04 Smart Markets
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
How does the basic model of the electricity economy look like?
consists of electricity & cash flows between electricity generator (= supplier) & end consumer (= demand)
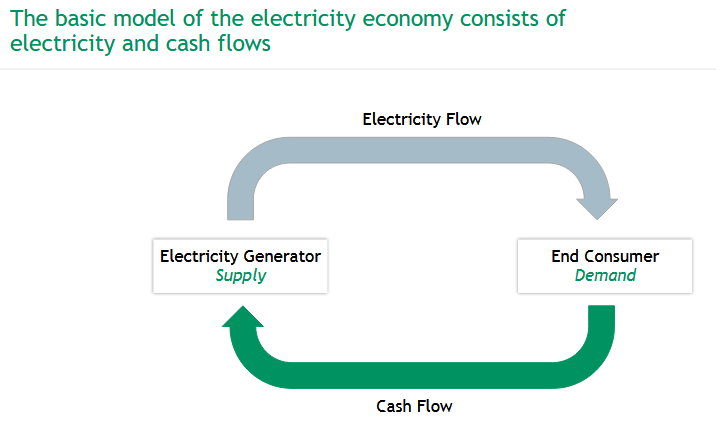
How can electricity be traded, and what are baseload, peakload, and blocks?
🔌 Electricity is traded as a product via:
Spot Market: Physical contracts for immediate delivery
Futures Market: Contracts for future delivery (e.g., options, futures)
Over the Counter (OTC): Direct trades without exchanges
📊 Products:
Baseload: Long-term basic supply
Peakload: Covers high-demand hours
Blocks: Quarter- to hourly-based segments to match load profiles
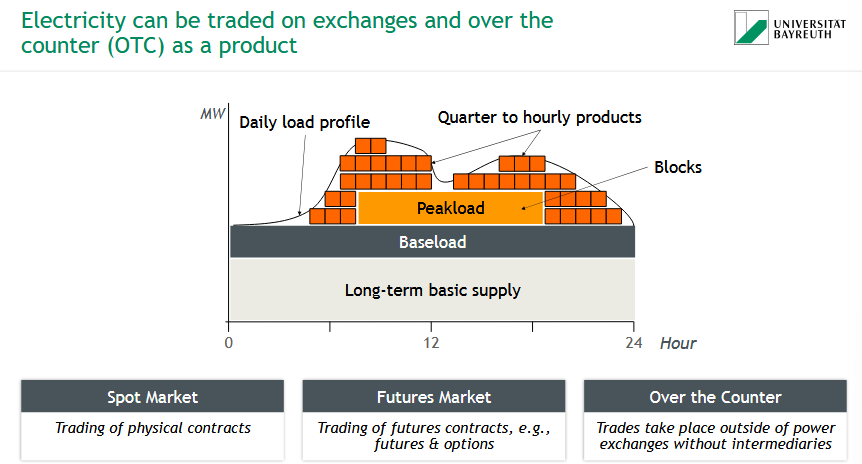
How is electricity generation aligned with demand, and what are base, medium, and peak loads?
⚡ Generation matches demand by activating power plants in stages:
Base Load = constant minimum demand: Nuclear & brown coal (run continuously)
Medium Load = rises during day: Gas & hard coal (ramp up during the day, flexible)
Peak Load = short spikes in demand: Pumped-storage & oil (cover sudden spikes)
💡 Renewables (e.g. PV, wind)
Have fast startup (<1 min)
Prioritized as base load due to feed-in laws
📈 Demand curve fluctuates; system responds dynamically
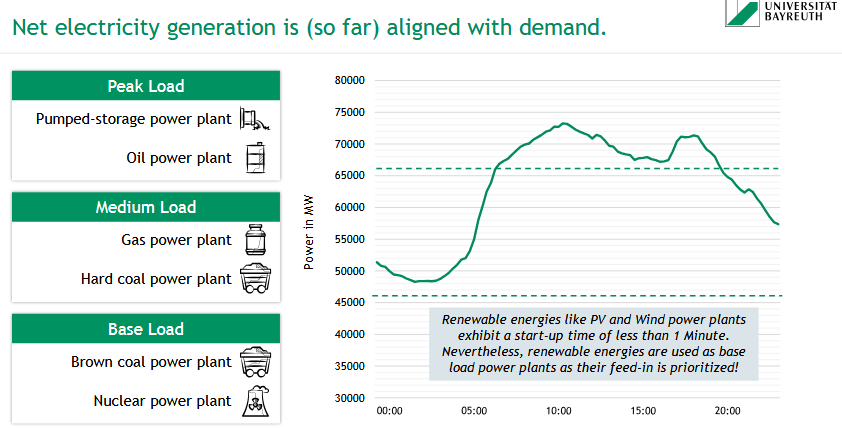
How do start-up times define base, medium, and peak load power plants?
🕒 Start-up time determines load role:
🟡 Base Load:
Nuclear (~24 h), Brown Coal (2–6 h)
🟠 Medium Load:
Hard Coal (2–4 h), Gas (~15 min)
🔴 Peak Load:
Oil & Pumped Storage (few minutes)
Hot Start: <8 h
Warm Start: 8–48 h
Cold Start: >48 h
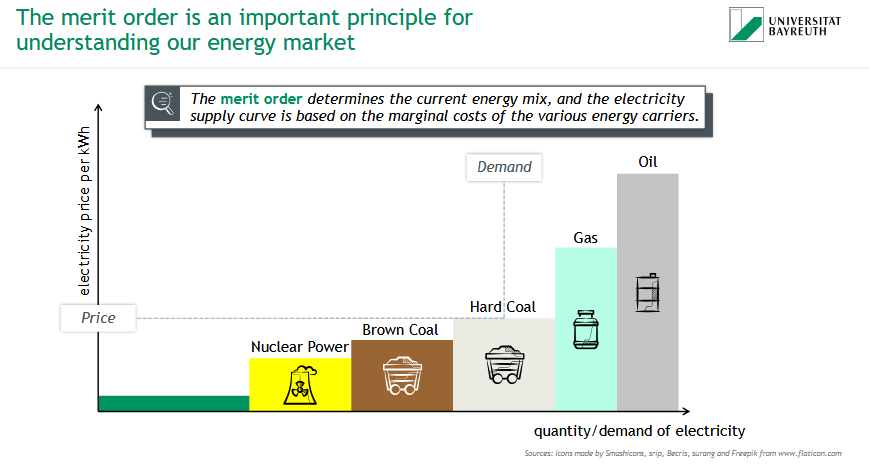
What is the merit order?
= important principle for understanding energy market
→ determines current energy mix, and the electricity supply curve is based on the marginal costs of the various energy carriers
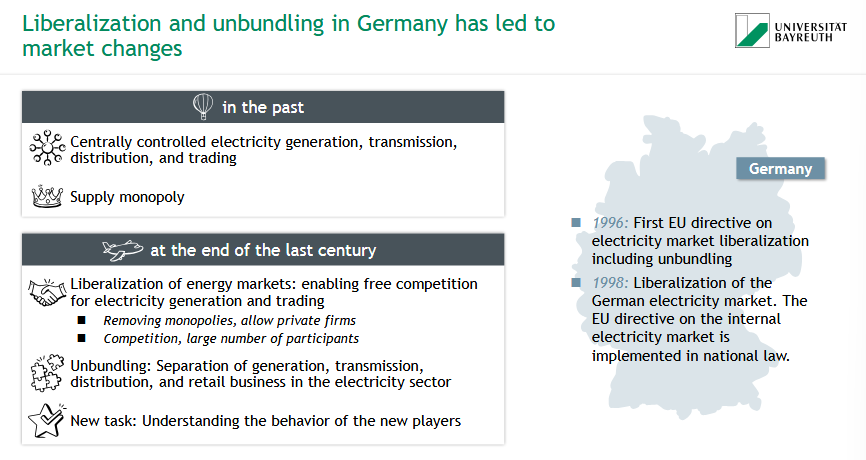
How have liberalization & unbundling led to market changes in Germany?
⚡ Before:
Centrally controlled system
Supply monopoly
🔄 Since late 1990s:
Liberalization: Open market, private competition
Unbundling: Separation of generation, transmission, distribution & retail
1996: EU directive
1998: German law implemented
🎯 New challenge: Understanding new market players & dynamics
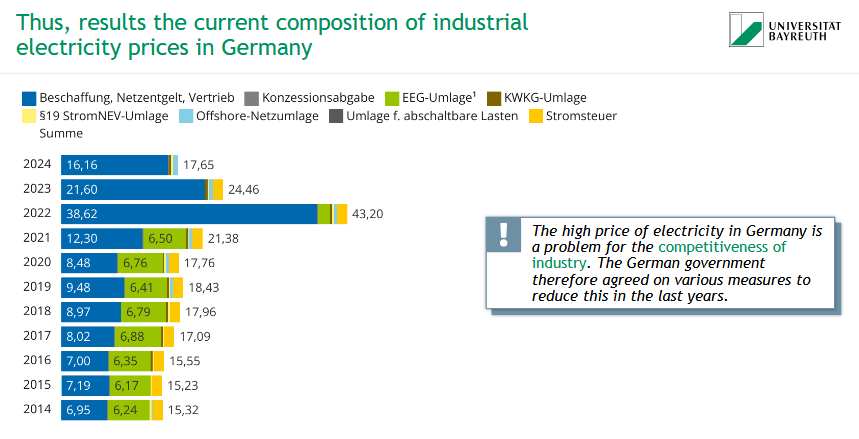
Why are electricity prices a concern for German industry?
💶 Electricity prices in Germany have been high and complex, made up of many components (e.g., procurement, grid fees, EEG levy, taxes)
⚠ This weakens industrial competitiveness
🛠 The government has introduced measures to reduce prices — especially in recent years (e.g., EEG levy reduction)
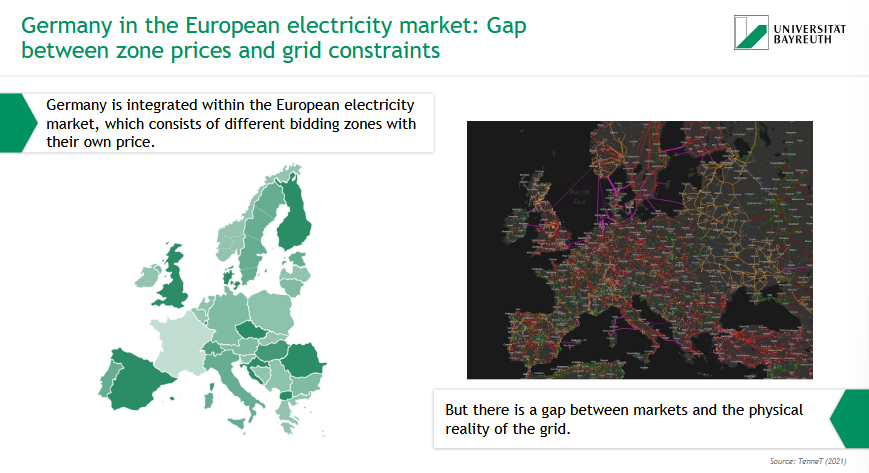
What challenge exists between electricity markets and the grid in Europe?
🌍 Germany is part of the European electricity market with different bidding zones, each setting its own price.
⚠ But: There's a gap between these market zones and the physical structure of the electricity grid.
➡ Result: Prices don’t always reflect real grid constraints (e.g., congestion or transmission limits)
What are the main problems with the electricity system?
⚠ We need market design because:
📉 Markets are incomplete:
Retail prices don’t match demand
Power flows are hard to control
Grid is physically limited
Storage is costly
💸 Markets are imperfectly competitive:
Long run: Entry barriers & few big players
Medium: High investment & slow construction
Short run: Volatile prices & inflexible demand
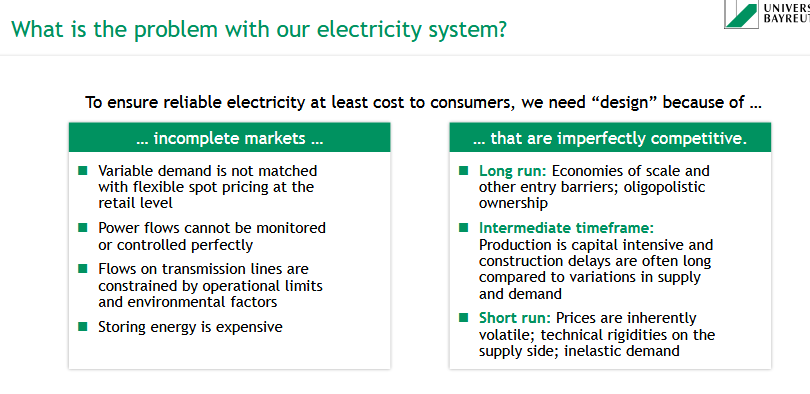
Why is Germany’s uniform electricity price zone problematic?
📌 In a uniform price zone, one market price applies everywhere — no regional differentiation.
🔌 Assumes unrestricted transport of electricity (➝ copper plate metaphor)
⚠ But:
Local grid bottlenecks exist
Requires redispatch (adjusting local generation)
🚫 This system gives insufficient incentives for:
Local flexibility
Long-term investment in energy-flexible tech
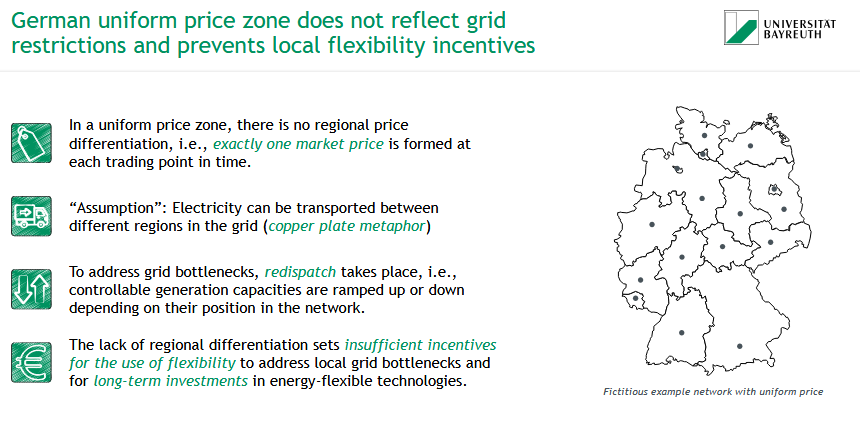
To which goals should an electricity market design contribute to?
🎯 Market objectives:
Efficiency (short- & long-run)
Security of supply
support of the broader economy & societa
Environmental protection
Human health & flourishing protection
Distributive justice
✅ Success factors:
Simplicity
transparency
Technological factors
legality
legitimacy
realizability in IT-systems
coordinated timing
integration & interconnection
incentives for market-conducive behaviour
Participation
Objective orientaiton
Goal: A market that ensures reliable, fair & sustainable electricity supply
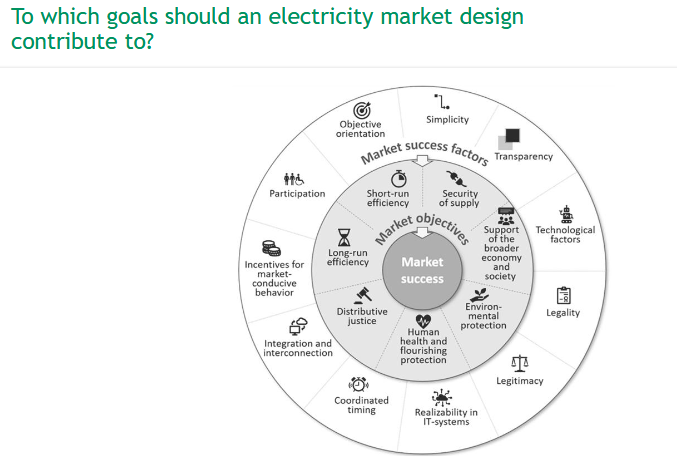
What is the difference between zonal and nodal electricity pricing?
🗺 Zonal Pricing:
One price per region (zone)
Reflects grid limits between, but not within zones
Simpler, but can give wrong signals
📍 Nodal Pricing:
One price per node (location)
Reflects actual grid bottlenecks
Enables better investment & grid operation
More complex, but most efficient
✅ Nodal pricing supports flexibility incentives & efficient grid use
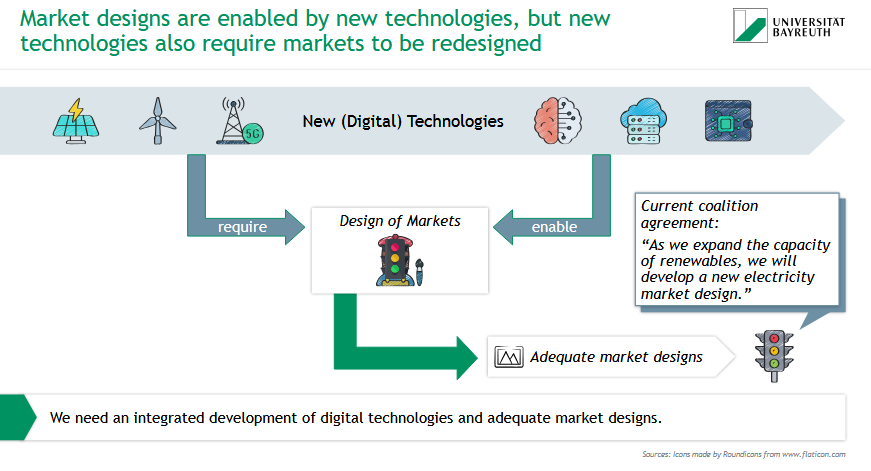
How are technologies and market design connected in the energy transition?
⚙ New (digital) technologies — like solar, wind, 5G, AI —
➡ require updated electricity market design
✅ At the same time, market design
➡ enables effective use of these technologies
📢 German coalition agreement:
"We will develop a new electricity market design to match renewable expansion."
📌 Need: Integrated development of tech & market rules
What is the merit order and how does it influence the price of electricity?
The merit order is the sequence in which power plants are dispatched based on their marginal costs. It influences the electricity price because the price is set by the most expensive plant needed to meet demand.

What is the current market design of the German electricity market?
Germany currently operates a uniform market with a single bidding zone, where electricity prices are set by marginal-cost dispatch.

What are benefits and challenges of a market design with uniform pricing?
Uniform pricing profits from simplicity, transparency, and efficient dispatch across a single price zone, while challenges include a lack of locational signals for investment and congestion management, which can lead to inefficiencies and higher grid management costs.

How do digital technologies facilitate a successfully redesigned future market design?
New market designs like nodal pricing are enabled by new technologies, but new technologies also require markets to be redesigned.
