Evolutionary Bio Chapter 13
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Evolutionary Development
Study of how changes in embryonic development can lead to the evolution of new traits and how developmental processes themselves evolve over time
Bridges the gap between an organism's genetic code and its final form through the mechanisms that shape an organism from embryo to adult
Development
The progressive changes in size, shape, and function during the life of an organism by which its genetic potentials (genotype) are translated into functioning mature systems (phenotype)
Parallelism
Pattern from simple to complex seen everywhere
Aristotle: Scala naturae
Great Chain of Being
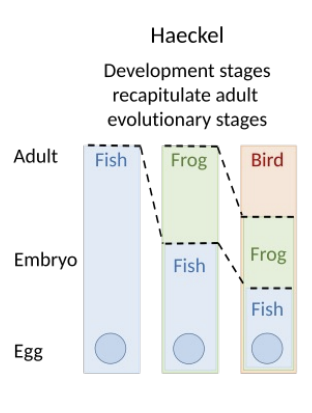
Biogenic law by Ernst Haeckel
“Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny” – development of “higher” animals repeats phylogenetic ancestry
Modern Understanding by Karl von Baer
During development, general, totipotent traits develop before specialized traits that distinguish different species
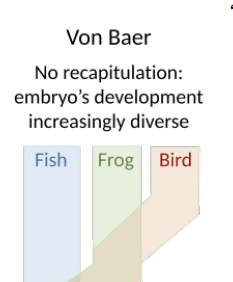
Prediction implicit
Structures that appear early very resistant to evolutionary change
Heterochrony
Some genes change rate or sequence of development, and thus timing at which developmental stages occur
Sequence heterochrony
The order of events has flipped in development
Flour beetles
Acceleration relative to flies
Differences in rates of developmental in homologous nerve clusters tied to locomotion, vision, spatial orientation
Paedomorphosis - Heterochrony
Slower somatic development
Progenesis - Paedomorphosis
Advanced sexual maturation and unchanged appearance of traits
Neoteny - Paedomorphosis
Slower developmental rates and retarded appearance of traits
Post-Displacement - Paedomorphosis
Retarded onset of organ growth
Peramorphosis - Heterochrony
Acceleration of somatic development
Peramorphosis - Heterochrony
Acceleration of somatic development
Hypermorphosis - Peramorphosis
Unchanged appearance of somatic traits
Retarded appearance of reproductive traits
Acceleration - Peramorphosis
Accelerated appearance of somatic traits
Unchanged appearance of reproductive traits
Pre-Displacement - Peramorphosis
Advanced onset of organ growth
Homeotic genes (Master regulators)
Determine identity and positioning of anatomical structures during development
Critical for construction of phenotype (which is where selection acts)
Gene products from combinations of homeotic genes act as activation signatures that generate instructional map for where structures should develop
Hox genes
Set of homeotic genes that affect anterior to posterior positioning of structures on the embryo’s body by encoding transcription factors
Recognize DNA motifs (in combination with cofactors) to activate or repress sets of target genes.
What are regulated by spatial and temporal pattern of HOX genes?
Cell migration
Differentiation programs
Identity
Structural formation
Regulatory enhancers and Regulatory silencers
Turn the expression of their targets on or off
Homeobox
Same 180-base pair sequence in homeotic genes in a wide array of animal species – allowed for identification of many other homeotic genes
Collinearity
As more Hox genes discovered, position of Hox genes on chromosomes corresponds to place on body that Hox gene regulates
cis-regulatory elements
Non-coding stretch of DNA that lies outside of gene but is involved in the timing and level of that gene’s expression
Three-spine Stickleback
Cis-regulatory enhancer inserted into genome of freshwater fish
Developed same pelvic morphology as marine fish
Heliconius
Reddish color associated with transcription factor optix
Recombinational rearrangements of cis-regulatory domains across lineages drive color patterns
Gene duplication
Establishment of multiple copies of same gene (paralogs) - generate new developmental pathways
Hox duplications contribute to …
body plan complexity in vertebrates
Duplicate genes influence gene expression by
Increasing histone production
Increasing rRNA
Increasing transcription/translation products
Subfunctionalization
Duplicate genes can divide work done by single gene
Neofunctionalization
Duplicated genes can diverge with others taking on new function
Ancestral chordates have…
neural crest cell progenitors
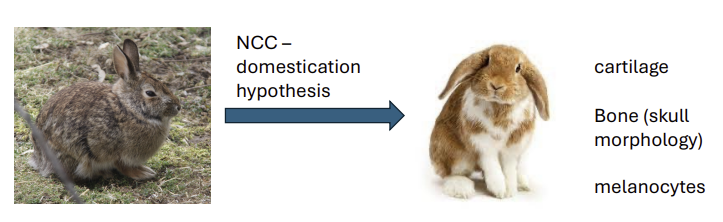
Neural crest cells
Migrate to ultimate destination – implications for domestication
Brain nccs associated with HPA -axis.
Select for lower stress responses (calmer)
Select for fewer/slower nccs migrating to head/brain