containment - lecture 13 - HIV / AIDS
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
EXAM; students should be able to discuss what the “combination HIV prevention approach” consists of and on what principles it is based and possible stakeholders to be involved
difference between HIV /AIDS and other infectious diseases
long time between infection of HIV / AIDS and getting ill / dying (10 years)
only 3 months after infection you can test for HIV
epidemiological data about HIV/AIDS
9 million people currently living on HIV/AIDS not on drugs (ART) → many children get it via their mother, dependence of females in the families.
1.3 million people newly infected in 2024
31.6 million people on ART in 2024
630000 million people died from aids related illnesses in 2023
sub saharan africa and HIV/AIDS
15% of the population live in africa
64% of all PLHIV lives in africa (20.8 million in ESA and 4.8 million in WCA
in 2023 for the first time more new HIV infections happened outside of sub saharan africa than i n this continent → how is this possible
in Russia and Ukraine more drug injecting (needle sharing) → more HIV/AIDS there now
important abbreviations
FSW → female sex worker
ISW → informal sex worker
MSM → men having sex with men
MSW → male sex worker
PWID → people who inject drugs
TG → transgender
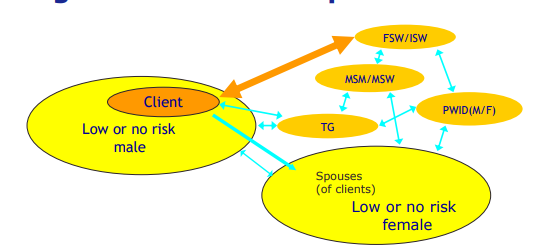
dynamics of HIV epidemics
key populations at higher risk of HIV exposure
94% of new infections outside sub-saharan africa within key populations
51% of new infections in sub-saharan africa within key populations.
in the picture there should also be a circle for children
concentrated epidemic
an HIV epidemic where infection is high in specific subpopulations but remains low in the general population.
discriminatory and punitive HIV related laws in 2024
the more policies that do not allow to talk about the marginalized groups (sexuality education, sex workers) → leads to less education more infectious diseases
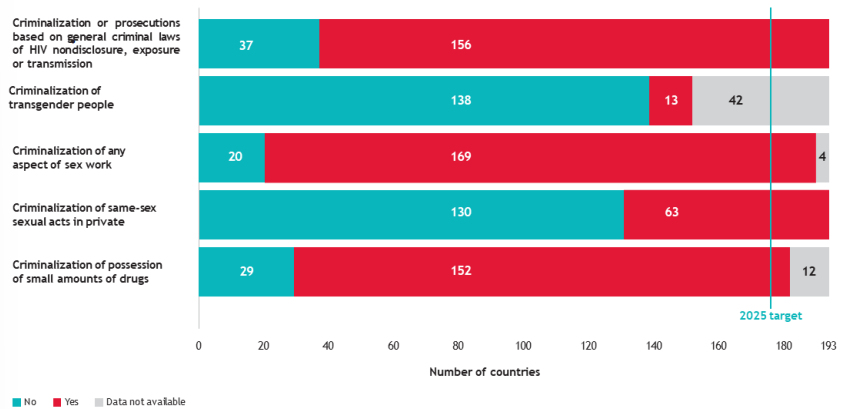
risk of acquiring HIV (injecting drugs, msm, fsm, tg women)
injecting needles highest change to get infected → direct contamination into the blood.
difference injecting intramuscular or intravenous → intramuscular reduces risk (this is recommended)
risk 35times higher than a person not injecting drugs
2nd highest risk group is female sex workers
30 times higher chance than adult women
men who have sex with men
28 times higher than adult men
transgender women
14 times higher than adult women
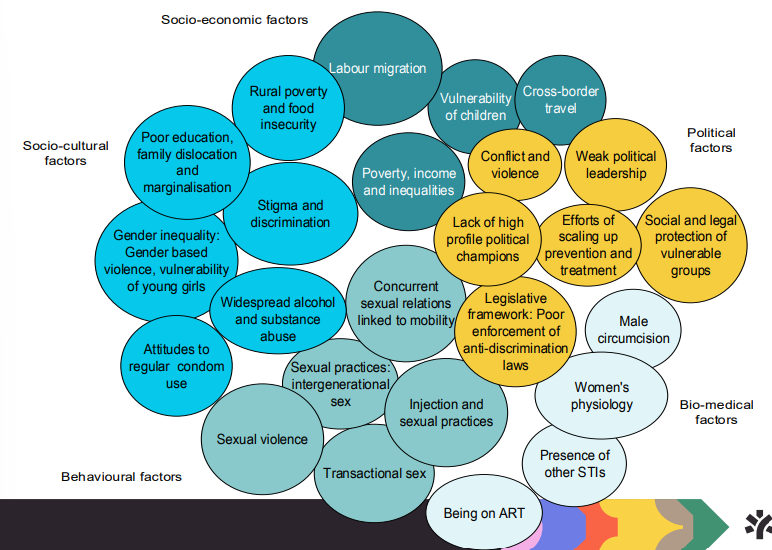
biomedical, behavioural, and structural fators
in sub Saharan Africa 6/7 new HIV infections amongst age group → 15-19 years (girls)
intergenerational sex (old man, young girl)
child marriage
concurrent sexual relationships → having multiple partners → puts you at additional risk of having AIDS/HIV
this is because the viral load goes up and no time to go down before next sexual partner
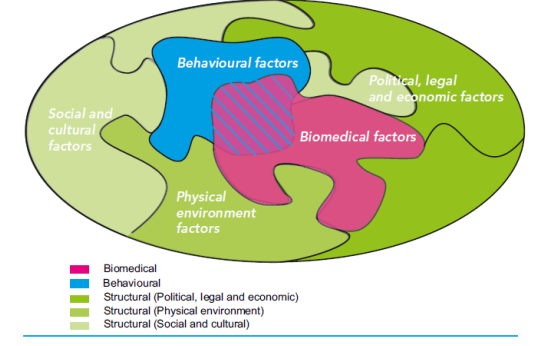
HIV combination prevention
addresses biomedical, behavioural and structural factors.
example structural environment factors→ prison, detention center, sex work sites.
structural → political, legal, economic factors
structural → physical environment
structural → social and cultural
principles HIV combination prevention
rights based, evidence informed and community owned
mix of biomedical, behavioural, and structural interventions
prioritized HIV prevention needs of particular individuals and communities to have the greatest sustainable impact on reducing new infections
tailor-made to national and local needs and conditions
mix of programmatic and policy actions
actions planned and managed synergistically over an adequate period of time
evidence informed versus evidence based
in public health very hard to do RCTs