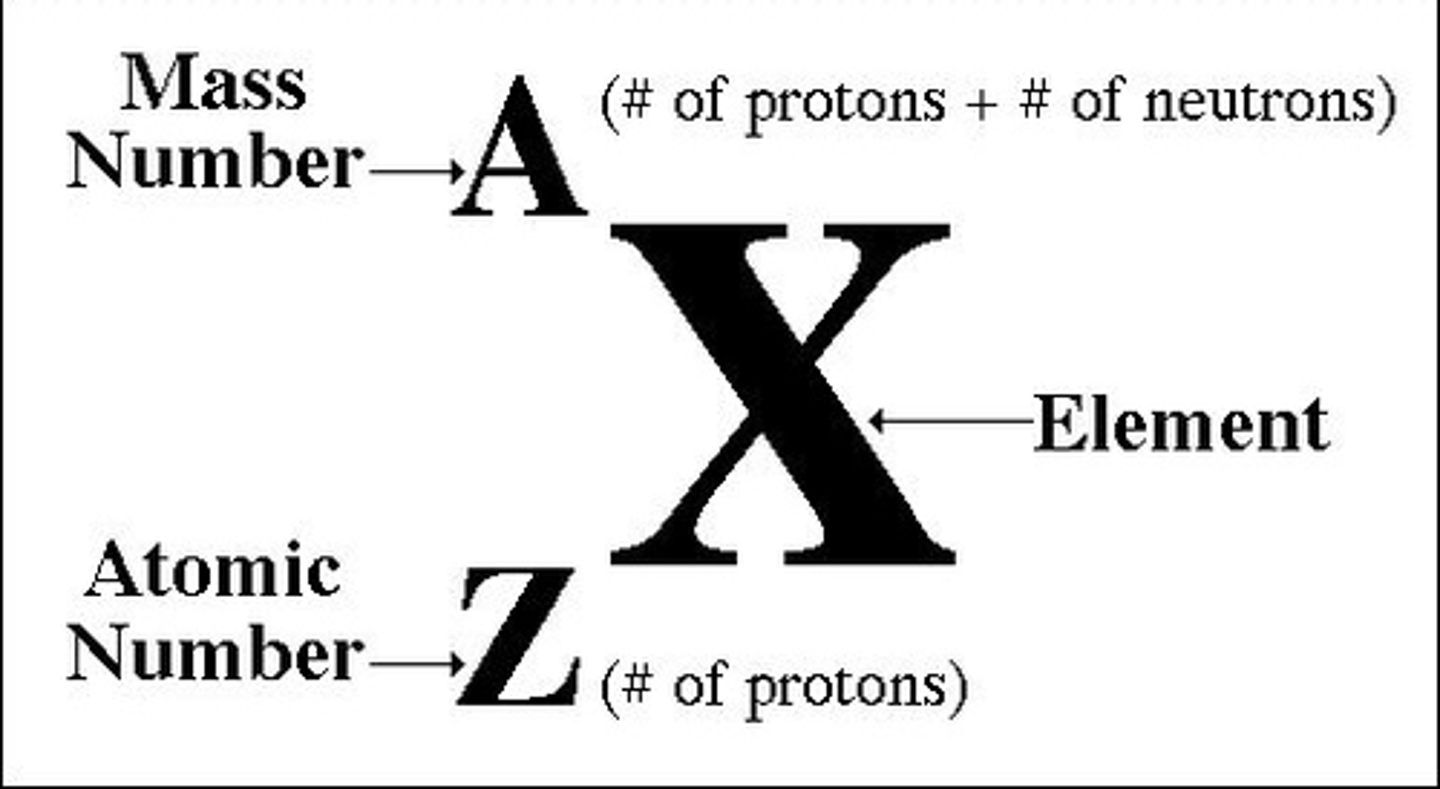
Number of neutrons in atom
mass number - atomic number
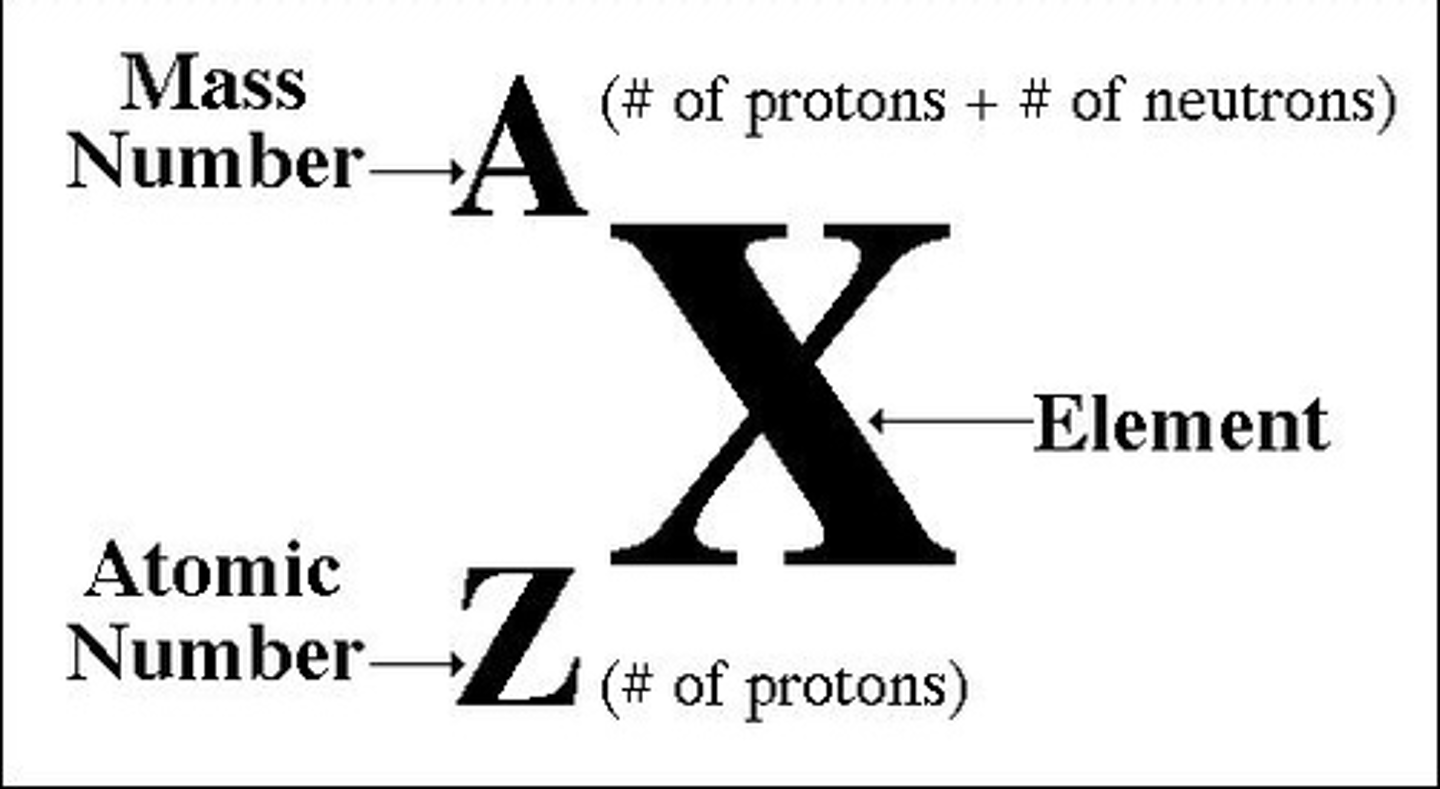
Number of electrons in an atom
is the same as the number of protons
Relative atomic mass
The weighted average mass of an atom of an element compared with one-twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
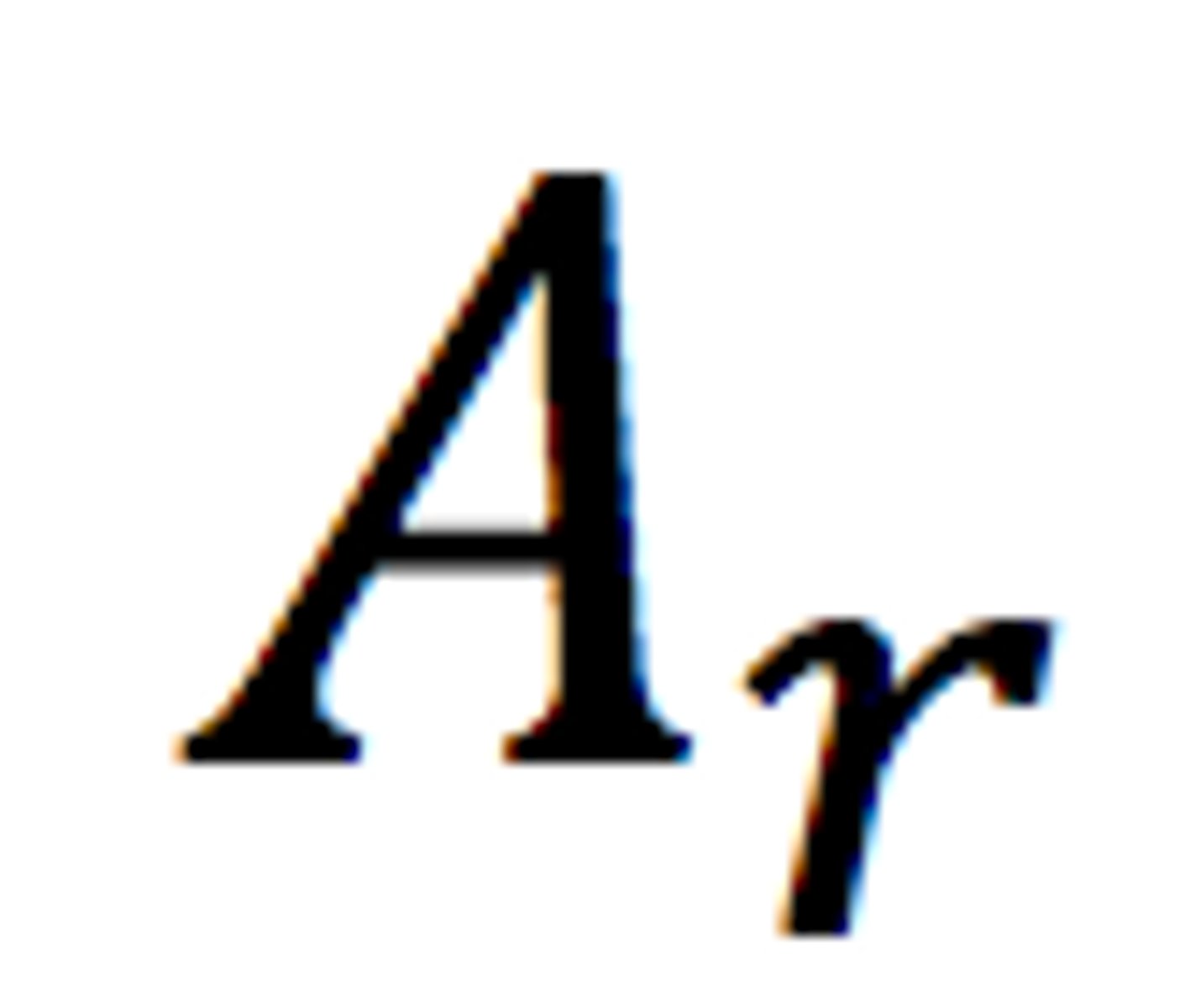
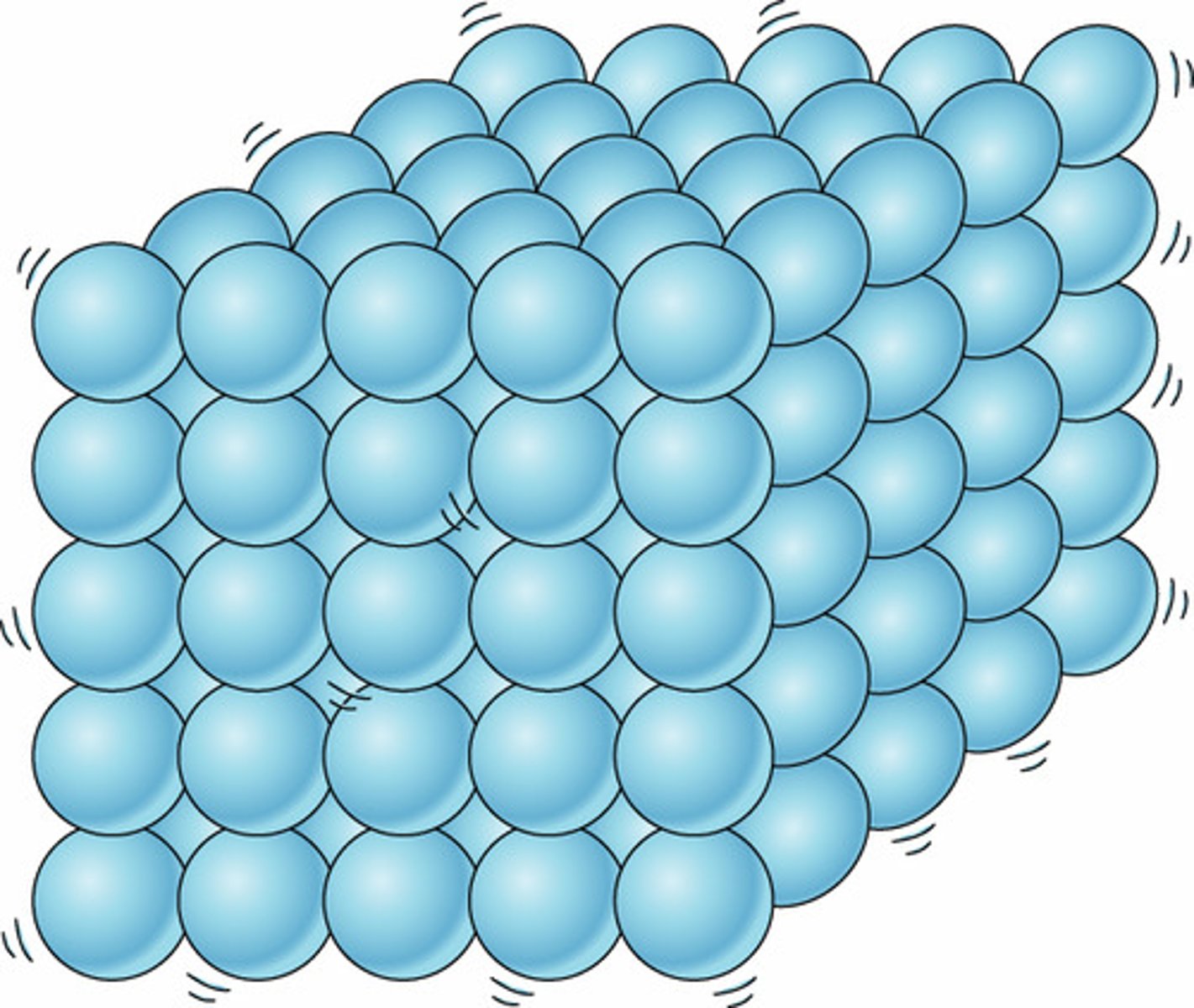
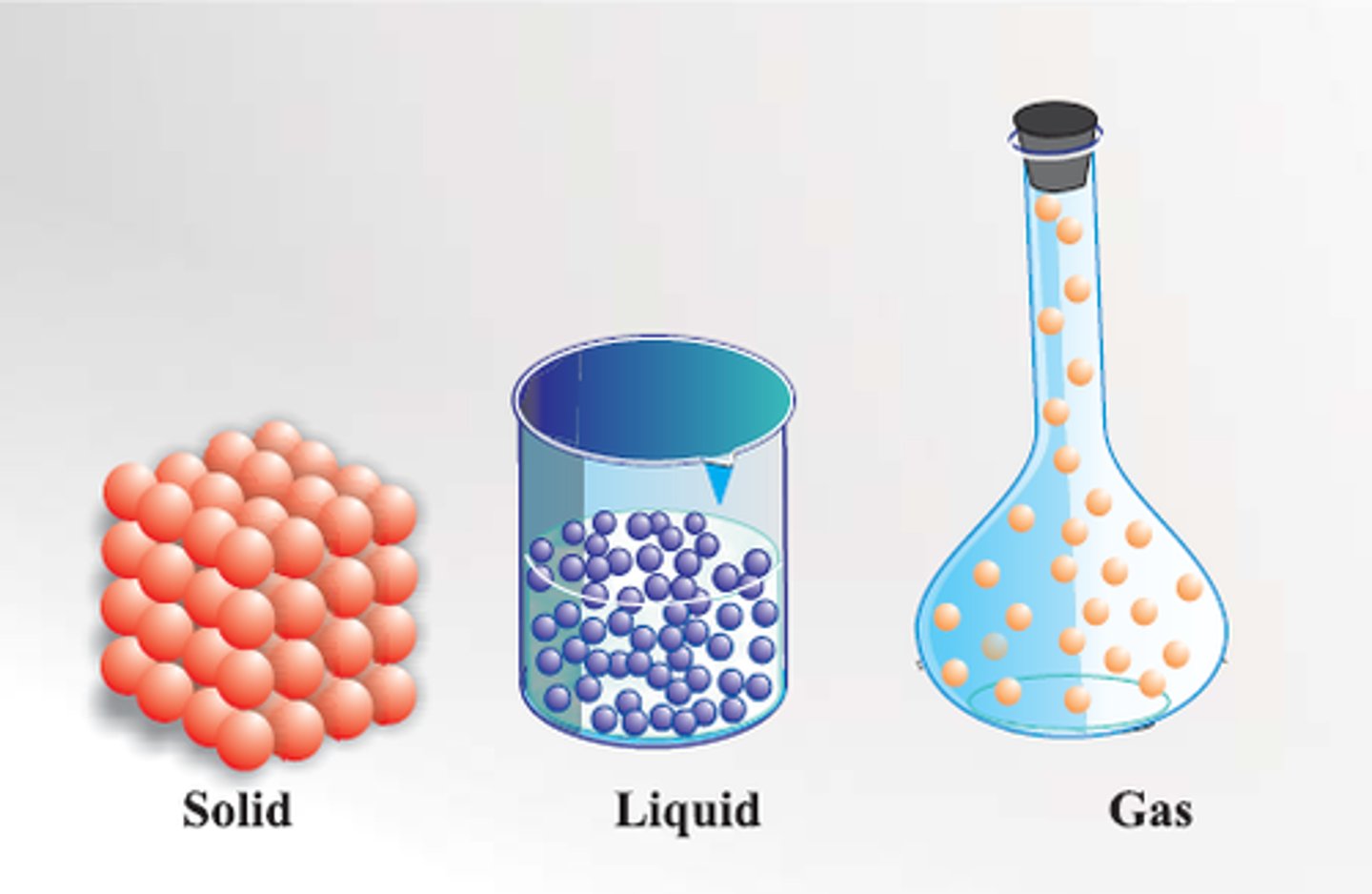
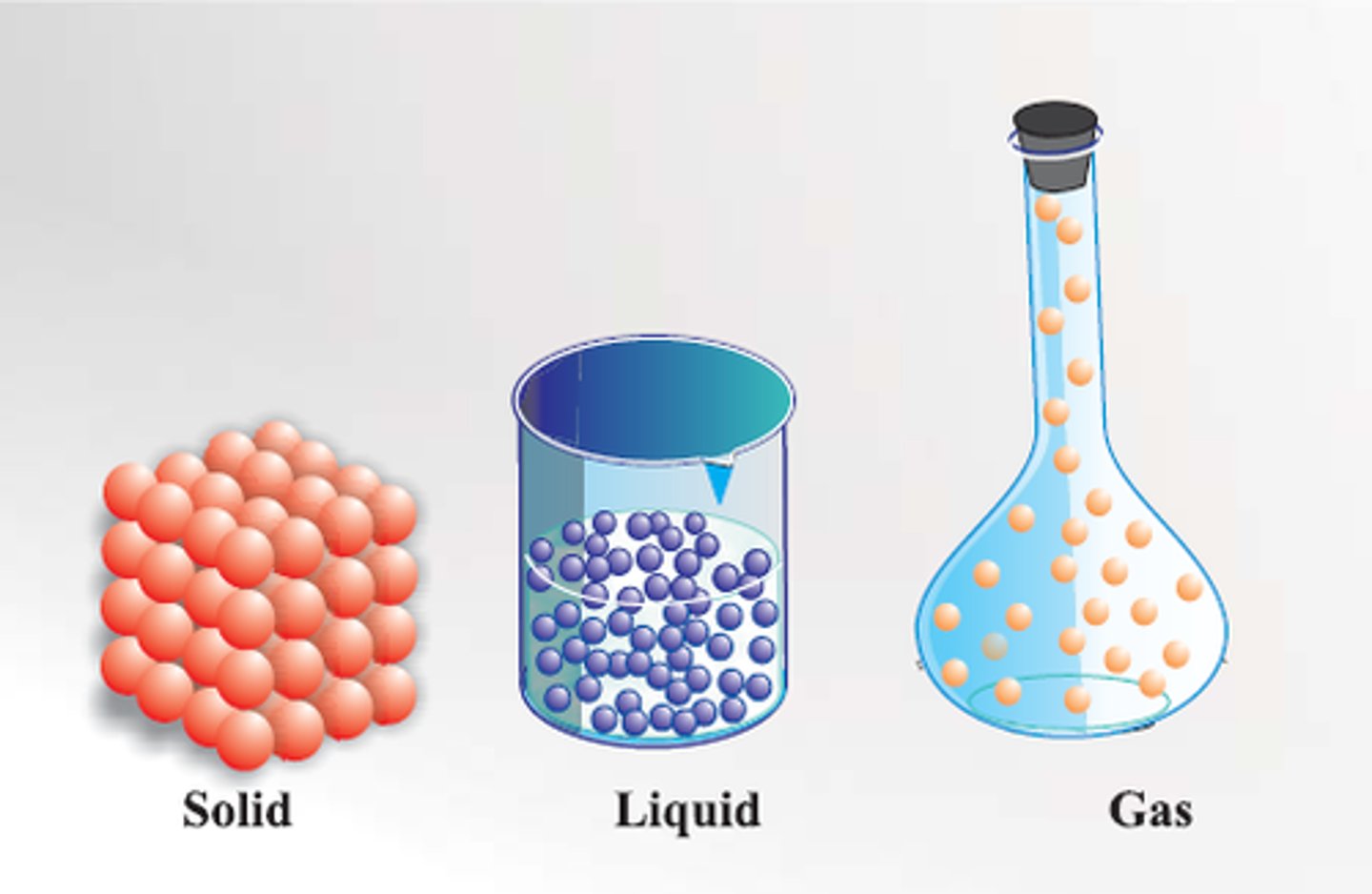
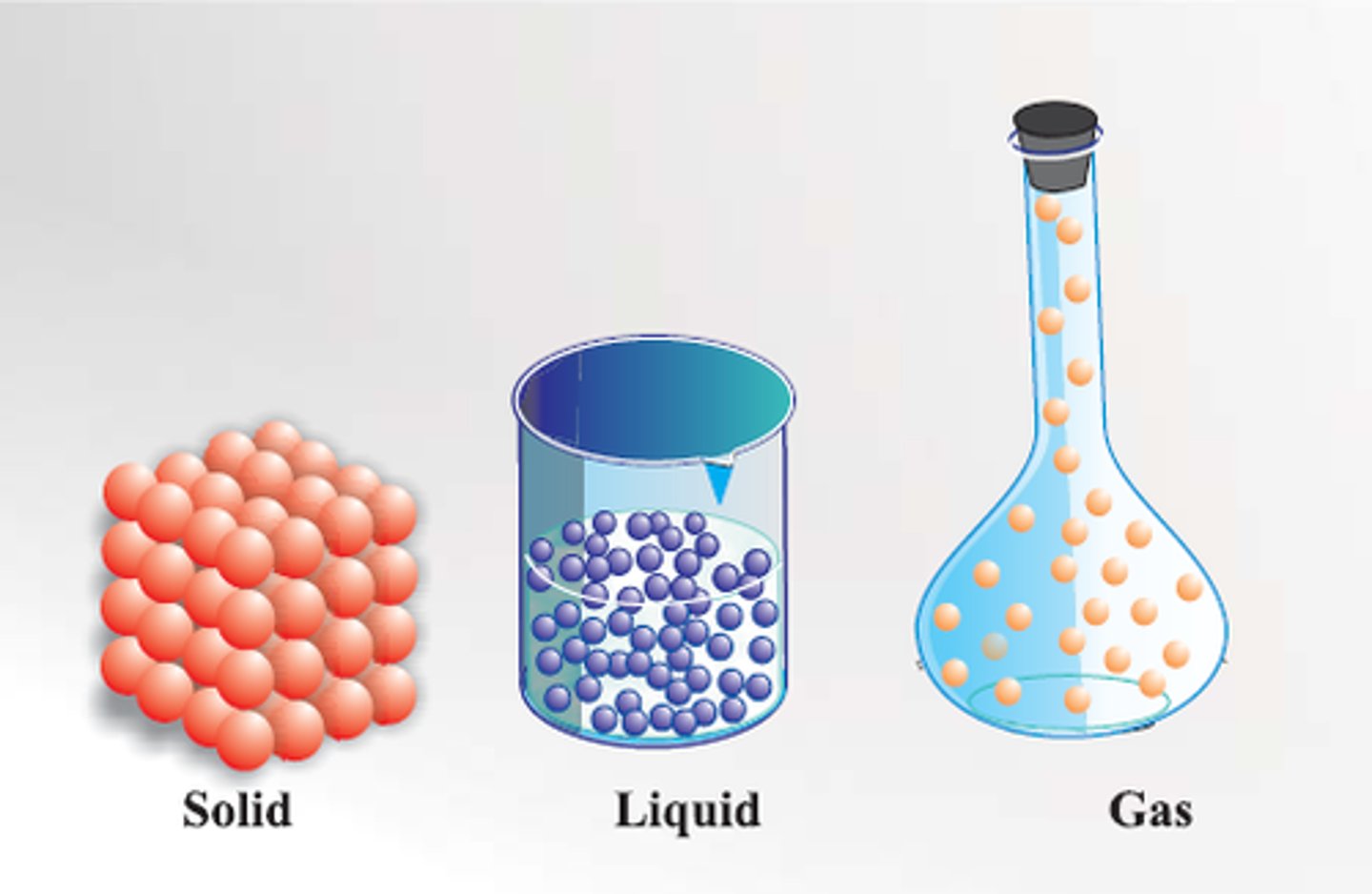
Solid
Definite shape and volume
Liquid
Definite volume but no definite shape
Gas
No definite shape or volume
Melting point
The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid

Boiling point
The temperature at which a liquid changes to a gas

Particle theory
Matter is made up of tiny particles which are represented as small solid spheres which are constantly moving.
Uses of particle theory
Explaining changes of state
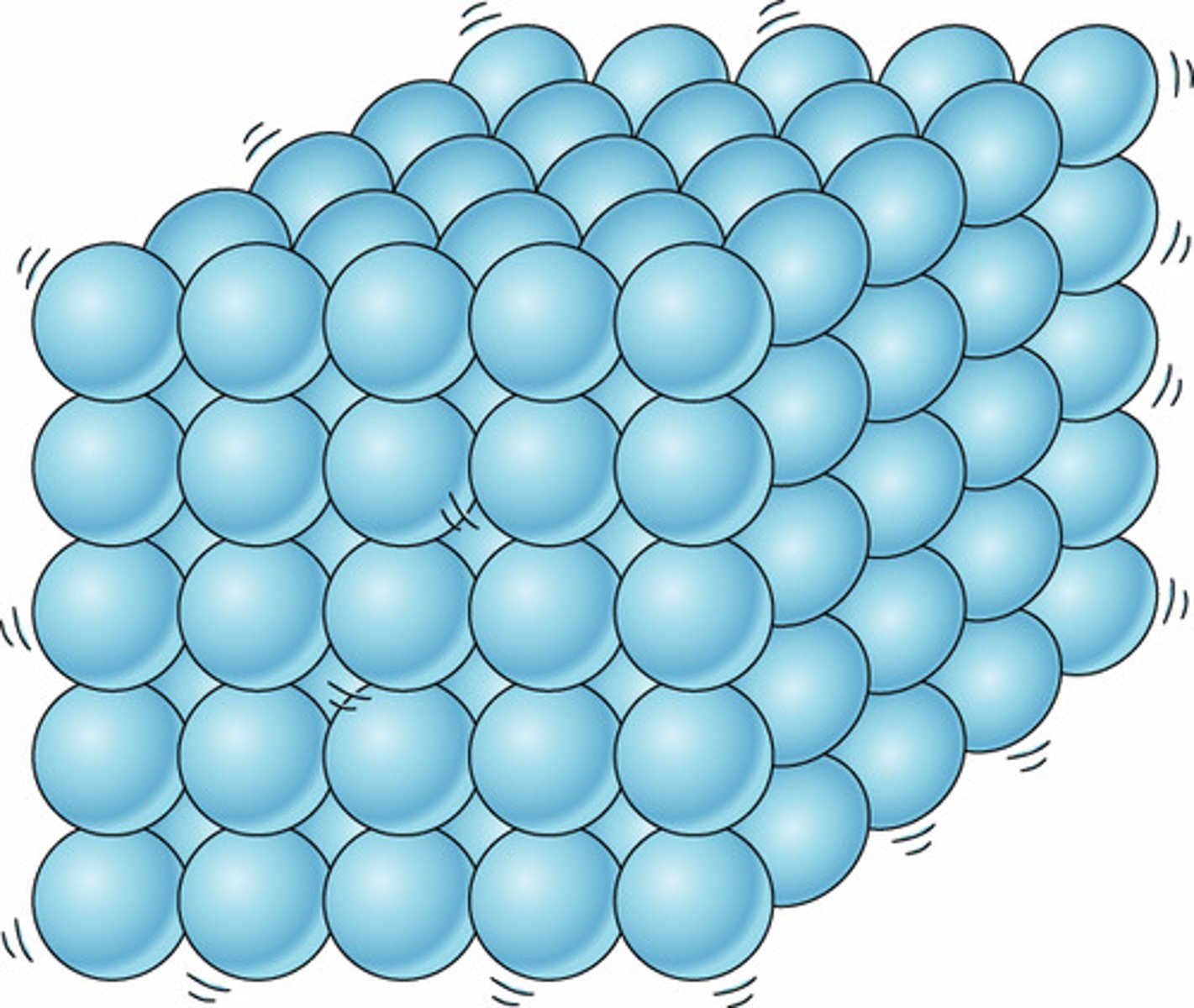
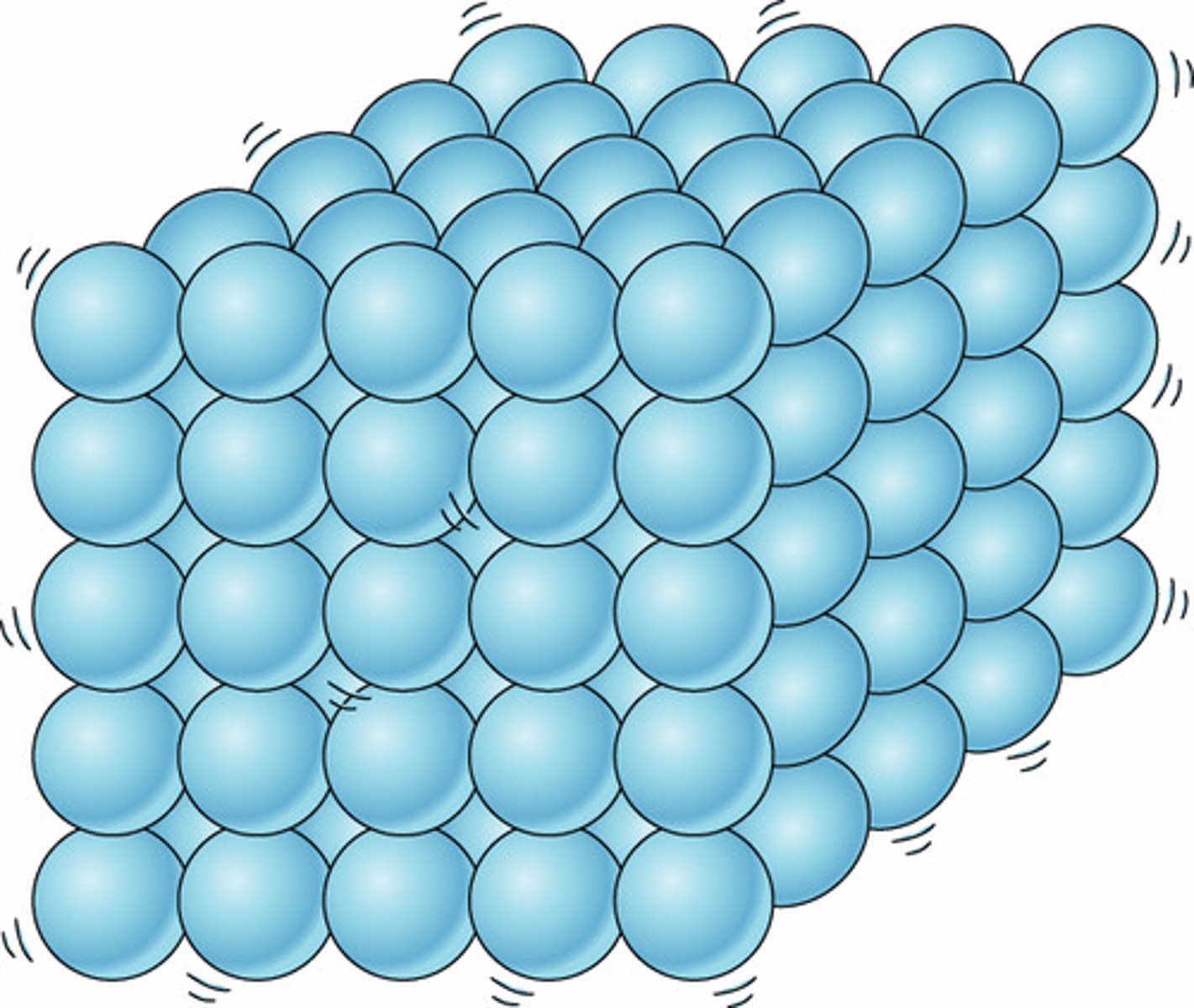
Movement of particles in a solid
Vibrate about a fixed position
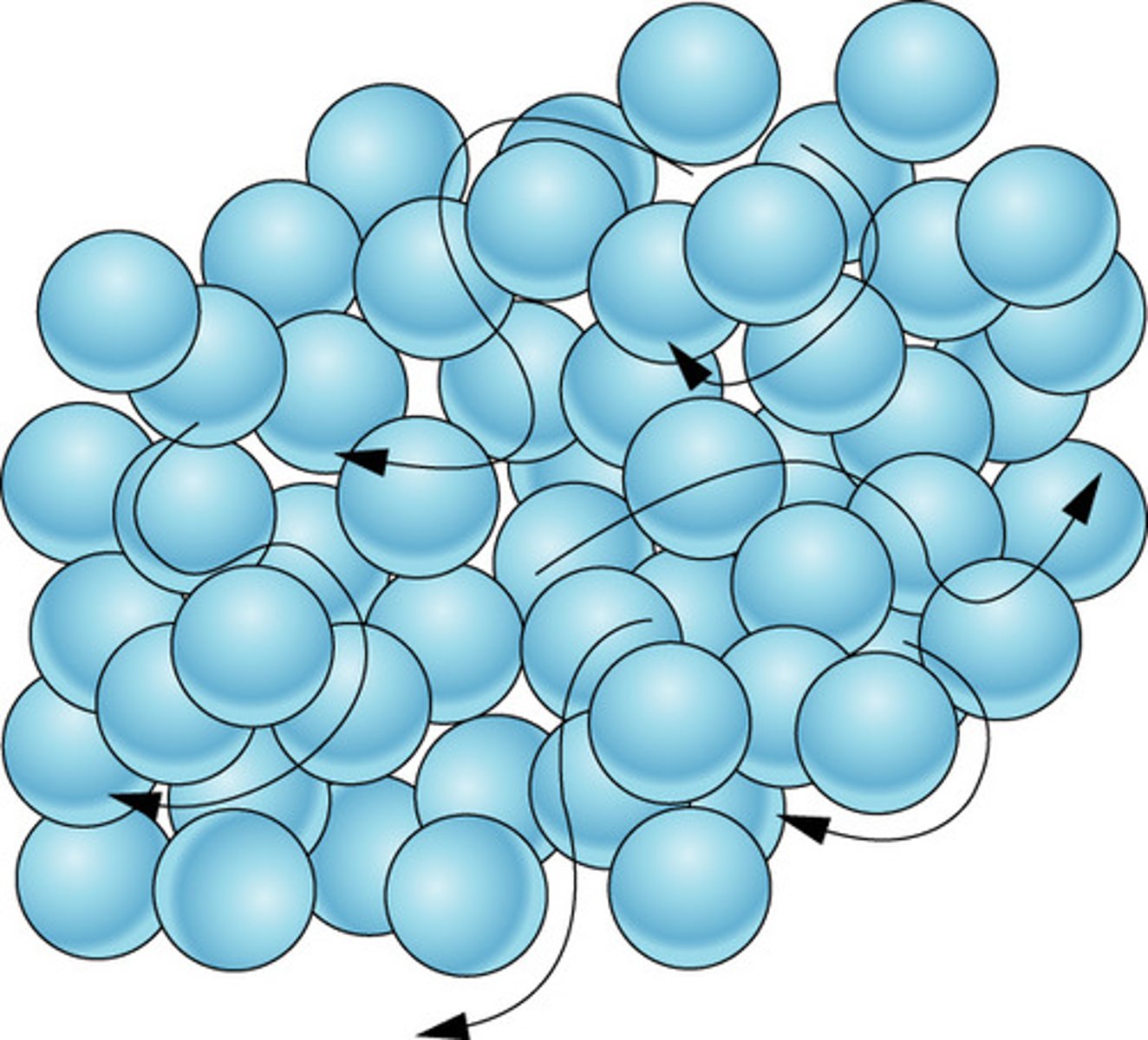
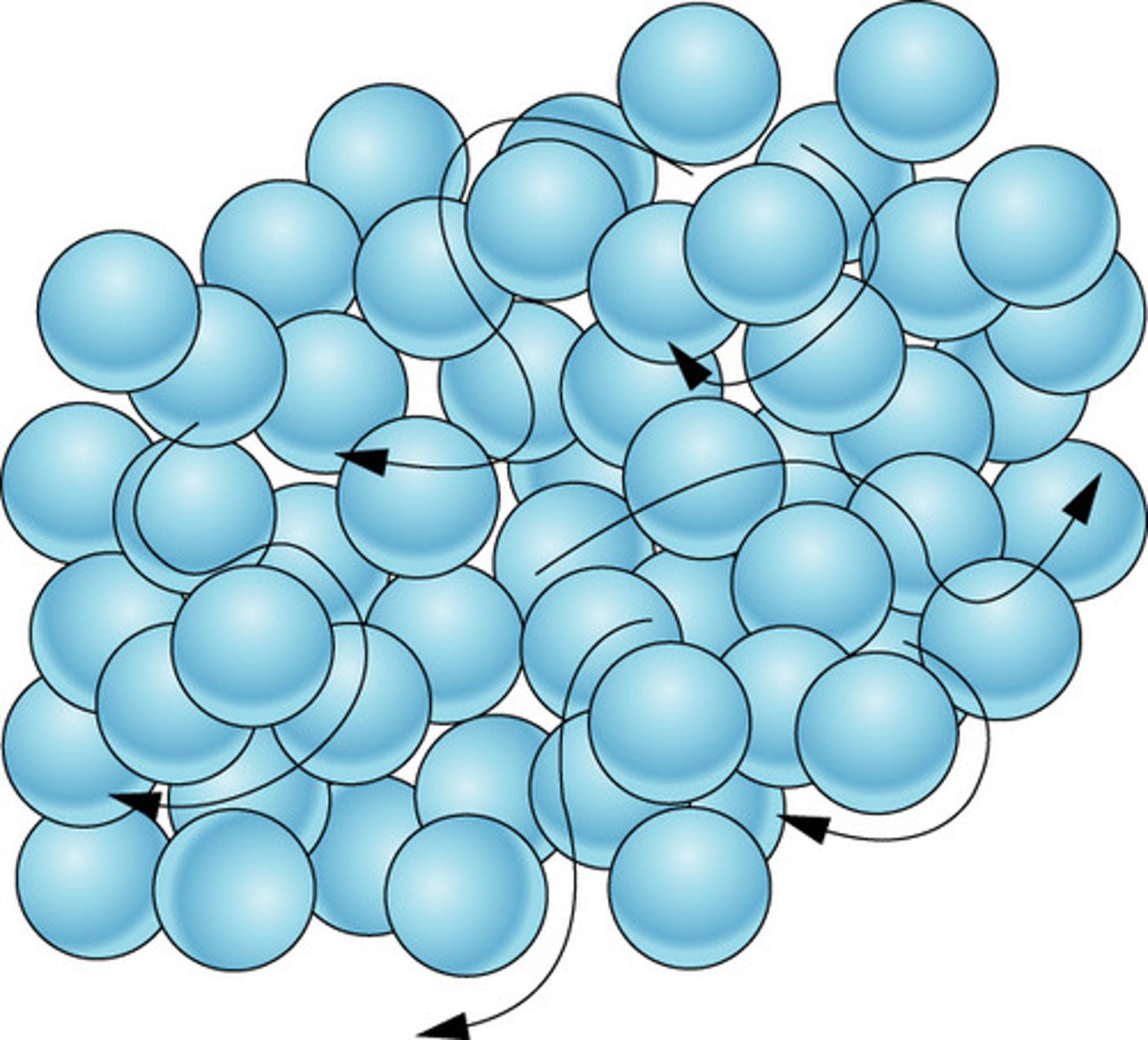
Movement of particles in a liquid
Move around and slide past one another
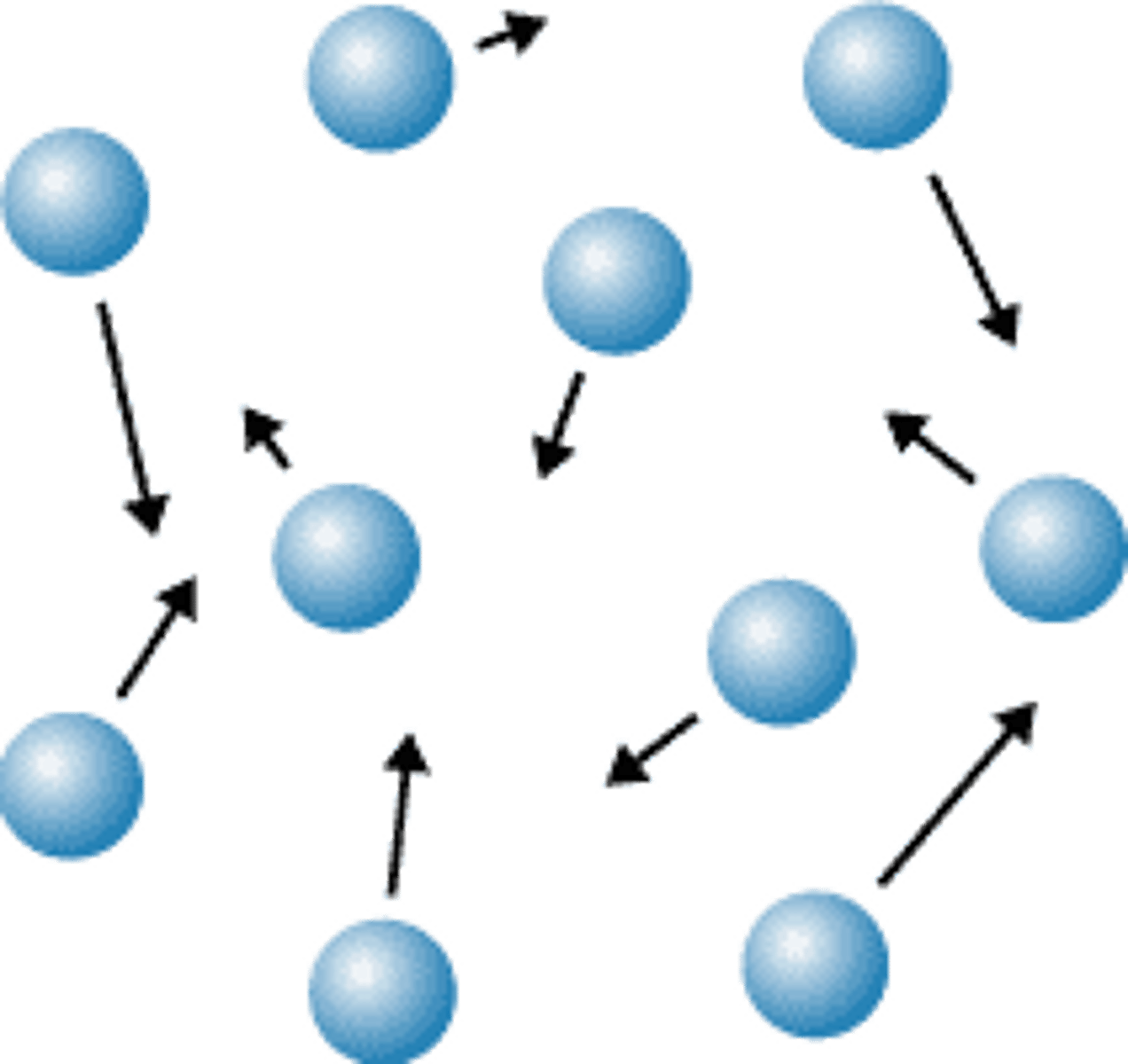
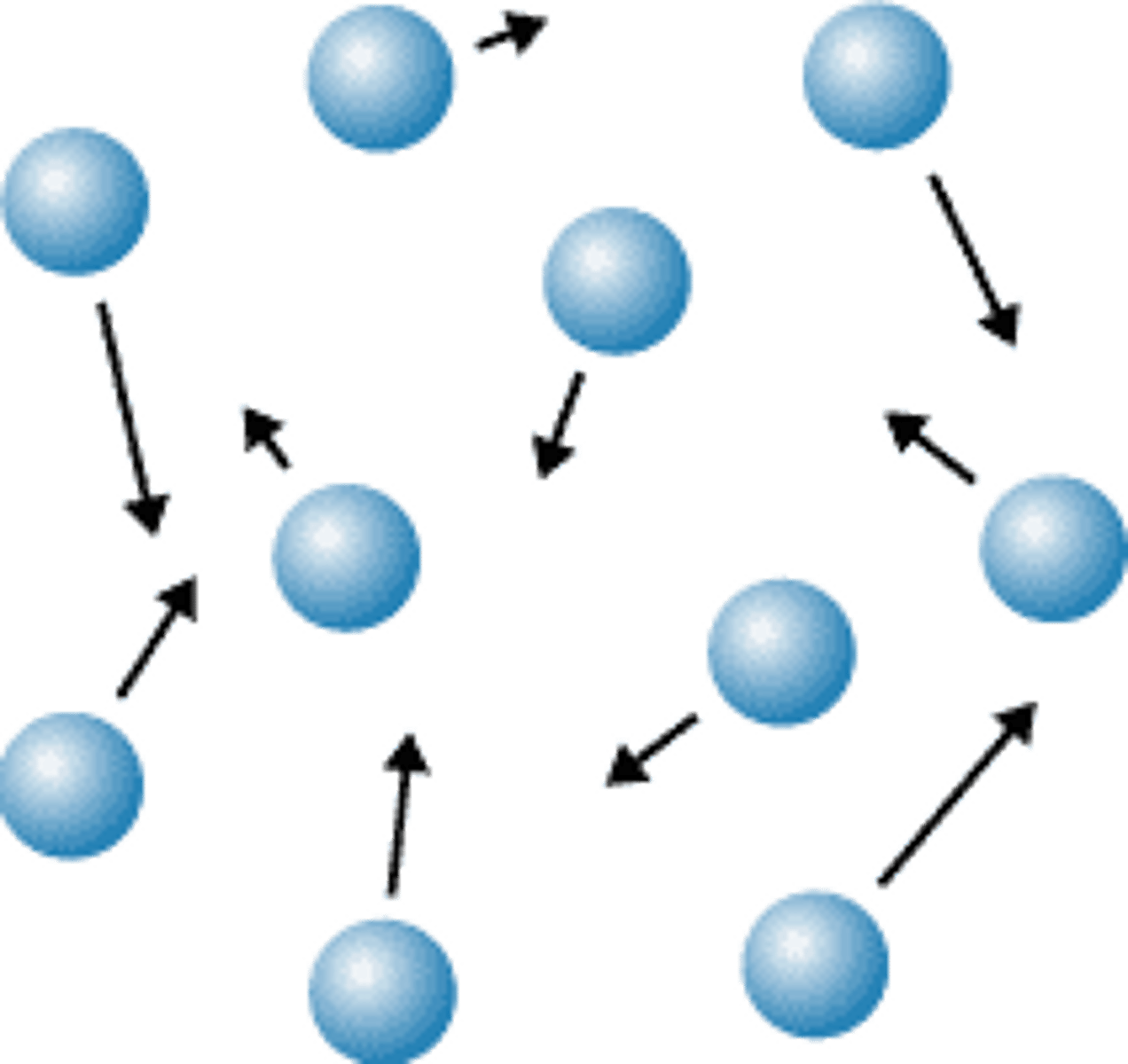
Movement of particles in a gas
Move freely and quickly in all directions
Limitations of particle theory
Does not take into account forces between particles, size of particles, space between particles
Solid --> Liquid
Melting
Liquid --> Solid
Freezing
Liquid --> Gas
Boiling
Gas --> Liquid
Condensing
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space
(s)
Solid
(l)
Liquid
(g)
Gas
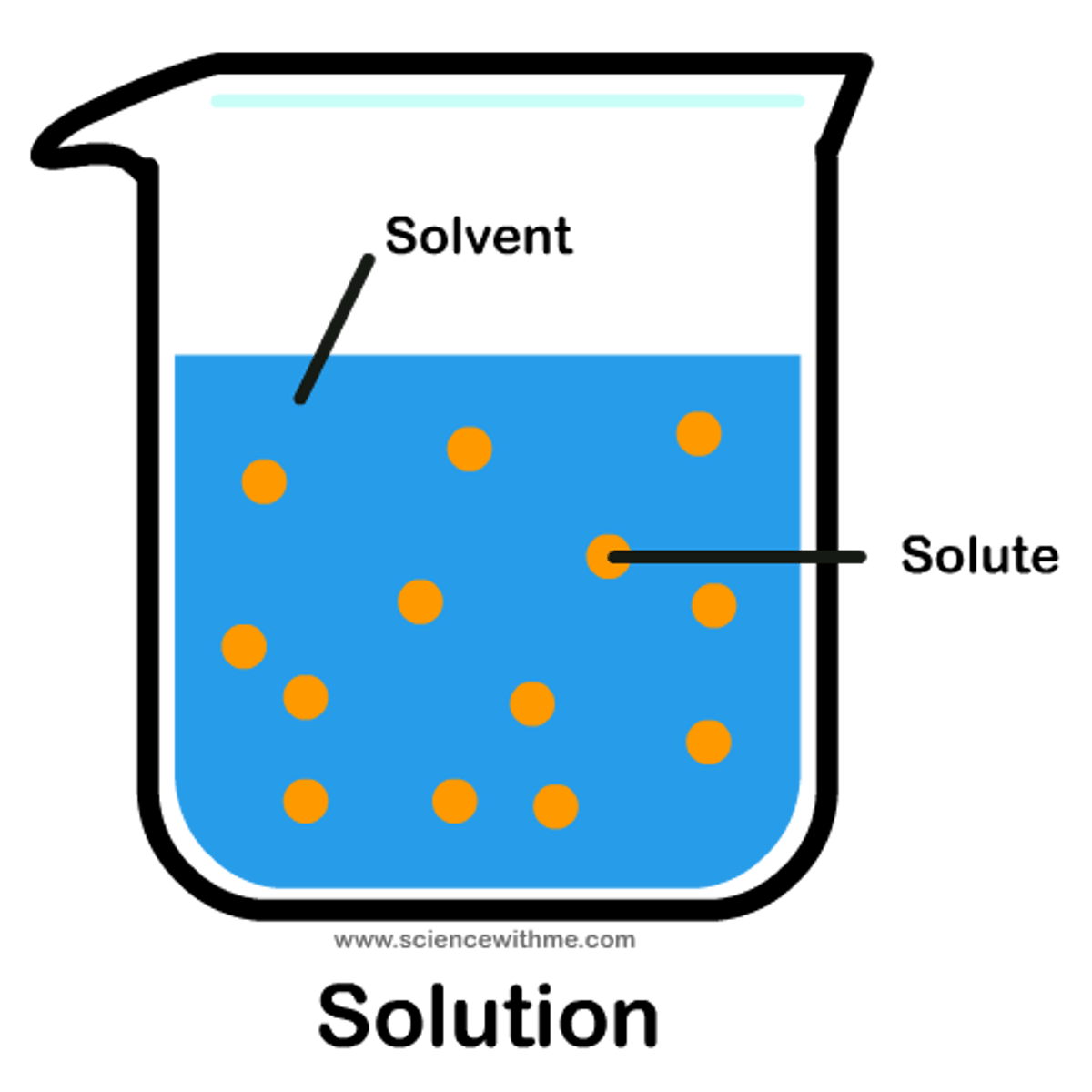
(aq)
aqueous (dissolved in water)
When a substance is heated
Particles stay the same size but move further apart, causing the substance to expand

When a substance cools
Particles stay the same size, but move closer together, causing the substance to contract

Metals
Elements which form positive ions
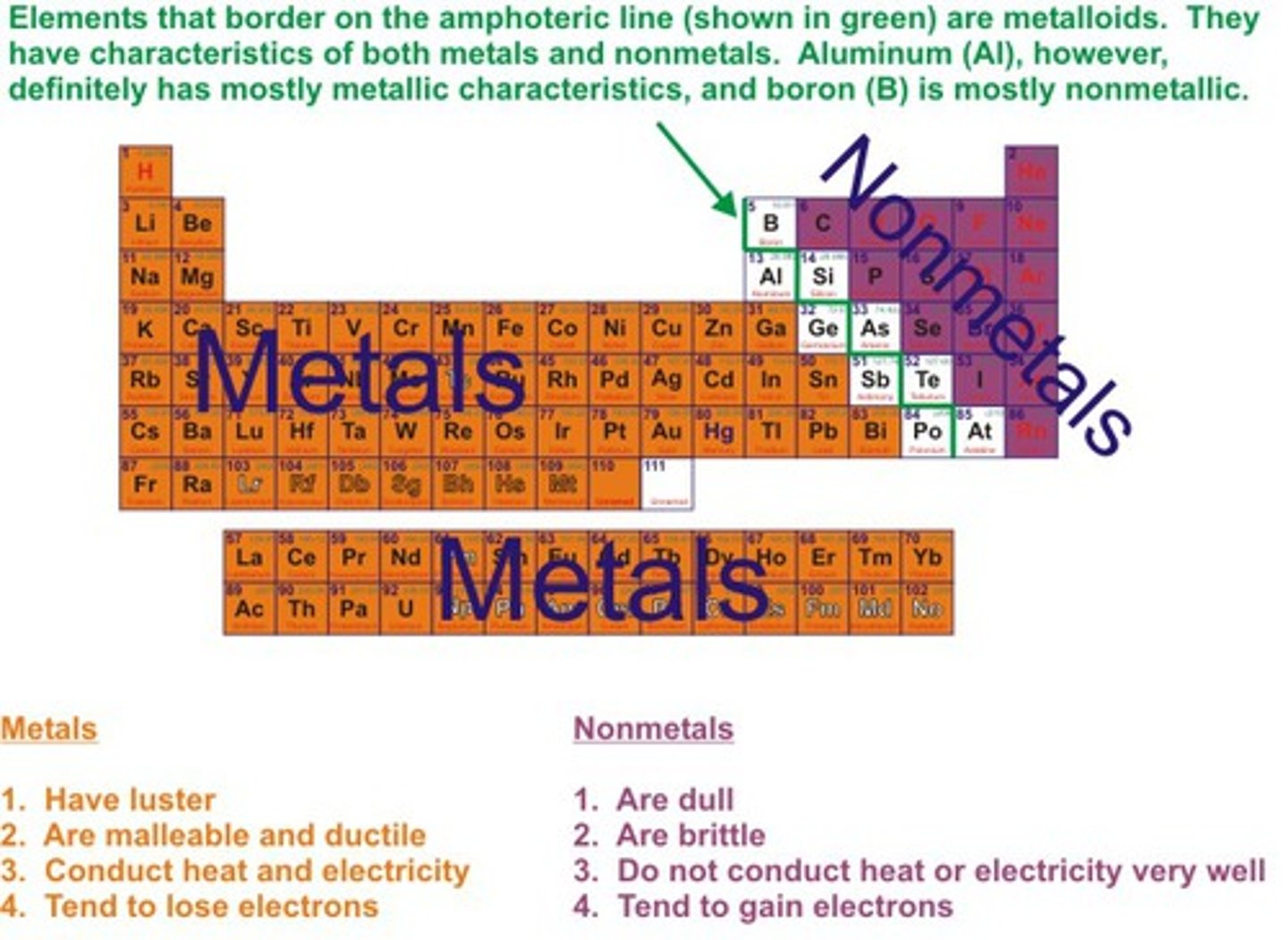
Non-metals
Elements form negative ions
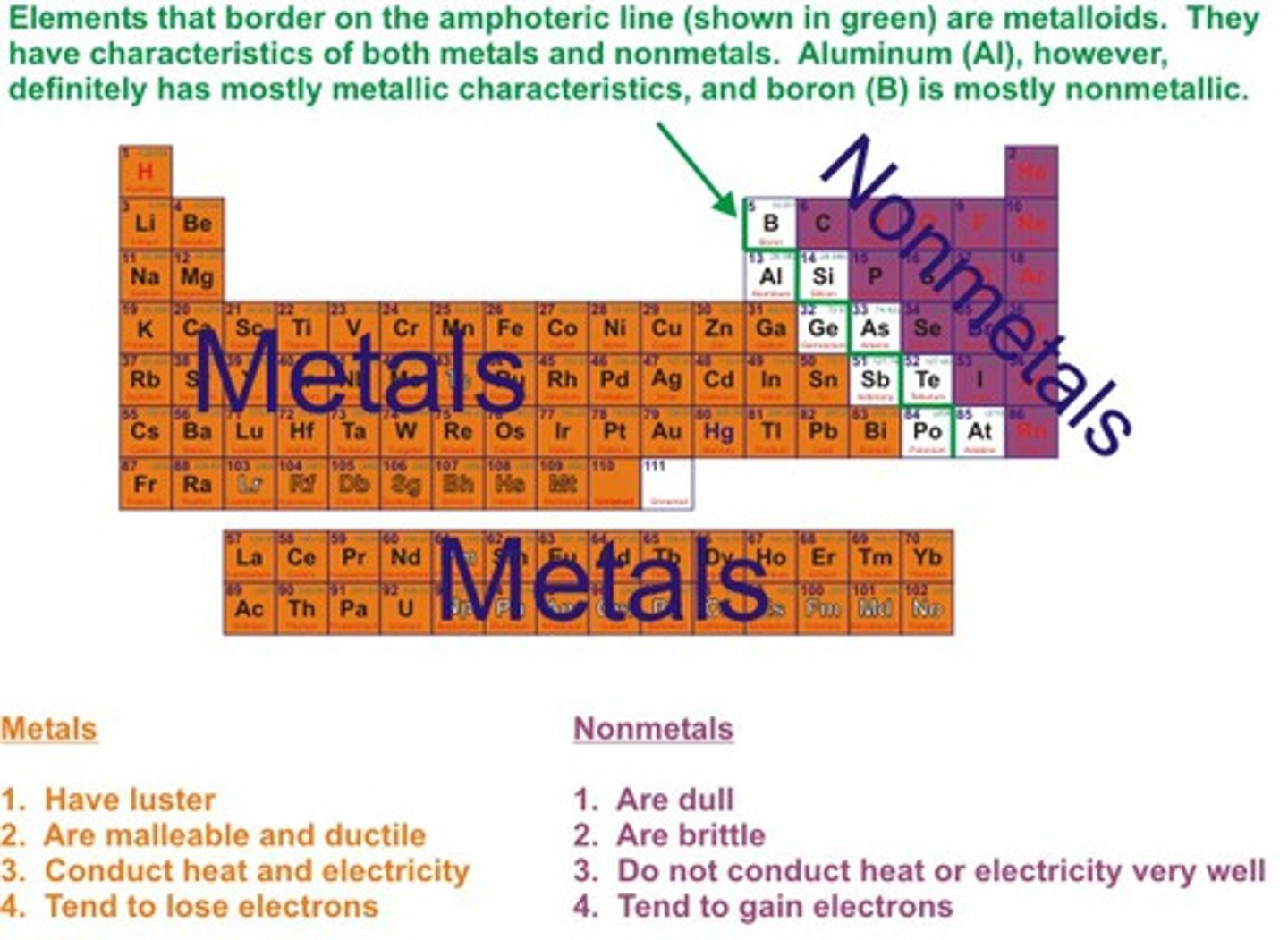
Metals position on periodic table
on the left hand side
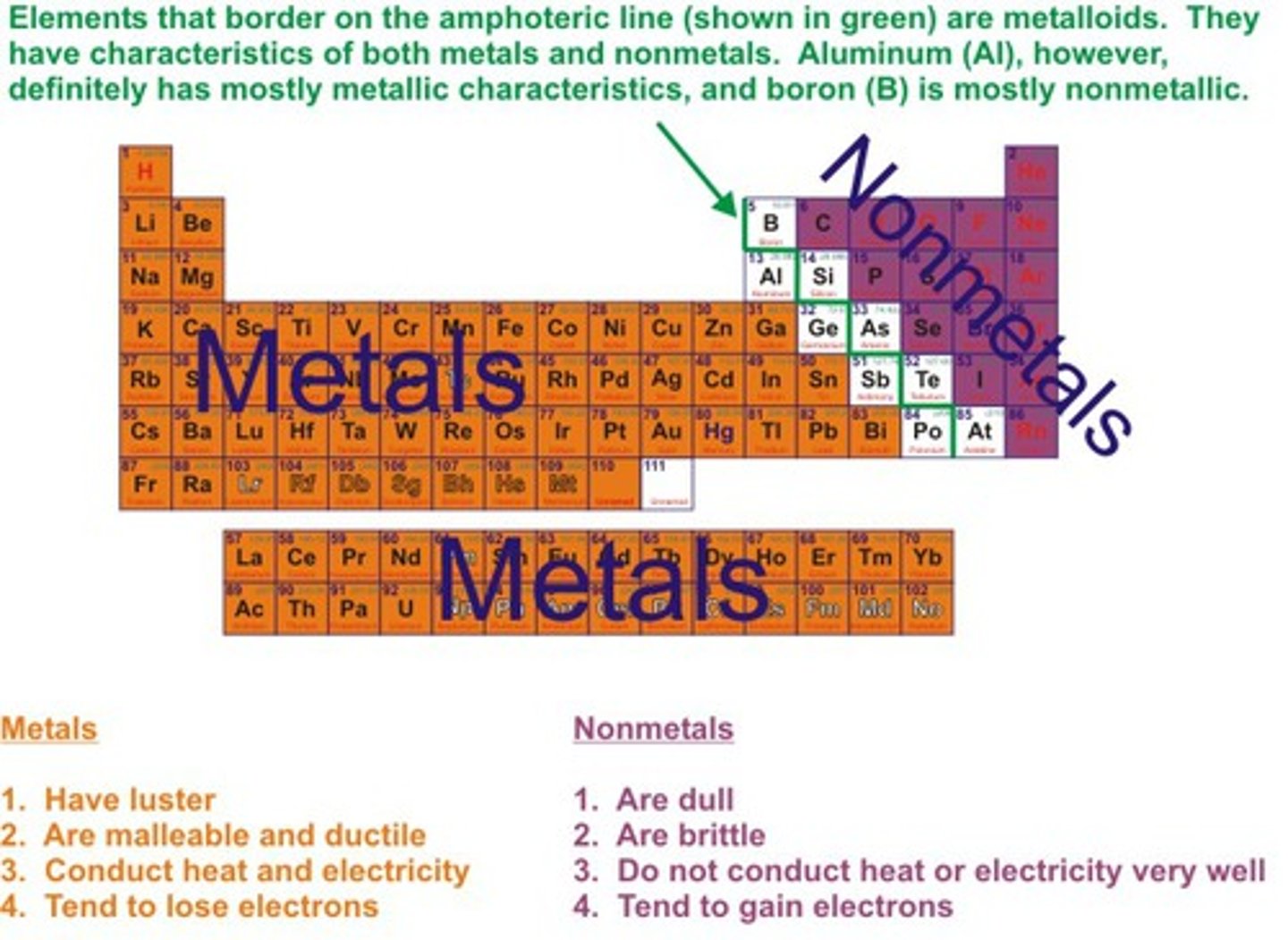
Non-metals position on periodic table
on the right hand side
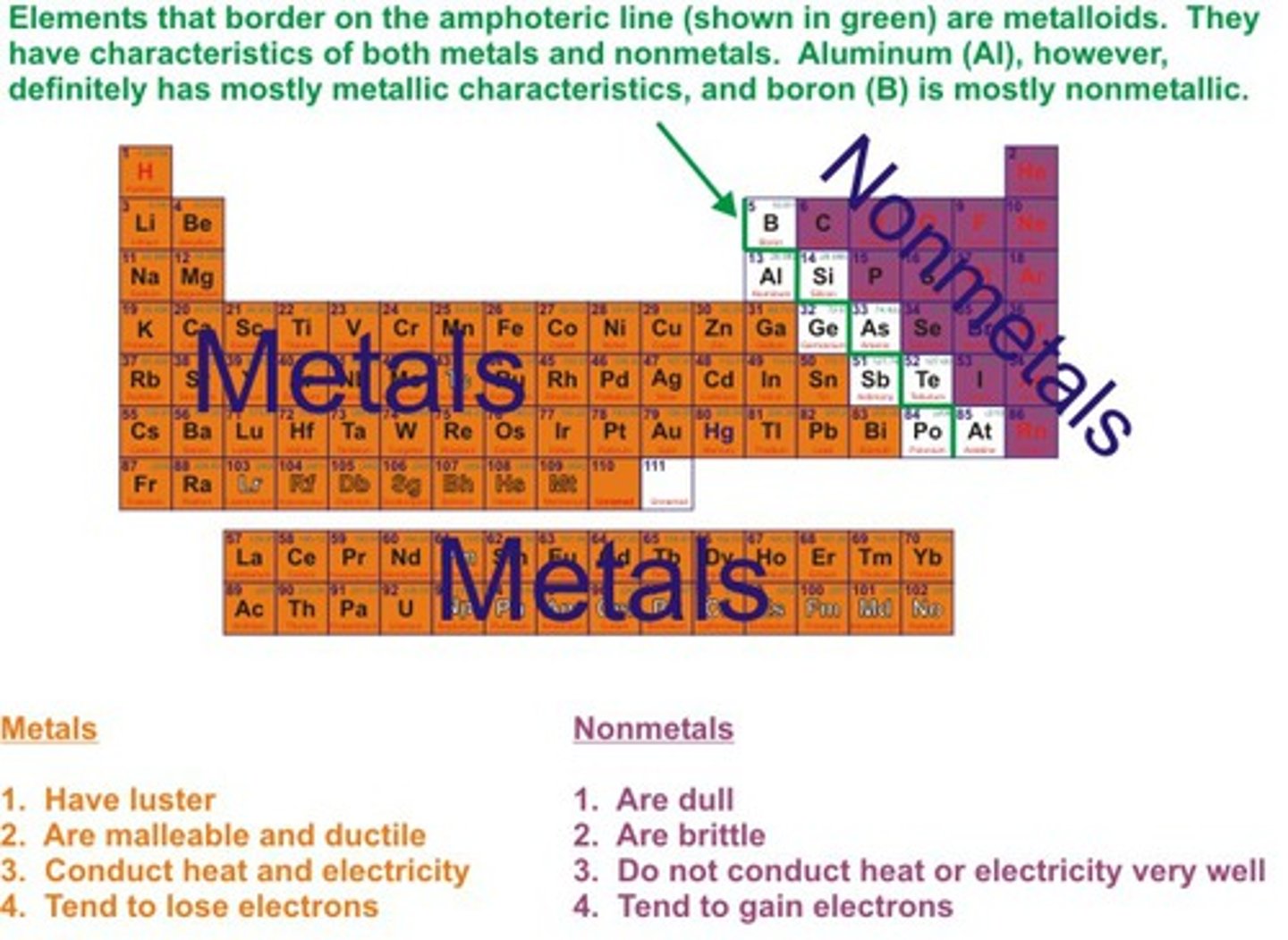
Physical properties of metals
Shiny, malleable, ductile, good conductors of heat and electricity

Physical properties of non-metals
Dull, brittle, insulators of heat and electricty, liquids and gases at room temperature

Malleable
easy to shape or bend

Ductile
Easily stretched into a wire

Good conductor of heat
Allows heat energy to travel through with ease
Good conductor of electricity
Allows electrical current to flow through with ease
Brittle
Easily broken

Insulator of heat
A material that does not allow heat to pass through easily

Insulator of electricity
A material that does not allow electric current to pass through easily
pH of metal oxides
Acidic
pH of non-metal oxides
Basic
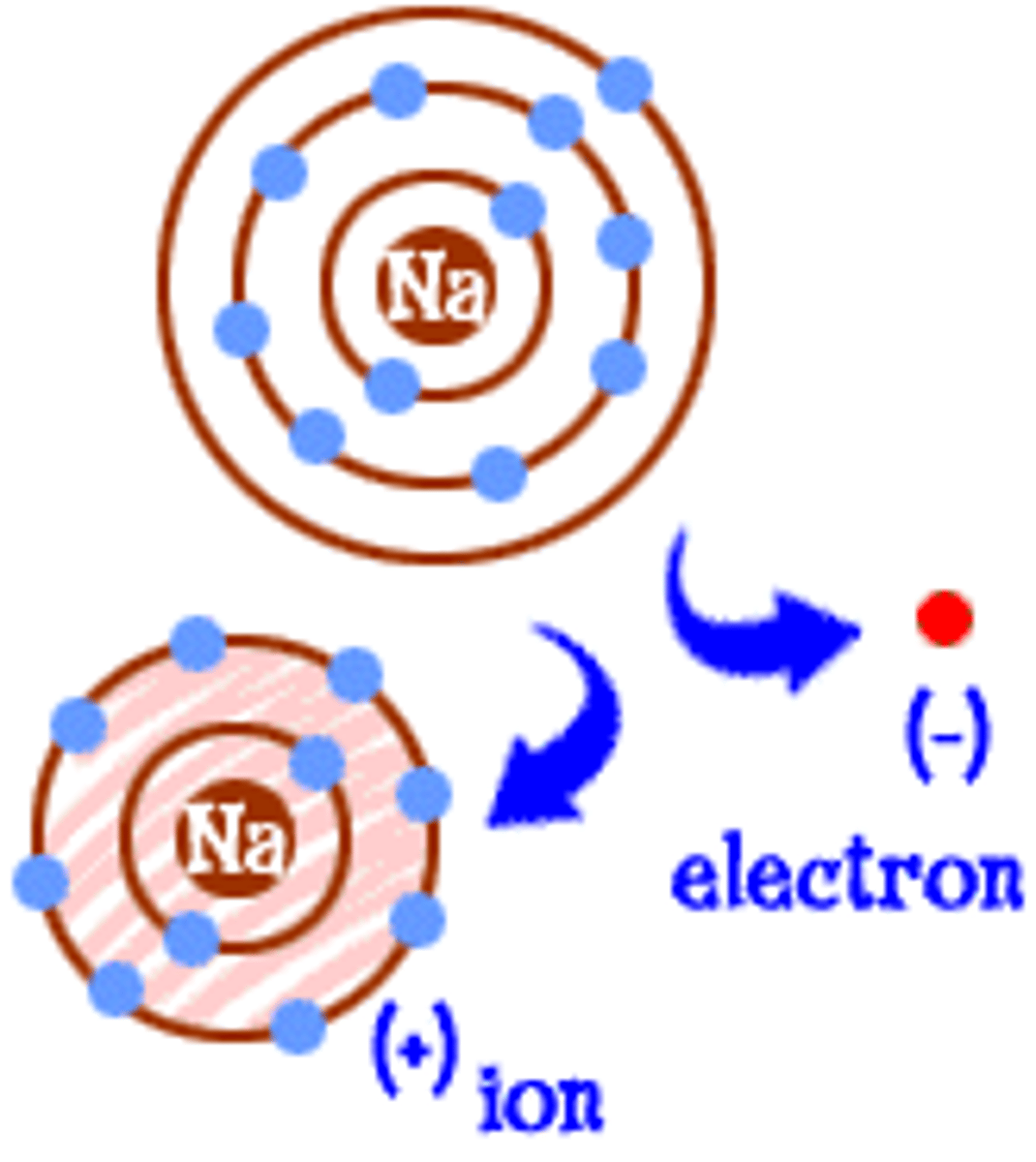
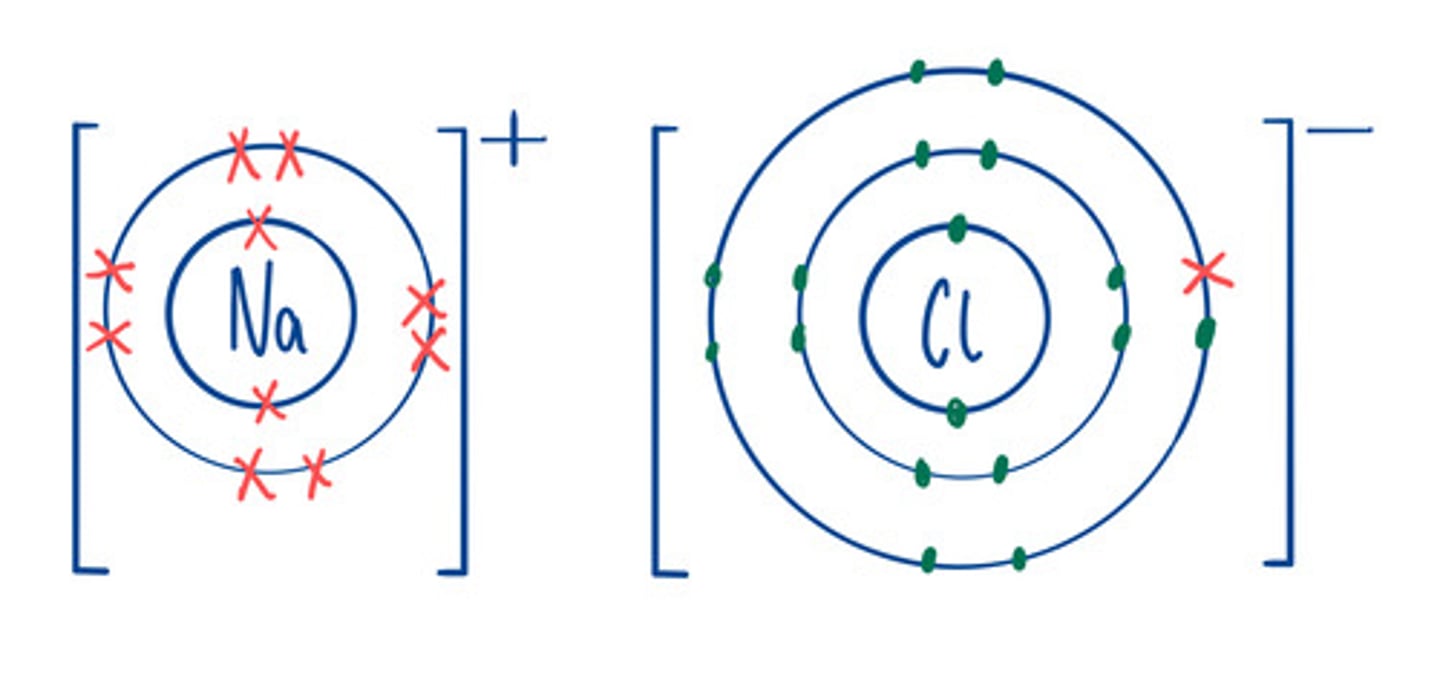
Ion
An atom or group of atoms that has lost or gained electrons and therefore a positive or negative charge.
Polyatomic ion
An ion that is made of more then one atom
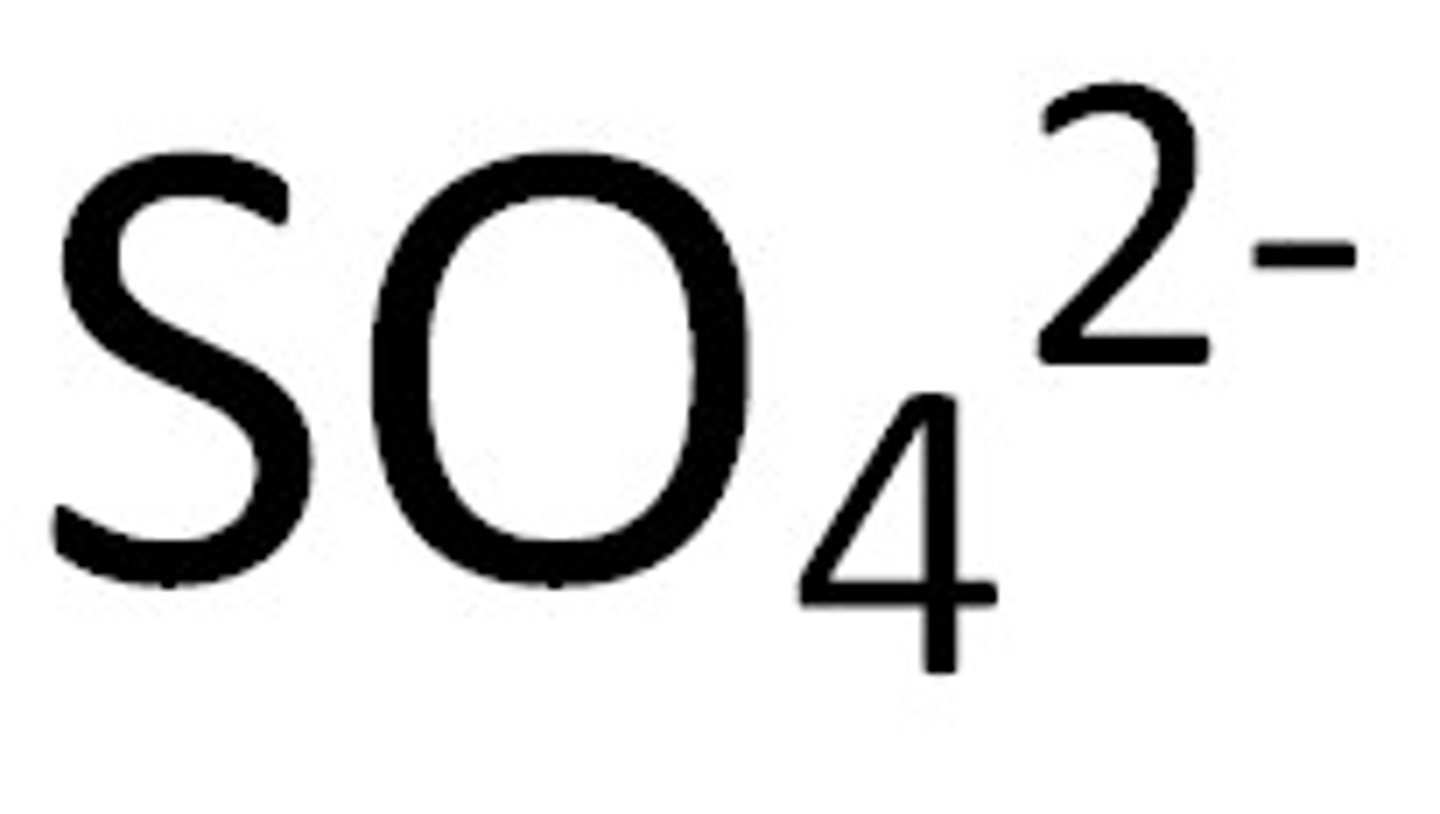
Metal ion
an atom which has lost electrons forming a positive ion
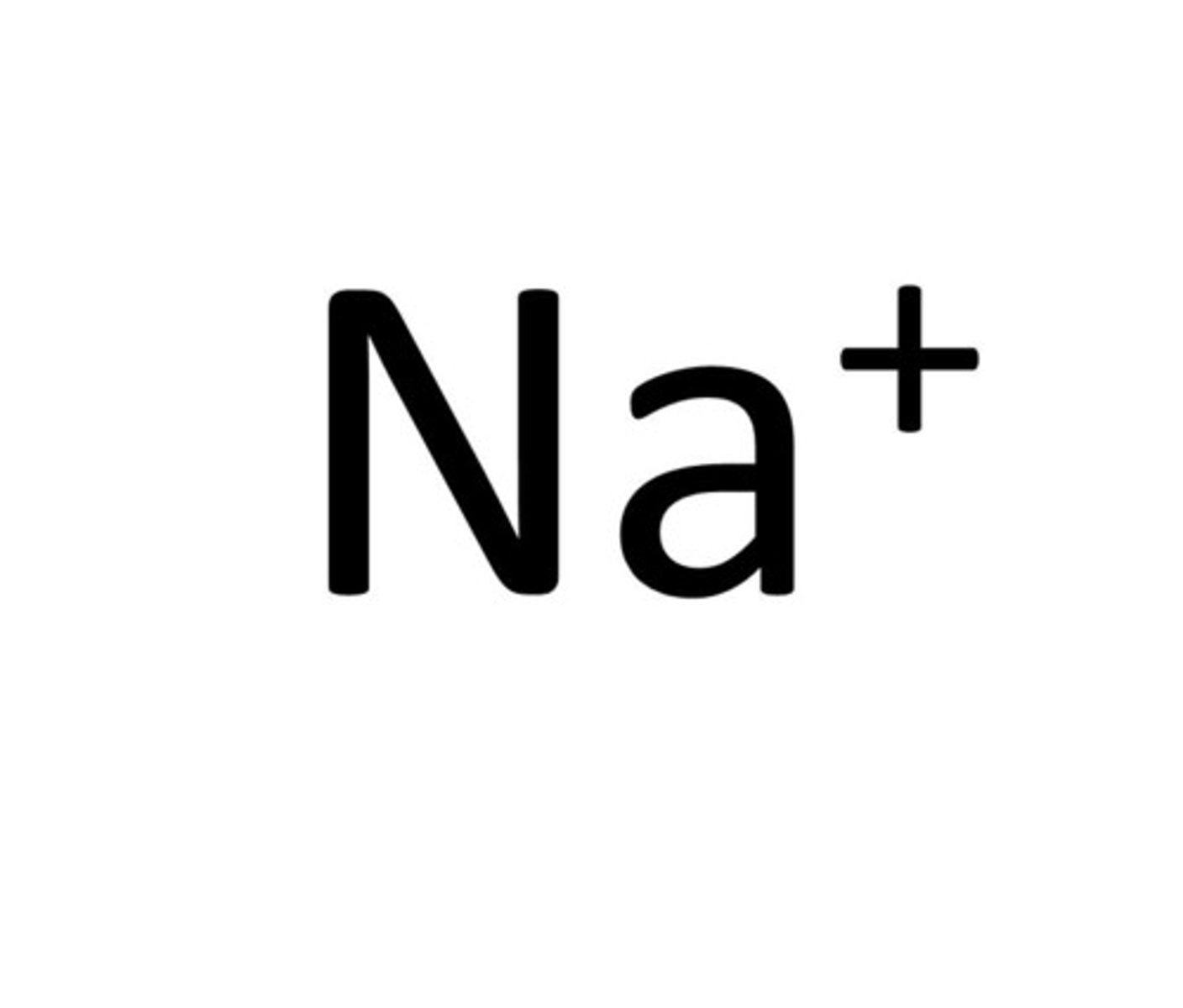
Non-metal ion
an atom which has gained electrons forming negative ions.

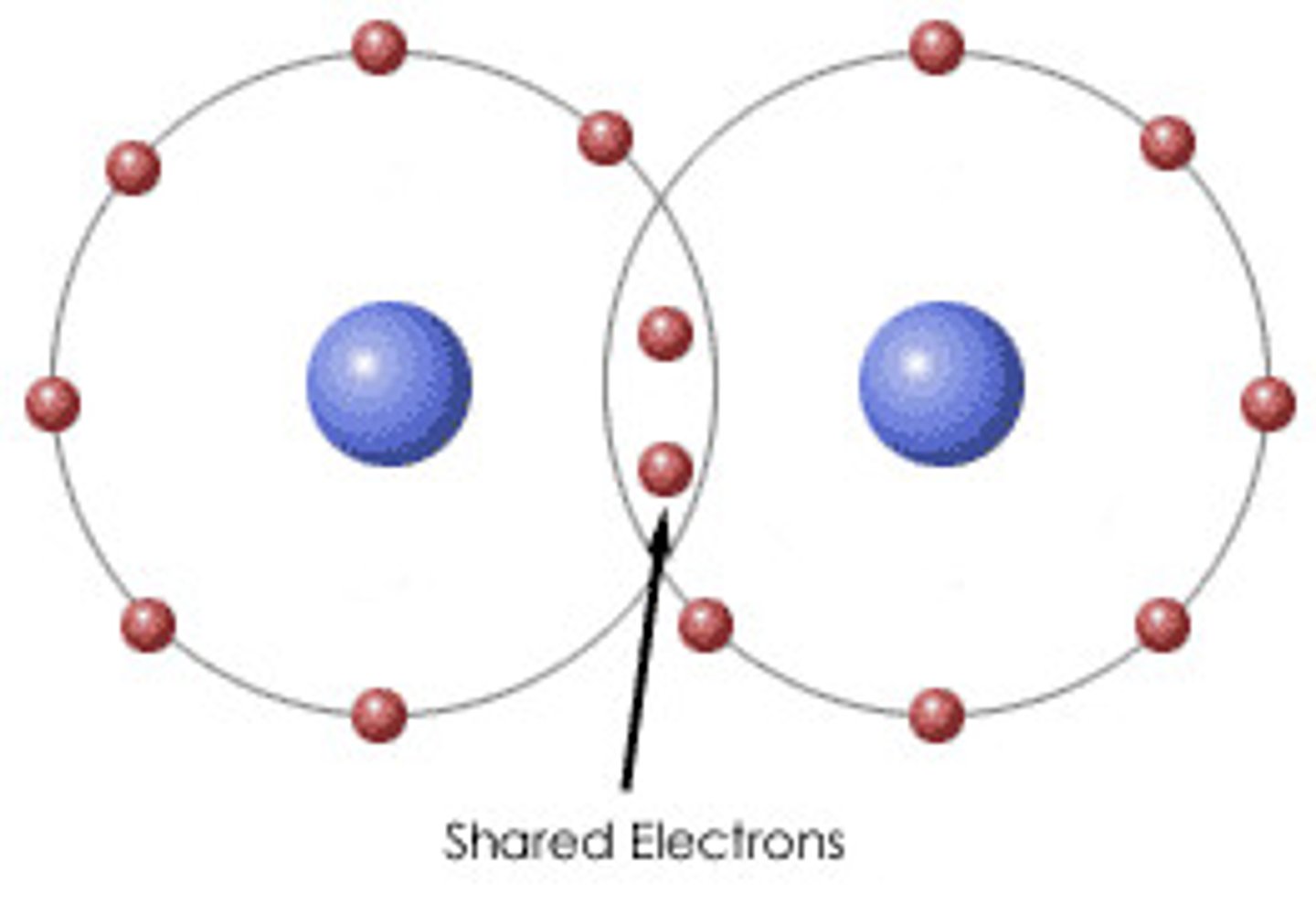
Covalent bond
a shared pair of electrons
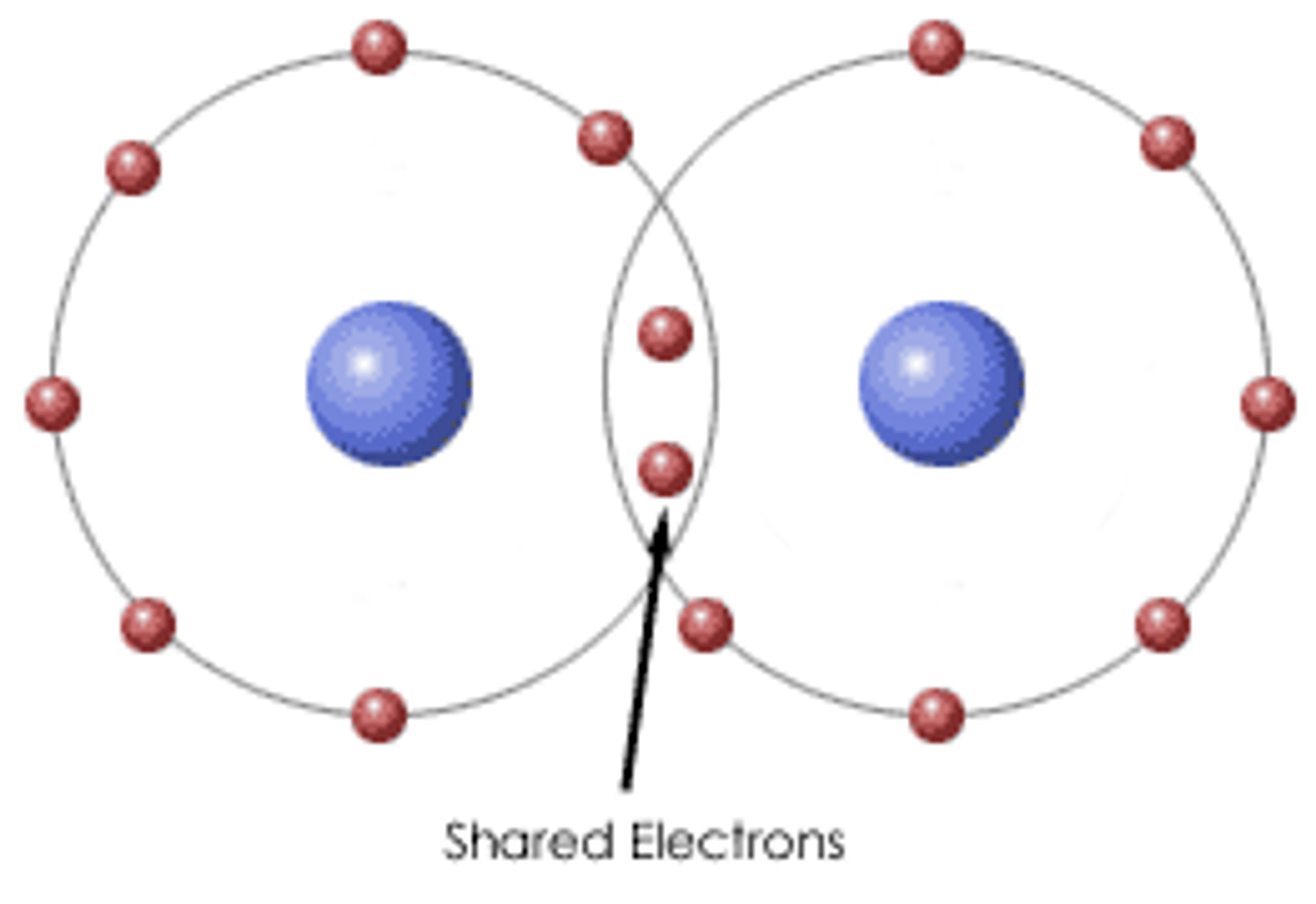
Molecule
two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
Metallic bonding
Positively charged metal ions are surrounded by delocalised outer electrons
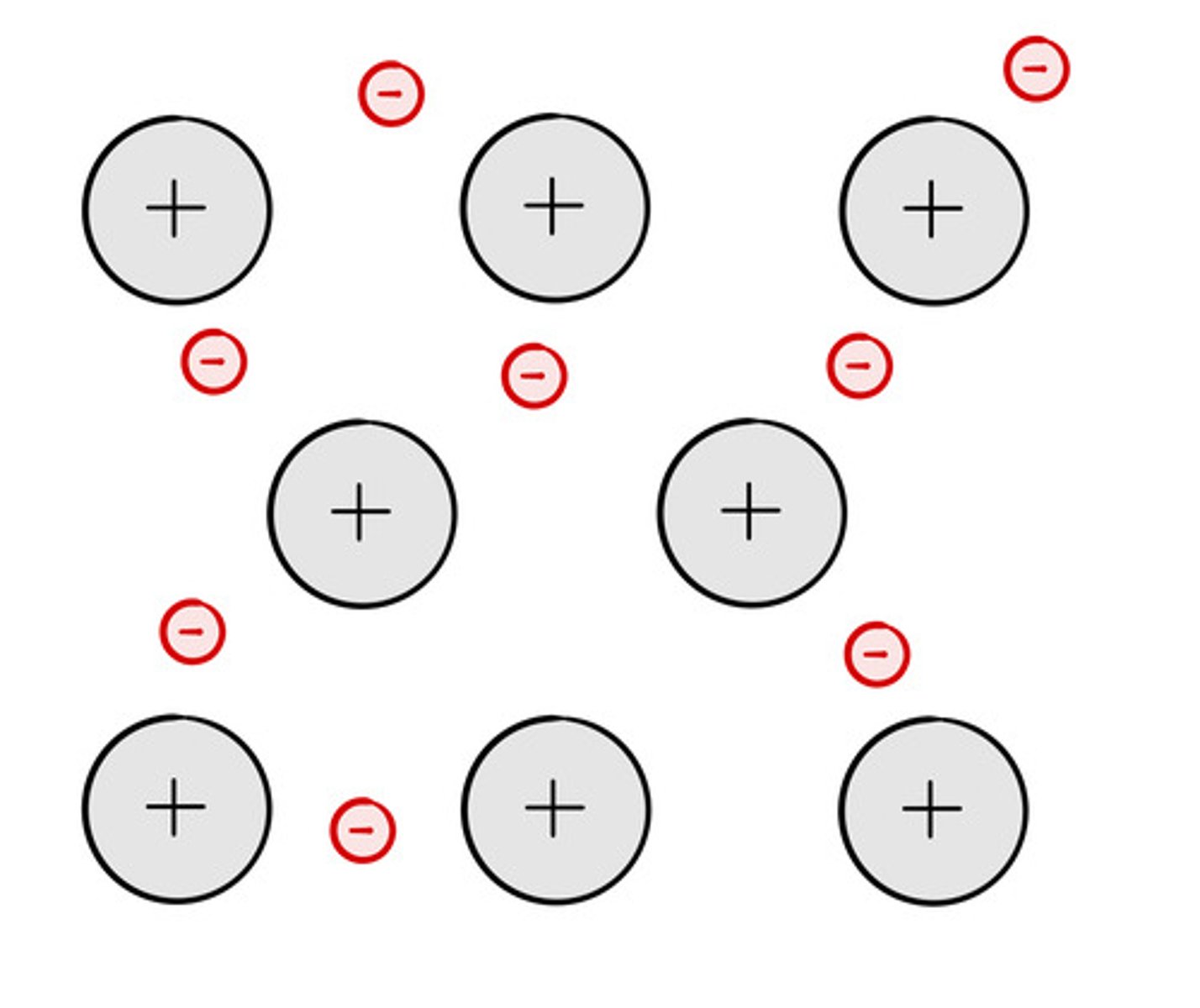
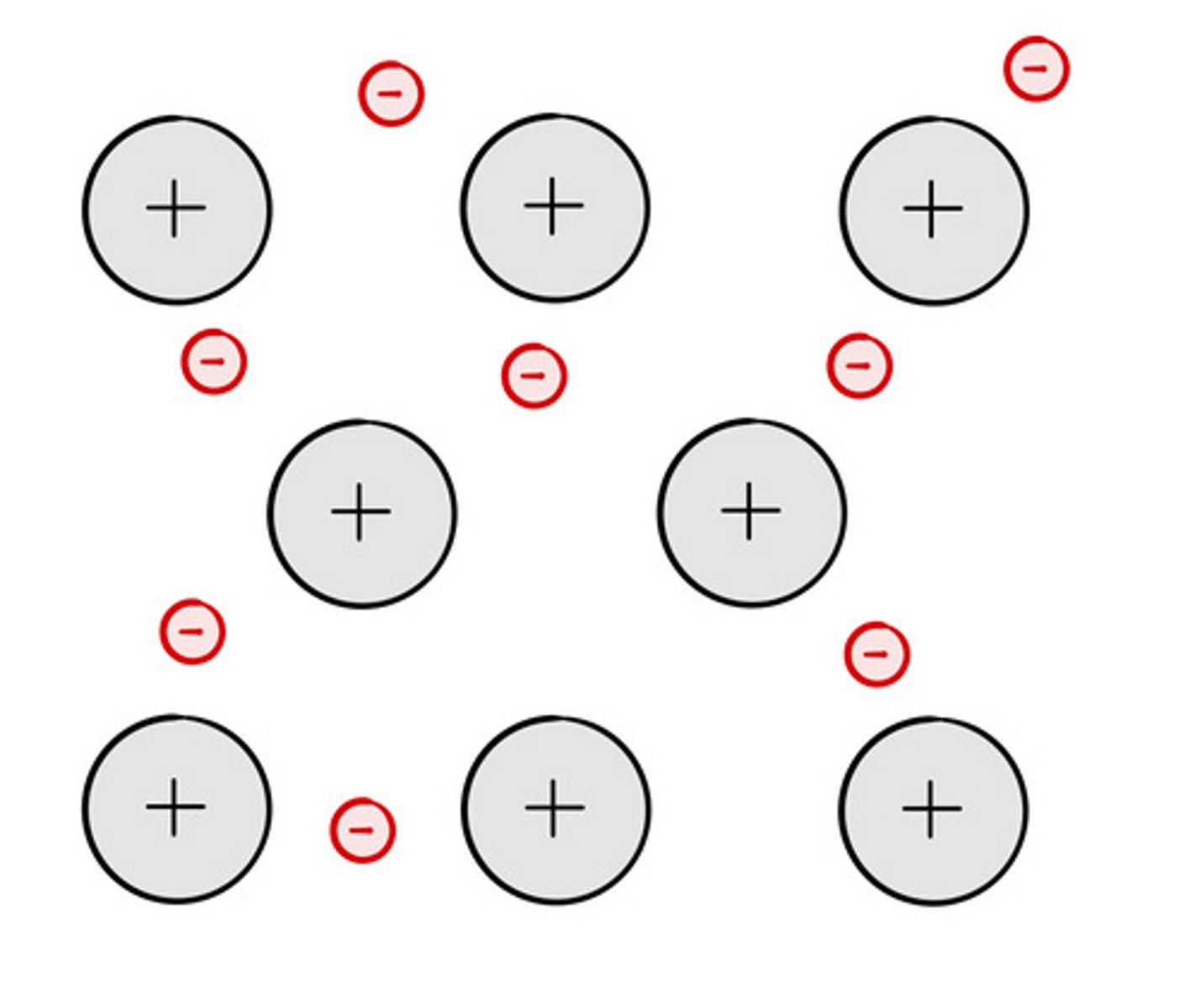
Particles in an ionic compound
Positive and negative ions
Particle in a simple covalent substance
Molecules
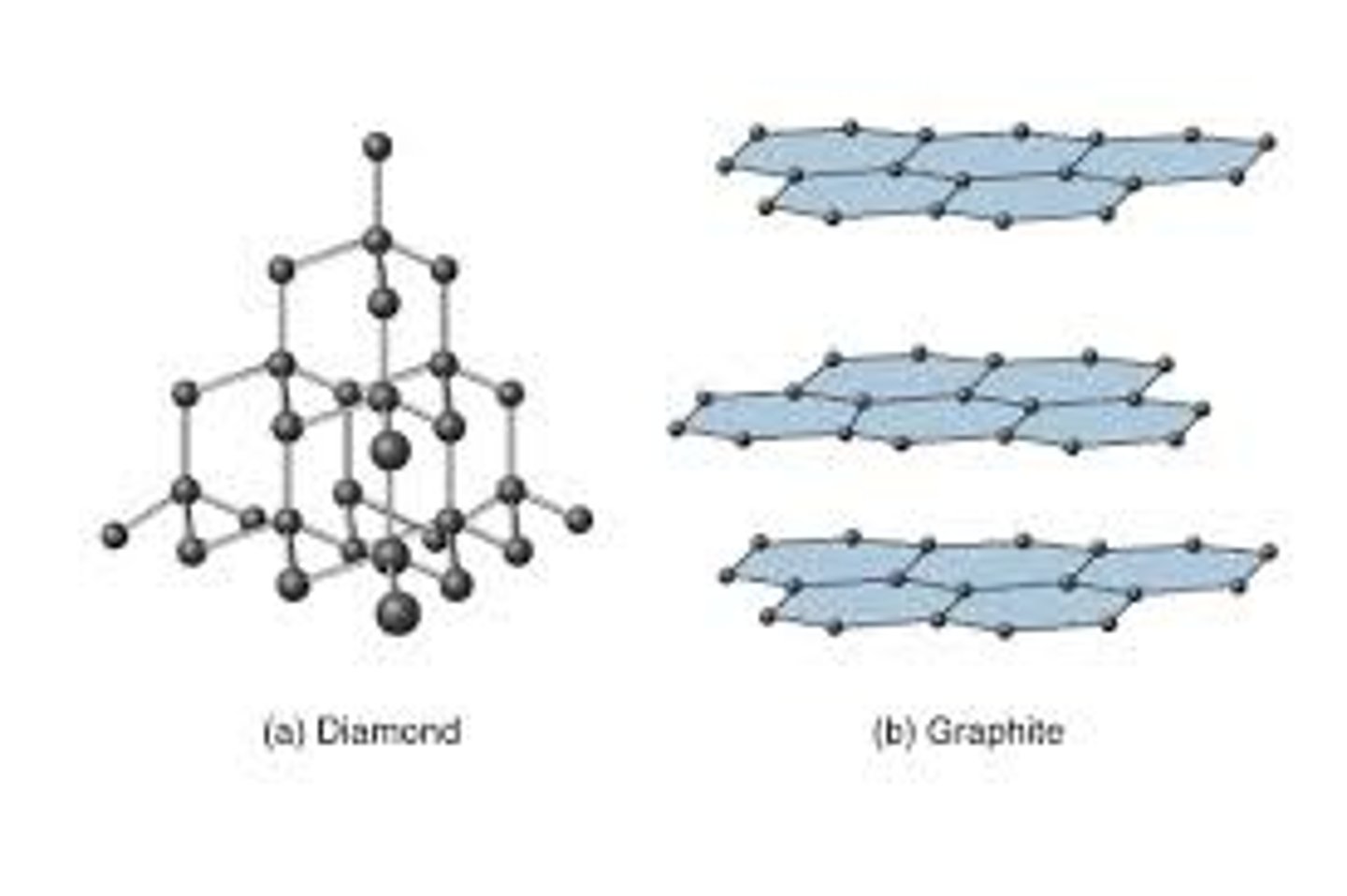
Particles in a giant covalent substance
Covalently bonded atoms
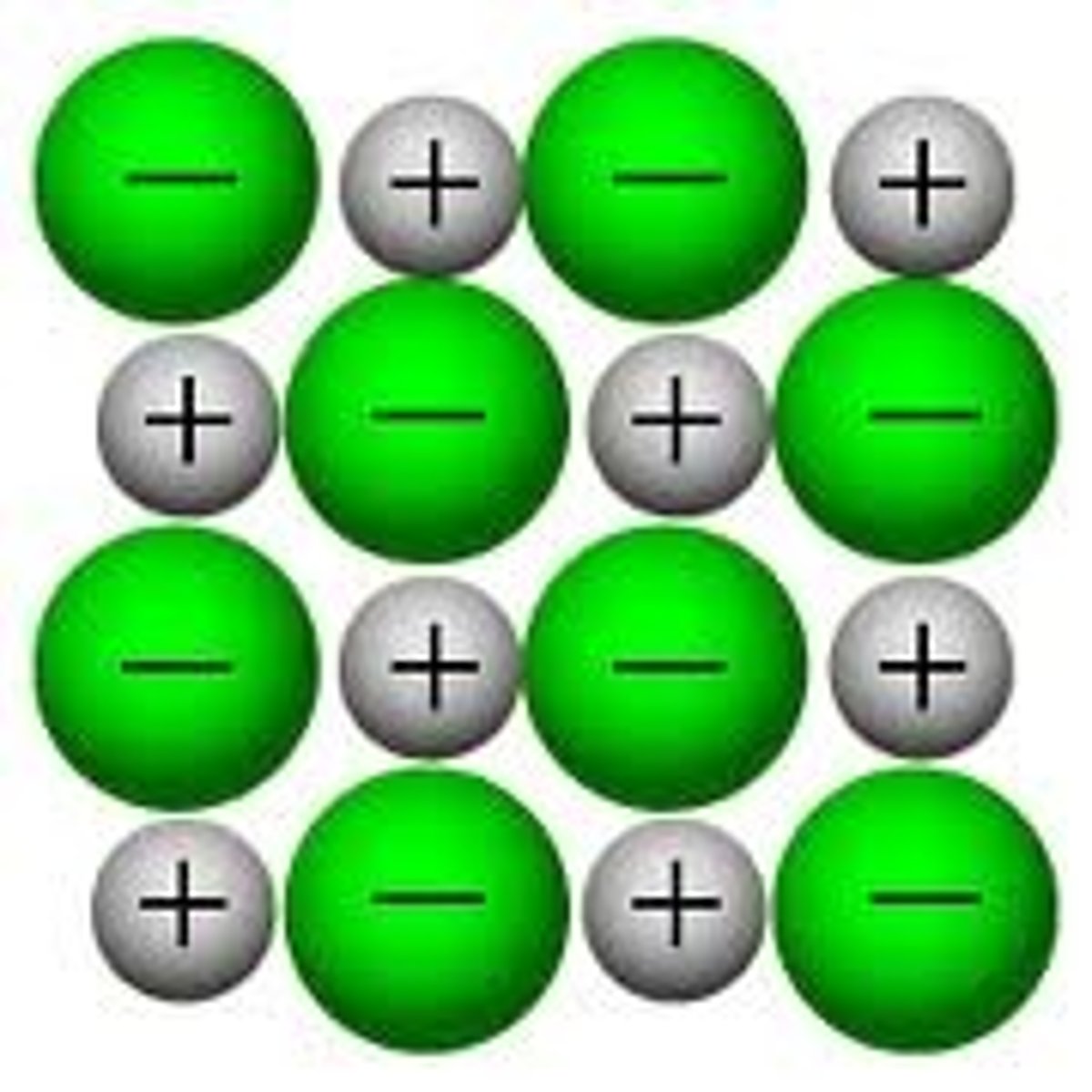
Particles in a metallic substance
Positive ions and delocalised electrons
Electrostatic forces of attraction
Strong forces of attraction between oppositely charged particles
Elements that form ionic compounds
Metals and non-metals together
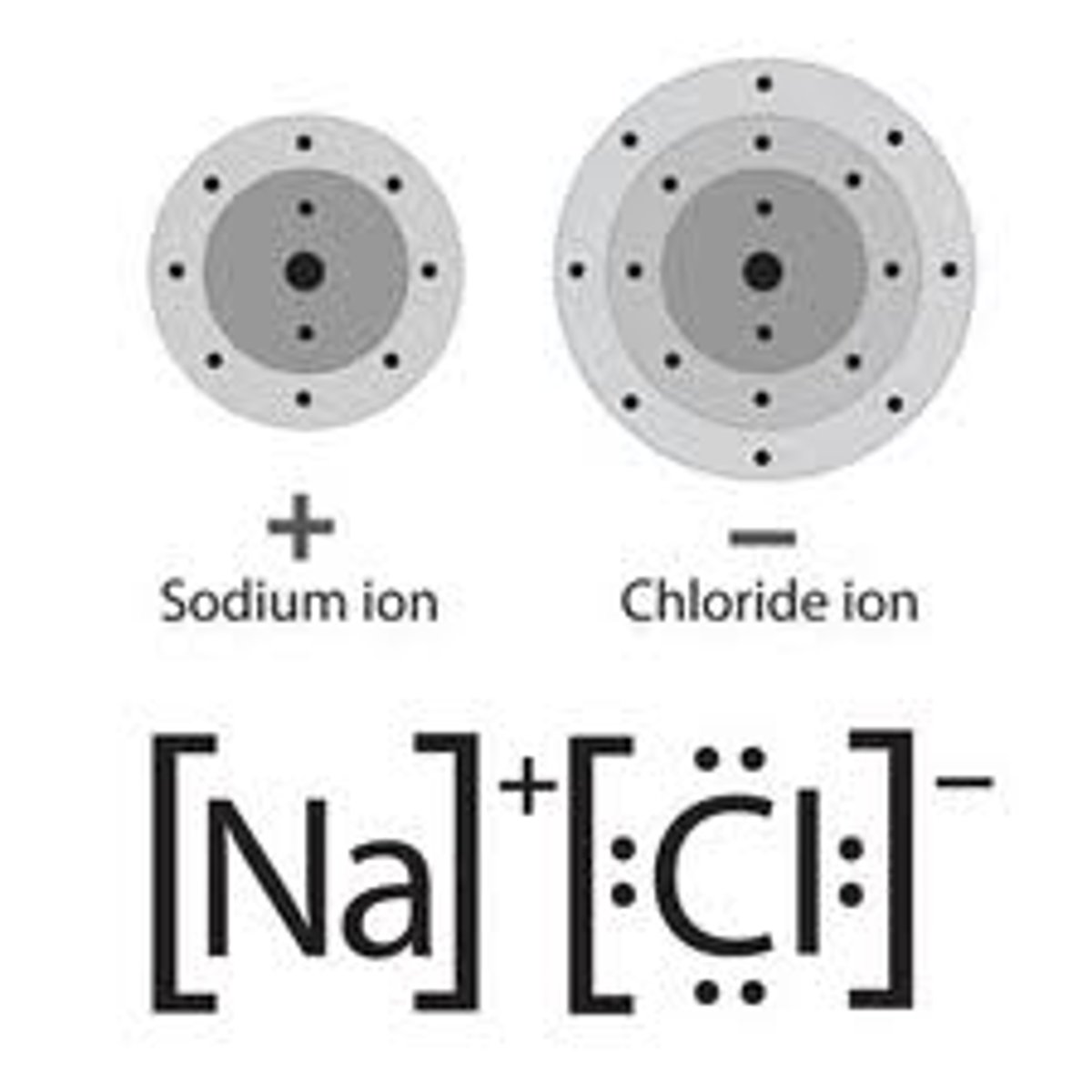
Elements that form covalent bonds
non-metals
Elements that form metallic bonds
metals and alloys

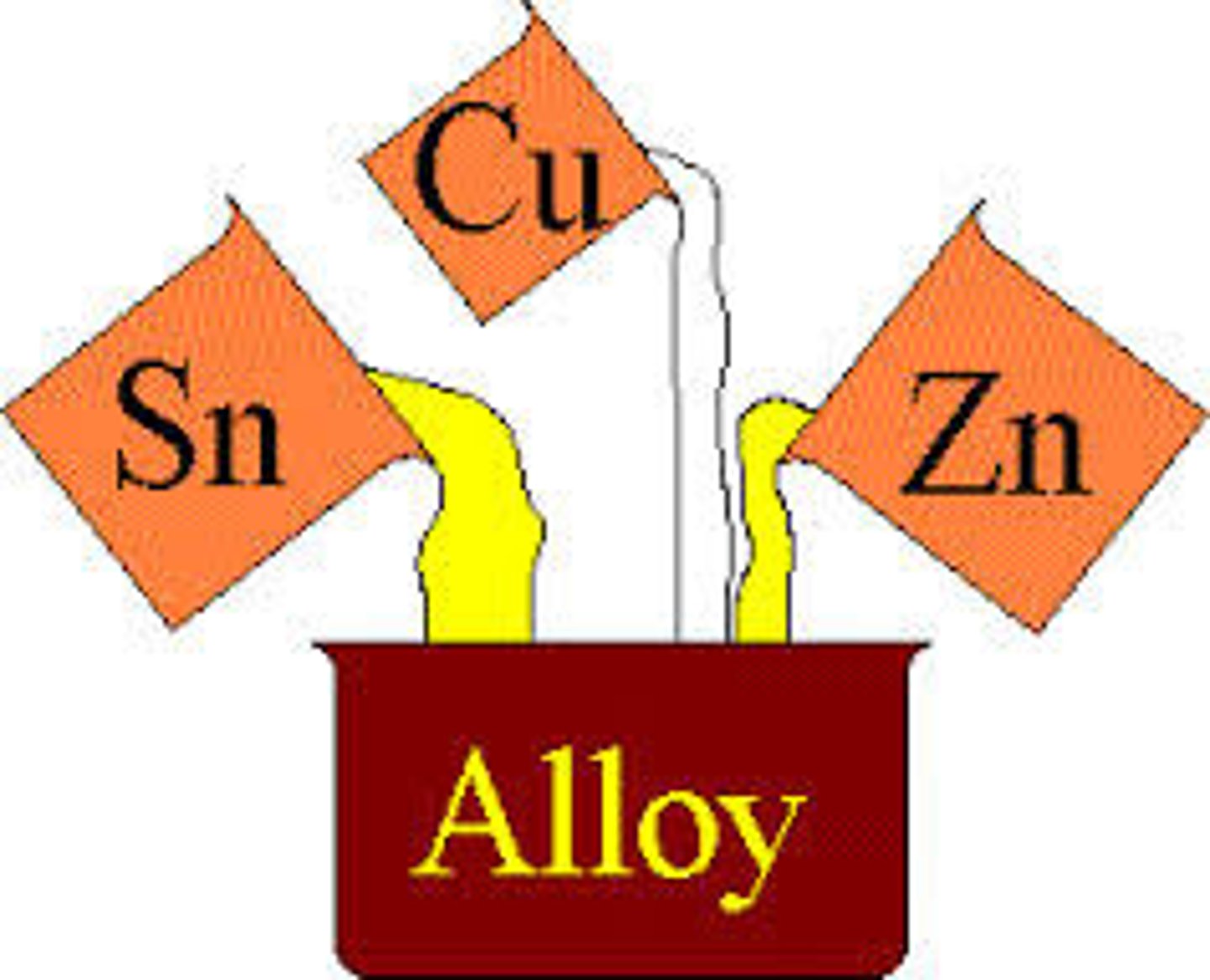
Alloy
A metal mixed with other elements
Formation of metal ions
Atoms lose outer electrons
Metals
Elements that form positive ions
Formation of non-metal ions
Atoms gain electrons
Charge on non-metal ions
Negative
Group 1 ions charge
+1
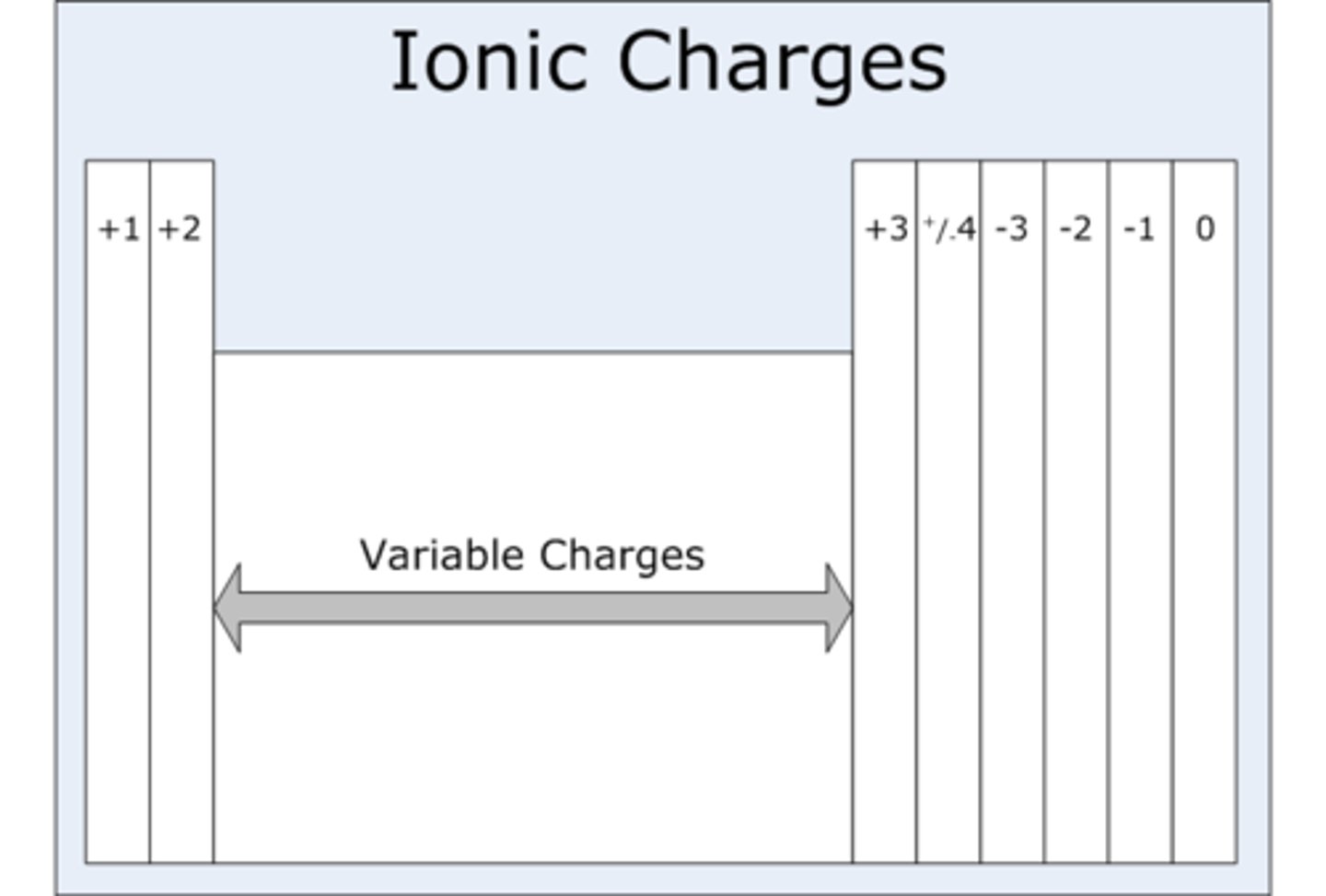
Group 2 ions charge
+2
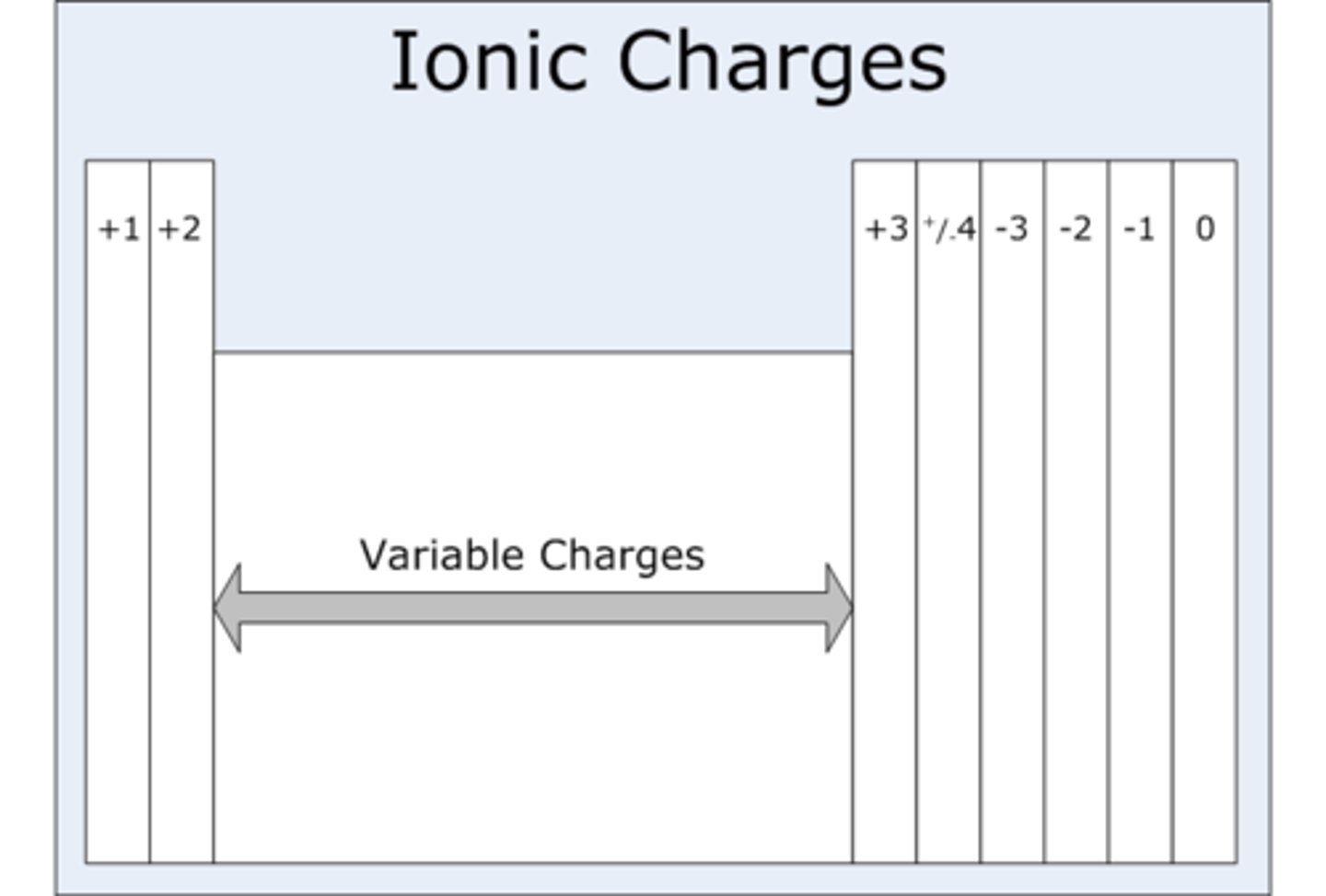
Group 6 (IUPAC group 16) ions charge
-2
Group 7 (IUPAC group 17) ions charge
-1
Electron structure of ions
Same as the nearest noble gas
Giant structure
A huge 3D network of atoms or ions
lattice
Regular arrangement of particles.
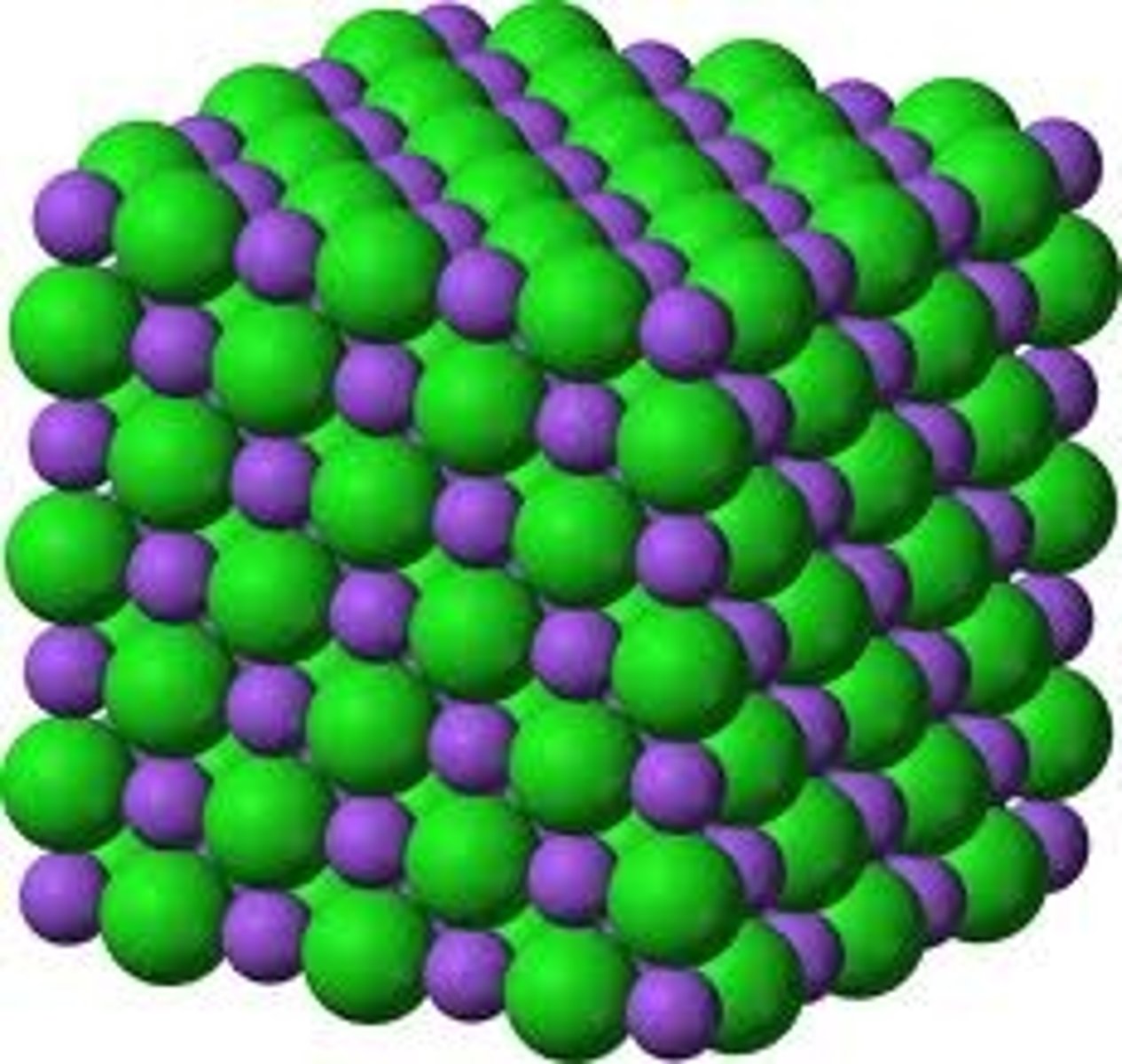
Giant ionic lattice
A huge, 3D, regular structure of oppositely charged ions, held together by electrostatic forces.
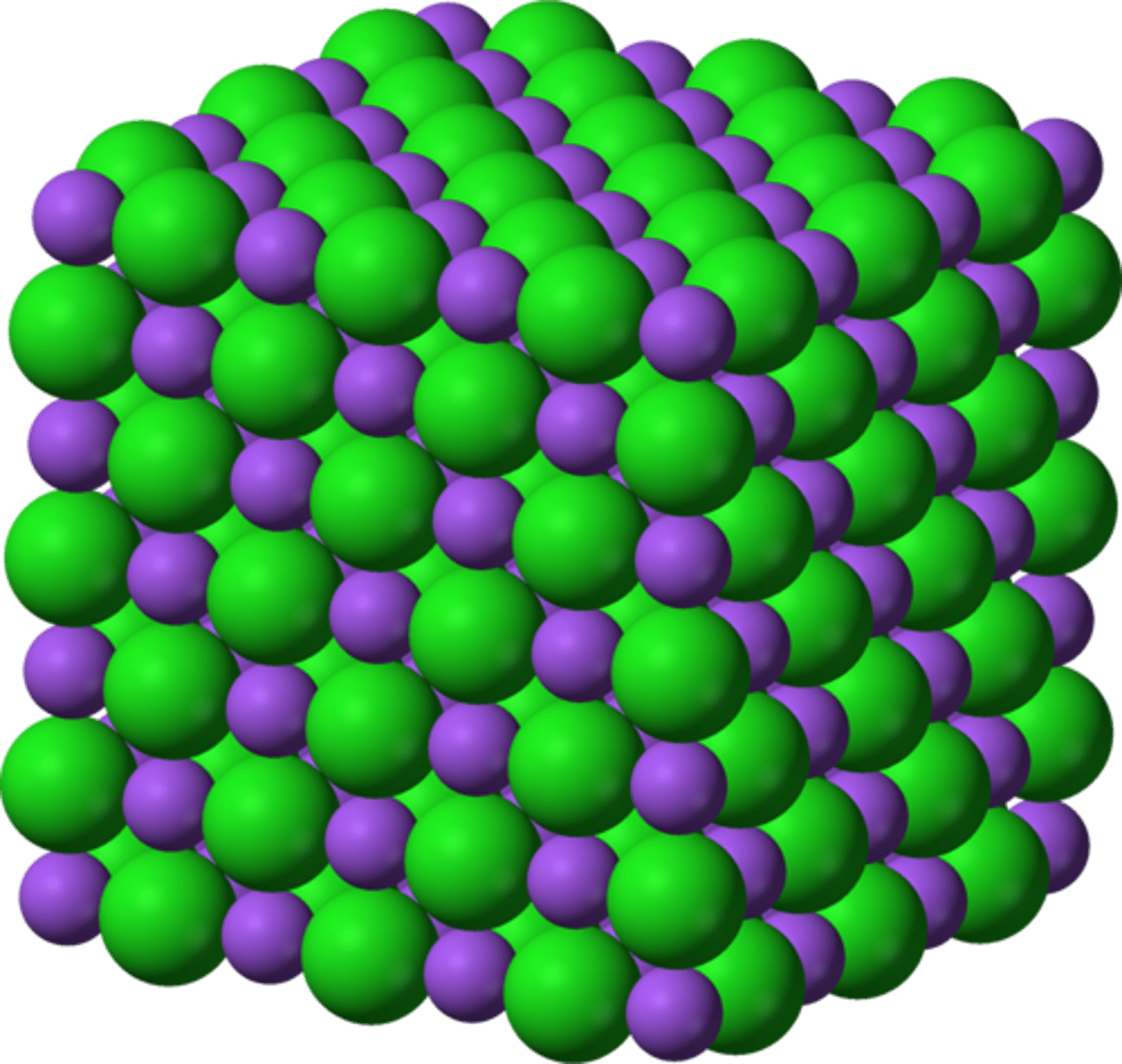
Examples of Ionic compounds
NaCl, MgO
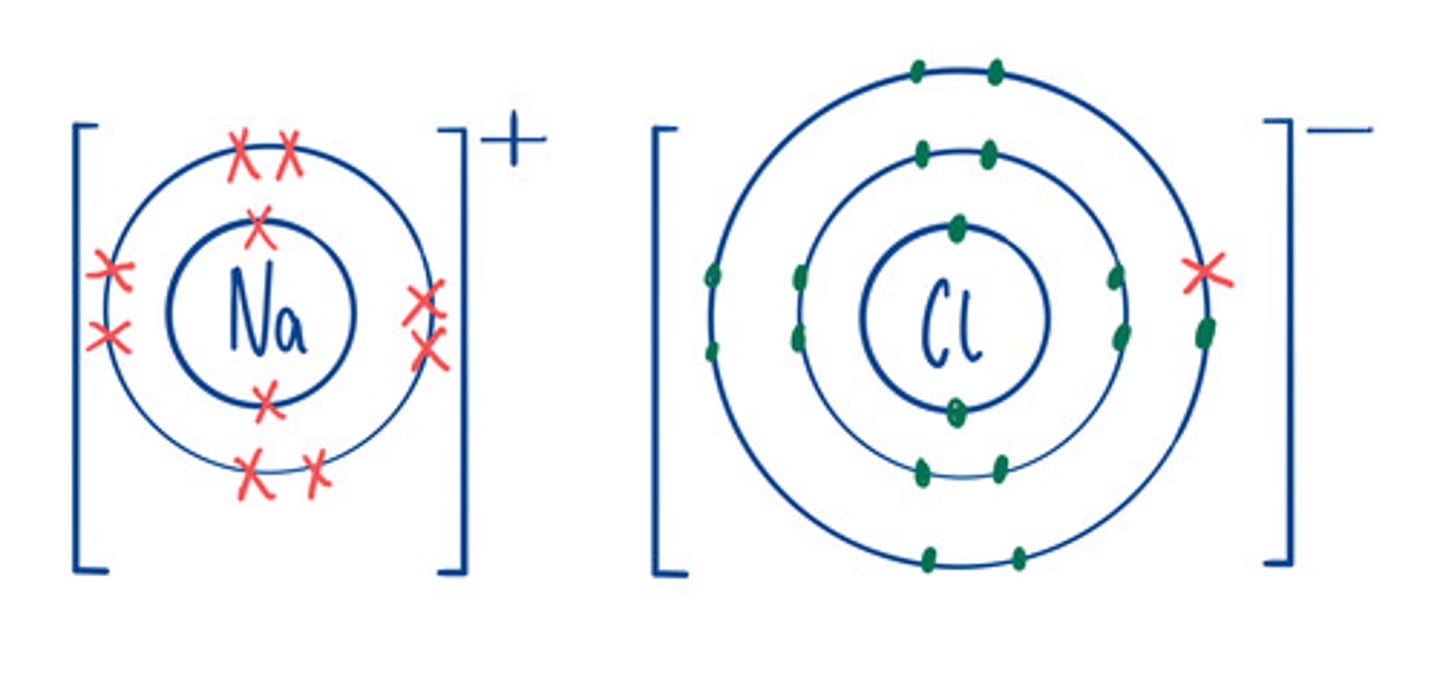
Limitations of dot and cross diagram
Looks like the compound only contains a few ions