8. MCQs Urinary System. Regulation of Body Fluids. Acid-Base Balance.
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
The cortical nephrons are characterized by:
a) shorter loop of Henle and peritubular capillary network;
b) longer loop of Henle and peritubular capillary network;
c) longer loop of Henle and vasa recta;
d) shorter loop of Henle and vasa recta;
e) none of the above mentioned.
The cortical nephrons are characterized by:
a) shorter loop of Henle and peritubular capillary network;
b) longer loop of Henle and peritubular capillary network;
c) longer loop of Henle and vasa recta;
d) shorter loop of Henle and vasa recta;
e) none of the above mentioned.
The control of water excretion in the kidney is controlled by:
a) the antidiuretic hormone (ADH);
b) the medulla oblongata;
c) atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP);
d) sodium level in the blood;
e) potassium level in the blood.
The control of water excretion in the kidney is controlled by:
a) the antidiuretic hormone (ADH);
b) the medulla oblongata;
c) atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP);
d) sodium level in the blood;
e) potassium level in the blood.
On which of the following the kidneys have direct effect?
a) blood pressure and water electrolyte balance;
b) body temperature;
c) the level of glucose in plasma;
d) smooth muscle tone of airways;
e) ovulation.
On which of the following the kidneys have direct effect?
a) blood pressure and water electrolyte balance;
b) body temperature;
c) the level of glucose in plasma;
d) smooth muscle tone of airways;
e) ovulation.
Glucose reabsorption occurs in the:
a) proximal tubule;
b) loop of Henle;
c) distal tubule;
d) cortical collecting duct;
e) medullary collecting duct.
Glucose reabsorption occurs in the:
a) proximal tubule;
b) loop of Henle;
c) distal tubule;
d) cortical collecting duct;
e) medullary collecting duct.
Renin is secreted by:
a) cells in the macula densa;
b) cells in the proximal tubule;
c) cells in the distal tubule;
d) juxtaglomerular cells;
e) cells in the peritubular capillary bed.
Renin is secreted by:
a) cells in the macula densa;
b) cells in the proximal tubule;
c) cells in the distal tubule;
d) juxtaglomerular cells;
e) cells in the peritubular capillary bed.
Renin release:
a) is triggered by increased sympathetic activity and low Na+ level in the distal tubules;
b) increases when systemic arterial pressure rises;
c) directly activates angiotensin converting enzyme;
d) is increased when the level of circulating cathecholamines is low;
e) increase when there is hyperhydration.
Renin release:
a) is triggered by increased sympathetic activity and low Na+ level in the distal tubules;
b) increases when systemic arterial pressure rises;
c) directly activates angiotensin converting enzyme;
d) is increased when the level of circulating cathecholamines is low;
e) increase when there is hyperhydration.
The glomerulus:
a) has both afferent and efferent arterioles;
b) contains capillaries, which are at a higher hydrostatic pressure than the peritubular capillaries;
c) filters 20% of the renal plasma flow;
d) contains renin-secreting cells;
e) all of the above.
The glomerulus:
a) has both afferent and efferent arterioles;
b) contains capillaries, which are at a higher hydrostatic pressure than the peritubular capillaries;
c) filters 20% of the renal plasma flow;
d) contains renin-secreting cells;
e) all of the above.
The total volume of water in the body is:
a) 6 - 8 % of body weight;
b) 5 L;
c) 45 - 47% of body weight;
d) 140 L;
e) increased with age.
The total volume of water in the body is:
a) 6 - 8 % of body weight;
b) 5 L;
c) 45 - 47% of body weight;
d) 140 L;
e) increased with age.
The following occurs in the proximal tubule of the nephron:
a) reabsorption of glucose and most of the water;
b) secretion of most water;
c) passive transport of sodium;
d) secretion of bicarbonate;
e) passive transport of amino acids.
The following occurs in the proximal tubule of the nephron:
a) reabsorption of glucose and most of the water;
b) secretion of most water;
c) passive transport of sodium;
d) secretion of bicarbonate;
e) passive transport of amino acids.
The antidiuretic hormone (ADH):
a) decreases the osmolarity of urine;
b) decreases the volume of final urine;
c) increases the reabsorption of water in the proximal tubules;
d) is synthesized in the posterior pituitary gland;
e) increases the excretion of glucose.
The antidiuretic hormone (ADH):
a) decreases the osmolarity of urine;
b) decreases the volume of final urine;
c) increases the reabsorption of water in the proximal tubules;
d) is synthesized in the posterior pituitary gland;
e) increases the excretion of glucose.
Regarding the kidneys:
a) there are 1.3 million nephrons in each kidney and more blood flows through the renal cortex than the renal medulla;
b) they produce aldosterone;
c) they receive 12% of the cardiac output at rest;
d) the blood flow through the renal cortex is lower compared to that in the renal medulla;
e) they secrete natriuretic peptide.
Regarding the kidneys:
a) there are 1.3 million nephrons in each kidney and more blood flows through the renal cortex than the renal medulla;
b) they produce aldosterone;
c) they receive 12% of the cardiac output at rest;
d) the blood flow through the renal cortex is lower compared to that in the renal medulla;
e) they secrete natriuretic peptide.
During physiological intake of water and salts:
a) osmotic pressure of ECF is higer than is ICF;
b) osmotic pressure of ICF is higer than is ECF;
c) osmotic pressure of ECF is equal to those is ICF;
d) the volume of ECF is higer then those of ICF;
e) none of them.
During physiological intake of water and salts:
a) osmotic pressure of ECF is higer than is ICF;
b) osmotic pressure of ICF is higer than is ECF;
c) osmotic pressure of ECF is equal to those is ICF;
d) the volume of ECF is higer then those of ICF;
e) none of them.
During hyperventilation is observed:
a) metabolic acidosis;
b) respiratory acidosis;
c) metabolic alcolosis;
d) respiratory alcolosis;
e) isohydria.
During hyperventilation is observed:
a) metabolic acidosis;
b) respiratory acidosis;
c) metabolic alcolosis;
d) respiratory alcolosis;
e) isohydria.
The glomerular capillaries have the following functions:
a) blood plasma filtration and formation of primary urine;
b) hormone secretion;
c) water secretion;
d) formation of primary urine;
e) dip into the medullary pyramids alongside the loops of Henle.
The glomerular capillaries have the following functions:
a) blood plasma filtration and formation of primary urine;
b) hormone secretion;
c) water secretion;
d) formation of primary urine;
e) dip into the medullary pyramids alongside the loops of Henle.
During hypoventilation is observed:
a) metabolic acidosis;
b) respiratory acidosis;
c) metabolic alcolosis;
d) respiratory alcolosis;
e) isohydria.
During hypoventilation is observed:
a) metabolic acidosis;
b) respiratory acidosis;
c) metabolic alcolosis;
d) respiratory alcolosis;
e) isohydria.
The renal blood flow:
a) doesn't depend on autoregulation;
b) is regulated by metabolites produced in the kidneys;
c) is not connected with the autoregulation of the glomerular filtration;
d) is autoregulated and is closely related to the autoregulation of the glomerular filtration;
e) doesn't influence the metabolic processes in the kidneys.
The renal blood flow:
a) doesn't depend on autoregulation;
b) is regulated by metabolites produced in the kidneys;
c) is not connected with the autoregulation of the glomerular filtration;
d) is autoregulated and is closely related to the autoregulation of the glomerular filtration;
e) doesn't influence the metabolic processes in the kidneys.
Which of the following substances has a clearance equal to the renal plasma flow?
а) РАН
b) glucose;
c) urea;
d) water;
e) inulin.
Which of the following substances has a clearance equal to the renal plasma flow?
а) РАН = Para-animohippuric acid
b) glucose;
c) urea;
d) water;
e) inulin.
In kidneys, the atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP):
a) decreases sodium and water excretion via urine;
b) increases sodium and water excretion via urine;
c) stimulates the secretion of renin;
d) stimulates the secretion of aldosterone;
e) has no effect.
In kidneys, the atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP):
a) decreases sodium and water excretion via urine;
b) increases sodium and water excretion via urine;
c) stimulates the secretion of renin;
d) stimulates the secretion of aldosterone;
e) has no effect.
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is decreased when:
a) renal blood flow is high;
b) renal blood flow is low and afferent arteriolar tone is high;
c) renal blood flow is high and efferent arteriolar tone is low;
d) renal blood flow is high and efferent arteriolar tone is high;
e) effective filtration surface area is increased.
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is decreased when:
a) renal blood flow is high;
b) renal blood flow is low and afferent arteriolar tone is high;
c) renal blood flow is high and efferent arteriolar tone is low;
d) renal blood flow is high and efferent arteriolar tone is high;
e) effective filtration surface area is increased.
Water excretion by the kidney is due to:
a) osmosis;
b) active transport into the lumen;
c) passive secretion in the collecting tubules;
d) solvent drag;
e) facilitated diffusion.
Water excretion by the kidney is due to:
a) osmosis;
b) active transport into the lumen;
c) passive secretion in the collecting tubules;
d) solvent drag;
e) facilitated diffusion.
Kidneys produce:
a) erythropoietin;
b) ADH;
c) angiotensin II;
d) ANP;
e) cholecalciferol.
Kidneys produce:
a) erythropoietin;
b) ADH;
c) angiotensin II;
d) ANP;
e) cholecalciferol.
Increase in GFR occurs when there is:
a) increased sympathetic stimulation;
b) decreased renal blood flow;
c) hypoproteinaemia;
d) ureteric obstruction;
e) none of the above.
Increase in GFR occurs when there is:
a) increased sympathetic stimulation;
b) decreased renal blood flow;
c) hypoproteinaemia;
d) ureteric obstruction;
e) none of the above.
In kidneys, the cortisol:
a) reduces glomerular filtration;
b) increases glomerular filtration;
c) decreases the renal vascular resistance;
d) decreases the secretion of renin;
e) inhibits diuresis.
In kidneys, the cortisol:
a) reduces glomerular filtration;
b) increases glomerular filtration;
c) decreases the renal vascular resistance;
d) decreases the secretion of renin;
e) inhibits diuresis.
The volume of primary urine per 24 hours is about:
a) 1000 ml;
b) 180 L;
c) 18 L;
d) 50 L;
e) 8 L.
The volume of primary urine per 24 hours is about:
a) 1000 ml;
b) 180 L;
c) 18 L;
d) 50 L;
e) 8 L.
All factors mentioned below trigger the thirst except:
a) plasma osmolality over 295 mOsm.kg-1;
b) angiotensin II;
c) antidiuretic hormone (ADH);
d) hypervolemia;
e) dry mucosa in the mouth.
All factors mentioned below trigger the thirst except:
a) plasma osmolality over 295 mOsm.kg-1;
b) angiotensin II;
c) antidiuretic hormone (ADH);
d) hypervolemia;
e) dry mucosa in the mouth.
The countercurrent exchange system includes:
a) glomerulus and macula densa;
b) proximal convoluted tubule and distal convoluted tubule;
c) loop of Henle and collecting tubule;
d) afferent arteriole and efferent arteriole;
e) ureters and bladder.
The countercurrent exchange system includes:
a) glomerulus and macula densa;
b) proximal convoluted tubule and distal convoluted tubule;
c) loop of Henle and collecting tubule;
d) afferent arteriole and efferent arteriole;
e) ureters and bladder.
In kidneys, the nitric oxide (NO):
a) increases the renal vascular resistance;
b) stimulates the absorption of Na+ in the collecting ducts;
c) suppresses the absorption of Na+ in the distal tubule and stimulates the secretion of renin;
d) reduces the secretion of renin;
e) increases the reabsorption of water triggered by antidiuretic hormone.
In kidneys, the nitric oxide (NO):
a) increases the renal vascular resistance;
b) stimulates the absorption of Na+ in the collecting ducts;
c) suppresses the absorption of Na+ in the distal tubule and stimulates the secretion of renin;
d) reduces the secretion of renin;
e) increases the reabsorption of water triggered by antidiuretic hormone.
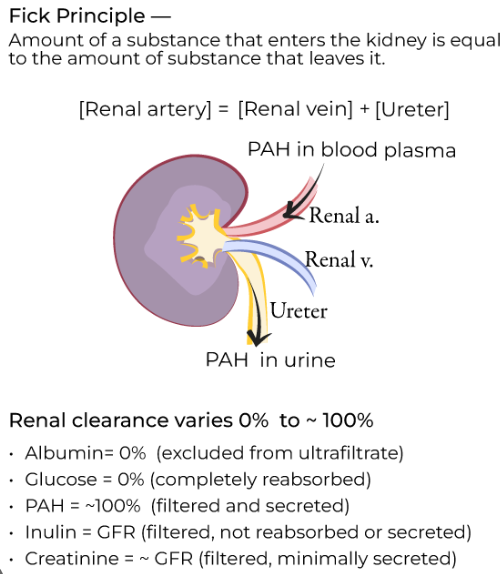
The renal clearance of a substance (Cx):
a) is inversely related to its urinary concentration (Ux);
b) is directly related to the rate of urine formation, and is expressed in units of volume per unit time;
c) is directly related to its plasma concentration (Px);
d) is expressed in mm Hg;
e) must fall in the presence of metabolic poisons.
The renal clearance of a substance (Cx):
a) is inversely related to its urinary concentration (Ux);
b) is directly related to the rate of urine formation, and is expressed in units of volume per unit time;
c) is directly related to its plasma concentration (Px);
d) is expressed in mm Hg;
e) must fall in the presence of metabolic poisons.

In the fluid in the distal part of the proximal convoluted tubule:
a) urea concentration is higher than in Bowman's capsule;
b) pH is less than 6 when the kidneys are excreting an acid urine;
c) glucose concentration is similar to that in plasma;
d) osmolality is about 25 per cent that of glomerular filtrate;
e) bicarbonate concentration is higher than in plasma.
In the fluid in the distal part of the proximal convoluted tubule:
a) urea concentration is higher than in Bowman's capsule;
b) pH is less than 6 when the kidneys are excreting an acid urine;
c) glucose concentration is similar to that in plasma;
d) osmolality is about 25 per cent that of glomerular filtrate;
e) bicarbonate concentration is higher than in plasma.
When water absorption is stimulated, the result is:
a) water diuresis;
b) osmotic diuresis;
c) antidiuresis;
d) high volume of final urine with low concentration of the dissolved substances;
e) high volume of final urine with high concentration of the dissolved substances.
When water absorption is stimulated, the result is:
a) water diuresis;
b) osmotic diuresis;
c) antidiuresis;
d) high volume of final urine with low concentration of the dissolved substances;
e) high volume of final urine with high concentration of the dissolved substances.
In the kidneys, bradykinin:
a) has expressed vasoconstriction and stimulates the reabsorption of Na+ in the distal tubules;
b) has well expressed vasodilation effect and suppresses the absorption of Na+ in the distal tubules;
c) has expressed vasodilation effect and suppresses the absorption of Na+ in the proximal tubules;
d) inhibits diuresis;
e) inhibit the renal perfusion.
In the kidneys, bradykinin:
a) has expressed vasoconstriction and stimulates the reabsorption of Na+ in the distal tubules;
b) has well expressed vasodilation effect and suppresses the absorption of Na+ in the distal tubules;
c) has expressed vasodilation effect and suppresses the absorption of Na+ in the proximal tubules;
d) inhibits diuresis;
e) inhibit the renal perfusion.
The effects of endothelin-1 on the renal tubules are:
a) increase of the effect of antidiuretic hormone on the reabsorption of water in the collecting duct and decreased diuresis;
b) stimulation of renin and aldosterone secretion;
c) reduction of atrial sodium uretic peptide secretion;
d) stimulation of diuresis and excretion of sodium;
e) decreased vascular resistance and increased cortical blood flow.
The effects of endothelin-1 on the renal tubules are:
a) increase of the effect of antidiuretic hormone on the reabsorption of water in the collecting duct and decreased diuresis;
b) stimulation of renin and aldosterone secretion;
c) reduction of atrial sodium uretic peptide secretion;
d) stimulation of diuresis and excretion of sodium;
e) decreased vascular resistance and increased cortical blood flow.
When a patient's mean arterial blood pressure falls by 50%:
a) renal blood flow increases;
b) glomerular filtration increases;
c) there is a decrease in the circulating aldosterone level;
d) renal vasoconstriction occurs;
e) urinary output is increased.
When a patient's mean arterial blood pressure falls by 50%:
a) renal blood flow increases;
b) glomerular filtration increases;
c) there is a decrease in the circulating aldosterone level;
d) renal vasoconstriction occurs;
e) urinary output is increased.
The cells of the distal convoluted tubule:
a) reabsorb about 50% of the water filtered by the glomeruli;
b) reabsorb all filtered aminoacide;
c) reabsorb all filtered proteins;
d) reabsorb sodium in exchange for hydrogen or potassium ions;
e) determine the final composition of urine.
The cells of the distal convoluted tubule:
a) reabsorb about 50% of the water filtered by the glomeruli;
b) reabsorb all filtered aminoacide;
c) reabsorb all filtered proteins;
d) reabsorb sodium in exchange for hydrogen or potassium ions;
e) determine the final composition of urine.
The excretion of xenobiotics in the kidneys is carried out by:
a) filtration or filtration and additional reabsorption in the distal tubule;
b) filtration or filtration and additional secretion in the distal tubule;
c) filtration or filtration and additional secretion in the proximal tubule;
d) secretion in the collecting duct;
e) filtration and additional absorption in the proximal tubule.
The excretion of xenobiotics in the kidneys is carried out by:
a) filtration or filtration and additional reabsorption in the distal tubule;
b) filtration or filtration and additional secretion in the distal tubule;
c) filtration or filtration and additional secretion in the proximal tubule;
d) secretion in the collecting duct;
e) filtration and additional absorption in the proximal tubule.
Urea:
a) and glucose have different molar concentrations in normal blood;
b) clearance is higher, than creatinin's one;
c) is actively secreted by the renal tubular cells into the tubular fluid;
d) concentration in blood may rise ten-fold after a high protein meal;
e) stimulates diuresis when its blood concentration is increased.
Urea:
a) and glucose have different molar concentrations in normal blood;
b) clearance is higher, than creatinin's one;
c) is actively secreted by the renal tubular cells into the tubular fluid;
d) concentration in blood may rise ten-fold after a high protein meal;
e) stimulates diuresis when its blood concentration is increased.
The renal clearance of:
a) inulin provides the estimation of glomerular filtration rate.
b) chloride increases after an injection of aldosterone.
c) PAH falls when the PAH load exceeds the Tm for PAH;
d) urea is higher than that of inulin;
e) inulin is dependent of its plasma concentration.
The renal clearance of:
a) inulin provides the estimation of glomerular filtration rate.
b) chloride increases after an injection of aldosterone.
c) PAH falls when the PAH load exceeds the Tm for PAH;
d) urea is higher than that of inulin;
e) inulin is dependent of its plasma concentration.
Aldosterone:
a) is a steroid hormone, secreted by the adrenal medulla;
b) production ceases following removal of the kidneys and their juxtaglomerular cells;
c) production decreases in treatment with drugs which block angiotensin-converting enzyme;
d) secretion results in increased potassium reabsorption by the nephron;
e) secretion results in increased plasma volume.
Aldosterone:
a) is a steroid hormone, secreted by the adrenal medulla;
b) production ceases following removal of the kidneys and their juxtaglomerular cells;
c) production decreases in treatment with drugs which block angiotensin-converting enzyme;
d) secretion results in increased potassium reabsorption by the nephron;
e) secretion results in increased plasma volume.
In the kidneys, over 70% of the filtrated Na+ is:
a) secreted in the proximal tubule via passive transport;
b) secreted in the proximal tubule with energy expenditure;
c) reabsorbed in the proximal tubule via basolateral active transport;
d) secreted in the proximal tubule via basolateral absorption in the proximal tubule via basolateral active transport;
e) secreted in the collecting duct passively.
In the kidneys, over 70% of the filtrated Na+ is:
a) secreted in the proximal tubule via passive transport;
b) secreted in the proximal tubule with energy expenditure;
c) reabsorbed in the proximal tubule via basolateral active transport;
d) secreted in the proximal tubule via basolateral absorption in the proximal tubule via basolateral active transport;
e) secreted in the collecting duct passively.
The renal clearance:
a) of glucose is above 0, if the plasma concentration of a given substance is below 11 mmol.L-1
b) of urea is higher than creatinin's one;
c) of glucose provides an estimate of renal plasma flow;
d) of phosphate is decreased by parathormone;
e) of proteins is normally zero.
The renal clearance:
a) of glucose is above 0, if the plasma concentration of a given substance is below 11 mmol.L-1
b) of urea is higher than creatinin's one;
c) of glucose provides an estimate of renal plasma flow;
d) of phosphate is decreased by parathormone;
e) of proteins is normally zero.
Secretion of renin:
a) occurs in the stomach during infancy.
b) is stimulated by the hormone angiotensin I.
c) is stimulated by a fall in extracellular fluid volume and leads to raised levels of angiotensin II in the blood;
d) inhibits the secretion of aldosterone;
e) inhibits ACTH secretion by the pituitary gland.
Secretion of renin:
a) occurs in the stomach during infancy.
b) is stimulated by the hormone angiotensin I.
c) is stimulated by a fall in extracellular fluid volume and leads to raised levels of angiotensin II in the blood;
d) inhibits the secretion of aldosterone;
e) inhibits ACTH secretion by the pituitary gland.
In kidneys potassium is:
a) filtrated and secreted in the proximal tubule mainly via paracellular transport;
b) filtrated freely and reabsorbed the proximal tubule mainly via paracellular transport;
c) filtered freely and reabsorbed via symport with Na+ in the distal tubule;
d) filtered freely and reabsorbed in the proximal tubule mainly via symport with Na+.
e) filtrated freely and reabsorbed in the collecting duct mainly via paracellular transport.
In kidneys potassium is:
a) filtrated and secreted in the proximal tubule mainly via paracellular transport;
b) filtrated freely and reabsorbed the proximal tubule mainly via paracellular transport;
c) filtered freely and reabsorbed via symport with Na+ in the distal tubule;
d) filtered freely and reabsorbed in the proximal tubule mainly via symport with Na+.
e) filtrated freely and reabsorbed in the collecting duct mainly via paracellular transport.
Long-standing obstruction of the urethra may cause:
a) enlargement of the prostate gland;
b) dystrophy of the bladder muscle;
c) dilation of the ureters and reduction of the glomerular filtration rate;
d) increase and reduction of the glomerular filtration rate;
e) a decrease in residual volume in the bladder.
Long-standing obstruction of the urethra may cause:
a) enlargement of the prostate gland;
b) dystrophy of the bladder muscle;
c) dilation of the ureters and reduction of the glomerular filtration rate;
d) increase and reduction of the glomerular filtration rate;
e) a decrease in residual volume in the bladder.
Emptying of the urinary bladder may be less effective if:
a) the sympathetic nerves carrying afferent information from bladder to the spinal cord are cut;
b) the pelvic nerves are cut or anticholinergic drugs are administered;
c) cholinergic agonists are administered;
d) alpha-adrenergic receptor antagonists are administered;
e) beta-adrenergic receptor blockers are administered.
Emptying of the urinary bladder may be less effective if:
a) the sympathetic nerves carrying afferent information from bladder to the spinal cord are cut;
b) the pelvic nerves are cut or anticholinergic drugs are administered;
c) cholinergic agonists are administered;
d) alpha-adrenergic receptor antagonists are administered;
e) beta-adrenergic receptor blockers are administered.
Bicarbonate, phosphate and ammonia buffer systems are:
a) cellular buffer systems;
b) elements of renal regulation of pH;
c) elements of respiratory regulation of pH;
d) systems for maintaining optimal pH of the stomach;
e) enzyme systems of digestion.
Bicarbonate, phosphate and ammonia buffer systems are:
a) cellular buffer systems;
b) elements of renal regulation of pH;
c) elements of respiratory regulation of pH;
d) systems for maintaining optimal pH of the stomach;
e) enzyme systems of digestion.
In all cases mentioned below there is metabolic alkalosis except:
a) in uremia;
b) in severe vomiting;
c) in hyper aldosteronism;
d) in case of intake of NaHCO3-
e) in case of prolonged treatment with some diuretics.
In all cases mentioned below there is metabolic alkalosis except:
a) in uremia;
b) in severe vomiting;
c) in hyper aldosteronism;
d) in case of intake of NaHCO3-
e) in case of prolonged treatment with some diuretics.
A patient with chronic renal failure usually has:
a) a decreased blood uric acid;
b) an increased blood urea and blood uric acid;
c) an increased creatinine clearance;
d) an increased acid-base disturbance when he or she vomits;
e) an increased acid-base problem on a low protein diet.
A patient with chronic renal failure usually has:
a) a decreased blood uric acid;
b) an increased blood urea and blood uric acid;
c) an increased creatinine clearance;
d) an increased acid-base disturbance when he or she vomits;
e) an increased acid-base problem on a low protein diet.
Cutting the sympathetic nerves to the urinary bladder may cause:
a) difficulty in emptying the bladder;
b) loss of tone in the internal sphincter of the bladder and loss of pain sensation in the bladder;
c) loss of tone in the external sphincter of the bladder;
d) increased pain sensation in the bladder;
e) infertility in the female.
Cutting the sympathetic nerves to the urinary bladder may cause:
a) difficulty in emptying the bladder;
b) loss of tone in the internal sphincter of the bladder and loss of pain sensation in the bladder;
c) loss of tone in the external sphincter of the bladder;
d) increased pain sensation in the bladder;
e) infertility in the female.
A long-standing increase in arterial pCO2 (respiratory acidosis) leads to:
a) an increase in renal bicarbonate formation;
b) a decrease in urinary ammonium salts;
c) a decrease in plasma potassium concentration;
d) an increase of the mono-hydrogen/di-hydrogen phosphate ratio in urine;
e) a decrease in urinary bicarbonate excretion.
A long-standing increase in arterial pCO2 (respiratory acidosis) leads to:
a) an increase in renal bicarbonate formation;
b) a decrease in urinary ammonium salts;
c) a decrease in plasma potassium concentration;
d) an increase of the mono-hydrogen/di-hydrogen phosphate ratio in urine;
e) a decrease in urinary bicarbonate excretion.
The inhibition of the antidiuretic hormone (ADH) by alcohol, would have the following effect:
a) constriction of the afferent arteriole;
b) inhibition of diuresis;
c) stimulation of water conservation;
d) constriction of the efferent arteriole;
e) reduction in water reabsorption by the kidneys.
The inhibition of the antidiuretic hormone (ADH) by alcohol, would have the following effect:
a) constriction of the afferent arteriole;
b) inhibition of diuresis;
c) stimulation of water conservation;
d) constriction of the efferent arteriole;
e) reduction in water reabsorption by the kidneys.
Reabsorption of amino acids from the filtrate requires many different protein carriers because:
a) denaturation may occur;
b) this transport is not competitive;
c) there are only 10 different amino acids;
d) transport of amino acids is typically highly specific;
e) glucose inhibits amino acid transport.
Reabsorption of amino acids from the filtrate requires many different protein carriers because:
a) denaturation may occur;
b) this transport is not competitive;
c) there are only 10 different amino acids;
d) transport of amino acids is typically highly specific;
e) glucose inhibits amino acid transport.
Reabsorption (transport) of both Na+ and glucose together from the renal lumen is an example of:
a) facilitated diffusion;
b) secondary passive transport;
c) primary direct active transport;
d) secondary indirect active antiport;
e) secondary indirect active symport.
Reabsorption (transport) of both Na+ and glucose together from the renal lumen is an example of:
a) facilitated diffusion;
b) secondary passive transport;
c) primary direct active transport;
d) secondary indirect active antiport;
e) secondary indirect active symport.
Drinking a litre of water:
a) increases secretion of antidiuretic hormone;
b) reduces the plasma sodium concentration;
c) increases osmolarity of the urine;
d) causes body cells to shrink;
e) decreases the specific gravity of the body.
Drinking a litre of water:
a) increases secretion of antidiuretic hormone;
b) reduces the plasma sodium concentration;
c) increases osmolarity of the urine;
d) causes body cells to shrink;
e) decreases the specific gravity of the body.
An acid-base buffer system:
a) can be a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base;
b) can be a solution of sodium and bicarbonate ions;
c) prevents any change in pH when acid is added;
d) works best when acid and base are equal in concentration;
e) is hemoglobin as an example of intracelular buffer.
An acid-base buffer system:
a) can be a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base;
b) can be a solution of sodium and bicarbonate ions;
c) prevents any change in pH when acid is added;
d) works best when acid and base are equal in concentration;
e) is hemoglobin as an example of intracelular buffer.
Acidosis in a patient may lead to:
a) increased urinary excretion of potassium.
b) hypoventilation.
c) a blood pH of less than 5.5.
d) an urinary pH of less than 5.5.
e) tetany.
Acidosis in a patient may lead to:
a) increased urinary excretion of potassium.
b) hypoventilation.
c) a blood pH of less than 5.5.
d) an urinary pH of less than 5.5.
e) tetany.
A rise in the osmolality of extracellular fluid may lead to:
a) thirst and release of vasopressin;
b) increased water reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubules;
c) a decrease of vasopressin secretion;
d) an increase in intracellular fluid volume;
e) suppression of sweat secretion.
A rise in the osmolality of extracellular fluid may lead to:
a) thirst and release of vasopressin;
b) increased water reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubules;
c) a decrease of vasopressin secretion;
d) an increase in intracellular fluid volume;
e) suppression of sweat secretion.
Raised blood pH and bicarbonate level are consistent with:
a) metabolic acidosis;
b) partly compensated respiratory alkalosis;
c) a reduced pCO2;
d) chronic renal failure with a raised pCO2;
e) a history of persistent vomiting of gastric contents.
Raised blood pH and bicarbonate level are consistent with:
a) metabolic acidosis;
b) partly compensated respiratory alkalosis;
c) a reduced pCO2;
d) chronic renal failure with a raised pCO2;
e) a history of persistent vomiting of gastric contents.
A patient with partly compensated respiratory acidosis:
a) must have a raised pCO2;
b) must have a raised bicarbonate concentration [HCO3-]
c) may have evidence of renal compensation .;
d) may have respiratory failure due to hypoventilation;
e) all of the above.
A patient with partly compensated respiratory acidosis:
a) must have a raised pCO2;
b) must have a raised bicarbonate concentration [HCO3-]
c) may have evidence of renal compensation .;
d) may have respiratory failure due to hypoventilation;
e) all of the above.
Sodium retention:
a) occurs for several days after major surgery;
b) expands the extracellular fluid volume;
c) expands the blood volume;
d) increases the severity of oedema;
e) all of the above.
Sodium retention:
a) occurs for several days after major surgery;
b) expands the extracellular fluid volume;
c) expands the blood volume;
d) increases the severity of oedema;
e) all of the above.
Alkalosis occurs when:
a) pH ≤ 7.35;
b) pH of the arterial blood is ≥ 7.45;
c) there is an increase in the concentration of H+;
d) pH of the arterial blood is ≥ 7.00;
e) there is no correct answer.
Alkalosis occurs when:
a) pH ≤ 7.35;
b) pH of the arterial blood is ≥ 7.45;
c) there is an increase in the concentration of H+;
d) pH of the arterial blood is ≥ 7.00;
e) there is no correct answer.
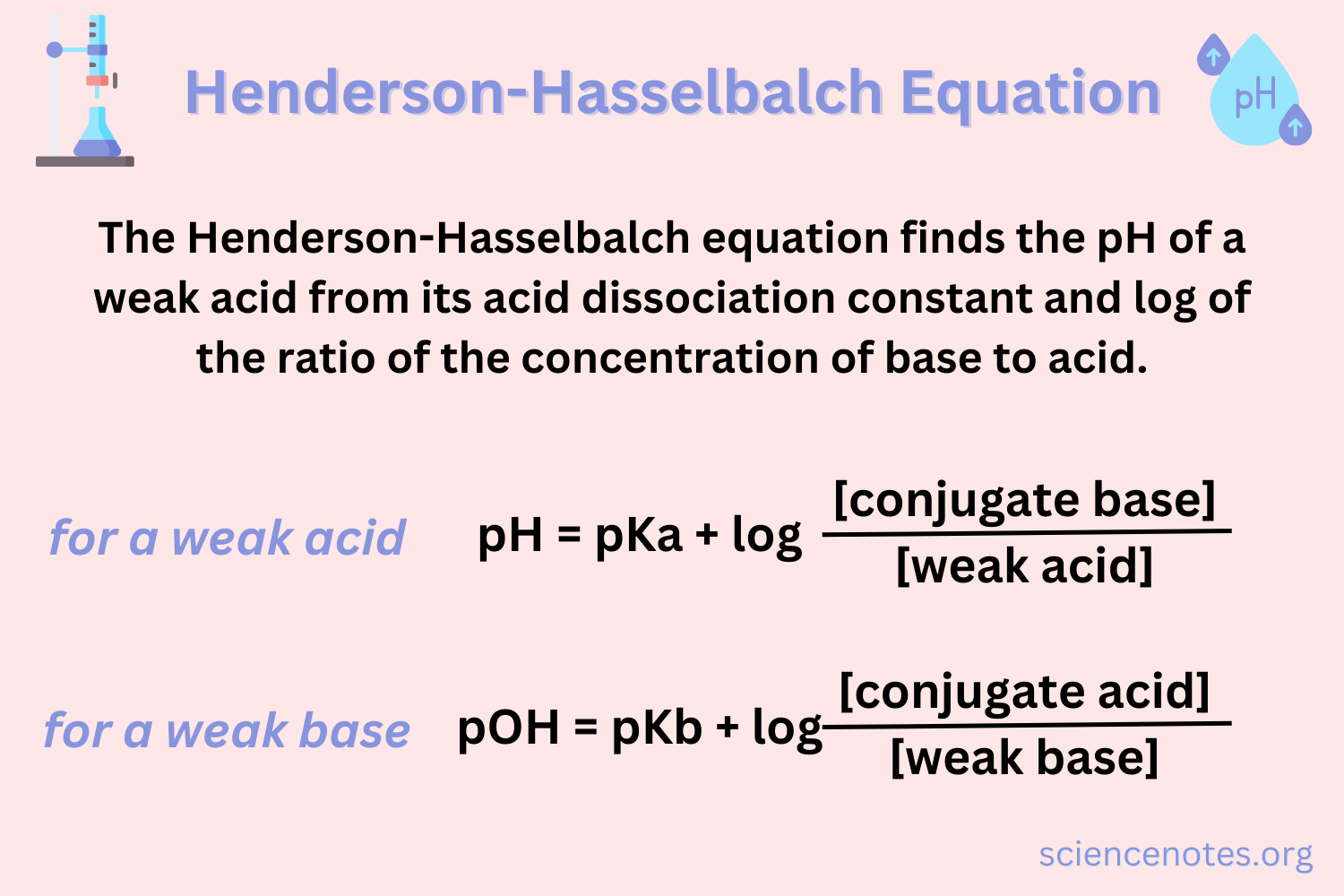
In concern with hydrogen carbonic buffer system, according to Henderson-Hasselbach equation:
a) pH increases when HCO3- concentration increases;
b) pH increases when CO2 tension increases;
c) pH decreases when HCO3- concentration increases;
d) pH decreases when CO2 tension increases;
e) pH decreases when CO2 tension increases and increases when HCO3- concentration increases.
In concern with hydrogen carbonic buffer system, according to Henderson-Hasselbach equation:
a) pH increases when HCO3- concentration increases;
b) pH increases when CO2 tension increases;
c) pH decreases when HCO3- concentration increases;
d) pH decreases when CO2 tension increases;
e) pH decreases when CO2 tension increases and increases when HCO3- concentration increases.
Raised level of calcium in the blood (hypercalcaemia):
a) may occur when parathyroid activity decreases;
b) may occur when the plasma protein level falls;
c) may occur in chronic renal failure;
d) increases the risk of stone formation in the urinary tract;
e) causes increased excitability of nerve and muscle.
Raised level of calcium in the blood (hypercalcaemia):
a) may occur when parathyroid activity decreases;
b) may occur when the plasma protein level falls;
c) may occur in chronic renal failure;
d) increases the risk of stone formation in the urinary tract;
e) causes increased excitability of nerve and muscle.
Thirst is stimulated by:
a) increase in plasma osmolality and volume;
b) increase in plasma osmolality and decrease in volume;
c) decrease in osmolality and increase in volume;
d) decrease in plasma osmolality and volume;
e) increase in intracelular volume.
Thirst is stimulated by:
a) increase in plasma osmolality and volume;
b) increase in plasma osmolality and decrease in volume;
c) decrease in osmolality and increase in volume;
d) decrease in plasma osmolality and volume;
e) increase in intracelular volume.
The reference interval of plasma osmolarity is:
a) 190 - 200 mOsm.L-1;
b) 120 ml·min-1;
c) 280 - 285 mOsm.L-1;
d) 7.36 - 7.44 pH;
e) 1100 - 1200 mOsm·kg-1.
The reference interval of plasma osmolarity is:
a) 190 - 200 mOsm.L-1;
b) 120 ml·min-1;
c) 280 - 285 mOsm.L-1;
d) 7.36 - 7.44 pH;
e) 1100 - 1200 mOsm·kg-1.
Urea:
a) in the urine doesn't depend on the amount of proteins in the diet;
b) doesn't contribute to the establishment of the osmotic gradient in the medullary pyramids and to the formation of concentrated urine in the collecting ducts;
c) contributes to the establishment of the osmotic gradient in the medullary pyramids and to the formation of concentrated urine in the collecting ducts;
d) in the urine doesn't vary with the amount of urea filtered;
e) transport is not mediated by urea transporters.
Urea:
a) in the urine doesn't depend on the amount of proteins in the diet;
b) doesn't contribute to the establishment of the osmotic gradient in the medullary pyramids and to the formation of concentrated urine in the collecting ducts;
c) contributes to the establishment of the osmotic gradient in the medullary pyramids and to the formation of concentrated urine in the collecting ducts;
d) in the urine doesn't vary with the amount of urea filtered;
e) transport is not mediated by urea transporters.
All but except one are followed by thirst:
a) plasma osmolality above 295 mOsm·kg-1;
b) angiotensin II;
c) ADH;
d) hypervolemia;
e) dry oral mucosa.
All but except one are followed by thirst:
a) plasma osmolality above 295 mOsm·kg-1;
b) angiotensin II;
c) ADH;
d) hypervolemia;
e) dry oral mucosa.
The volume of ECF is regulated by:
a) the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system;
b) atrial nauriuretic peptide;
c) catheholamines;
d) sympathetic division of the ANS;
e) all of the above.
The volume of ECF is regulated by:
a) the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system;
b) atrial nauriuretic peptide;
c) catheholamines;
d) sympathetic division of the ANS;
e) all of the above.
For the buffer capacity of the blood of highest significance is the:
a) haemoglobin buffer system;
b) protein buffer system;
c) phosphate buffer system;
d) hydrogen carbonate buffer system;
e) ammonia buffer system.
For the buffer capacity of the blood of highest significance is the:
a) haemoglobin buffer system;
b) protein buffer system;
c) phosphate buffer system;
d) hydrogen carbonate buffer system;
e) ammonia buffer system.
All statements about ADH are correct, except the following:
a) ADH is secreted by the posterior pituitary;
b) ADH secretion is regulated by plasma osmolality;
c) ADH increases the tubular reabsorption of K+;
d) ADH increases reabsorption of water in the distal and collecting tubules;
e) ADH is synthesized in the hypothalamus.
All statements about ADH are correct, except the following:
a) ADH is secreted by the posterior pituitary;
b) ADH secretion is regulated by plasma osmolality;
c) ADH increases the tubular reabsorption of K+;
d) ADH increases reabsorption of water in the distal and collecting tubules;
e) ADH is synthesized in the hypothalamus.
H+ ions are secreted:
a) in the ascending limb of Henle;
b) in the proximal tubule;
c) along the nephron parallel with the reabsorption of HCO3- ions;
d) in the descending limb of Henle;
e) collecting tubule.
H+ ions are secreted:
a) in the ascending limb of Henle;
b) in the proximal tubule;
c) along the nephron parallel with the reabsorption of HCO3- ions;
d) in the descending limb of Henle;
e) collecting tubule.
Most of the filtrated calcium is:
a) secreted in the collecting ducts;
b) passively reabsorbed in the proximal tubules;
c) reabsorbed in the collecting ducts;
d) reabsorbed in connection with the secretion of H+;
e) reabsorbed parallel to HCO3- along the whole nephron.
Most of the filtrated calcium is:
a) secreted in the collecting ducts;
b) passively reabsorbed in the proximal tubules;
c) reabsorbed in the collecting ducts;
d) reabsorbed in connection with the secretion of H+;
e) reabsorbed parallel to HCO3- along the whole nephron.
The secretion of H+ in the tubular fluid is achieved by:
a) osmosis and diffusion;
b) diffusion and primary active transport;
c) primary and secondary active transport;
d) secondary active transport;
e) diffusion only.
The secretion of H+ in the tubular fluid is achieved by:
a) osmosis and diffusion;
b) diffusion and primary active transport;
c) primary and secondary active transport;
d) secondary active transport;
e) diffusion only.
In acidosis, the kidneys:
a) increase the excretion of H+ and HCO3-;
b) decrease the excretion of H+ and increase the reabsorbtion of HCO3-;
c) increase the excretion of H+ and reabsorbtion of HCO3-;
d) decrease the excretion of H+ and reabsorbtion of HCO3-;
e) none of the above.
In acidosis, the kidneys:
a) increase the excretion of H+ and HCO3-;
b) decrease the excretion of H+ and increase the reabsorbtion of HCO3-;
c) increase the excretion of H+ and reabsorbtion of HCO3-;
d) decrease the excretion of H+ and reabsorbtion of HCO3-;
e) none of the above.
In alcalosis, the kidneys:
a) decrease the excretion of H+ and increase the reabsorbtion of HCO3-;
b) decrease the excretion of H+;
c) decrease the indirect reabsorbtion of HCO3-;
d) increase the indirect reabsorbtion of HCO3-;
e) decrease the excretion of H+ and increase the excretion of HCO3-;
In alcalosis, the kidneys:
a) decrease the excretion of H+ and increase the reabsorbtion of HCO3-;
b) decrease the excretion of H+;
c) decrease the indirect reabsorbtion of HCO3-;
d) increase the indirect reabsorbtion of HCO3-;
e) decrease the excretion of H+ and increase the excretion of HCO3-;
The formation of the final urine is due to:
a) filtration, diffusion and secretion;
b) reabsorbtion, osmosis and diffusion;
c) glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorbtion and secretion;
d) filtration, secretion and paracrinia;
e) all of the above.
The formation of the final urine is due to:
a) filtration, diffusion and secretion;
b) reabsorbtion, osmosis and diffusion;
c) glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorbtion and secretion;
d) filtration, secretion and paracrinia;
e) all of the above.
Normal diuresis per 24h is about:
a) 500 ml;
b) 1.5 - 2 L;
c) 5 L;
d) 120 - 180 L.
e) 15 L.
Normal diuresis per 24h is about:
a) 500 ml;
b) 1.5 - 2 L;
c) 5 L;
d) 120 - 180 L.
e) 15 L.
The volume of plasma, totally cleared from a substance when passing through the kidneys per 1 minute (second) is called:
a) diuresis;
b) formation of final urine;
c) glomerular filtration;
d) transport maximum;
e) clearance.
The volume of plasma, totally cleared from a substance when passing through the kidneys per 1 minute (second) is called:
a) diuresis;
b) formation of final urine;
c) glomerular filtration;
d) transport maximum;
e) clearance.
The glomerular filtration is estimated via the clearance of:
а) РАНА;
b) glucose;
c) urea;
d) creatinin;
e) sodium.
The glomerular filtration is estimated via the clearance of:
а) РАНА;
b) glucose;
c) urea;
d) creatinin;
e) sodium.
The transport maximum (Tmax) of glucose is:
a) 125 ml.min-1;
b) 300 - 370 mg.min-1;
c) 2.8 - 6.1 mmol.L-1;
d) up to 11.1 mmol-L-1;
e) none of the above.
The transport maximum (Tmax) of glucose is:
a) 125 ml.min-1;
b) 300 - 370 mg.min-1;
c) 2.8 - 6.1 mmol.L-1;
d) up to 11.1 mmol-L-1;
e) none of the above.
If the clearance of a substance is higher than the clearance of inulin:
a) the substance is additionally reabsorbed in the tubules;
b) the substance is additionally secreted in the tubules;
c) the substance is either additionally reabsorbed or secreted;
d) the substance is transported with proteins in the tubules;
e) the substance is secreted in the proximal more than in the distal tubule.
If the clearance of a substance is higher than the clearance of inulin:
a) the substance is additionally reabsorbed in the tubules;
b) the substance is additionally secreted in the tubules;
c) the substance is either additionally reabsorbed or secreted;
d) the substance is transported with proteins in the tubules;
e) the substance is secreted in the proximal more than in the distal tubule.
If the clearance of a substance is lower than the clearance of inulin:
a) the substance is additionally reabsorbed in the tubules;
b) the substance is neither reabsorbed, neither secreted;
c) the substance is additionally secreted in the tubules;
d) the substance is co-transported with proteins in the tubules;
e) the substance is secreted in the proximal more than in the distal tubule.
If the clearance of a substance is lower than the clearance of inulin:
a) the substance is additionally reabsorbed in the tubules;
b) the substance is neither reabsorbed, neither secreted;
c) the substance is additionally secreted in the tubules;
d) the substance is co-transported with proteins in the tubules;
e) the substance is secreted in the proximal more than in the distal tubule.
The human kidneys can concentrate the final urine up to:
a) 100 mOsm.L-1;
b) 120 mOsm.L-1;
c) 295 mOsm.L-1;
d) 7.36 - 7.44.L-1;
e) 1200 mOsm.L-1;
The human kidneys can concentrate the final urine up to:
a) 100 mOsm.L-1;
b) 120 mOsm.L-1;
c) 295 mOsm.L-1;
d) 7.36 - 7.44.L-1;
e) 1200 mOsm.L-1;
The factors determining glomerular filtration are:
a) hemodynamic, colloid-osmotic pressures;
b) hemodynamic, reabsorptive pressures;
c) hemodynamic, colloid-osmotic, intracapsular pressures;
d) intraabdominal, hemodynamic, colloid-osmotic pressures;
e) filtration, reabsorptive pressures.
The factors determining glomerular filtration are:
a) hemodynamic, colloid-osmotic pressures;
b) hemodynamic, reabsorptive pressures;
c) hemodynamic, colloid-osmotic, intracapsular pressures;
d) intraabdominal, hemodynamic, colloid-osmotic pressures;
e) filtration, reabsorptive pressures.
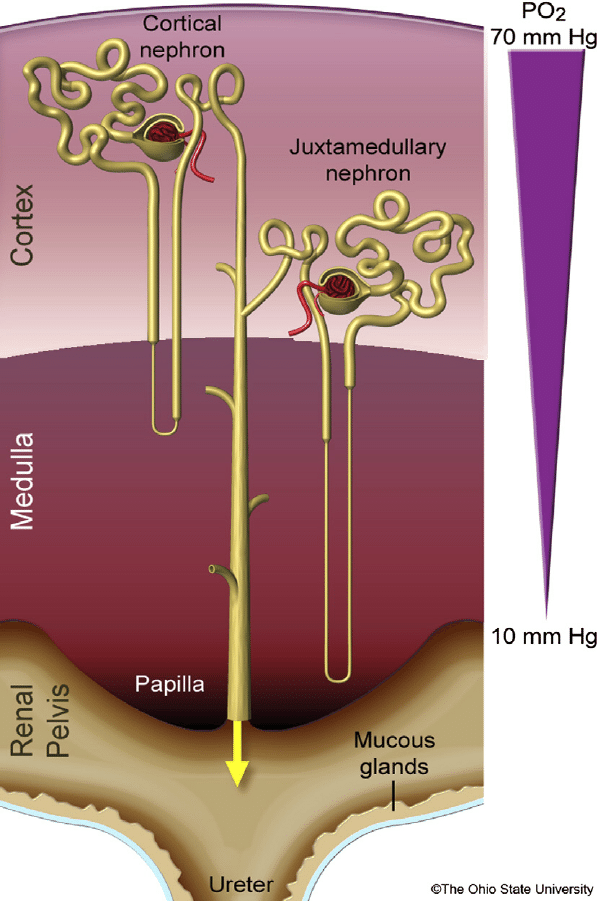
What is specific about juxtaglomerular nephrons, is that:
a) the glomerules are located in the outer part of cortex;
b) have longer loops of Henle, reaching papilles;
c) their efferent arterioles give rise of peritubular capillary network;
d) the glomerules are located in the inner part of cortex (near medulla) and their efferent arterioles give rise of vasa recta in medulla;
e) there is no correct answer.
What is specific about juxtaglomerular nephrons, is that:
a) the glomerules are located in the outer part of cortex;
b) have longer loops of Henle, reaching papilles;
c) their efferent arterioles give rise of peritubular capillary network;
d) the glomerules are located in the inner part of cortex (near medulla) and their efferent arterioles give rise of vasa recta in medulla;
e) there is no correct answer.
Glomerular filtration will increase except:
a) the mean arterial blood pressure is above 180 mm Hg;
b) hypoproteinemia;
c) there is constriction of the afferent arteriole;
d) there is constriction of the efferent arteriole;
e) there is vasodilation.
Glomerular filtration will increase except:
a) the mean arterial blood pressure is above 180 mm Hg;
b) hypoproteinemia;
c) there is constriction of the afferent arteriole;
d) there is constriction of the efferent arteriole;
e) there is vasodilation.
What is the percentage of water reabsorbed in the tubules, under the control of ADH?
a) 100%;
b) 85%;
c) 50%;
d) 15%;
e) 0%.
What is the percentage of water reabsorbed in the tubules, under the control of ADH?
a) 100%;
b) 85%;
c) 50%;
d) 15%;
e) 0%.
In all mentioned bellow cases a metabolic acidosis can be find except:
a) diabetes mellitus;
b) severe diarrhea;
c) intensive physical exercise;
d) severe vomiting;
e) renal failure.
In all mentioned bellow cases a metabolic acidosis can be find except:
a) diabetes mellitus;
b) severe diarrhea;
c) intensive physical exercise;
d) severe vomiting;
e) renal failure.
The volume of glomerular filtration is about:
a) 125 ml·min-1 primary urine;
b) 600 - 700 ml·min-1 primary urine;
c) 1200 - 1300 ml·min-1 primary urine;
d) 5 L·min-1 primary urine;
e) 170 L·min-1 primary urine.
The volume of glomerular filtration is about:
a) 125 ml·min-1 primary urine;
b) 600 - 700 ml·min-1 primary urine;
c) 1200 - 1300 ml·min-1 primary urine;
d) 5 L·min-1 primary urine;
e) 170 L·min-1 primary urine.
All statements about aldosterone are correct except:
a) is secreted by the adrenal cortex;
b) acts on distal and collective tubules;
c) increases the reabsorption of Na+;
d) increases the tubular reabsorption of K+;
e) its secretion is controlled by angiotensin II.
All statements about aldosterone are correct except:
a) is secreted by the adrenal cortex;
b) acts on distal and collective tubules;
c) increases the reabsorption of Na+;
d) increases the tubular reabsorption of K+;
e) its secretion is controlled by angiotensin II.
The human kidneys can dilute the final urine up to:
a) 120 ml min-1;
b) 100 mOsm.L-1;
c) 295 mOsm kg-1;
d) 7.36 - 7.44 pH;
e) 1200 mOsm.L-1.
The human kidneys can dilute the final urine up to:
a) 120 ml min-1;
b) 100 mOsm.L-1;
c) 295 mOsm kg-1;
d) 7.36 - 7.44 pH;
e) 1200 mOsm.L-1.
All the following substances are synthesized in the kidneys, except:
a) prostaglandines;
b) bradykinins;
c) ADH;
d) calcitriol;
e) renin.
All the following substances are synthesized in the kidneys, except:
a) prostaglandines;
b) bradykinins;
c) ADH;
d) calcitriol;
e) renin.
Which of the following are reabsorbed in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle:
a) Na+;
b) Mg2+;
c) Ca2+;
d) water;
e) H+.
Which of the following are reabsorbed in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle:
a) Na+;
b) Mg2+;
c) Ca2+;
d) water;
e) H+.
Which of the following is/are reabsorbed in the descending limb of the loop of Henle?
a) Na+;
b) Cl;
c) Ca2+;
d) K+;
e) water.
Which of the following is/are reabsorbed in the descending limb of the loop of Henle?
a) Na+;
b) Cl;
c) Ca2+;
d) K+;
e) water.
Which statement is correct:
a) the loop of Henle is permeable for salts and weakly permeable for water;
b) the descending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable for Na+ and K+ and weakly permeable for Cl-;
c) the thick segment of the ascending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable for ions;
d) the ascending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable for water and weakly permeable for ions;
e) the descending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable for salts and weakly permeable for water.
Which statement is correct:
a) the loop of Henle is permeable for salts and weakly permeable for water;
b) the descending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable for Na+ and K+ and weakly permeable for Cl-;
c) the thick segment of the ascending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable for ions;
d) the ascending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable for water and weakly permeable for ions;
e) the descending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable for salts and weakly permeable for water.
The concentration of the final urine is due to:
a) the countercurrent multiplying mechanism in the collecting tubule;
b) the countercurrent exchanger of peritubular capillary network;
c) the countercurrent multiplying mechanism in the loop of Henle and ADH;
d) the effective absorption pressure;
e) the glomerular filtration.
The concentration of the final urine is due to:
a) the countercurrent multiplying mechanism in the collecting tubule;
b) the countercurrent exchanger of peritubular capillary network;
c) the countercurrent multiplying mechanism in the loop of Henle and ADH;
d) the effective absorption pressure;
e) the glomerular filtration.
The secretion of renin is stimulated by:
a) increased parasympathetic tone;
b) increased sympathetic tone;
c) increased extracellular fluid;
d) decreased level of adrenalin;
e) increased Na+ in the tubular fluid.
The secretion of renin is stimulated by:
a) increased parasympathetic tone;
b) increased sympathetic tone;
c) increased extracellular fluid;
d) decreased level of adrenalin;
e) increased Na+ in the tubular fluid.
The atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) has the following effect/s:
a) increased absorption of Na+;
b) decreased excretion of Na+ and water;
c) increased excretion of Na+ passively followed by water and generalized vasodilatation;
d) decreased reabsorption of water;
e) generalized vasoconstriction.
The atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) has the following effect/s:
a) increased absorption of Na+;
b) decreased excretion of Na+ and water;
c) increased excretion of Na+ passively followed by water and generalized vasodilatation;
d) decreased reabsorption of water;
e) generalized vasoconstriction.
In the juxtaglomerular apparatus are found:
a) α-adrenergic receptors;
b) α2-adrenergetic receptors;
c) ß1-adrenergetic receptors;
d) ß2-adrenergetic receptors;
e) M1-cholinergic receptors.
In the juxtaglomerular apparatus are found:
a) α-adrenergic receptors;
b) α2-adrenergetic receptors;
c) ß1-adrenergetic receptors;
d) ß2-adrenergetic receptors;
e) M1-cholinergic receptors.
In osmotic diuresis:
a) the decrease in the volume of the final urine is due to solutes which are not absorbed in the renal tubules;
b) the increase in the volume of the final urine is due to solutes which are nor absorbed in the renal tubules;
c) the decrease in the volume of the final urine is due to water which is not absorbed;
d) the increased urine flow is due to increased water reabsorption;
e) the mechanisms do not differ from these in water diuresis.
In osmotic diuresis:
a) the decrease in the volume of the final urine is due to solutes which are not absorbed in the renal tubules;
b) the increase in the volume of the final urine is due to solutes which are nor absorbed in the renal tubules;
c) the decrease in the volume of the final urine is due to water which is not absorbed;
d) the increased urine flow is due to increased water reabsorption;
e) the mechanisms do not differ from these in water diuresis.
The secretion of less than 500 ml final urine per 24 hours is termed:
a) polyuria;
b) polydypsia;
c) oliguria;
d) anuria;
e) glucosuria.
The secretion of less than 500 ml final urine per 24 hours is termed:
a) polyuria;
b) polydypsia;
c) oliguria;
d) anuria;
e) glucosuria.