molecules of life
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Whats the definition of an organic molecule?
One that contains carbon
Whats the definition of a bio molecule?
Organic molecule that is commonly associated with life
Whats the 4 biomolecules?
Carbohydrates
Nucleic acids
Lipids
Proteins
Whats the general formula of carbohydrates?
CnH2nOn
Whats the formula for glucose and ribose?
Glucose = C6H12O6
Ribose = C5H10O5
What’re some qualities of carbohydrates?
Most are hydrophilic
Water soluble
Very abundant in nature
What’s the role of carbohydrates and provide examples
Used for structure and energy
Almost all eukaryotic cells can use glucose for energy and can store some form of glucose (monomer or polymer) for energy
Many proteins and lipids are modified by the addition of carbohydrates
What are nucleotides and nucleosides involved in?
Energy metabolism and signaling/ communication
What does a nucleotide consist of?
Nucleobase/ nitrogenous basE
Phosphate group
5 carbon sugar
What does a nucleoside contain?
Only nitrogenous base and sugar
NO PHOSPHATE
What does the structure of the nitrogenous base determine?
It determines whether the nucleobase is Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, Thymine or Uracil
What’re some different forms of molecules with adenine?
AMP, ADP, ATP
What is ATP?
Basic molecule of energy storage in most organisms, including mammals
Whats is adenosine?
A nucleoside, works as a neurotransmitter/ signalling molecule
Whats cyclic AMP important for?
Important signaling molecule within cells
What are some molecules containing guanine?
GMP, GDP, GTP
What is GTP?
It’s an energy source in many physiological chemical reactions
Whats cyclic GMP used for?
Important signaling molecule within cells
What’re some features of lipids?
Generally hydrophobic
Contain mostly carbon and hydrogen (a few oxygen atoms, nitrogen, phosphorus)
Generally non-polar
Whatre some examples of lipids?
Fatty acids
Glycerides
Phospholipids and sphingolipids
Steroids
Oxylipins
Are lipids water soluble?
No cuz non polar and water is polar
What’re some roles of lipids?
Important for structure of cells/ cell membrane cuz its waterproof and pliable
Energy source
Communication (within cells and between cells)
What’re fatty acids generally?
Long unbranched hydrocarbon chain with 8-28 carbons
Has carboxyl (=acidic) functional group
Whats the difference between saturated and unsaturated FA?
Saturated = no double bonds, forms straight chain
Unsaturated = double bonds, has a kink
What happens the more double bonds a FA has?
The less likely it’ll be solid at room temp
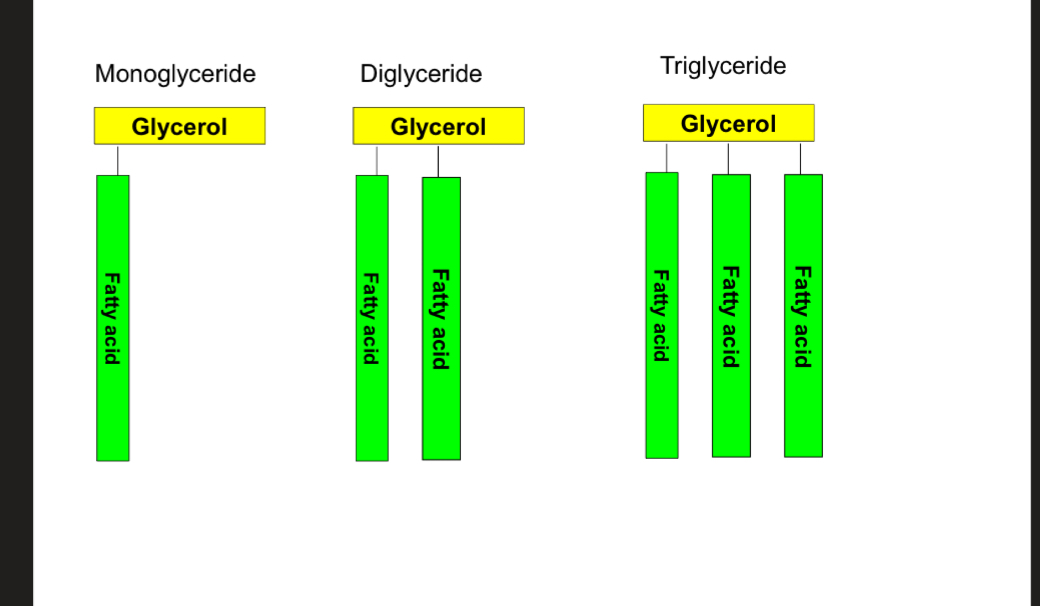
What’re glycerides?
Derivative of FA
FA + glycerol = glyceride
Involves a dehydration reaction where water is lost
What’re the 3 types of glycerides?
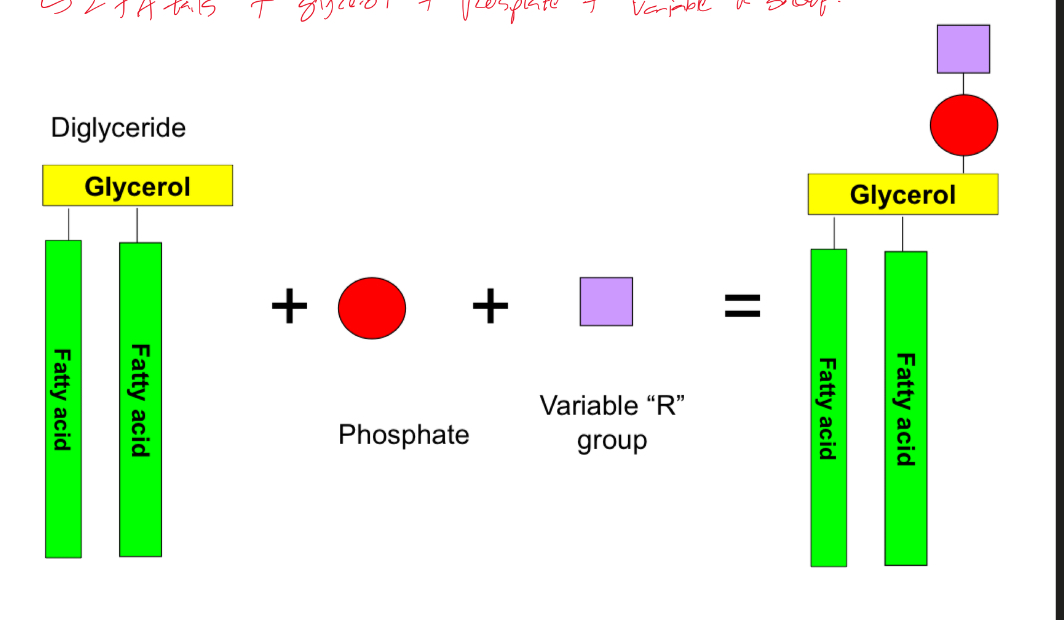
What’re phospholipids?
A derivative of glycerides
2 FA tails + glycerol + phosphate + variable R group
Amphipathic
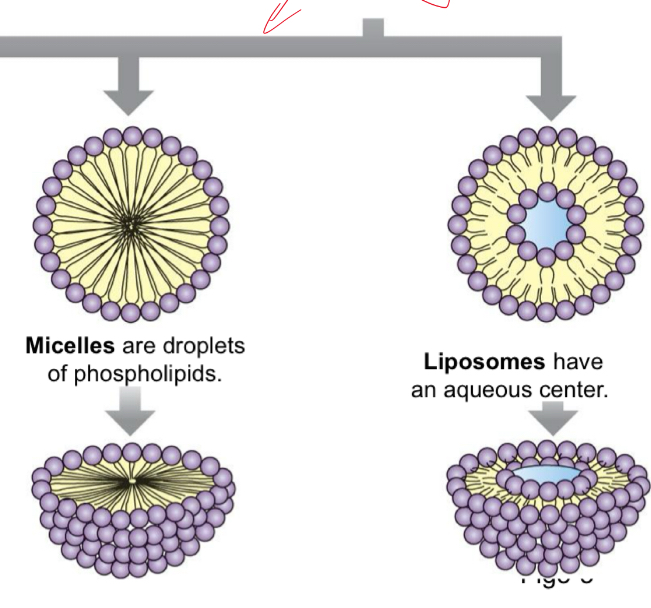
What can form if you shake up a beaker with water and phospholipids?
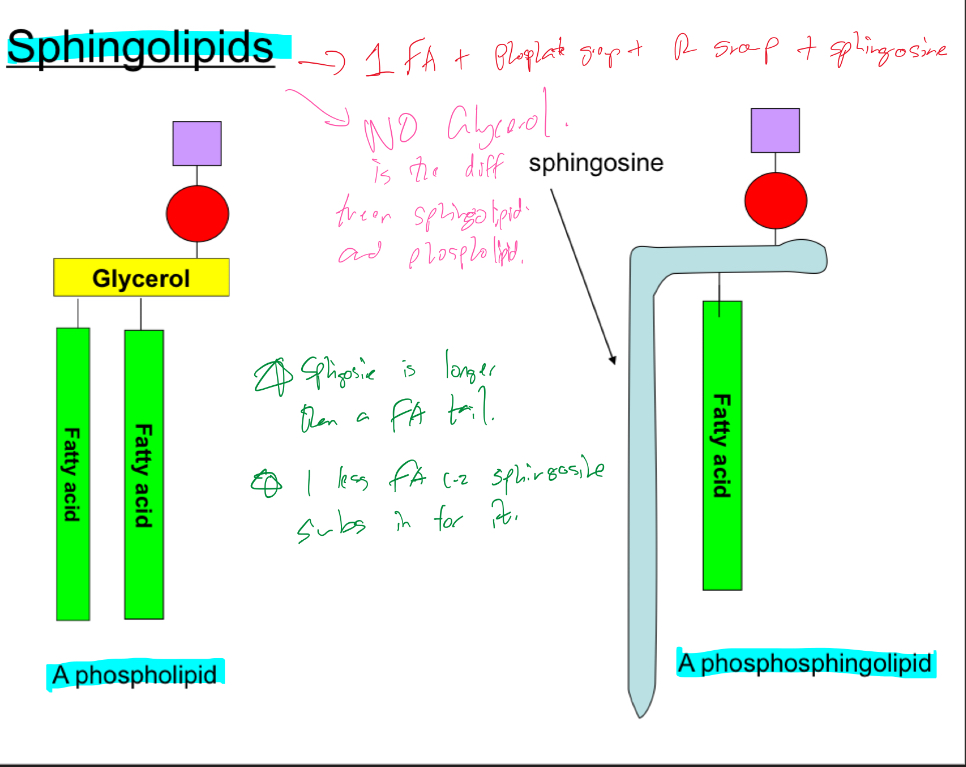
What’re sphingolipids?
They contain FA + phosphate group + R group + sphingospine
Sphingospine is longer than an FA tail
Whats the difference between phospholipid and sphingolipids?
No glycerol in Sphingolipids
1 less FA in sphingolipid cuz sphingospine subs in for it
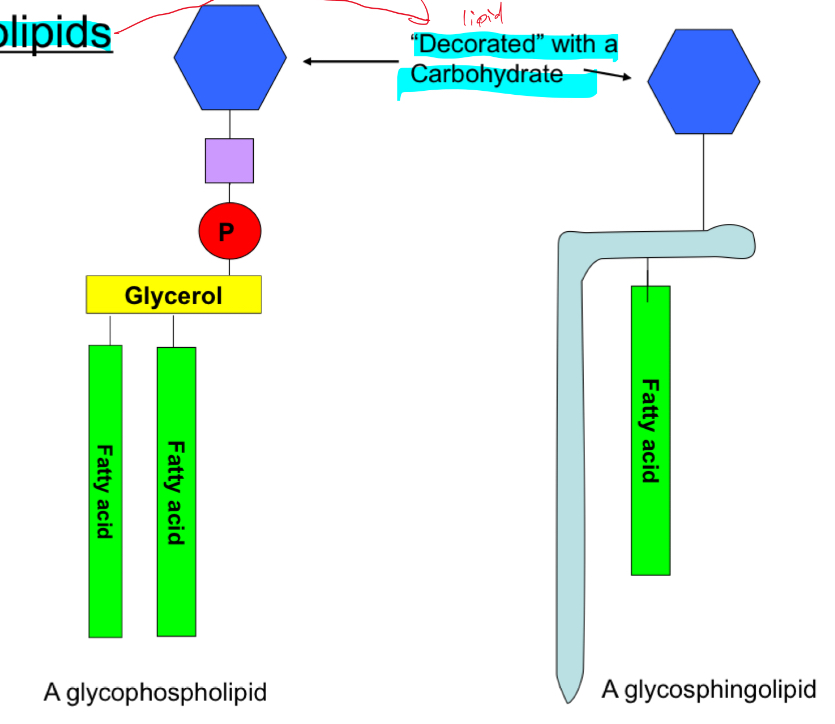
What’re glycolipids?
Decorated with a carbohydrate
What does the basic structure of a steroid contain?
Basic structure consists of 3 six-carbon rings plus 1 five-carbon ring
Totalling 17 Carbons
What do different R groups in steroids do?
Confer different function
What roles do steroids have?
Communication = Testosterone
Structure = Cholesterol
What’re oxylipins?
Oxygenated metabolites of fatty acids
What’re Eicosanoids?
Subset of oxylipins which are a polyunsaturated fatty acid, having a length of 20 carbon atoms
What’re oxylipins derived from?
Arachidonic acid, or other unsaturated fatty acids
What’re the roles of oxylipins?
Not generally stored, but synthesized as needed, main function is communication within cells and between cells
Inflammation, pain, platelet aggregation
Includes prostaglandins and leukotrienes
What’re some general features of proteins?
Some amino acids are acidic, basic, polar, non-polar
Proteins are macromolecules
Linear chains of amino acids
How many amino acids are essential and non-essential?
9 are essential: need to consume them
11 are non-essential: we can synthesize them
Whats a short chain of AA called?
A peptide
Whats a long chain of AA called?
Proteins
What’re the different categories of proteins?
Primary structure
Secondary structure
Tertiary structure
Quaternary structure
What determines the complex structures of proteins?
The amino acids that make them up
What do all amino acids have?
They all have a carboxyl group (COOH), an amino group (NH2), and a hydrogen attached to the same carbon. The fourth bond of the carbon attaches to a variable R group
Whats primary structure of protein?
Sequence of amino acids
Whats secondary protein structure?
alpha helix and beta pleated sheets
Determined by pattern of hydrogen bonds between the amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone
Whats tertiary structure?
Overall 3D arrangement of the polypeptide chain in space: determined by side chain interactions and secondary structures
Whats quaternary structure?
How multiple proteins interact with each other
Fibrous proteins: Collagen
Globular proteins: Hemoglobin
How many proteins does the genome encode for?
33,000 proteins
In a mammalian cell, how many proteins are expressed?
10,000 to 15,000
Whats the difference between fibrous vs globular proteins?
Fibrous proteins are generally insoluble
Globular are usually soluble
7 categories of soluble protein
What’re the 7 categories of soluble protein?
Enzymes
Membrane transporters
Signal molecules (ligand)
Membrane receptors
Binding proteins
Regulatory proteins
Immunoglobulins
What must a protein do to do something?
It must interact with or bind to other proteins, molecules or ions
At a binding site
How vague or specific is protein binding?
Very specific: binds to a specific molecule in a specific way
Whats a ligand?
A molecule that binds to a protein binding site is called a ligand
Whats an endogenous ligand?
Something natural in your body: for example a hormone or neurotransmitter (Ex: insulin)
Whats a non-endogenous ligand?
May be a drug or toxin for example (Ex: snake venom)
Whats the difference between weak and strong affinity?
High affinity means it binds strongly
Weak affinity means weak binding
What’s an agonist?
A ligand that binds to a protein binding site and alters the state of the protein, resulting in a biological response (Ex: insulin)
A hormone or neurotransmitter or a drug activating a receptor for example
Causes a response/ activator
Whats an antagonist?
A ligand that reduces the action of an agonist (ie: binds but causes no biological response)
Also called inhibitors, blockers
Whats the 2 ways agonists and antagonists may be?
Competitive
Allosteric
What happens when agonists and antagonists are competitive?
Act to block an agonist at its normal binding site
Competes to bind at same binding site
What happens when agonists and antagonists are allosteric?
Act to block a competitive agonist by binding to the the protein away from the binding site and inactivate the binding site
What can the rate of proteins/ activity be modulated by?
Cofactors
Physical factors
ph, temperature
Modulation
What occurs in covalent modification in modulation?

What are phosphorylation and dephosphorylation?
Processes that modulate rates of protein binding and activity
Turns “up” or “down” rate of activity
Whats the protein responsible that catalyzes the phosphorylation of casein and became known as protein kinase?
Liver enzyme
How many proteins in a typical mammalian cell are covalently bound to phosphate?
1/3 of the proteins
Where is the phosphate added in phosphorylation?
On one of the amino acid side chains chains of a protein.
Is phosphorylation reversible?
Yes, by dephosphorylation
What’re the most common targets of phosphate?
Hydroxyl groups of serine, threonine, tyrosine or histidine amino acid side chains
What’re some advantages of the use of phosphorylation/ dephosphorylation as a control mechanism?
It is rapid, taking as little as a few seconds
It doesnt require new proteins to be made or degraded
It is easily reversible
Can external signals activate protein kinases and phosphotases?
Yes
In animal cells what’re phosphorylation cascades mediated by?
2 types of kinases
Serine/ threonine kinases
Whats the second outcome in response to phosphorylation of a signal?
