Chapter 16
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
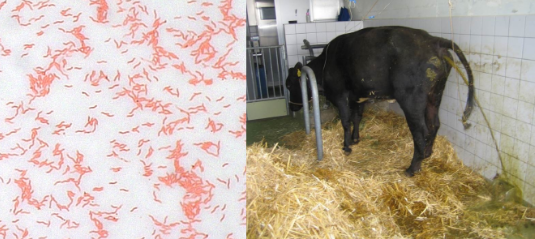
Classic shape of Campylobacter
Comma-shaped, “seagull wing,” spiral rods
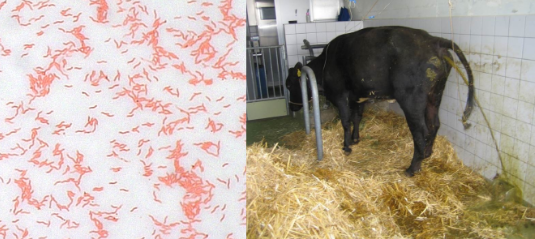
Gram reaction of Campylobacter
Gram-negative
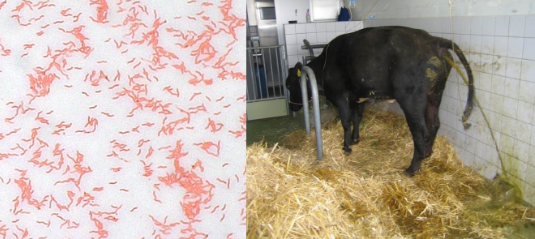
Is Campylobacter motile?
Yes, highly motile; darting corkscrew motion
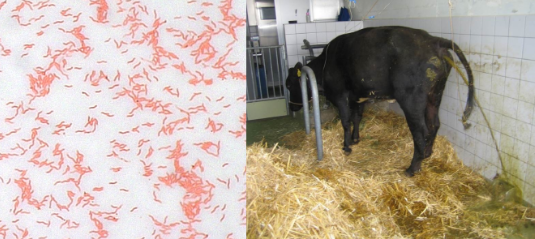
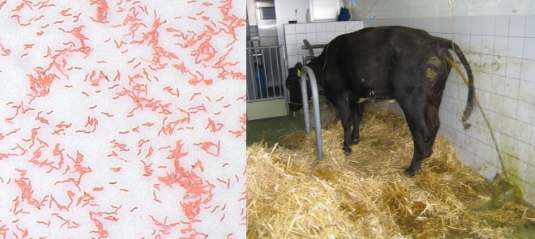
Type of shape of Campylobacter
Helical, curved, pleomorphic; paired forms look like gull wings
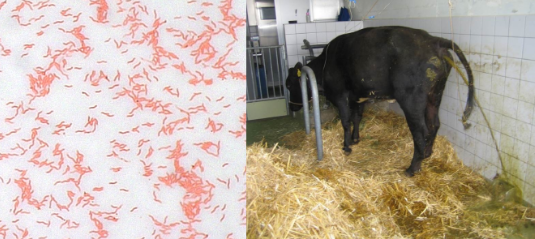
Clinical signs of Campylobacter in animals
Diarrhea (sometimes bloody), fever, abdominal pain, infertility, abortion in cattle
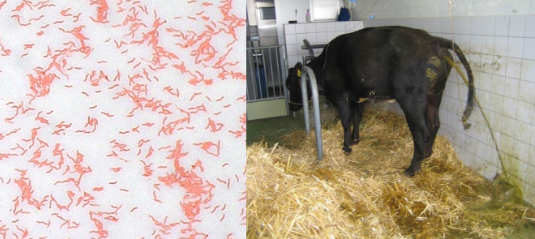
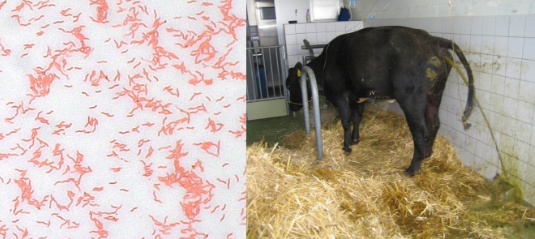
Clinical signs of Campylobacter in humans
Vomiting, diarrhea (bloody), fever, abdominal pain; may be asymptomatic
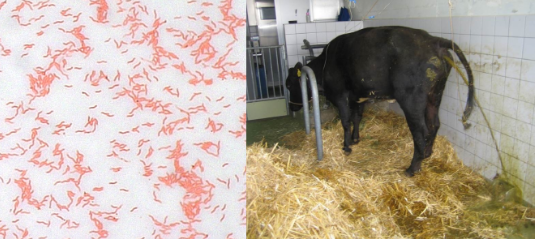
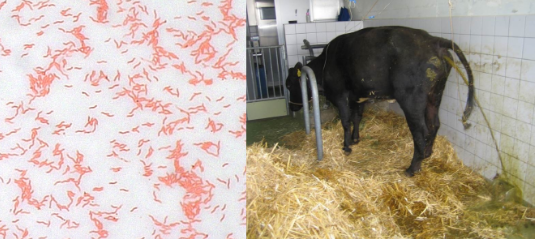
Treatment for Campylobacter
Antibiotics and supportive fluids
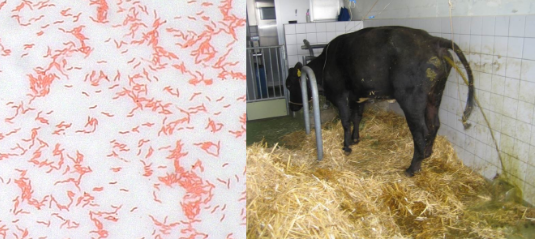
Does Campylobacter grow at 37°C?
It grows at room temperature; does not grow at 42°C; 37°C is possible but not optimal for all species























What is the problem with the Leptospira vaccine?


Clinical signs of Leptospira in cattle


Tests for Leptospira


Very difficult; requires special conditions; dark-field microscopy preferredand may not yield successful results.