Neonatology and the Premature Infant
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Prematurity
Babies born before 37 weeks gestation (10.4% of infants in the USA)
39 weeks gestation (unless medically indicated)
The WHO recommends NOT inducing labor prior to
22 - <25 weeks
Border of viability for neonates
under 28 weeks
Extreme preterm
28-31 6/7 weeks
Very preterm
32-36 6/7 weeks
Moderate to late preterm
37-41 6/7
Term
greater than 42 weeks
Post term
Gestational age (term vs. preterm), amniotic fluid clarity, addition risk factors, plan for umbilical cord management
What are the 4 questions of the pre-delivery report
Is the baby term gestation, is the tone good, is the baby crying
What are the 3 question for time of birth
delay cord clamping for 60 sec (raises hemoglobin, establishes RBC volume), evaluate infant on the mother (keep them together), the infant is warm, stimulate, and dry, airway is clear (bulb suction as needed)
If the answer to the time of birth questions is YES
Start with drying, stimulating and clearing the airway (BIG ONE), if hr is under 100 start PPV, consider intubation or LMA (laryngeal mask airway), if hr under 60 start chest compression, place central line, give emergency meds, determine if baby will stay with family or go to NICU
If the answer to the time of birth questions is NO
Activity (muscle tone, are they moving), Pulse (over 100, less than 100, absent), Grimace (reflex irritability), appearance (skin color - blue vs pink), respiration (cry, irregular or absent)
What is the APGAR Score (1 min and 5 min is required)? Big number good
Meds (Mg, general anesthesia, analgesics/narcotics), placenta previa, placenta abruption, nuchal cord, prolapsed cord
Maternal causes of low APGAR scores
Prematurity, intrauterine growth restriction, infant of a DM mother, hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy, congenital anomalies (congenital diaphragmatic hernia, spinal muscular atrophy, renal agenesis, CNS anomalies)
Neonatal causes of low APGAR scores
intraventricular hemorrhage, Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy, neonatal abstinence syndrome
Common neurological problems in neonates
Retinopathy of prematurity
Common ophthalmology problems in neonates
RDS, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, aspiration pneumonia
Common respiratory problems in neonates
PDA, congenital cardiac defect, hypotension
Common cardiac problems in neonates
necrotizing enterocolitis, feeding intolerance, failure to thrive
Common FENGI problems in neonates
thrombocytopenia, hyperbilirubinemia, DIC
Common Heme problems in neonates
early onset group B strep sepsis, late onset sepsis
Common ID problems in neonates
Intraventricular Hemorrhage (IVH)
Bleeding within the thin walled capillary bed of the germinal matrix near the lateral ventricles - usually in infants less than 30 weeks and under 1500g (3.3 lbs)
Low birth weight, decreased gestational age (under 32 weeks), chorioamnionitis at delivery (inflammatory response), maternal hypertension (METH), genetic
Prenatal risk factors of IVH
Mode of delivery, neonatal transport (airplane pressure), hemodynamic instability, mechanical ventilation/pneumo, CO2 level shifts, hypoxia, acidosis
Peri/postnatal risk factors for IVH
Antenatal steroids for all mothers at risk for premature delivery
Preventative measures for IVH - prenatal
experienced delivery team, optimized delivery time, decreased stimulation for 1st 96 hours of life (keep flat, no movement), Small baby protocol (no daily weight, keep midline, minimize touch times)
Preventative measures for IVH - peri/postnatal
Asymptomatic, hypotension, bulging anterior fontanelle, apnea, seizures, coma, drop in Hct
Signs and Symptoms of IVH
All infants less than 32 weeks and/or less than 1500 g by day 7 of life at the latest
Screening protocols for IVH
Head u/s
First line imaging for IVH 🏆
bleeding in the germinal matrix - no shadowing on U/S
Grade 1 IVH
Bleeding within the lateral ventricles
Grade 2 IVH
Bleeding within the lateral ventricles (covers 75%) resulting in dilation of the ventricles
Grade 3 IVH
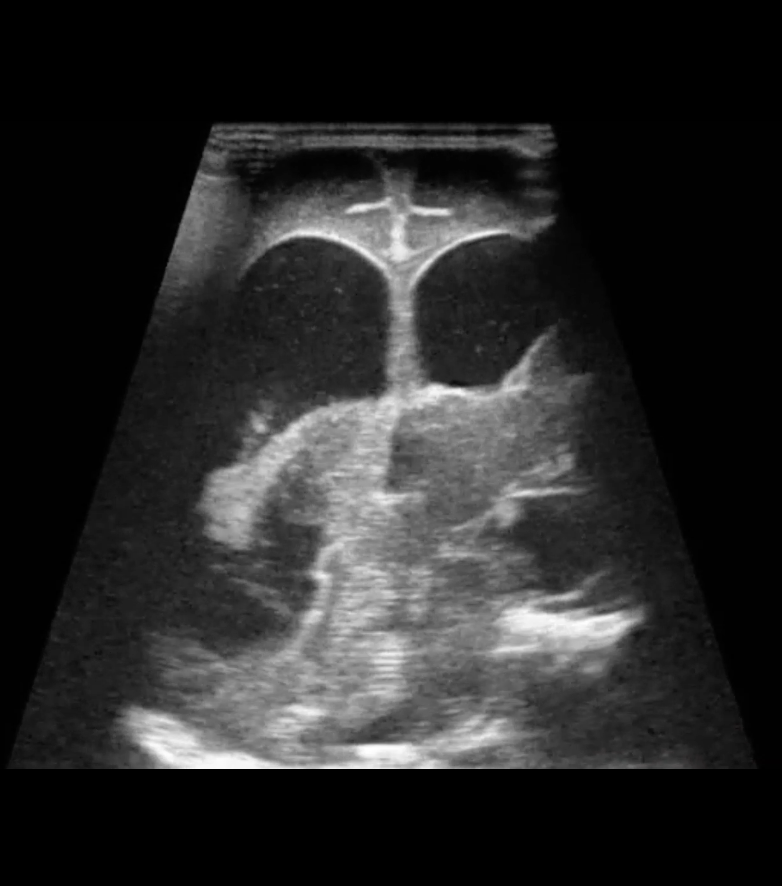
ANY Bleeding within the periventricular white matter
Grade 4 IVH
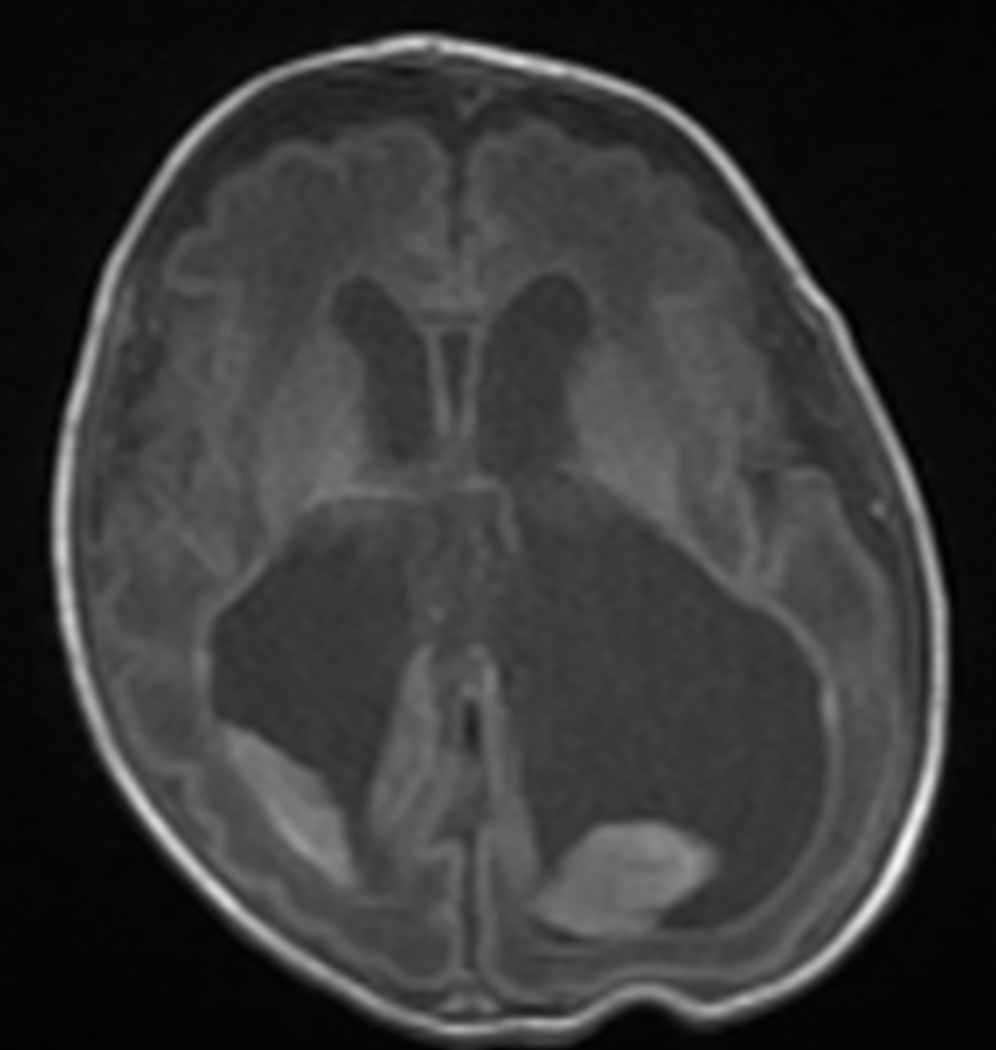
Blood transfusion (Hct low), respiratory support, Na Supplementation, serial lumbar punctures (draws off CSF to decrease ventricle size → shunts may need to be placed), long term follow up with neurodevelopmental clinic
Supportive care of IVH
low risk for moderate to severe neurodevelopmental delays and cerebral palsy
Long term outcomes of grade 1 and 2 IVH
30-60% risk neurodevelopmental delays or Cerebral palsy; 4x increase risk of death
Long term outcomes of grade 3 and 4 IVH
Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS, AKA hyaline membrane deficiency)
A deficiency of surfactant resulting in high surface tension in lungs, premature infants are at the greatest risk (surfactant by type II alveolar cells is not expressed until week 20)
prematurity, infant of DM mother, surfactant inactivation (aspiration of blood or meconium), lung inflammation
Risk factors for RDS
antenatal steroids
Prenatal preventative measures for RDS
Tachypnea (60+), nasal flaring (increased air intake), grunting (increased PEEP), intercostal retractions (increased lung volume), tachycardia, cyanosis, apneic episode with progression
Signs and symptoms of RDS
Diffuse ground grass on CXR, CO2 over 60, PaO2 decreased, BD increased, loss of A lines and pleural line abnormalities on U/S
Diagnostics of RDS
Non-invasive positive pressure ventilation (may require intubation if apnea present, watch the pressures if you give surfactant), surfactant administration (within the 1st 6 hours, must be intubated), nasal CPAP is 1st line
Treatment of RDS - patient specific
CO 60+, FiO2 30+%
Rules for surfactant administration - maintain SpO2 above 90%
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
A long term outcome of RDS, that is defined by required oxygen support and/or mechanical ventilation at 28 days of life or 36 weeks corrected gestational age - may require home oxygen or tracheostomy
Ductus arteriosus
Diverts blood from the pulmonary arteries to the aorta bypassing the lungs
decrease in the circulation of PGs and increase in O2
What causes the closure of the ductus ateriosus?
Prematurity, low birth weight, RDS (pressure in lungs may pop it open), diuretic usage, genetics, rubella 2nd trimester
Risk factors for PDA
volume overload that is affecting the lungs
Indications for treating a PDA
antenatal steroids
Preventative measures for PDA
Asymptomatic; washing machine, holosystolic murmur, failure to thrive, pulmonary over circulation, persistent need for respiratory support, widened pulse pressure (ductals steal), DOE, fatigue, cyanosis, clubbing
Signs and Symptoms of PDA
Echo
Diagnostics for PDA
NSAIDs (indomethacin (watch bowel), tylenol, ibuprofen (watch kidneys)), Ligation (bedside procedure), Piccolo (preterms under 700g)
Treatment for PDA
CoA, severe pulmonary HTN, R-L shunting
CARDIO REMINDER - When are we NOT closing a PDA (give PGs)
favorable if that’s the only thing, surgical management may lead to greater mortality risk
Long term outcomes of PDA
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)
A disorder characterized by ischemic necrosis of the intestinal mucosa, severe inflammation, invasion of enteric gas forming organisms, and dissection of gas into the bowel wall - most common GI emergency in preterms
Under 32 weeks, RDS, PDA, other comorbidities, ductal steal (poor perfusion), corticosteroids, ibuprofen, hyperosmolar formula
Risk factors for NEC
Feeding intolerance (most common), distended abd (measure after every feed), apnea, desaturations, bradycardia, hypothermia, bloody stool, dusky abd, lethargy
Signs and Symptoms of NEC
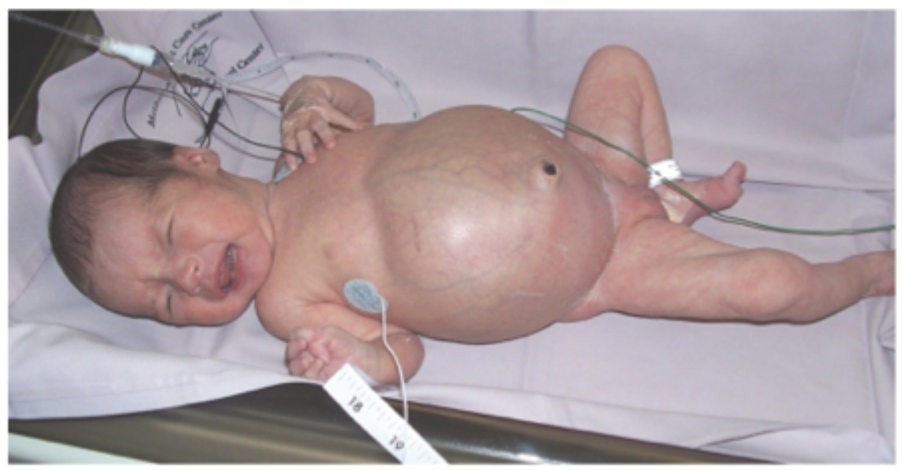
Dilated bowel loops (ileus), pneumatosis intestinalis (railroad tracks), free air (football sign),
KUB X-ray findings for NEC - confirm with U/S
Kidney, ureter, bladder X-rays, CBC (thrombocytopenia, leukocytosis), blood cultures, evidence of DIC
Diagnostics for NEC
NPO place replogle (specialized drain), Abx (pip-tazo), fluid management, serial KUBs
Gameplan for mild to moderate NEC
surgical consult, exploratory surgery with removal of dead bowel
Gameplan for severe NEC (presence of free air)
accounts for 10% of NICU deaths, 42% mortality in infants under 750 g (1.6 lbs), poor long term growth
Outcomes in NEC
PDA, RDA, NEC, prematurity
Risk factors for failure to thrive (a failure to gain weight appropriately)
licensed dietician
Failure to thrive is most appropriately managed by a…
Optimal growth is 20-30g/kg/da - fortification of formula or breast milk
treatment plan for failure to thrive
calcium 150-220 mg/kg/day, phosphorus 75-140 mg/kg/day, vitamin D 400 IU/day, Iron 3-6 mg/kg/day
Optimization of vitamins and minerals in failure to thrive
Hep B (if over 2000 g), DTAP, PCV13, IPV, NO ROTOVIRUS
Vaccines recommended in the NICU
All infants get Beyforus (RSV monoclonal antibody), try to convince the family to get vaxxed as well
RSV prophylaxis
monitor growth, coordinate care, vaccinations, neurodevelopmental assessment, social concerns/obstacles
It is recommended that all preterm infants follow up in a NICU specific clinic during the 1st 2 years of life to…