Digestive System
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
digestive tract
muscular tube that extends from the oral cavity to the anus
Accessory organs
not part of the digestive tract, but assist in digestion
defecation
elimination of wastes from the body, feces
Peritoneal fluid
produced by the peritoneum, Lubricates surfaces and reduces friction and irritation
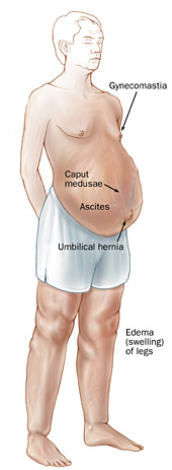
Ascites
abdominal swelling due to buildup of peritoneal fluid (Associated with liver disease, kidney disease and heart failure)
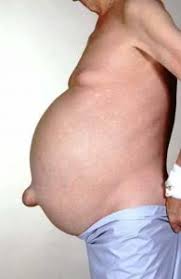
mesenteries
double sheets of peritoneal membrane that suspend portions of digestive tract within the peritoneal cavity
Falciform ligament
stabilizes the position of the liver relative to the diaphragm and abdominal wall, marks the path of the fetal umbilical vein
Muscularis mucosae
thin layer of smooth muscle and elastic fibers deep to the lamina propria, Muscle contractions alter the shape of the lumen. Moves epithelial plates and groves.
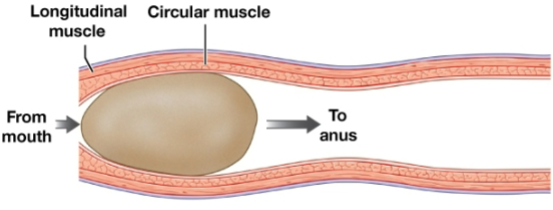
Peristalsis
waves of muscular contractions that move a bolus along the length of the digestive tract
Uvula
dangling process at the posterior margin of the soft palate that prevents food from entering the pharynx too soon
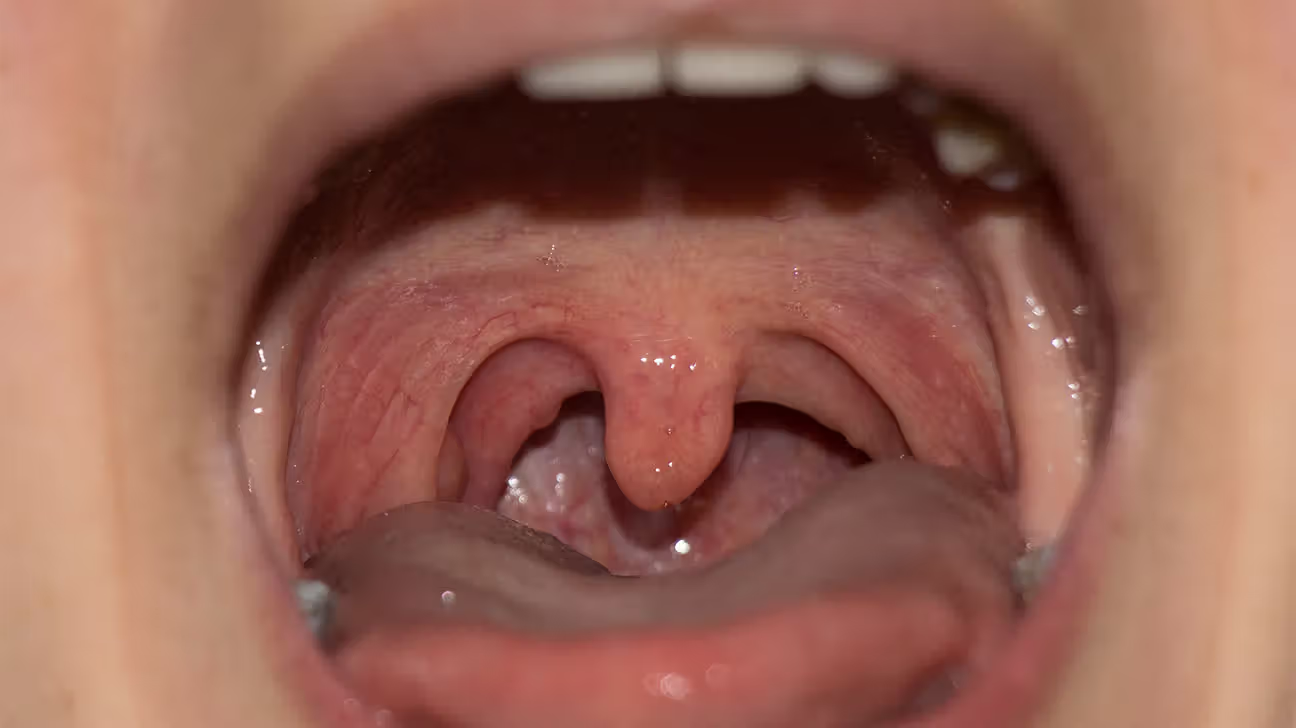
Frenulum of tongue
thin fold of mucous membrane along inferior midline, which connects the tongue to the floor of the oral cavity
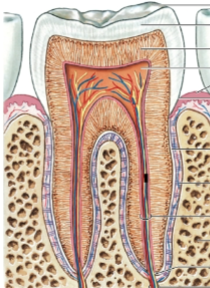
Enamel
hard calcified substance that covers the dentin, covers the crown of a tooth
Parotid glands
Located inferior to the zygomatic arch. Produce serous secretion containing salivary amylase, an enzyme that break down starches. A blockage of the ducts would interfere with carbohydrate digestion in the mouth
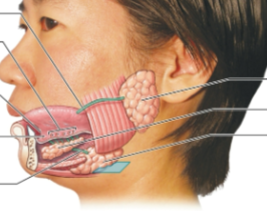
Sublingual glands
Covered by the mucous membrane of the floor of the mouth, produce mucus, which acts as a buffer and lubricant

GERD
Resting muscle tone keeps the esophagus closed to
prevent air from entering and backflow of materials
from the stomach (upper and lower esophageal
sphincters) lower esophageal sphincter is too loose allowing
acidic chyme into the esophagus
Buccal phase Deglutition (swallowing)
First phase, Voluntary, Bolus (food) enters oropharynx
Stomach Functions
Temporary storage of ingested food, Denaturation of proteins, Mechanical digestion with muscular contractions, Initiation of protein digestion (questions is function all of the following except)
Ghrelin
This hormone functions to stimulate hunger
Cardia
around the junction with the esophagus, Region of the stomach that the esophagus connects to
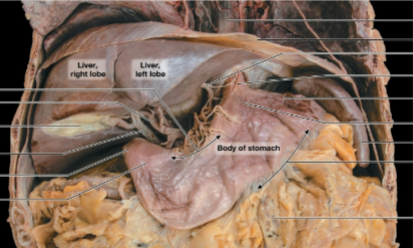
Pyloric part
between the body and the duodenum, Empties into the duodenum
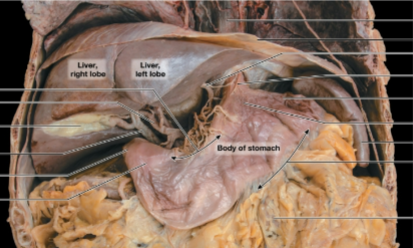
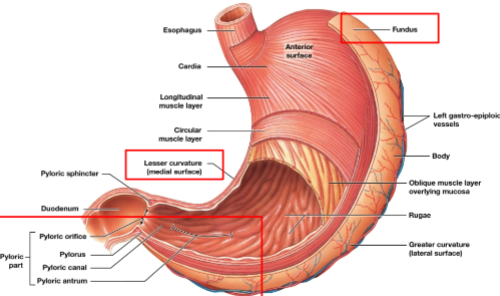
Pyloric Part, Fundus, Lesser curvature
Label all red boxes. (Very important)
Gastric pits
shallow depressions that open onto the gastric surface
Parietal cells
Secrete intrinsic factor
Chief cells
Secrete pepsinogen (is converted to pepsin (enzyme that digest
proteins))
Rennin (chymosin)
coagulates milk proteins, Stomachs of newborn infants also produce enzymes
important for the digestion of milk
G cells
produce the hormone gastrin
D cells
release hormone somatostatin (which inhibits release of gastrin)
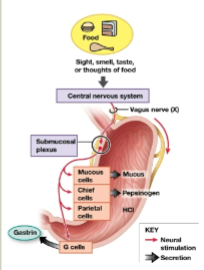
Cephalic phase
Controlled by the CNS, CNS sensory or cognitive activation stimulates the stomach
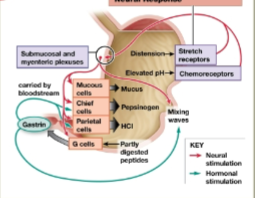
Gastric phase
Triggered by food entering into the stomach
Pancreatic juice
alkaline (pH 7.5-8.8) and contains digestive buffers, enzymes, water, and ions. Secretion is triggered by secretin and CCK
Pancreatic juice response to Secretin
Secretes a fluid rich in bicarbonate ion
Pancreatic juice response to CCK
Secretes a fluid rich in enzymes
bile
The liver synthesizes _______. Which contains water, ions, bilirubin, cholesterol and salts. The salts break lipid droplets apart (emulsification) and promote the absorption of lipids
portal hypertension
A blood clot blocking flow through the liver might
cause_________
gallbladder
bile is stored in the _______
cystic duct
_______ from the gallbladder unites with the common hepatic duct to form the bile duct
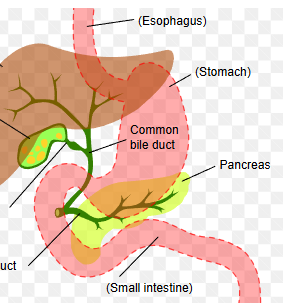
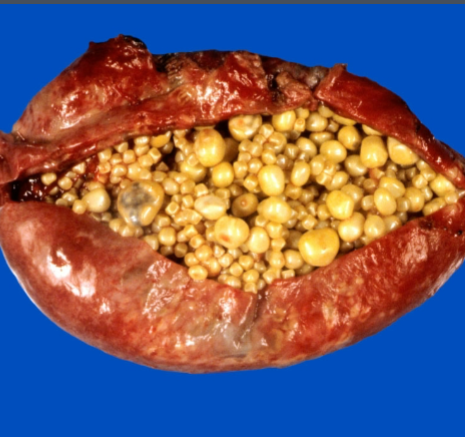
Cholecystitis
inflammation of the gallbladder
Small intestine
Long, muscular tube, Chemical digestion is completed, 90% of nutrient absorption occurs
Circular fold
permanent, transverse folds in the intestinal lining, Increase the surface area for absorption
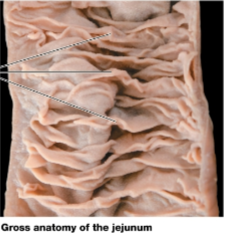
Intestinal villi
fingerlike projections of the mucosa, Covered by simple columnar epithelium with
microvilli that form the brush border, Increase the surface area for absorption
Ileum
has no circular folds in its distal portion, Lamina propria contains Peyer's patches
Brush border enzymes
integral membrane proteins on intestinal microvilli
Gastroenteric reflex
stimulates motility and secretion along entire small intestine
Gastroileal reflex
triggers opening of the ileocecal valve and allows materials to pass from the small intestine into the large intestine, Moves some chyme into the colon
Secretin
released when chyme arrives in the duodenum
Gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP)
secreted when lipids and carbohydrates enter the small intestine. Inhibits gastric activity and promotes the release of insulin
1. Stomach
2. Duodenum
3. Jejunum
4. Ileum
5. Cecum
Structure food passes through GI system:
Digestive enzymes
Break molecular bonds in large organic molecules, such as carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, in a process called hydrolysis
Bile salts
emulsify lipids
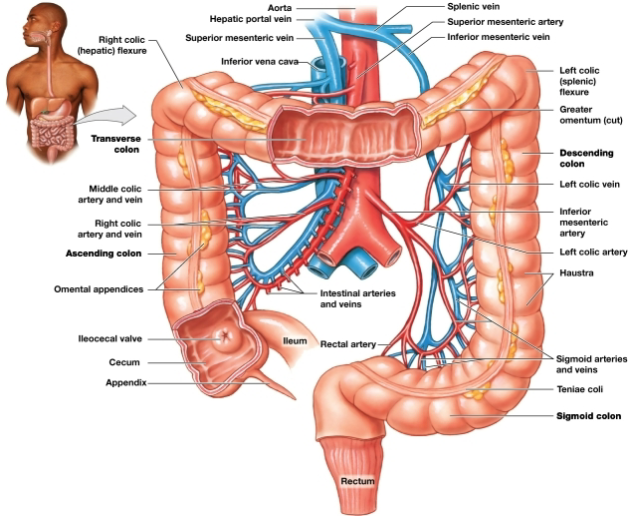
Cecum
pouchlike initial segment, Receives and stores materials arriving from the ileum via the ileocecal valve
Appendix
slender, hollow worm-like structure attached to posteromedial surface of the cecum
Colon
largest segment of large intestine
Haustra
pouches in the wall of the colon that permit expansion and elongation
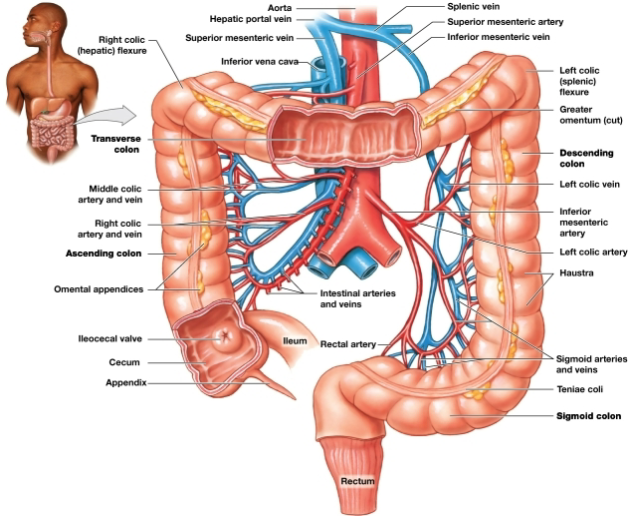
Teniae coli
longitudinal bands of smooth muscle that run along the outer surface of the colon, deep to the serosa
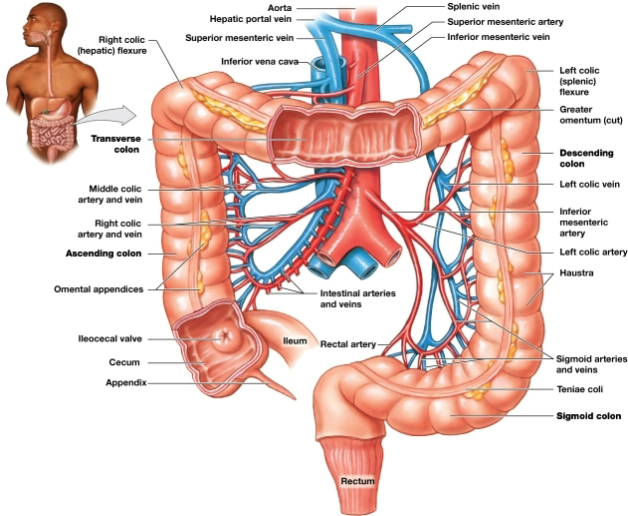
Transverse colon
Begins at the right hepatic colic flexure and crosses the abdomen from right to left
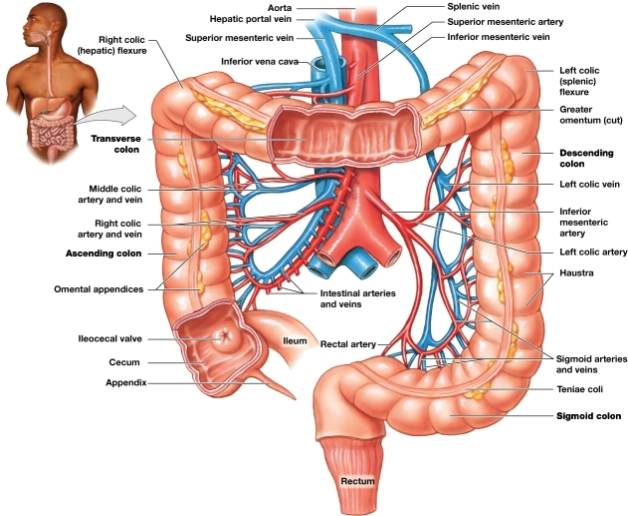
Descending colon
Proceeds inferiorly from the left splenic colic flexure along the left side of the abdomen to the iliac fossa
Vitamin K, Biotin, Vitamin
Vitamins produced by bacteria in the colon
Organic wastes
Bacteria in the large intestine convert bilirubin to urobilinogens and stercobilinogens. Color of feces due to heme breakdown
Elimination of feces- Defecation reflex
Requires the relaxation of the internal and external anal sphincters