Econ Ch 5 - Externalities, Environmental Policy, and Public Goods
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
An externality is _____.
A. anything that is external or not relevant to the production of a good or service.
B. a benefit realized by the purchaser of a good or service.
C. a cost paid for by the producer of a good or service.
D. a benefit or cost experienced by someone who is not a producer or consumer of a good or service.
D
What is a market failure?
A. It refers to a breakdown in a market economy because of widespread corruption in government.
B. It refers the inability of the market to allocate resources efficiently up to the point where marginal social benefit equals marginal social cost.
C. It refers to the inability of the market to allocate resources efficiently up to the point where marginal social benefit equals marginal private cost.
D. It refers to a situation where an entire sector of the economy (for example, the airline industry) collapses because of some unforeseen event.
B
Which of the following activities create a negative externality?
A. cleaning up the sidewalk on your block
B. repainting the house you live in to improve its appearance
C. graduating from college
D. keeping a junked car parked on your front lawn
D
A negative externality exists if _____.
A. the marginal private cost of producing a good or service exceeds the social cost.
B. there are price controls in a market.
C. there are quantity controls in a market.
D. the marginal social cost of producing a good or service exceeds the private cost.
D
How do externalities affect markets?
If a negative externality in production is present in a market, then
A. the private cost of production will be equal to the private benefit from consumption.
B. the social cost of production will be equal to the social benefit from consumption.
C. the private benefit from consumption will be different than the social benefit from consumption.
D. the private benefit from consumption will be different than the social
benefit from consumption.
E. consumer and producer surplus will be maximized
F. the private cost of production will be different than the social cost of production.
G. both A and C
H. both C and F
I. both B and E
H
How do externalities in the production of college educations result in market failure?
Because of externalities, the market for college educations will _____.
A. result in a price for college educations that is inefficiently low.
B. generate too much economic surplus.
C. provide insufficient college educations.
D. provide too many college educations.
E. result in a shortage of college educations.
C
How do property rights affect externalities and market failure?
A. Externalities and market failure will result from producers having all the property rights.
B. Externalities and market failure will result from incomplete property rights.
C. Externalities and market failure will not occur when property rights are difficult to enforce.
D. Externalities will be positive and market failure will not occur when property rights are divided equally among market participants.
E. Externalities will be positive and market failure will not occur when property rights are enforced.
B
What must be true for the Coase Theorem to hold?
For the Coase Theorem to hold, _____.
A. the externality must be positive.
B. the government must monitor the negotiations to obtain an agreement.
C. all parties to an agreement must be willing to accept a reasonable agreement
D. transaction costs to obtain an agreement must be high.
E. the parties to an agreement cannot know the full cost of the externality.
C
Consider the consumption of electricity.
What type of good is electricity?
Electricity is _____.
A. an externality.
B. a private good.
C. a quasi−public good.
D. a public good.
E. a common resource.
C
Suppose a new recreational neighborhood park would cost $20,000, including opportunity costs, to construct and maintain. If built, the park would be a public good. For simplicity, assume the neighborhood park would be used by three families, each of whom would derive a marginal benefit equivalent to $8,000 from the park.
Should the neighborhood park be built?
It [would, would not] be optimal for the park to be built.
If left to the private market, without private bargaining or government intervention, would the park be built?
Without private bargaining or government intervention, the park [would, would not] be built.
would, would not
Consider a can of Coke. Is the consumption of a can of Coke
rival and excludable?
The consumption of a can of Coke is _____.
A. quasi-rival and quasi-excludable.
B. rival and excludable.
C. rival and nonexcludable.
D. nonrival and nonexcludable.
E. nonrival and excludable.
B
Which of the following represents the true economic cost of production when firms produce goods that cause negative externalities?
A. the explicit cost of production.
B. the external cost of production.
C. the private cost of production.
D. the social cost of production.
D
A positive externality causes _____.
A. the marginal social benefit to be less than the marginal private cost at the market equilibrium.
B. the marginal social benefit to be equal to the marginal private cost at the market equilibrium.
C. the marginal social benefit to exceed the marginal private cost at the market equilibrium.
D. the marginal private benefit to exceed the marginal social cost at the market equilibrium.
C
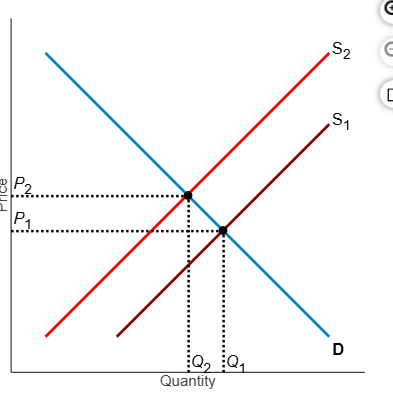
Refer to the diagram . Suppose the current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output because of an externality. The economically efficient output is Q2. In that case, the diagram shows _____.
A. the effect of an external benefit such as a subsidy granted to consumers of a good.
B. the effect of a positive externality in the production of a good.
C. the effect of a negative externality in the production of a good.
D. the effect of an external cost imposed on a producers.
C
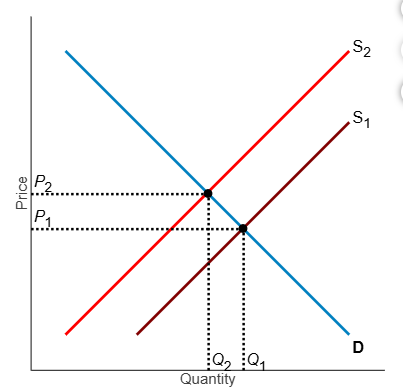
Refer to the diagram. If, because of an externality, the economically efficient output is Q2
and not the current equilibrium output of Q1, what does S1 represent?
A. the market supply curve reflecting implicit cost
B. the market supply curve reflecting social cost
C. the market supply curve reflecting external cost
D. the market supply curve reflecting private cost
D
Which of the following describes how a negative externality affects a competitive market?
A. The externality causes a difference between the private cost of production and the private benefit from consumption.
B. The externality causes consumer surplus to exceed producer surplus.
C. The externality causes a difference between the private cost of production and the social cost.
D. The externality causes a difference between the private cost of production and the equilibrium price.
C
When there is a positive externality, _____.
A. the social benefit received by consumers is greater than the private benefit.
B. the private benefit received by consumers is greater than the external benefit.
C. the private benefit received by consumers is greater than the private cost.
D. the private benefit received by consumers is greater than the social benefit.
A
Which of the following displays rivalry and excludability in consumption?
A. common resources
B. quasi−public goods
C. public goods
D. private goods
D
Which of the following displays non-rivalry and excludability in consumption?
A. common resources
B. quasi−public goods
C. public goods
D. private goods
B
Which of the following displays rivalry and non-excludability in consumption?
A. common resources
B. quasi−public goods
C. public goods
D. private goods
A
Which of the following displays non-rivalry and non-excludability in consumption?
A. common resources
B. quasi−public goods
C. public goods
D. private goods
C
How do externalities in the production of electricity result in market failure?
Because of externalities, the market for electricity will _____.
A. provide insufficient electricity
B. generate too much economic surplus.
C. result in a price for electricity that is inefficiently high
D. result in a surplus of electricity
E. provide too much electricity
E.
Assume the Mc Donald’s Big Mac is a private good. If so, then the McDonald’s Big Mac is [rival, nonrival] and [excludable, nonexcludable].
rival, excludable
Assume fish in a public lake are a common resource. If so, then fish in a public lake are [rival, nonrival] and [excludable, nonexcludable].
rival, excludable
When a negative externality exists, the private market produces _____.
A. more than the economically efficient output level.
B. products at a low opportunity cost.
C. less than the economically efficient output level.
D. products at a high opportunity cost.
A
A positive externality results when _____.
A. economists are sure that a good or service provides benefits to consumers.
B. people who live in one country benefit from the production of a good or service that occurs in another country.
C. people who are not directly involved in producing or paying for a good or service benefit from it.
D. someone pays for a good or service even though she is not directly affected by the production or consumption of it.
C
When production generates a negative externality, the true cost of production is the _____.
A. private cost of production.
B. social cost of production.
C. public cost of production.
D. average cost of production.
B